Содержание
- 2. Objectives of this Session Increase self-awareness Discover differences in people concerning energy source, information gathering, decision
- 3. By the end of class, you will be able to: Describe the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator Describe
- 4. Guidelines All workshop data should remain confidential Everyone has a preferred pathway to excellence We are
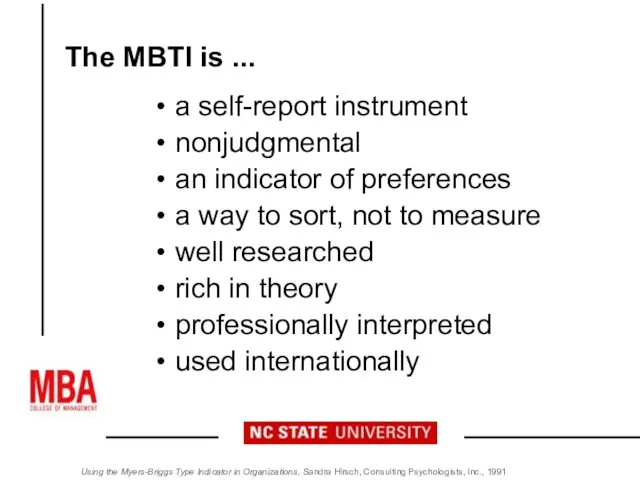
- 5. The MBTI is ... a self-report instrument nonjudgmental an indicator of preferences a way to sort,
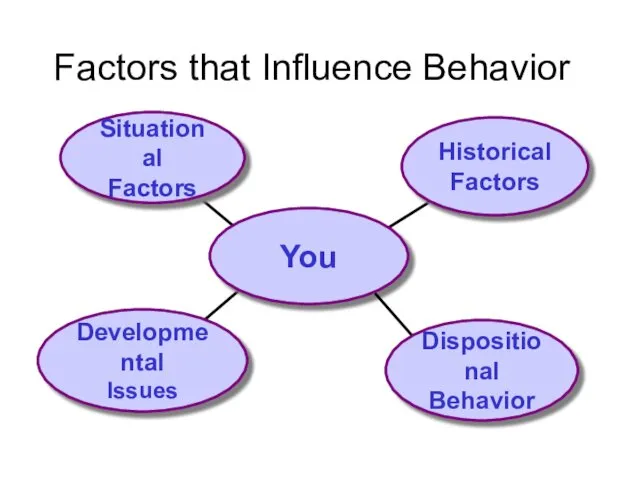
- 6. Factors that Influence Behavior You Situational Factors Historical Factors Developmental Issues Dispositional Behavior
- 7. Based on Swiss psychologist Carl Jung’s “Type” Theory (1920s) Behavior is individual and predictable Developed by
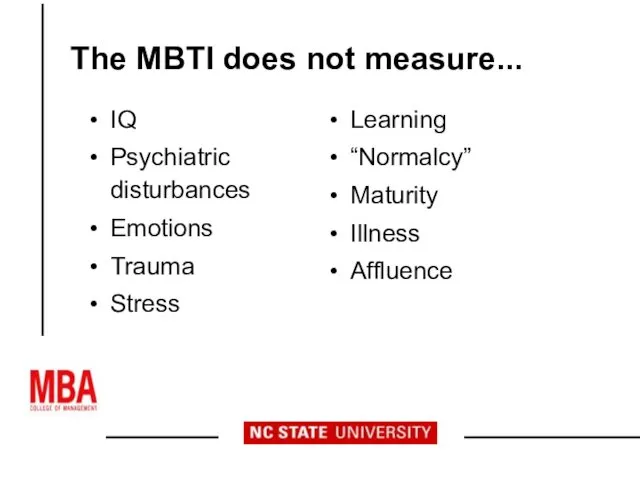
- 8. The MBTI does not measure... IQ Psychiatric disturbances Emotions Trauma Stress Learning “Normalcy” Maturity Illness Affluence
- 9. Unethical Uses of the MBTI... Hiring Selecting Promoting Rewarding
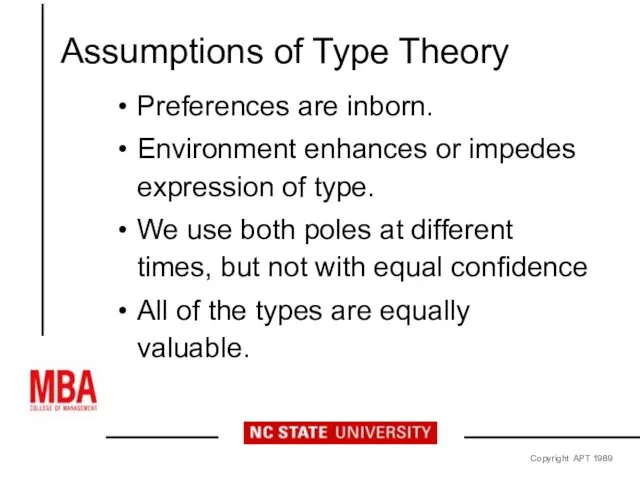
- 10. Assumptions of Type Theory Preferences are inborn. Environment enhances or impedes expression of type. We use
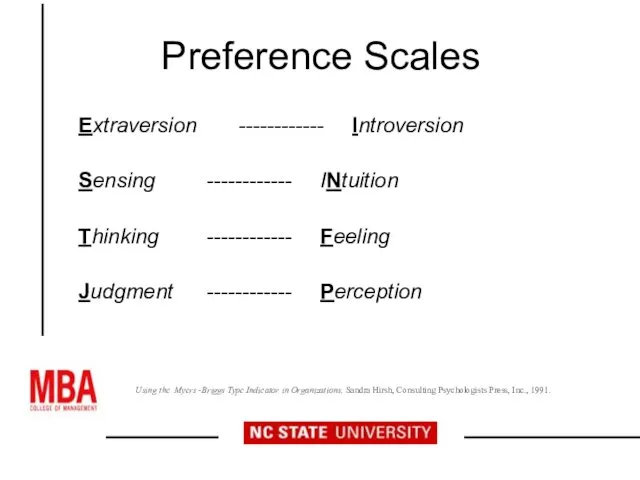
- 11. Preference Scales Extraversion ------------ Introversion Sensing ------------ INtuition Thinking ------------ Feeling Judgment ------------ Perception Using the
- 12. Attention focused outward: people, things, action Using trial and error with confidence Relaxed and confident Scanning
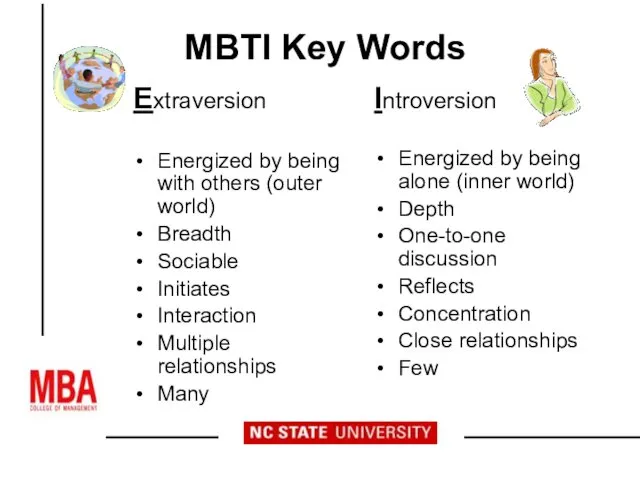
- 13. MBTI Key Words Extraversion Energized by being with others (outer world) Breadth Sociable Initiates Interaction Multiple
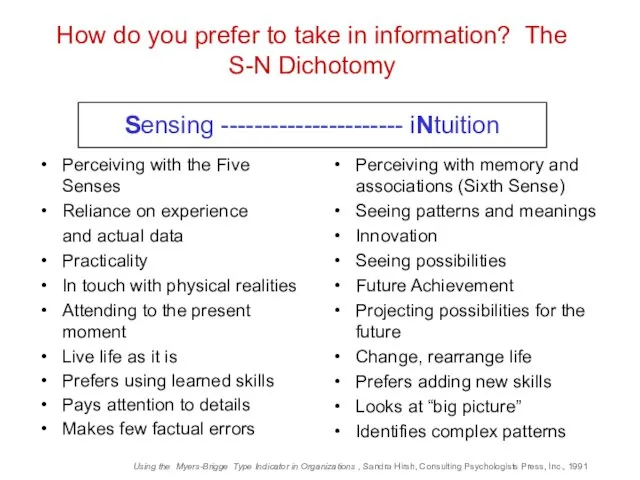
- 14. Perceiving with the Five Senses Reliance on experience and actual data Practicality In touch with physical
- 15. MBTI Key Words Sensing Facts Data Detail Realistic Literal Actuality Present Utility Sequential Repetition Conserve INtuition
- 16. Decisions based on the logic of the situation Uses cause and effect reasoning Strive for an
- 17. MBTI Key Words Thinking Analysis Objective Logic Impersonal Critique Reason Criteria Head Justice Analyze Feeling Sympathy
- 18. Focuses on completing task Deciding and planning Organizing and scheduling Controlling and regulating Goal oriented Wanting
- 19. MBTI Key Words Judging Scheduled Decisive Self-regimented Purposeful Organized Settled Plan ahead Control one’s life Set
- 20. MBTI Results
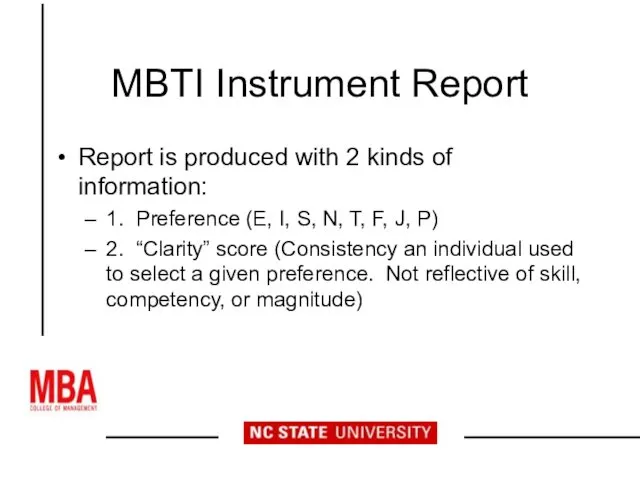
- 21. MBTI Instrument Report Report is produced with 2 kinds of information: 1. Preference (E, I, S,
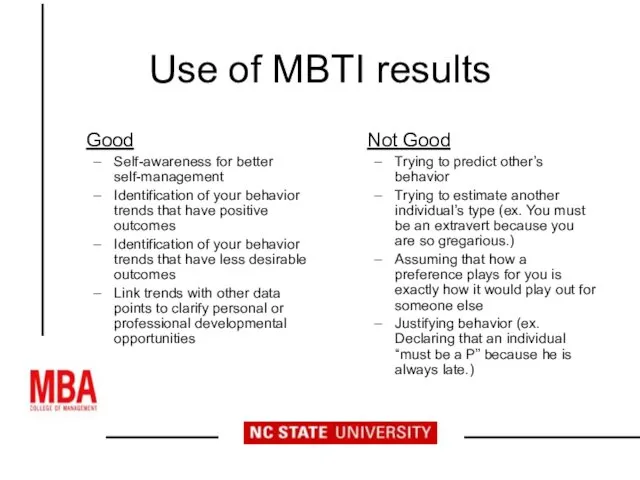
- 22. Use of MBTI results Good Self-awareness for better self-management Identification of your behavior trends that have
- 23. Remember… Personality type does not explain everything When it comes to people -- there are few
- 24. Experiential Exercises
- 26. Скачать презентацию














 Открытый урок по географии в 9 классе с использованием сингапурской методики.
Открытый урок по географии в 9 классе с использованием сингапурской методики. Врожденные пороки сердца
Врожденные пороки сердца ОАО Автоваз. Финансовая политика
ОАО Автоваз. Финансовая политика презентация о значении чтения книг Диск
презентация о значении чтения книг Диск 1654323467682_1654323455583_1654323445941_Prezentatsia_SA-3_2022_g (1)
1654323467682_1654323455583_1654323445941_Prezentatsia_SA-3_2022_g (1) Женщины А.С Пушкина
Женщины А.С Пушкина Презентация к уроку по химии Предмет органической химии. Органические вещества. Теория химического строения органических веществ
Презентация к уроку по химии Предмет органической химии. Органические вещества. Теория химического строения органических веществ Кровотечения. Первая помощь при кровотечениях
Кровотечения. Первая помощь при кровотечениях Как правильно написать научную статью
Как правильно написать научную статью Право собственности и другие вещные права на жилые помещения
Право собственности и другие вещные права на жилые помещения прил 10 презентация
прил 10 презентация ПЛАНЕТЫ ЗЕМНОЙ ГРУППЫ (МЕРКУРИЙ, ВЕНЕРА)
ПЛАНЕТЫ ЗЕМНОЙ ГРУППЫ (МЕРКУРИЙ, ВЕНЕРА) Ошибки в рекламе. Рекламное воздействие на потребителей. Словарь новейших слов иноязычной лексики
Ошибки в рекламе. Рекламное воздействие на потребителей. Словарь новейших слов иноязычной лексики Обособленные определения
Обособленные определения Транспортна подія на станції Верхівцеве, Придніпровської залізниці
Транспортна подія на станції Верхівцеве, Придніпровської залізниці Проблемы информационной безопасности
Проблемы информационной безопасности Рынок углеводородного сырья США
Рынок углеводородного сырья США Основные факторы рельефообразования
Основные факторы рельефообразования Дорогой любимой дочери от папы
Дорогой любимой дочери от папы Строение и свойства жидкостей. Испарение и конденсация. Насыщенный и ненасыщенный пар. Влажность воздуха
Строение и свойства жидкостей. Испарение и конденсация. Насыщенный и ненасыщенный пар. Влажность воздуха Павел Петрович Бажов
Павел Петрович Бажов Поэтапное благоустройство территории
Поэтапное благоустройство территории современные педагогические технологии как средство мотивации учебной деятельности на уроках химии
современные педагогические технологии как средство мотивации учебной деятельности на уроках химии Дифференциация звуков [Ч]-[Щ] в стихотворных текстах.
Дифференциация звуков [Ч]-[Щ] в стихотворных текстах. История ВЧК-НКВД 1920-1934
История ВЧК-НКВД 1920-1934 Разделение времени. The time
Разделение времени. The time Практические вопросы применения нормативных правовых актов в сфере оборота наркотических средств и психотропных веществ
Практические вопросы применения нормативных правовых актов в сфере оборота наркотических средств и психотропных веществ Образование как глобальный объект психологии высшей школы. Предмет и задачи психологии высшей школы
Образование как глобальный объект психологии высшей школы. Предмет и задачи психологии высшей школы