Содержание
- 2. Речь какого-нибудь лица, передаваемая буквально так, как она была произнесена, называется прямой речью (direct speech). Речь,
- 3. Direct Speech She says, "I phone my friends every day". (утвердительное предложение) Reported Speech She says
- 4. Direct Speech The grandfather says to Mary, “What mark did you get at school?” (вопросительное предложение)
- 5. Direct Speech The teacher said to the pupils, "Don't open your books.“ (просьба / приказ) Reported
- 6. При переводе предложения из прямой речи в косвенную соблюдаются следующие правила: 1. Запятая, отделяющая слова, вводящие
- 7. 2. Все личные и притяжательные местоимения изменяются по смыслу. Direct Speech Bob said, “I am learning
- 8. Direct Speech He said, "I don't like to watch cartoons.” Reported Speech He said (that) he
- 9. Direct Speech The manager says to Mike: “Does your father work at a factory?” Reported Speech
- 10. Direct Speech Kate said to her grandmother, "Help me to cook the soup, please!“ Reported Speech
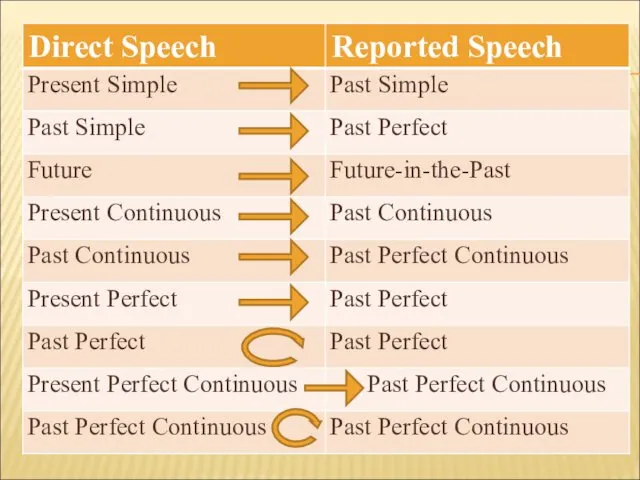
- 11. 3. При переводе из прямой речи в косвенную в первую очередь следует обращать внимание на грамматическое
- 12. а) Если глагол, вводящий косвенную речь, стоит в одном из настоящих или будущих времен, грамматическое время
- 13. Direct Speech Не says, "I can't remember where I've put the tickets. (Present Simple) Reported Speech
- 14. Direct Speech He has already said, "I can't remember where he's put the tickets. (Present Perfect)
- 15. Direct Speech If you ask him about the tickets, he'll say, "I can't remember where I've
- 16. b) Если глагол, вводящий косвенную речь, стоит в одном из прошедших времен, глагол в придаточном предложении
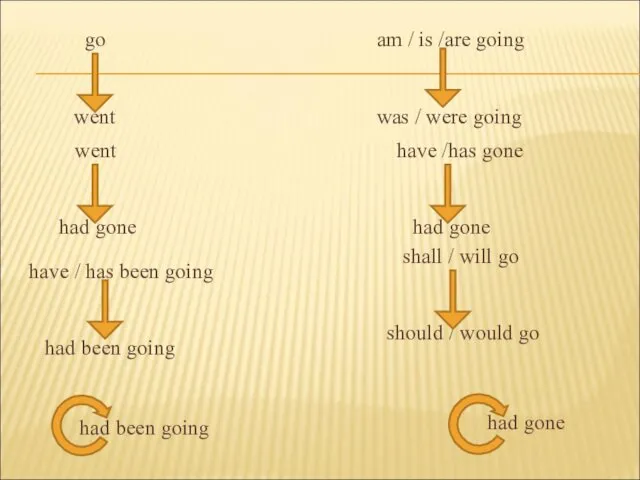
- 18. go went went had gone have / has been going had been going am / is
- 19. Direct Speech Tom said to the boys, “Who has tickets for “Hamlet”? (Present Simple) Reported Speech
- 20. Direct Speech Mary said, “I will do it after my arrival”. (Future Simple) Reported Speech Mary
- 21. Direct Speech Sam said, “He didn’t get on with his stepma”. (Past Simple) Reported Speech Sam
- 22. Правило согласования времен не действует в следующих случаях: 1) Если сказуемое в придаточном предложении выражает общеизвестное
- 23. Правило согласования времен не действует в следующих случаях: 2) Если в придаточном предложении указано время совершения
- 24. Правило согласования времен не действует в следующих случаях: 3) В предложениях, в придаточных которых употребляется сослагательное
- 25. 4. При переводе прямой речи в косвенную меняются также слова, обозначающие место и время действия.
- 26. Direct Speech She said, "I left Natalie a message an hour ago”. Reported Speech She said
- 27. Direct Speech The teacher said, "Did you read an English book last year?“ Reported Speech The
- 28. The boyfriend said, “Take this book, please”. Reported Speech The boyfriend asked her girl to take
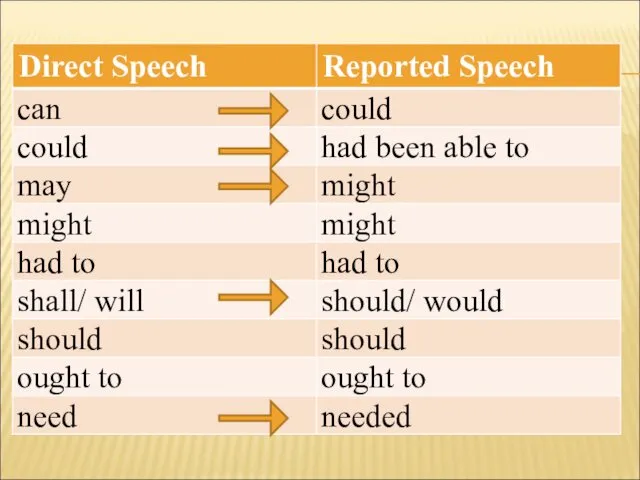
- 29. 5. Если в предложении содержатся модальные глаголы, то они подвергаются изменениям при переводе прямой речи в
- 31. Direct Speech Ann: "I can't skate." Reported Speech Ann says (that) she can't skate. Ann said
- 32. Direct Speech The teacher said, “You ought to be very serious about your homework. Reported Speech
- 33. Запомни! Глагол must заменяется в косвенной речи глаголом had, только когда must выражает необходимость совершения действия
- 34. 1. Direct Speech My mother said, “You must consult a doctor”. Reported Speech My mother said
- 35. 2. Direct Speech She said, "I must send him a telegram at once." Reported Speech She
- 37. Скачать презентацию































 Выпускной 4 класс Что? Где?Когда?
Выпускной 4 класс Что? Где?Когда? Презентация. Великобритания.
Презентация. Великобритания. Презентация История новогодней игрушки.
Презентация История новогодней игрушки. Основные принципы переработки сырья в производстве солода и пива
Основные принципы переработки сырья в производстве солода и пива Путешествие в страну Информатика
Путешествие в страну Информатика Развитие речи на прогулке, на кухне, на даче
Развитие речи на прогулке, на кухне, на даче ИКТ как средство взаимодействия участников образовательно-воспитательного процесса и социального окружения ДОУ
ИКТ как средство взаимодействия участников образовательно-воспитательного процесса и социального окружения ДОУ Фрезерование плоских поверхностей. Фрезерование наклонных и скосов
Фрезерование плоских поверхностей. Фрезерование наклонных и скосов Полиграфические материалы. Производство бумаги
Полиграфические материалы. Производство бумаги Диагностика электрооборудования автомобилей
Диагностика электрооборудования автомобилей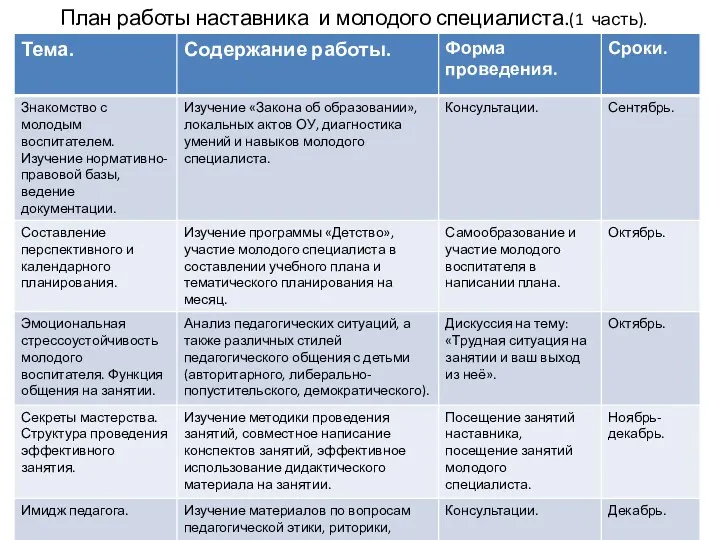 План работы наставника.
План работы наставника. Сообщающиеся сосуды
Сообщающиеся сосуды Музей в жизни города (ИЗО)
Музей в жизни города (ИЗО) Новый год. 2021
Новый год. 2021 Упражнения на развитие внимания детей младшего школьного возраста
Упражнения на развитие внимания детей младшего школьного возраста Correct the mistakes! GO!
Correct the mistakes! GO! Здоровое питание
Здоровое питание Методы многокритериального анализа альтернатив для слабоструктурированных проблем
Методы многокритериального анализа альтернатив для слабоструктурированных проблем Виды правонарушений. Преступление
Виды правонарушений. Преступление Презентация Лягушка - зелёное брюшко (сказочная история для язычка)
Презентация Лягушка - зелёное брюшко (сказочная история для язычка)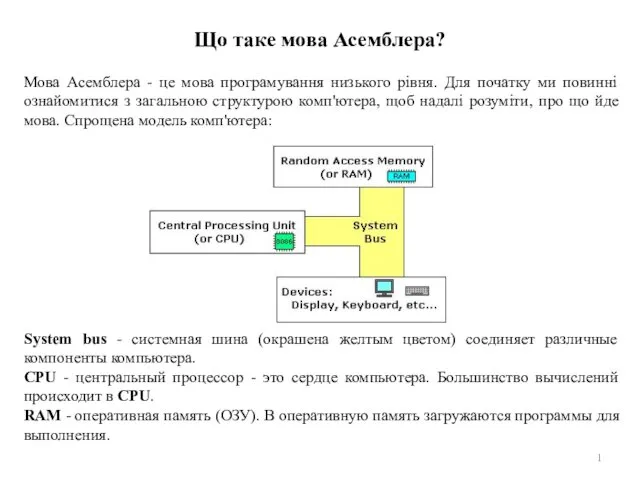 Цифрові технології. Мова Асемблера. (Тема 6-7)
Цифрові технології. Мова Асемблера. (Тема 6-7) Бас пен бет жарақаты кезіндегі қан кетуді тоқтату әдістері
Бас пен бет жарақаты кезіндегі қан кетуді тоқтату әдістері Проектирование и расчёт дощатого настила
Проектирование и расчёт дощатого настила Спуск эксплуатационной колонны
Спуск эксплуатационной колонны Плоскость, прямая, луч. 5 класс
Плоскость, прямая, луч. 5 класс Влияние мультфильмов на развитие ребенка дошкольного возраста
Влияние мультфильмов на развитие ребенка дошкольного возраста Организация работы регистратуры
Организация работы регистратуры Права ребенка
Права ребенка