- Главная
- Без категории
- Steel hardenability capacity and hardenability

Содержание
Слайд 2
Слайд 3
Слайд 4
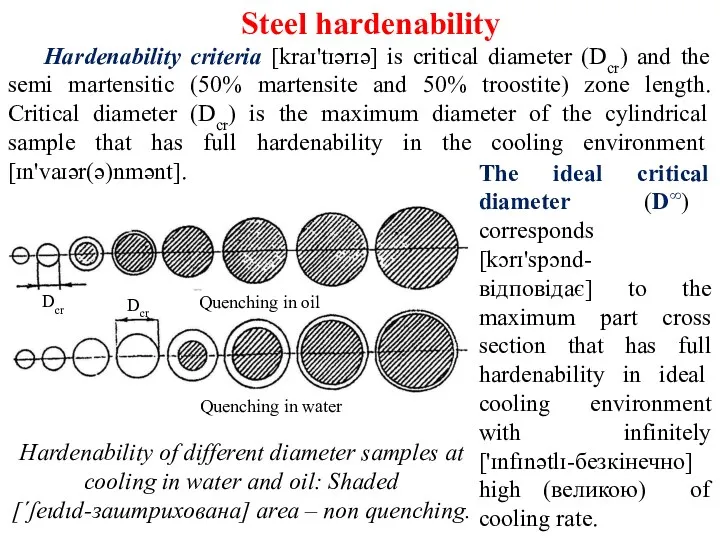
Steel hardenability
At the transition [træn'zɪʃ(ə)n-перехід] of the semi (напів) martensitic (50%
Steel hardenability
At the transition [træn'zɪʃ(ə)n-перехід] of the semi (напів) martensitic (50%
martensite and 50% troostite) to the martensitic structure (100% martensite) critical diameter (Dcr) decreases. Critical diameter (Dcr) decreases at replacement [rɪ'pleɪsmənt-зміна] of a cooling environment [ɪn'vaɪər(ə)nmənt-середовищe], for example of water to mineral oil (slide 18).
If necessary mechanical properties are provided by semi (напів) martensitic structure, for example structural steels, Dcr defined as D50.
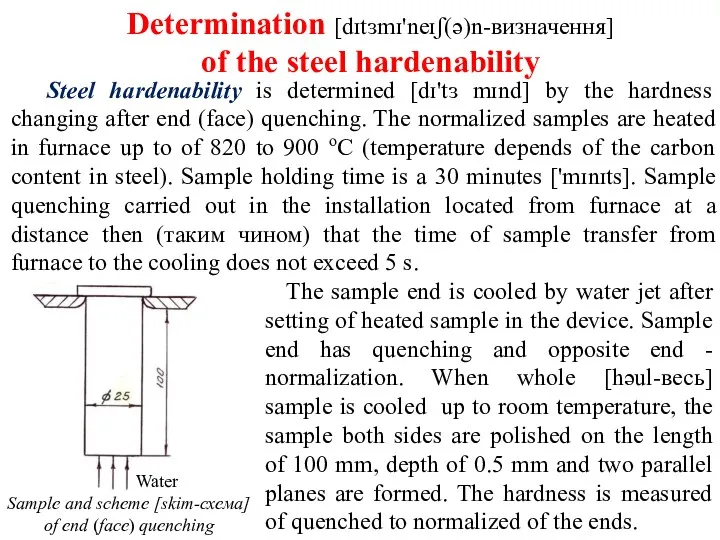
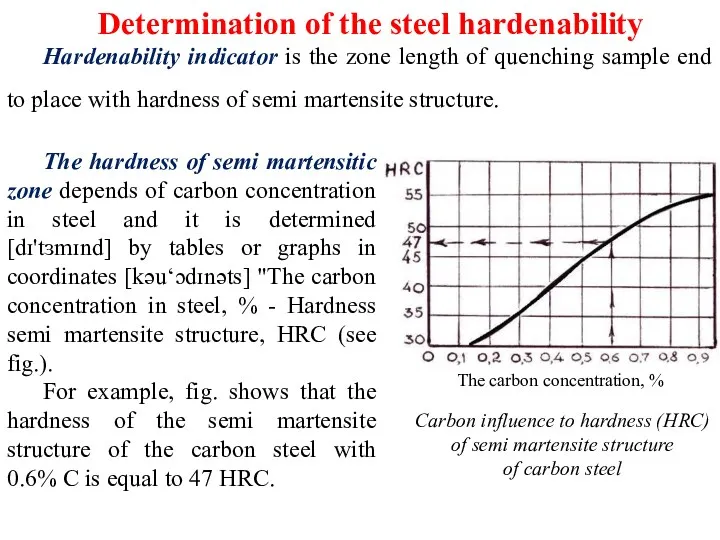
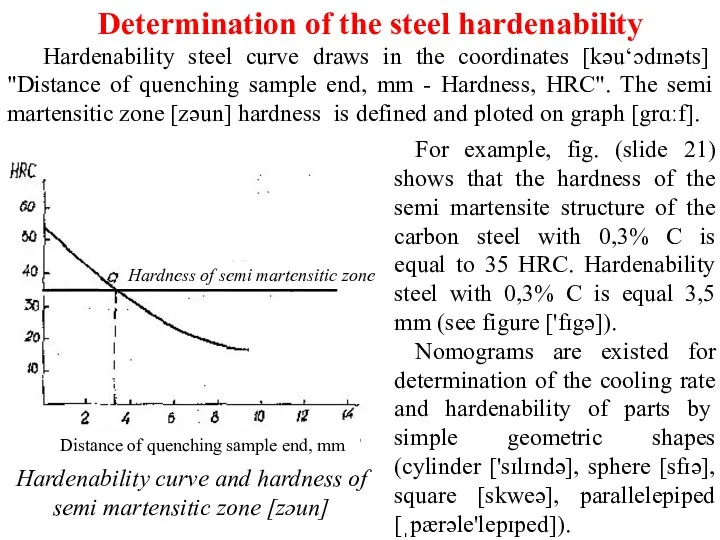
Structural steel hardenability is determined as the layer thickness that has semi martensitic structure. Semi martensitic structure hardness depends of the carbon concentration in steel and is determined by tables or graphs draw [drɔ-побудованими] in the coordinates of the “Carbon concentration, % - Hardness of semi martensitic zone, НRС”.
Tool steel hardenability is determined by the thickness of the hardened layer with martensitic structure. Hardness is НRС 60.
If necessary mechanical properties are provided by semi (напів) martensitic structure, for example structural steels, Dcr defined as D50.
Structural steel hardenability is determined as the layer thickness that has semi martensitic structure. Semi martensitic structure hardness depends of the carbon concentration in steel and is determined by tables or graphs draw [drɔ-побудованими] in the coordinates of the “Carbon concentration, % - Hardness of semi martensitic zone, НRС”.
Tool steel hardenability is determined by the thickness of the hardened layer with martensitic structure. Hardness is НRС 60.
Слайд 5
Слайд 6
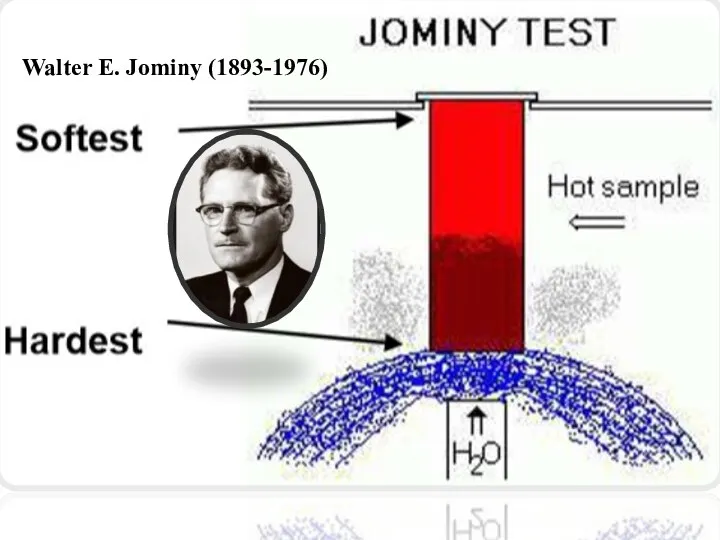
Walter E. Jominy (1893-1976)
Walter E. Jominy (1893-1976)
Слайд 7
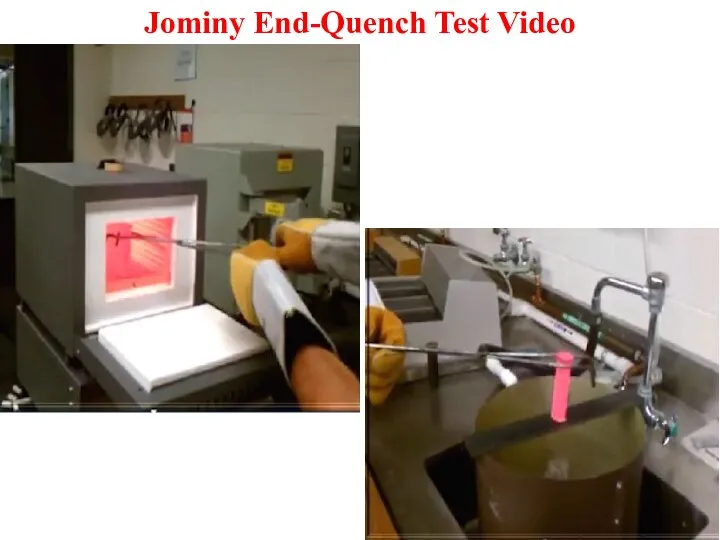
Jominy End-Quench Test Video
Jominy End-Quench Test Video
Слайд 8
Jominy End-Quench Test Video
Jominy End-Quench Test Video
Слайд 9
Слайд 10
- Предыдущая
Растительный и животный мир РоссииСледующая -
Мультимедийные устройства
![Steel hardenability At the transition [træn'zɪʃ(ə)n-перехід] of the semi (напів)](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/381532/slide-3.jpg)

 Автомобильная промышленость США
Автомобильная промышленость США Технология VLSM. Маски подсети переменной длины
Технология VLSM. Маски подсети переменной длины Стихотворение Г.Рублева Памятник
Стихотворение Г.Рублева Памятник Статистический анализ данных в MS Excel
Статистический анализ данных в MS Excel Здоровье педагога
Здоровье педагога Делегаты. (Лекция 10)
Делегаты. (Лекция 10) Закон о занятости населения в Российской Федерации
Закон о занятости населения в Российской Федерации Анотация к курсу Не боги горшки обжигали - лепка из глины.
Анотация к курсу Не боги горшки обжигали - лепка из глины. ПРЕЗЕНТАЦИЯ Использование ИКТ в работе учителя логопеда
ПРЕЗЕНТАЦИЯ Использование ИКТ в работе учителя логопеда урок технологии РОЗЫ ИЗ ПЛАСТИЛИНА
урок технологии РОЗЫ ИЗ ПЛАСТИЛИНА Порядок формирований спепендиального фонда на выплаты стипендий за счет средств федерального бюджета
Порядок формирований спепендиального фонда на выплаты стипендий за счет средств федерального бюджета Актуализация лексических навыков по теме Космос. План-конспект урока
Актуализация лексических навыков по теме Космос. План-конспект урока Научно-педагогическая практика в гимназии Альма-матер и гимназии №239. Основные трудности в педагогической деятельности
Научно-педагогическая практика в гимназии Альма-матер и гимназии №239. Основные трудности в педагогической деятельности Топ 10 посещаемых мною сайтов
Топ 10 посещаемых мною сайтов Великая Отечественная война. Красная армия и Вермахт. Цена победы
Великая Отечественная война. Красная армия и Вермахт. Цена победы Драма А.Н.Островского Гроза. Город Калинов и его обитатели
Драма А.Н.Островского Гроза. Город Калинов и его обитатели Основные виды помех средствам активной радиолокации
Основные виды помех средствам активной радиолокации Свойства металла
Свойства металла Дни воинской славы
Дни воинской славы Я - перспективная личность
Я - перспективная личность Презентация: из истории Памятника Архитектуры и культуры Краснодарского края Свято-Троицкого храма ст. Платнировской. 1906 - 2011
Презентация: из истории Памятника Архитектуры и культуры Краснодарского края Свято-Троицкого храма ст. Платнировской. 1906 - 2011 Правовое обучение. Сущность и место в правовом образовании. Методы и методические приемы в преподавании права. (Лекция 2)
Правовое обучение. Сущность и место в правовом образовании. Методы и методические приемы в преподавании права. (Лекция 2) Спирты. 9 класс
Спирты. 9 класс Сложение и вычитание чисел в пределах 1000 с переходом через разряд
Сложение и вычитание чисел в пределах 1000 с переходом через разряд Время. Скорость. Расстояние
Время. Скорость. Расстояние Конспект внеклассного занятия в 4 классе Своя игра 2 тур
Конспект внеклассного занятия в 4 классе Своя игра 2 тур Византийская Империя
Византийская Империя Предложение по созданию общегородского конкурса танца и моды между детскими садами Dancing Family
Предложение по созданию общегородского конкурса танца и моды между детскими садами Dancing Family