Содержание
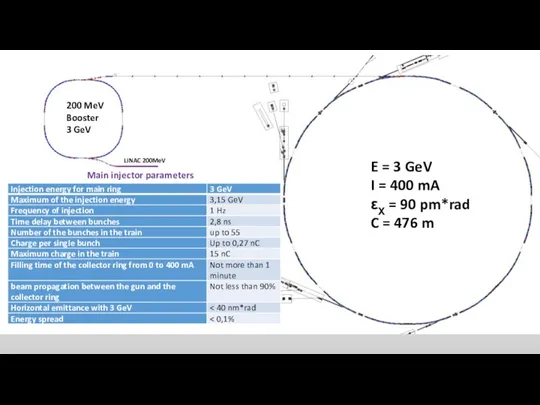
- 2. Main injector parameters E = 3 GeV I = 400 mA εX = 90 pm*rad C
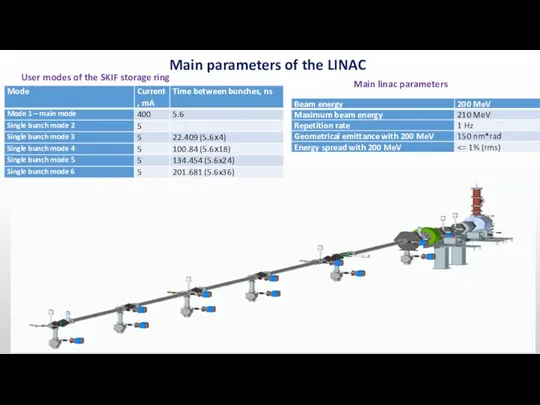
- 3. Main parameters of the LINAC Main linac parameters User modes of the SKIF storage ring
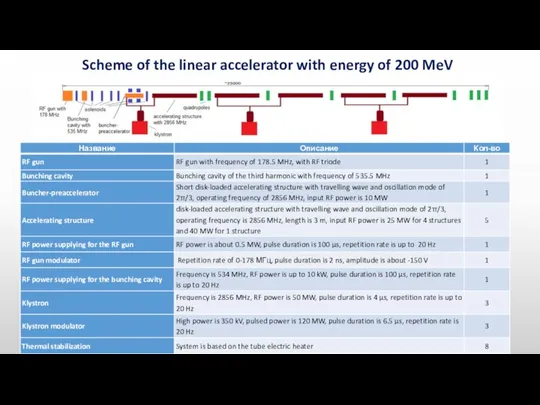
- 4. Scheme of the linear accelerator with energy of 200 MeV
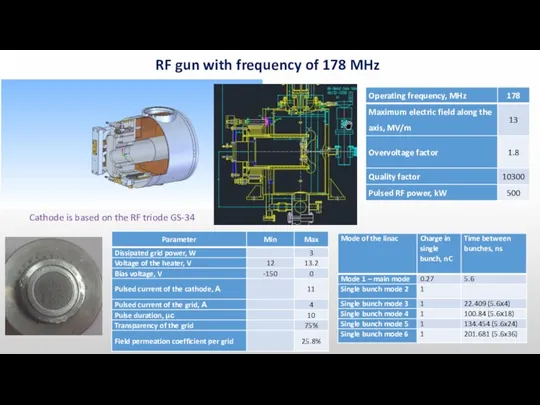
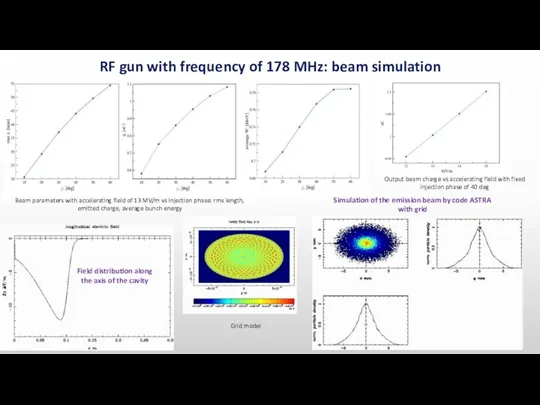
- 5. RF gun with frequency of 178 MHz Cathode is based on the RF triode GS-34
- 6. Field distribution along the axis of the cavity Simulation of the emission beam by code ASTRA
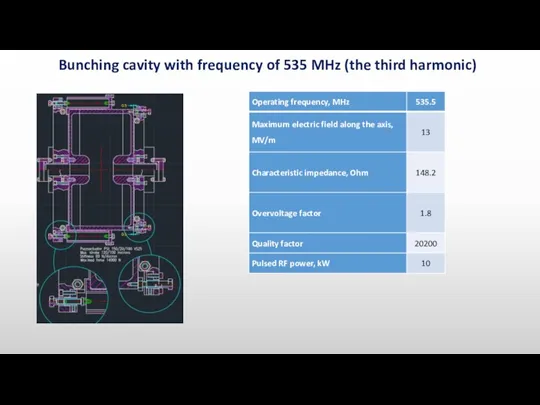
- 7. Bunching cavity with frequency of 535 MHz (the third harmonic)
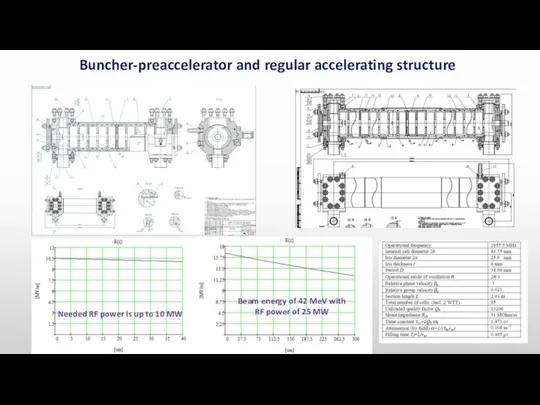
- 8. Buncher-preaccelerator and regular accelerating structure Beam energy of 42 MeV with RF power of 25 MW
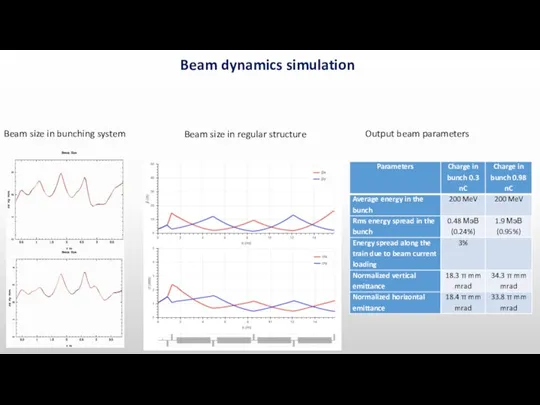
- 9. Beam dynamics simulation Beam size in bunching system Beam size in regular structure Output beam parameters
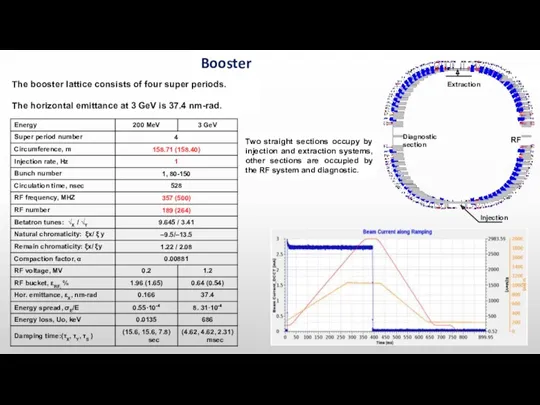
- 10. The booster lattice consists of four super periods. The horizontal emittance at 3 GeV is 37.4
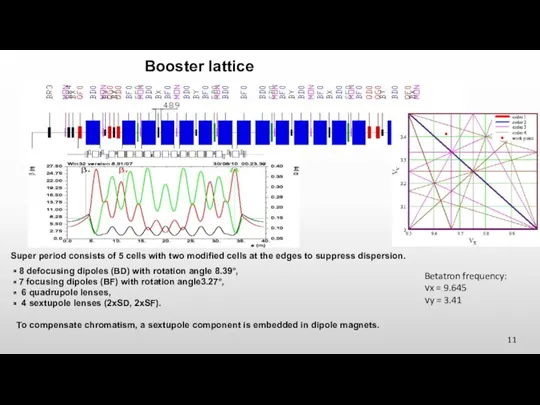
- 11. Booster lattice Super period consists of 5 cells with two modified cells at the edges to
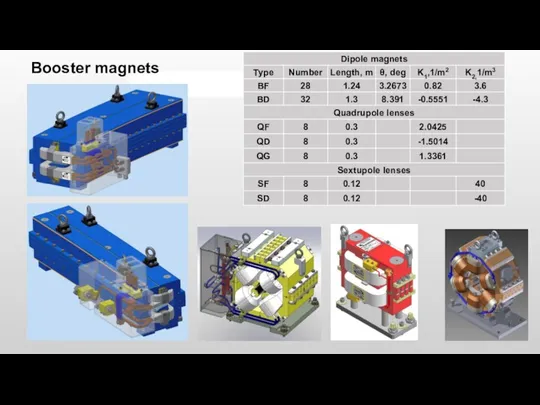
- 12. Main parameters of the booster magnets Booster magnets
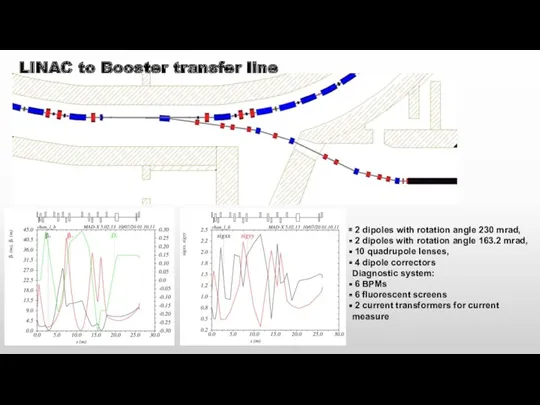
- 13. LINAC to Booster transfer line 2 dipoles with rotation angle 230 mrad, 2 dipoles with rotation
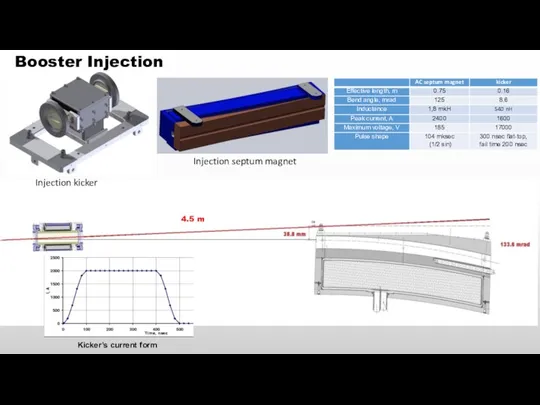
- 14. Booster Injection 4.5 m Kicker’s current form Injection kicker Injection septum magnet
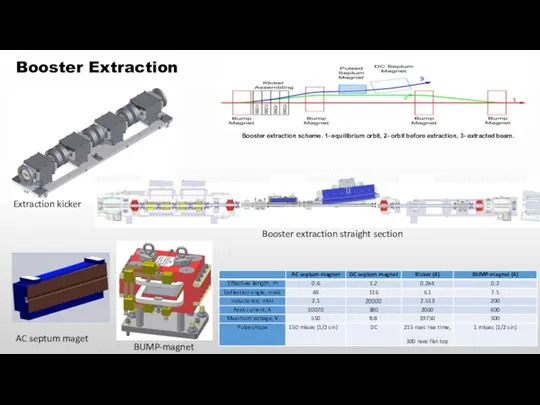
- 15. Booster extraction scheme. 1- equilibrium orbit, 2- orbit before extraction, 3- extracted beam. Booster Extraction Booster
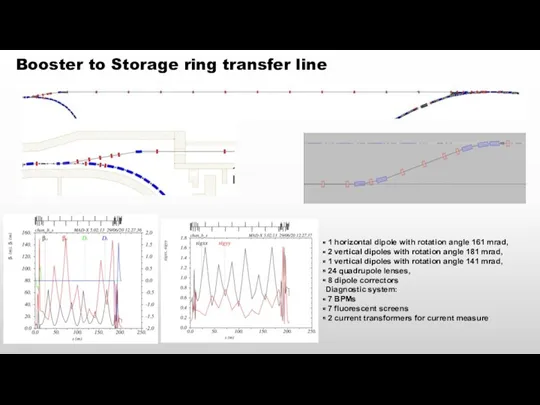
- 16. Booster to Storage ring transfer line 1 horizontal dipole with rotation angle 161 mrad, 2 vertical
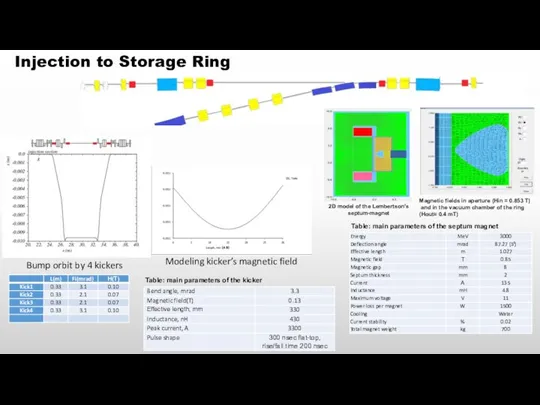
- 17. Injection to Storage Ring 2D model of the Lembertson’s septum-magnet Magnetic fields in aperture (Hin =
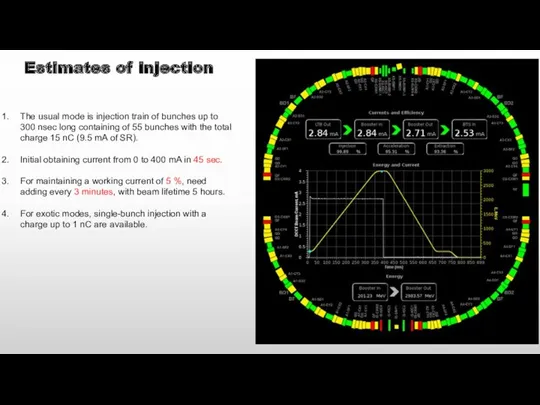
- 18. Estimates of injection The usual mode is injection train of bunches up to 300 nsec long
- 20. Скачать презентацию
 Любимые места моего района
Любимые места моего района Тренажер. Задание 20 ЕГЭ по русскому языку
Тренажер. Задание 20 ЕГЭ по русскому языку Русский модерн
Русский модерн Нейровизуализационные методы диагностики заболевании нервной системы
Нейровизуализационные методы диагностики заболевании нервной системы Фотоматериалы к проекту Путешествие по Золотому кольцу России Диск
Фотоматериалы к проекту Путешествие по Золотому кольцу России Диск Рекомендации по работе с родителями
Рекомендации по работе с родителями Характеристика, руководство, сопровождение сюжетно-ролевых игр
Характеристика, руководство, сопровождение сюжетно-ролевых игр История возникновения проблемы фирменного стиля
История возникновения проблемы фирменного стиля ИТ в сфере управления
ИТ в сфере управления ЕГЭ по русскому языку: выполнение тестовых заданий
ЕГЭ по русскому языку: выполнение тестовых заданий Субсидии на газификацию
Субсидии на газификацию Методика профессионального обучения
Методика профессионального обучения Угол. Измерение углов
Угол. Измерение углов акция засветись
акция засветись Childhood Education and References for Sustainable Education
Childhood Education and References for Sustainable Education Tattoo_salon
Tattoo_salon Джанни Родари, сказка Приключения Чиполлино
Джанни Родари, сказка Приключения Чиполлино Твой бюджет. Благоустройство детской площадки. Пулковский парк в Московском районе
Твой бюджет. Благоустройство детской площадки. Пулковский парк в Московском районе презентация Готовимся к школе
презентация Готовимся к школе Программа поэтапной работы над проектом
Программа поэтапной работы над проектом Мистецьке життя краю Тернопільщини
Мистецьке життя краю Тернопільщини Родительское собрание в 1 классе
Родительское собрание в 1 классе Игра Большая игра, посвященная юбилею пионерии.
Игра Большая игра, посвященная юбилею пионерии. Комбинационные логические устройства. Арифметико-логические устройства (АЛУ). Лекция 4
Комбинационные логические устройства. Арифметико-логические устройства (АЛУ). Лекция 4 Плотность нефти и нефтепродуктов
Плотность нефти и нефтепродуктов Автоматизация процесса пропарки и пропитки древесной щепы в производстве ХТММ
Автоматизация процесса пропарки и пропитки древесной щепы в производстве ХТММ Выставка исследовательская деятельность
Выставка исследовательская деятельность Праздник Ильин день
Праздник Ильин день