Содержание
- 2. TABLE OF CONTENTS :- Introduction. Fundamentals of sound. Anatomy of sound card. Connectivity in sound card.
- 3. Intrduction The voices in your computer made possible by the sound card. The sound card is
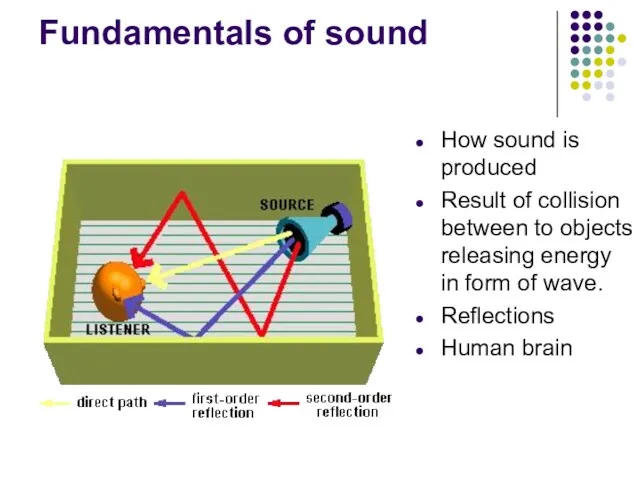
- 4. Fundamentals of sound How sound is produced Result of collision between to objects releasing energy in
- 5. What is Sound card Sound card is a board (consisting of circuits) that enables the computer
- 6. Anatomy of sound card A digital signal processor (DSP) that handles most computations A digital to
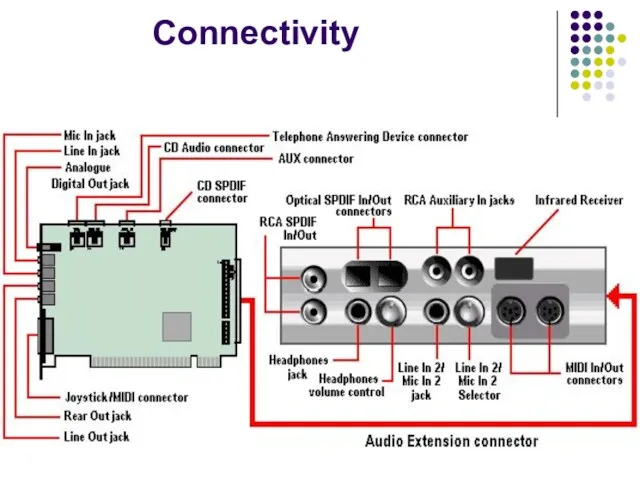
- 7. Connectivity
- 8. Sound card may be connected to: Headphones Amplified speakers An analog input source Microphone Radio Tape
- 9. Technologies used in sound card Frequency Modulation: The first widespread technology to be used in sound
- 10. Wavetable synthesis: Wave Table doesn't use carriers and modulators to create sound, but actual samples of
- 11. Determination of Quality of Instrument The quality of the original recordings The frequency at which the
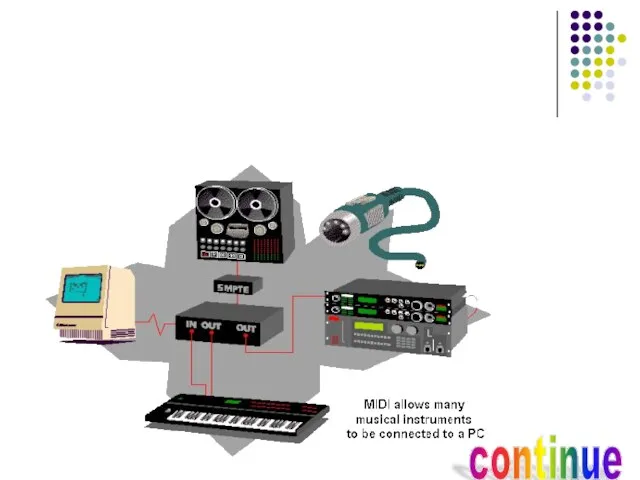
- 12. MIDI:- MIDI is Musical Instrument Digital Interface. Musicians often want to be able to control electronic
- 13. continue
- 14. Advantages of MIDI The advantages of MIDI : There are two main advantages of MIDI: -
- 15. Producing Sound : The sound card receives a continuous, analog-waveform input signal from the microphone jack.
- 16. The digital output from the ADC flows into the DSP. The DSP is programmed by a
- 17. Selection Criteria Interface: Sound cards can connect to the system using either an ISA slot or
- 18. Important Features: 3D Audio: 3D audio is a new technology that causes audio to basically "project"
- 19. Troubleshooting Sound Card One thing that a sound card is prone to is EMF. The electromagnetic
- 21. Скачать презентацию















 Подготовка к ЕГЭпо истории. Решений заданий. Часть 2
Подготовка к ЕГЭпо истории. Решений заданий. Часть 2 Доклад для воспитателей ДОУ на тему :Роль сказок в развитии детей дошкольного возраста
Доклад для воспитателей ДОУ на тему :Роль сказок в развитии детей дошкольного возраста Распознавание функций знаков препинаний
Распознавание функций знаков препинаний Анализ архитектуры исторического и современного города
Анализ архитектуры исторического и современного города И в шутку и в серьез о математике
И в шутку и в серьез о математике Подвесная железная дорога
Подвесная железная дорога Зудящие болезни кожи (дерматозы)
Зудящие болезни кожи (дерматозы) Verbnoe_voskresenie
Verbnoe_voskresenie Михаил Васильевич Ломоносов (1711 – 1765)
Михаил Васильевич Ломоносов (1711 – 1765) Достопримечательности города Астана
Достопримечательности города Астана Роль и место психологии в системе образования
Роль и место психологии в системе образования Принципы и методы обучения ИЯ
Принципы и методы обучения ИЯ Мал шаруашылығы өнімдерін техникалық реттеу саласында нормативтік құжаттар
Мал шаруашылығы өнімдерін техникалық реттеу саласында нормативтік құжаттар Разработка алгоритма диагностики, ремонта и технического обслуживания датчика обнаружения Feron Sen14/LX01
Разработка алгоритма диагностики, ремонта и технического обслуживания датчика обнаружения Feron Sen14/LX01 Строение и функции белков
Строение и функции белков Особенности собственных нужд АЭС с реакторами БН. (Лекция 5)
Особенности собственных нужд АЭС с реакторами БН. (Лекция 5) Основные принципы проектирования малоэтажных домов Ф.Л. Райта
Основные принципы проектирования малоэтажных домов Ф.Л. Райта Цифровой телевизионный сигнал
Цифровой телевизионный сигнал Электронные дидактические игры для старшей группы.
Электронные дидактические игры для старшей группы. урок технологии. Модель летней обуви.
урок технологии. Модель летней обуви. История фестивального движения
История фестивального движения Интеграция образовательных областей по ФГТ в планировании работы воспитателя
Интеграция образовательных областей по ФГТ в планировании работы воспитателя Magnetic plates
Magnetic plates Экспертный семинар Качество подготовки специалистов в российских вузах
Экспертный семинар Качество подготовки специалистов в российских вузах Именительный падеж
Именительный падеж Мультимедийное Занятие Мой родной край
Мультимедийное Занятие Мой родной край Political system in UK
Political system in UK Презентация к уроку географии в 8 классе
Презентация к уроку географии в 8 классе