Слайд 2

Overview
Definition of a bilevel problem and its general form
Optimality (KKT-type) conditions
Reformulation
of a general bilevel problem
Iterative (descent direction) methods
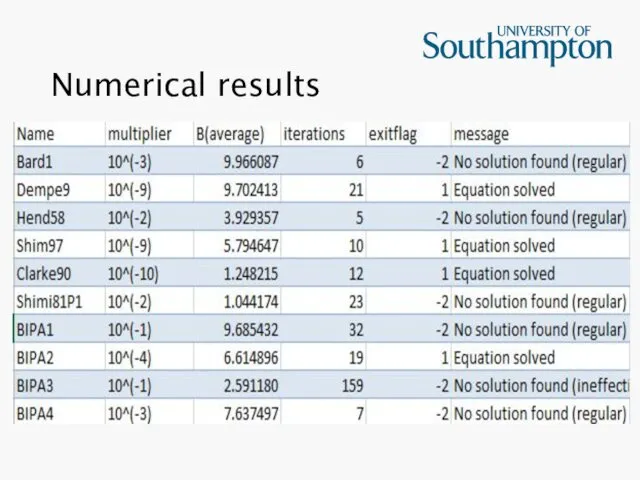
Numerical results
Слайд 3

Stackelberg Game (Bilevel problem)
Players: the Leader and the Follower
The Leader is
first to make a decision
Follower reacts optimally to Leader’s decision
The payoff for the Leader depends on the follower’s reaction
Слайд 4

Example
Taxation of a factory
Leader – government
Objectives: maximize profit and minimize pollution
Follower
– factory owner
Objectives: maximize profit
Слайд 5

General structure of a Bilevel problem
Слайд 6

Слайд 7
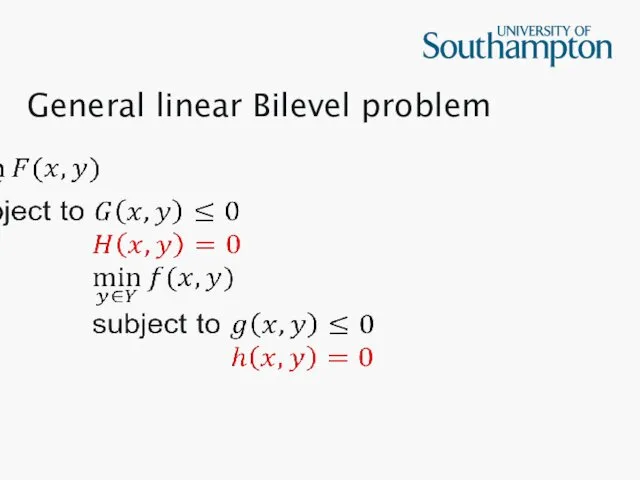
General linear Bilevel problem
Слайд 8
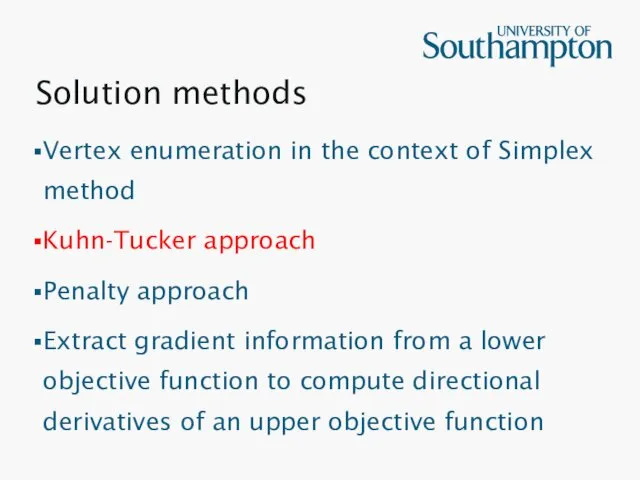
Solution methods
Vertex enumeration in the context of Simplex method
Kuhn-Tucker approach
Penalty approach
Extract
gradient information from a lower objective function to compute directional derivatives of an upper objective function
Слайд 9
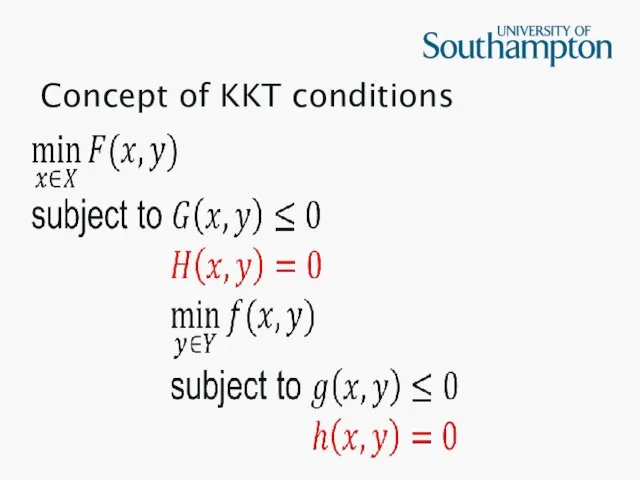
Concept of KKT conditions
Слайд 10
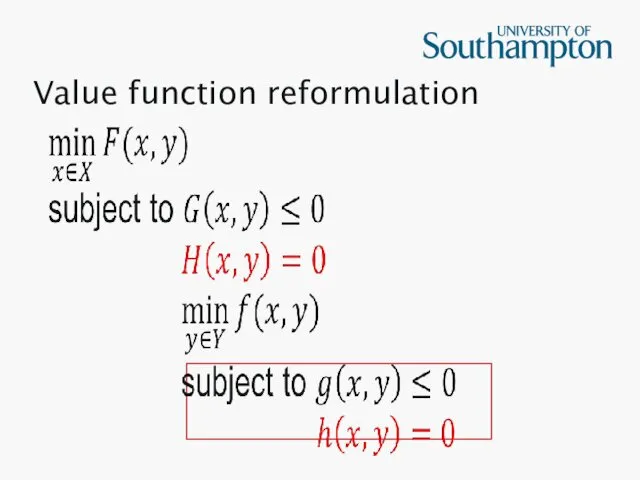
Value function reformulation
Слайд 11
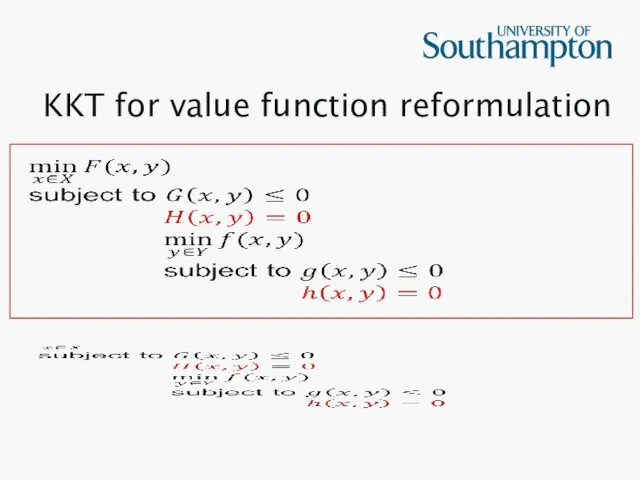
KKT for value function reformulation
Слайд 12

Слайд 13
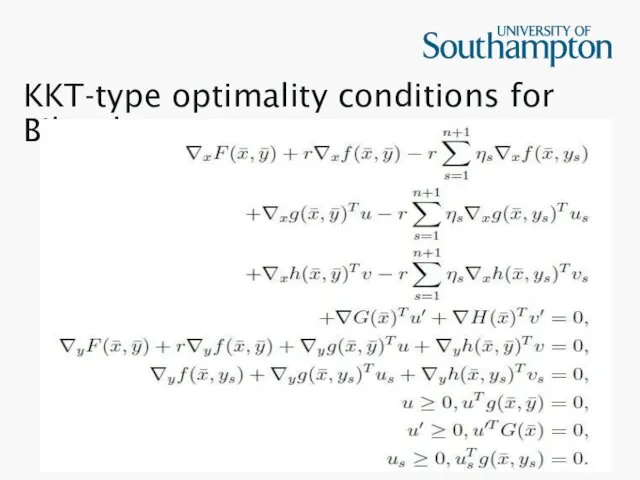
KKT-type optimality conditions for Bilevel
Слайд 14
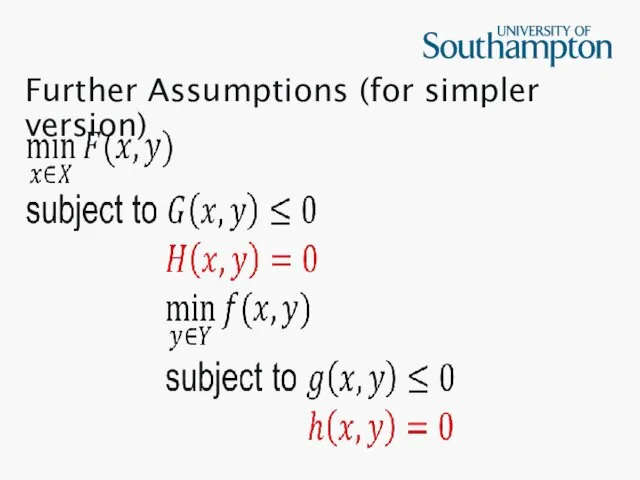
Further Assumptions (for simpler version)
Слайд 15
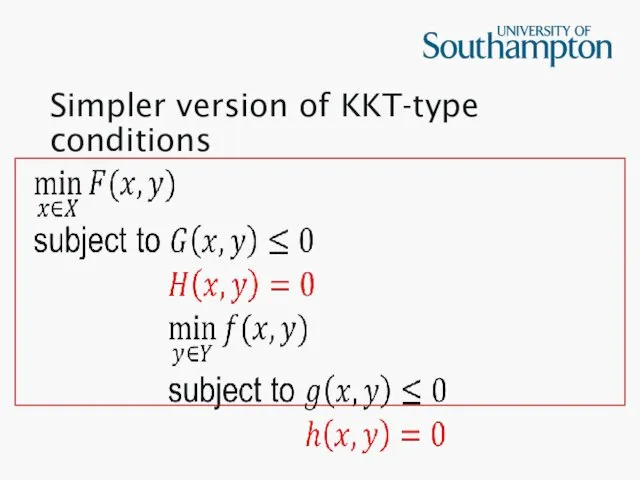
Simpler version of KKT-type conditions
Слайд 16
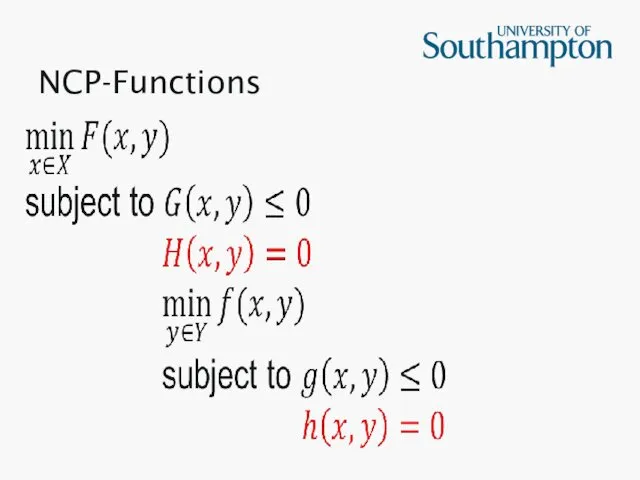
Слайд 17
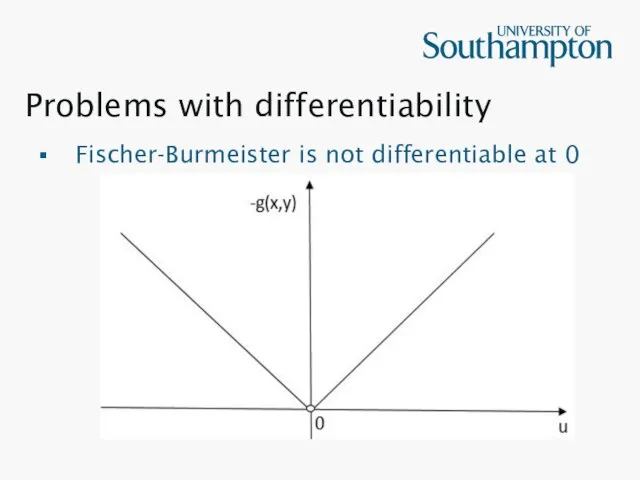
Problems with differentiability
Fischer-Burmeister is not differentiable at 0
Слайд 18
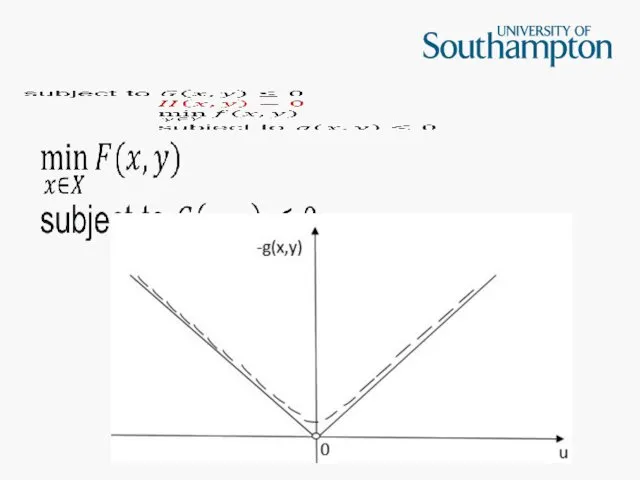
Слайд 19
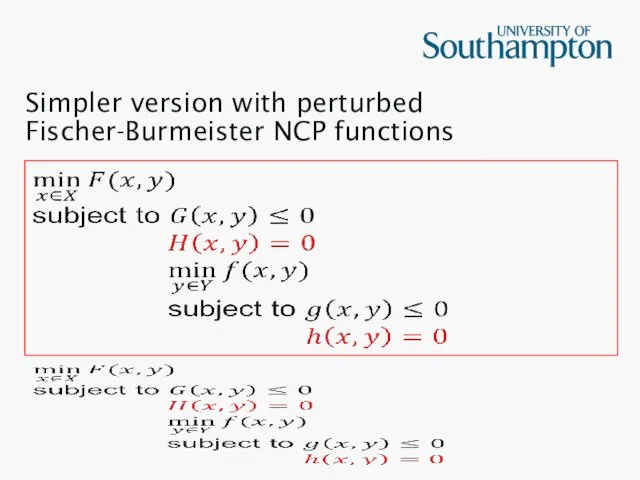
Simpler version with perturbed Fischer-Burmeister NCP functions
Слайд 20

Слайд 21

Слайд 22

Слайд 23
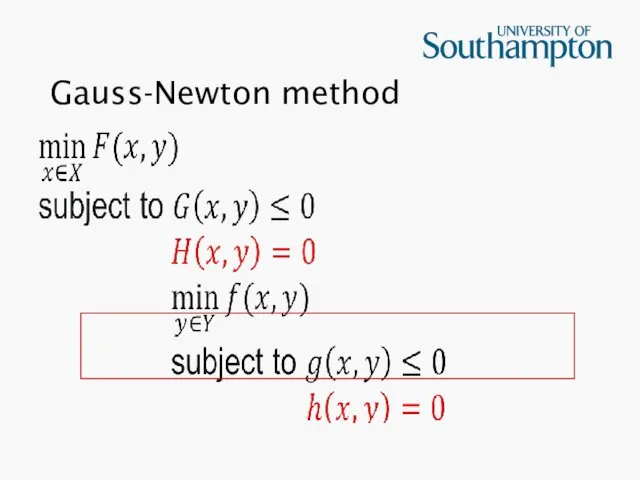
Слайд 24
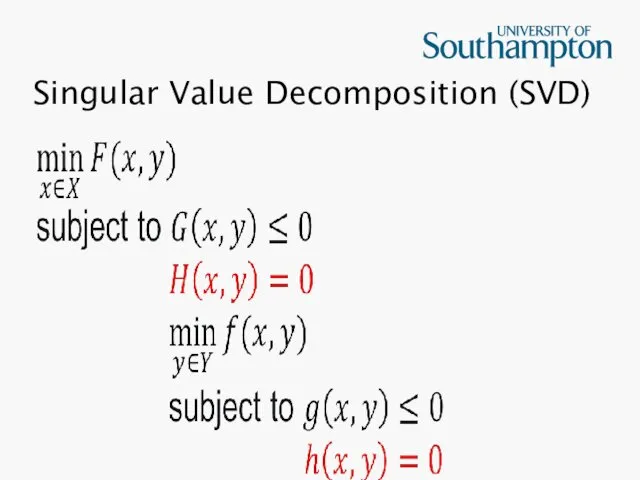
Singular Value Decomposition (SVD)
Слайд 25
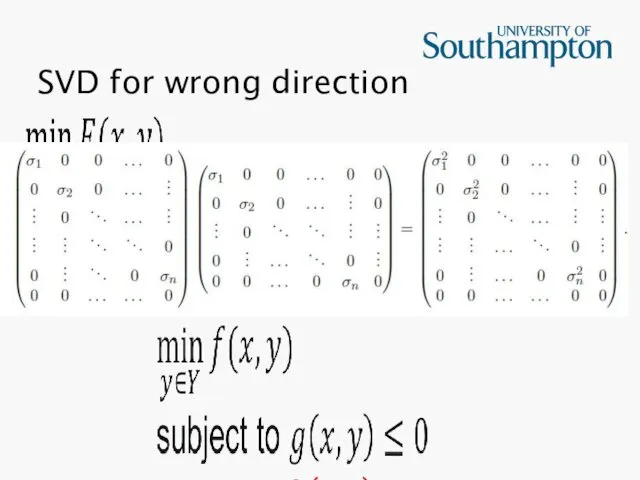
Слайд 26
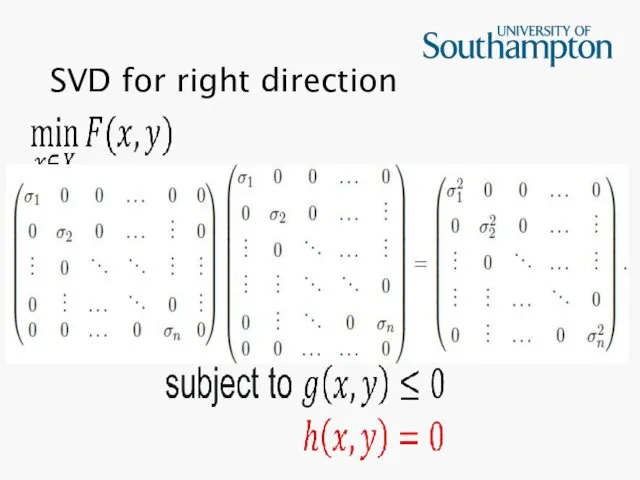
Слайд 27

Levenberg-Marquardt method
Слайд 28
Слайд 29

Слайд 30

Plans for further work
6. Construct the own code for Levenberg-Marquardt method
in the context of solving bilevel problems within defined reformulation.
7. Search for good starting point techniques for our problem. 8. Do the numerical calculations for the harder reformulation defined .
9. Code Newton method with pseudo-inverse.
10. Solve the problem assuming strict complementarity
11. Look at other solution methods.
Слайд 31

Слайд 32
































 Сложноподчиненные предложения
Сложноподчиненные предложения Методы и методические приемы обучения биологии
Методы и методические приемы обучения биологии Электродвигатели постоянного тока. Первый этап развития электродвигателя
Электродвигатели постоянного тока. Первый этап развития электродвигателя Булану мен конденсация
Булану мен конденсация Дерево тематик. Пассажиры
Дерево тематик. Пассажиры Этапы развития механизации ПРТС-работ. Организация погрузочно-разгрузочных, транспортных и складских работ
Этапы развития механизации ПРТС-работ. Организация погрузочно-разгрузочных, транспортных и складских работ Векторная графика в Web
Векторная графика в Web Презентация Коллекционирование как исследовательская практика ребёнка(Из опыта работы по программе А.И. Савенкова)
Презентация Коллекционирование как исследовательская практика ребёнка(Из опыта работы по программе А.И. Савенкова) деление десятичной дроби на натуральное число
деление десятичной дроби на натуральное число Типы климатов России разработка урока географии 8 класс
Типы климатов России разработка урока географии 8 класс Всероссийская олимпиада по искусству. Школьный этап. (9-11 класс)
Всероссийская олимпиада по искусству. Школьный этап. (9-11 класс) Рабочий отчет департамента аналитики компании IPO
Рабочий отчет департамента аналитики компании IPO There is, are
There is, are Презентация Виды современных велосипедов Диск
Презентация Виды современных велосипедов Диск Статистика посещения кинотеатров в России, 2009-2019 годы
Статистика посещения кинотеатров в России, 2009-2019 годы презентация результата совместного проекта с родителями
презентация результата совместного проекта с родителями Тест. Планеты Солнечной системы
Тест. Планеты Солнечной системы Презентации по основам православной культуры
Презентации по основам православной культуры Кодекс этической деятельности педагога
Кодекс этической деятельности педагога Развитие зрительного восприятия у детей с ОНР через игровую систему обучения
Развитие зрительного восприятия у детей с ОНР через игровую систему обучения Кітап оқуға баулу
Кітап оқуға баулу Летний профильный отряд по химии Волшебный мир химии
Летний профильный отряд по химии Волшебный мир химии Древняя Индия
Древняя Индия Ұлпа қабынуын емдеудің салыстырмалы сипаттамасы
Ұлпа қабынуын емдеудің салыстырмалы сипаттамасы Требования к хорошему кейсу
Требования к хорошему кейсу Как семейные традиции укрепляют семью
Как семейные традиции укрепляют семью Послеродовые гнойно-септические заболевания (перитонит, сепсис, токсико-инфекционный шок)
Послеродовые гнойно-септические заболевания (перитонит, сепсис, токсико-инфекционный шок) 7 класс: Население и страны Северной Америки
7 класс: Население и страны Северной Америки