Содержание
- 2. Examination of respiratory system History taking Enviromental Usability of the horse Enviromental conditio in stable Food
- 3. Examination of respiratory system General examination Heart rate, breath rate, lymph nodes, membrane mucus, temperature Detail
- 4. Upper respiratory tract disease Rhinitis Necrosis conchae Polyps Ethmoid hematoma Nasal neoplasma Sinusitis Pharyngitis Guttural pouch
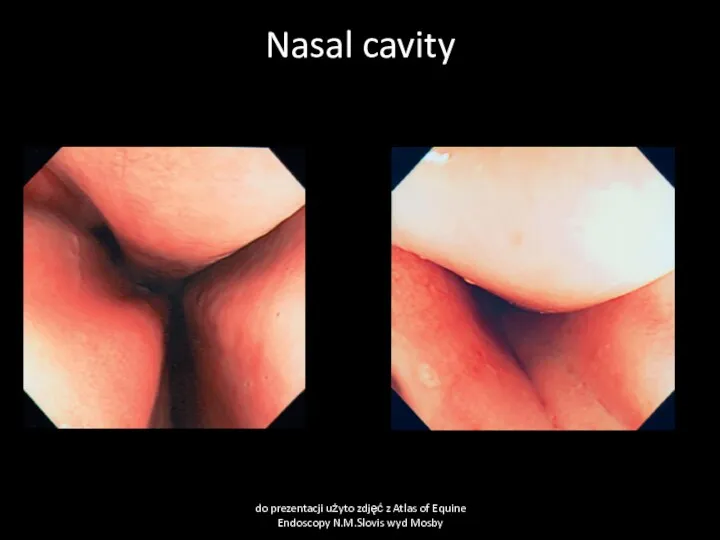
- 5. Nasal cavity do prezentacji użyto zdjęć z Atlas of Equine Endoscopy N.M.Slovis wyd Mosby
- 6. Rhinitis Cause: Virus infections-Infuenza, rhinovirus, herpesvirus, arteritis virus, adenovirus, reovirus, Bacterial infections -Streptococcus sp., glanders (Psudomonas
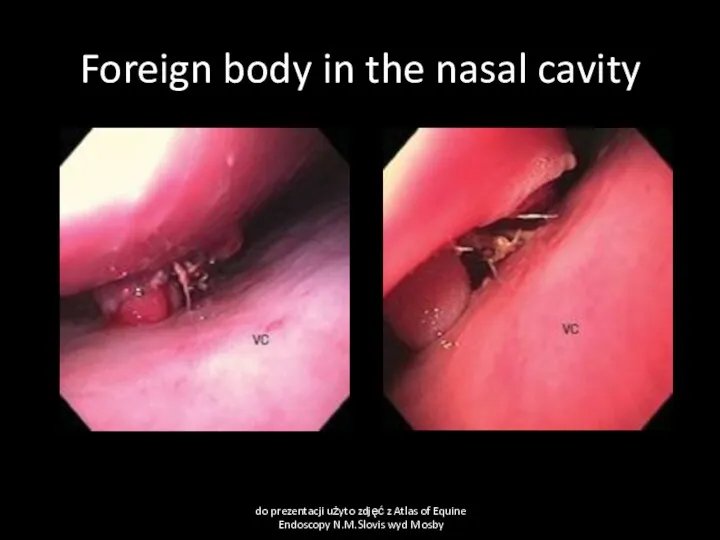
- 7. Foreign body in the nasal cavity do prezentacji użyto zdjęć z Atlas of Equine Endoscopy N.M.Slovis
- 8. Rhinitis Clinical pathology Virology Bacteriology Mycology Mainly to exclude or confirm infectious disease. In some cases
- 9. Necrosis conche Cause Bacterial or fungal infections. Clinical signs Muco-purulent, sometimes blood tinged, odorous discharge uni/bilateral.
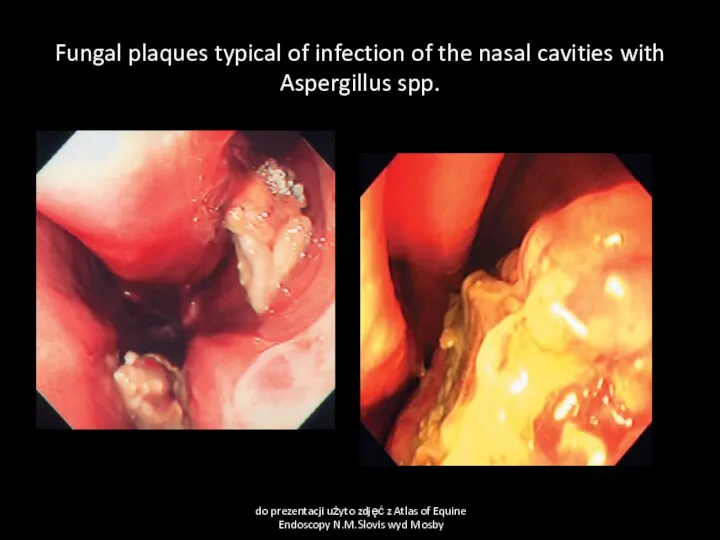
- 10. Fungal plaques typical of infection of the nasal cavities with Aspergillus spp. do prezentacji użyto zdjęć
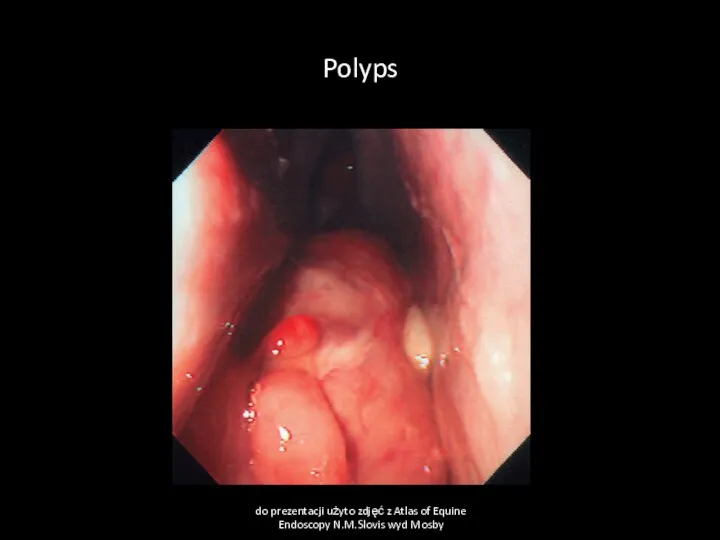
- 11. Polyps Cause Chronic inflamation of nasal mucous membranes of any cause Clinical sign Sero-muco-purulent nasal discharge
- 12. Polyps do prezentacji użyto zdjęć z Atlas of Equine Endoscopy N.M.Slovis wyd Mosby
- 13. Nasal neoplasma Cause Neoplasia- myxoma, fibroma, chondroma, osteochondroma, carcinoma, melanoma Clinical signs Uni/bilateral nasal discharge, sero-muco-purulent,
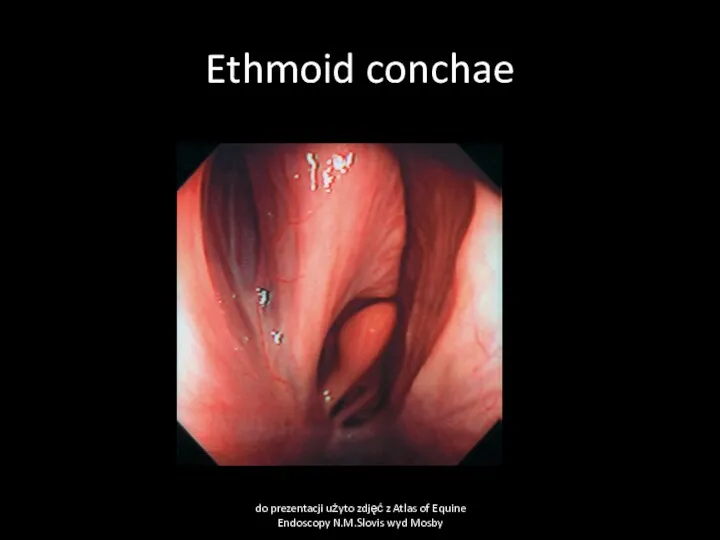
- 14. Ethmoid conchae do prezentacji użyto zdjęć z Atlas of Equine Endoscopy N.M.Slovis wyd Mosby
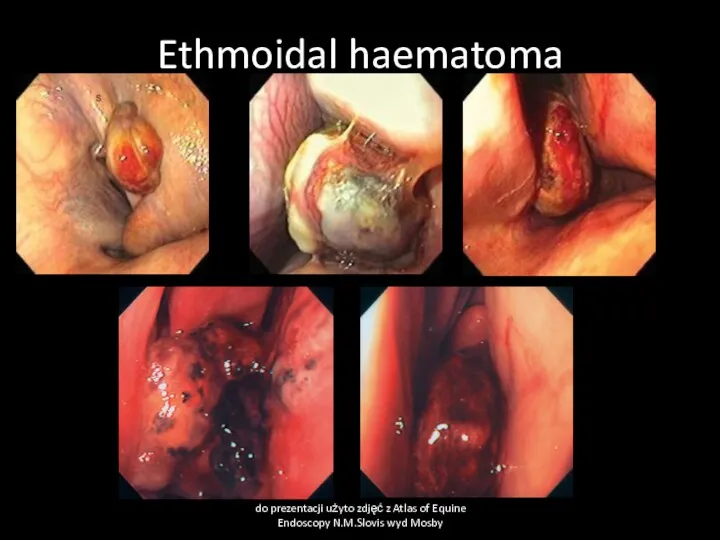
- 15. Ethmoidal hematoma Cause Neoplasia? Chronic infections, circulatory defect Clinical signs At the beginning usually unilaterally nasal
- 16. Ethmoidal haematoma do prezentacji użyto zdjęć z Atlas of Equine Endoscopy N.M.Slovis wyd Mosby
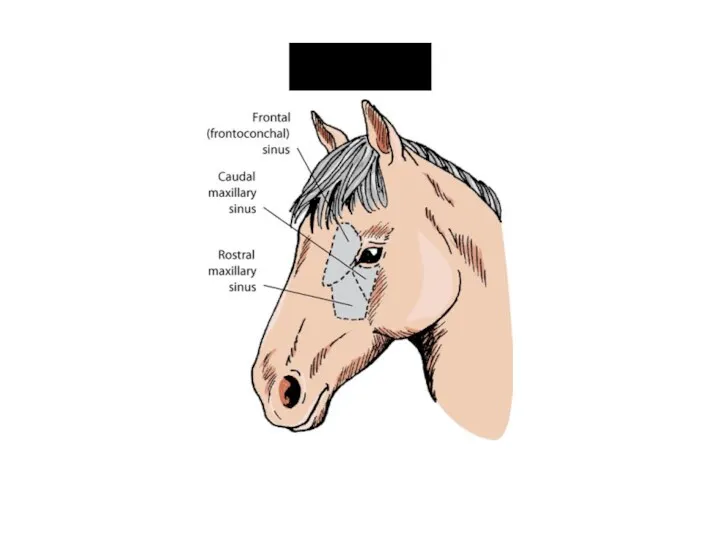
- 17. Sinuses
- 18. Sinusitis Cause Usually secondary to rhinitis, tooth problems, defects of sinus communication with nasal cavity Clinical
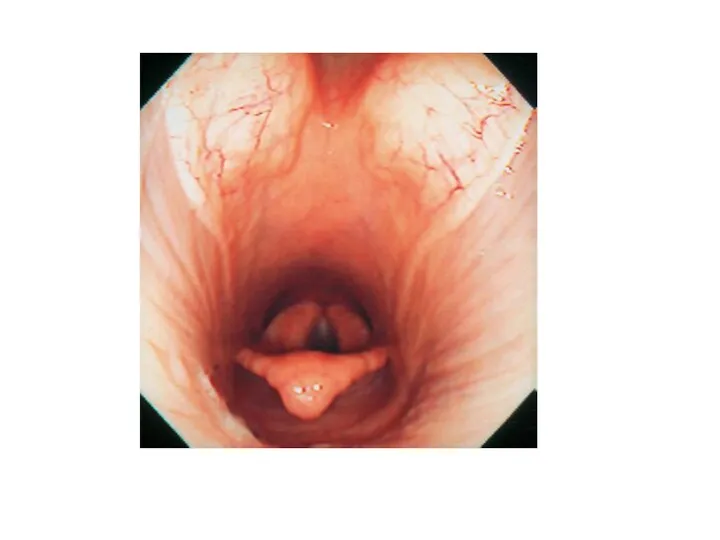
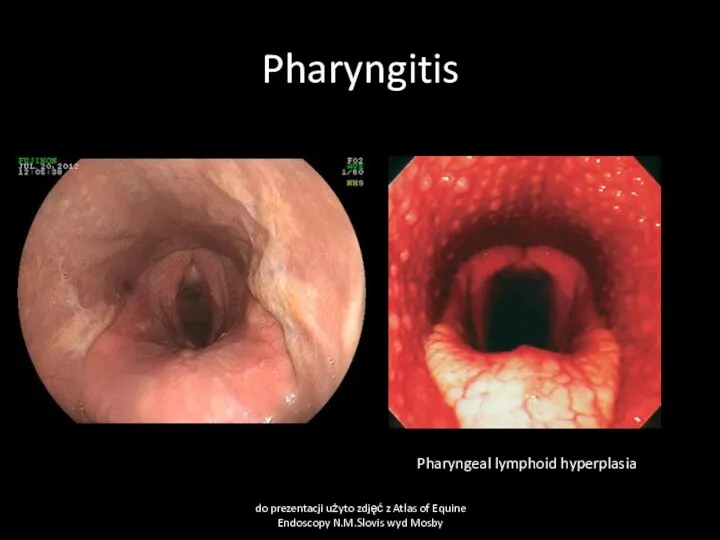
- 21. Pharyngitis Cause Viral infections- influenza, herpesvirus, adenovirus, arteritis virus, Bacterial infection-mainly Streptococcus spp. Physical trauma-stomach tube,
- 22. Pharyngitis Clinical signs decreased appetite, difficult swallowing, cough, increased temperature of swollen, painful throat and local
- 23. Pharyngitis do prezentacji użyto zdjęć z Atlas of Equine Endoscopy N.M.Slovis wyd Mosby Pharyngeal lymphoid hyperplasia
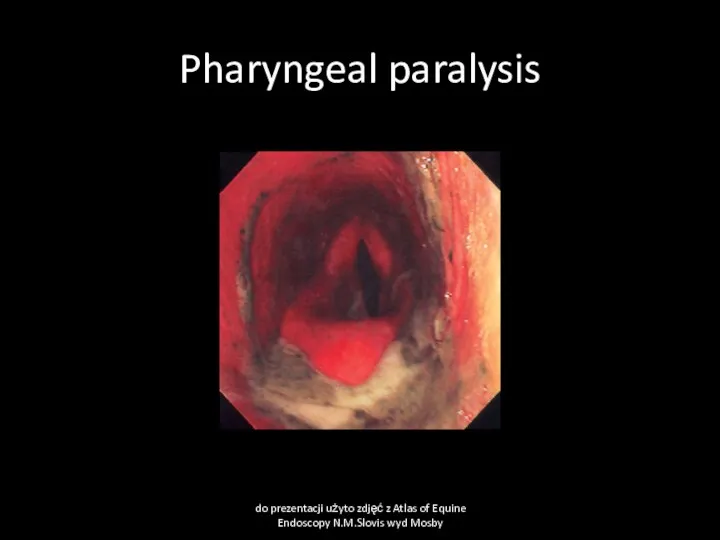
- 24. Pharyngeal paralysis do prezentacji użyto zdjęć z Atlas of Equine Endoscopy N.M.Slovis wyd Mosby
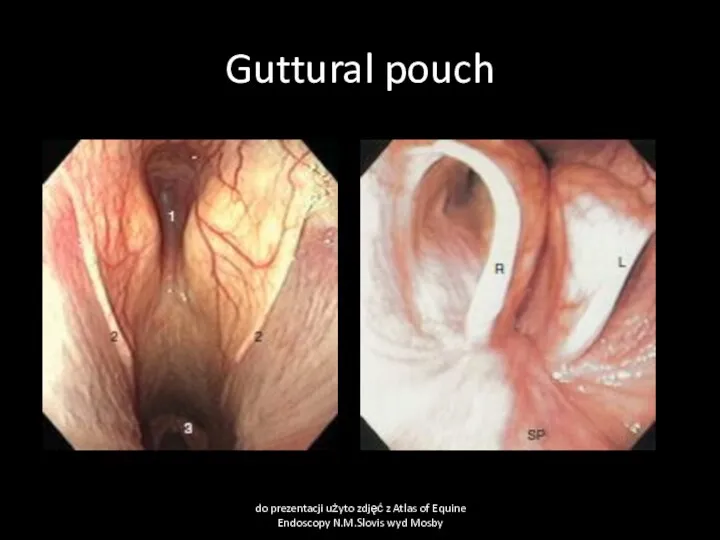
- 25. Guttural pouch do prezentacji użyto zdjęć z Atlas of Equine Endoscopy N.M.Slovis wyd Mosby
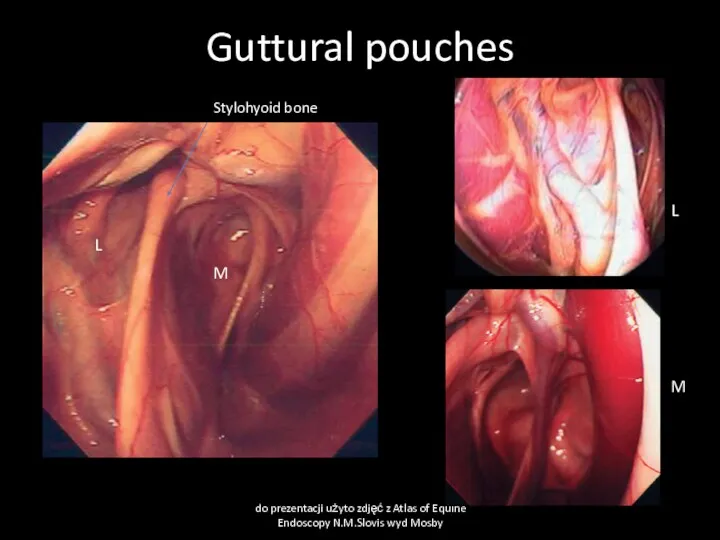
- 26. Guttural pouches do prezentacji użyto zdjęć z Atlas of Equine Endoscopy N.M.Slovis wyd Mosby Stylohyoid bone
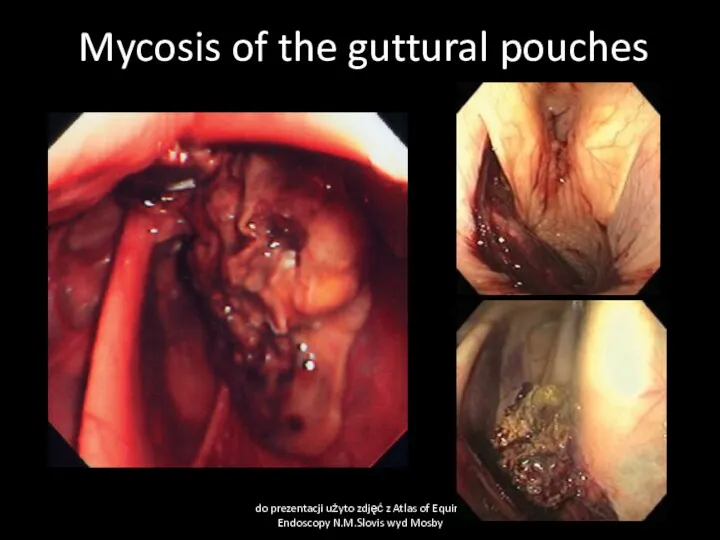
- 27. Guttural pouch mycosis Cause: Fungal infections- Aspergillus fumigatus often with bacterial contamination- Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Primary lesion
- 28. Mycosis of the guttural pouches do prezentacji użyto zdjęć z Atlas of Equine Endoscopy N.M.Slovis wyd
- 29. Guttural pouch mycosis Clinical pathology Endoscopy Mycolgy Bacteriology Hematology Treatment Local washing with antifungal drugs (econazol,
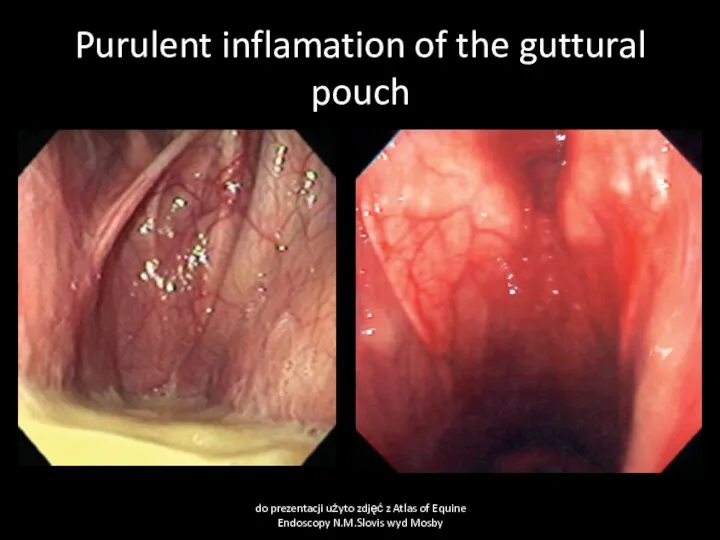
- 30. Guttural pouch empyema Cause: mainly Streptococcus spp. Infections, Clinical signs: Uni/bilateral muco-purulent nasal discharge, more obvious
- 31. Purulent inflamation of the guttural pouch do prezentacji użyto zdjęć z Atlas of Equine Endoscopy N.M.Slovis
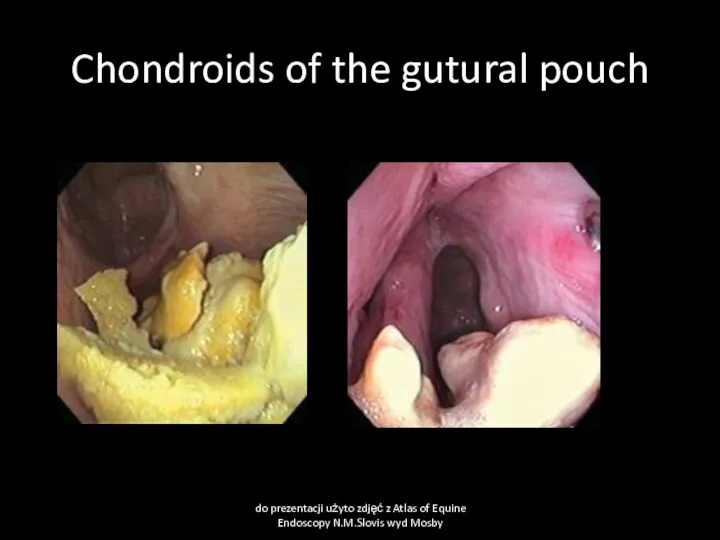
- 32. Guttural pouch chondroids Cause Inspissated guttural pouch exudate forms stones Clinical signs Swelling of guttural pouch
- 33. Chondroids of the gutural pouch do prezentacji użyto zdjęć z Atlas of Equine Endoscopy N.M.Slovis wyd
- 34. Guttural pouch tympany Cause Congenital defects of guttural pouch operculum Clinical signs Swelling of guttural pouch
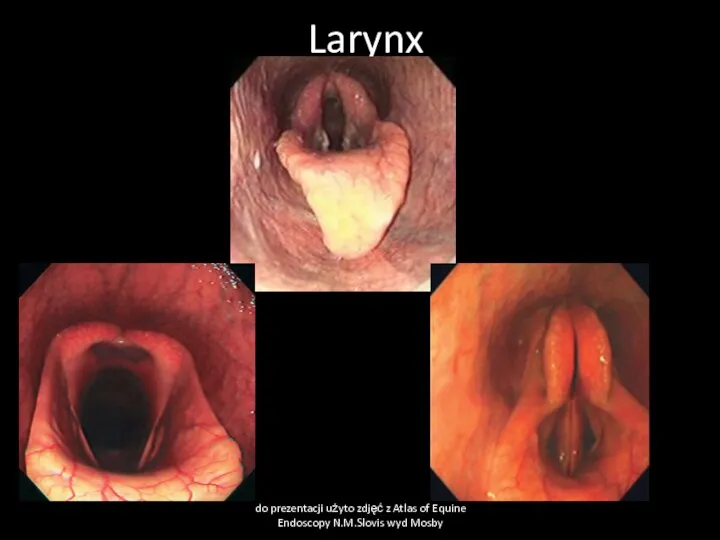
- 35. Larynx do prezentacji użyto zdjęć z Atlas of Equine Endoscopy N.M.Slovis wyd Mosby
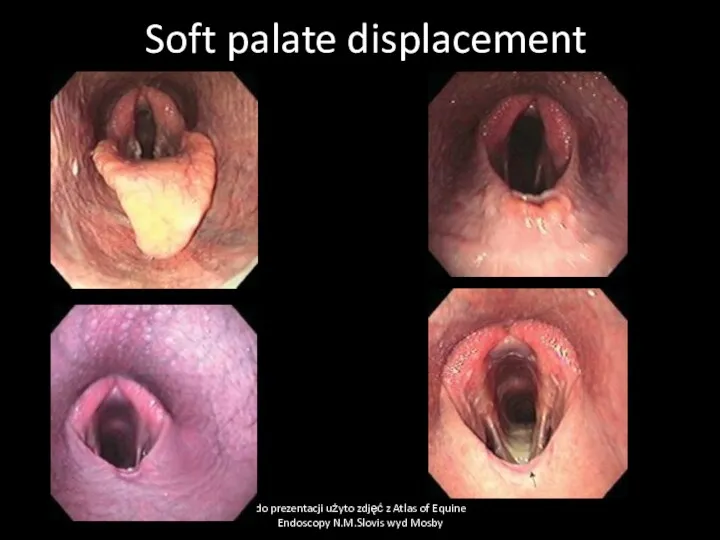
- 36. Soft palate displacement Cause Paresis of soft palate due to some neurological deficit, swelling of soft
- 37. Soft palate displacement do prezentacji użyto zdjęć z Atlas of Equine Endoscopy N.M.Slovis wyd Mosby
- 38. Aryepiglottic fold displacement (epiglottic entratment) Cause Edema of soft tissue close to epiglottis. Congenital shortening of
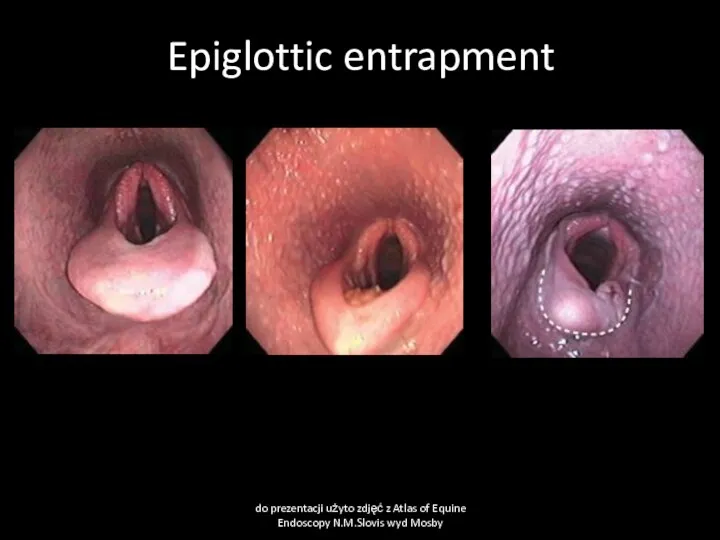
- 39. Epiglottic entrapment do prezentacji użyto zdjęć z Atlas of Equine Endoscopy N.M.Slovis wyd Mosby
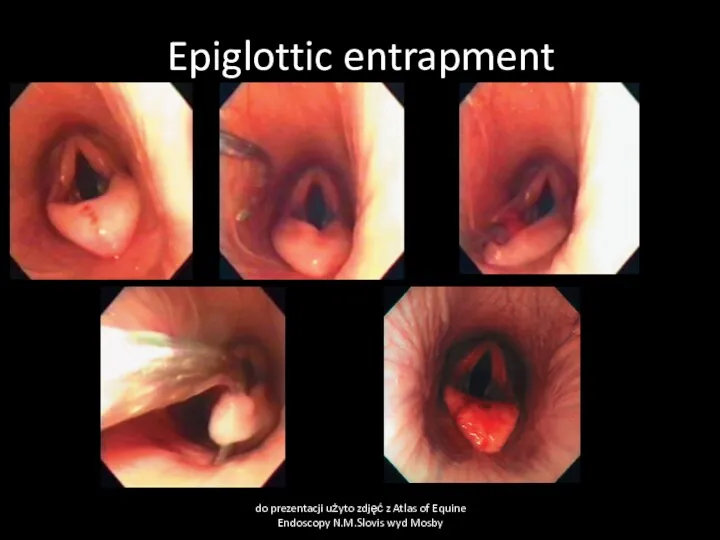
- 40. Epiglottic entrapment do prezentacji użyto zdjęć z Atlas of Equine Endoscopy N.M.Slovis wyd Mosby
- 41. Laryngitis Cause Viral infections- influenza, herpesvirus, adenovirus, arteritis virus, Bacterial infection-mainly Streptococcus spp. Physical trauma-stomach tube,
- 42. Laryngeal edema Cause Acute inflamation, allergy, irritant substances, surgery at larynx region Clinical signs Abnormal respiratory
- 43. Larynx neoplasms Cause Neoplasia-papilloma, carcinoma, adenoma, fibroma, chondroma Clinical signs: Nasal discharge- muco-purulent, blood tinged, often
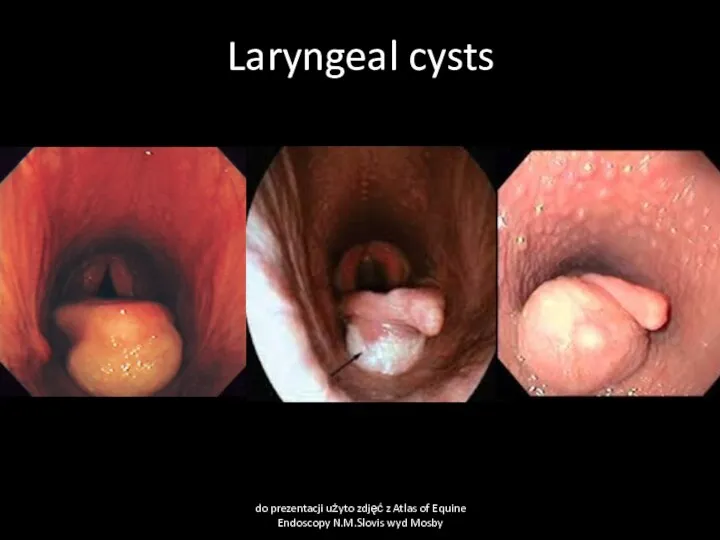
- 44. Larygeal cysts Cause Usually congenital cyst Clinical signs: abnormal laryngeal respiratory sound, dyspnea, cough Clinical pathology
- 45. Laryngeal cysts do prezentacji użyto zdjęć z Atlas of Equine Endoscopy N.M.Slovis wyd Mosby
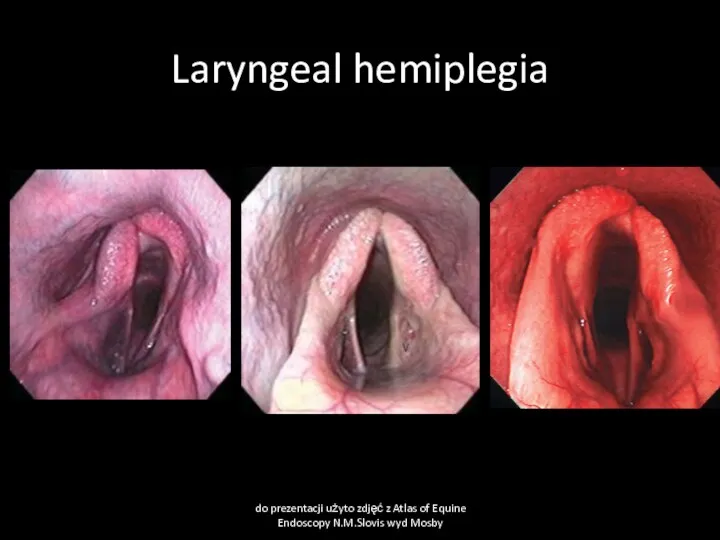
- 46. Laryngeal hemiplegia Cause Recurrent laryngeal nerve paralysis due to general neuropathy, inherited, poisonings, local swelling, fungal
- 47. Laryngeal hemiplegia do prezentacji użyto zdjęć z Atlas of Equine Endoscopy N.M.Slovis wyd Mosby
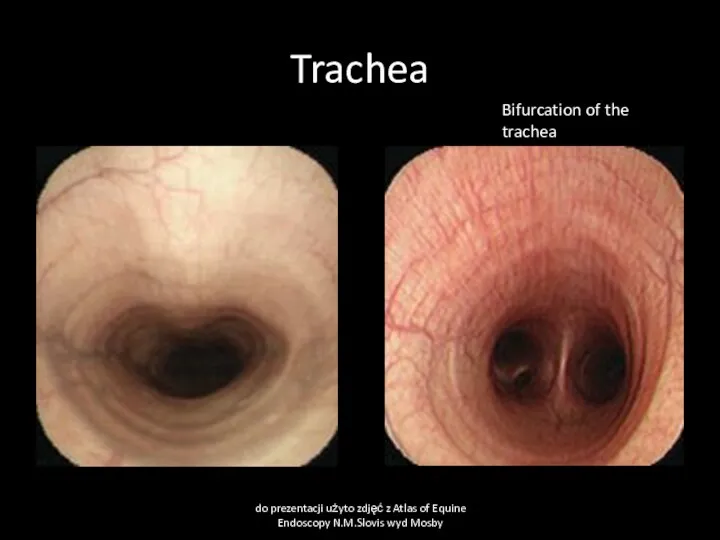
- 48. Trachea do prezentacji użyto zdjęć z Atlas of Equine Endoscopy N.M.Slovis wyd Mosby Bifurcation of the
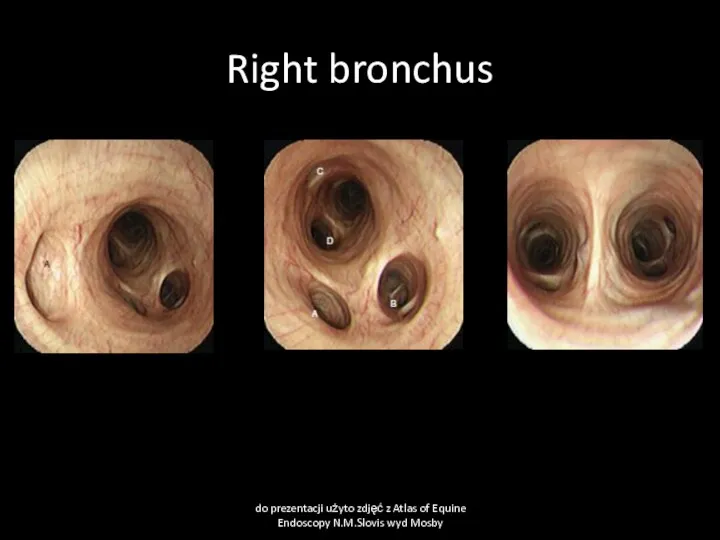
- 49. Right bronchus do prezentacji użyto zdjęć z Atlas of Equine Endoscopy N.M.Slovis wyd Mosby
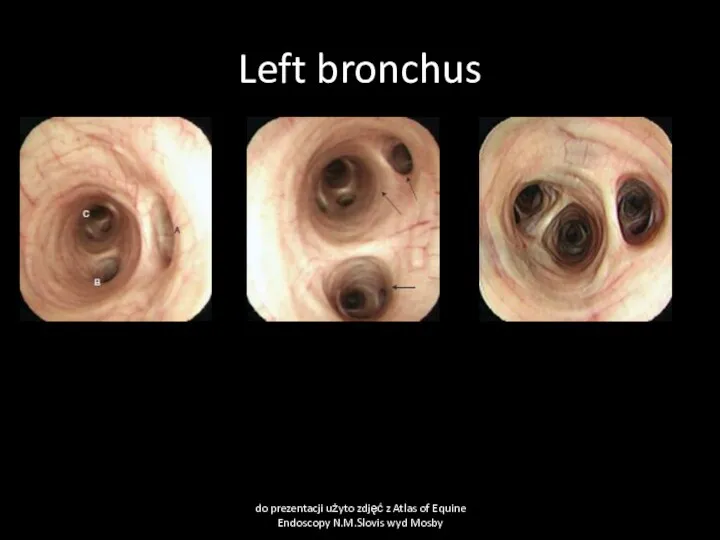
- 50. Left bronchus do prezentacji użyto zdjęć z Atlas of Equine Endoscopy N.M.Slovis wyd Mosby
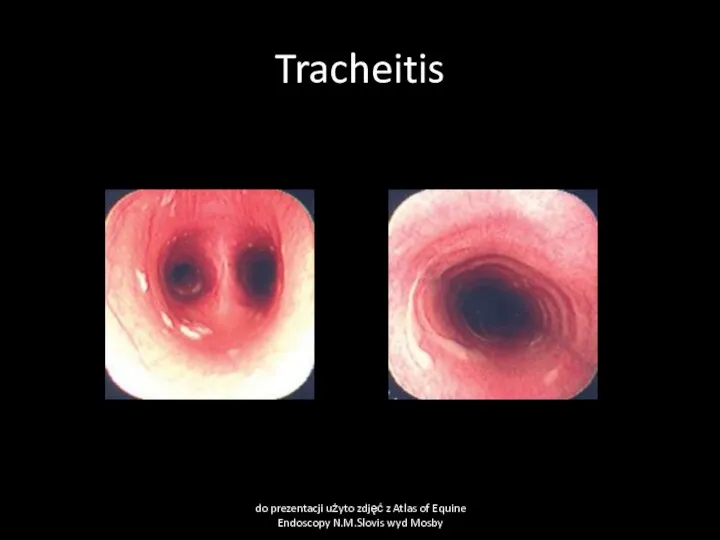
- 51. Tracheitis and bronchitis Cause Infection equine influenza, equine herpes virus, equine viral arteritis, streptococcal infections, other
- 52. Tracheitis do prezentacji użyto zdjęć z Atlas of Equine Endoscopy N.M.Slovis wyd Mosby
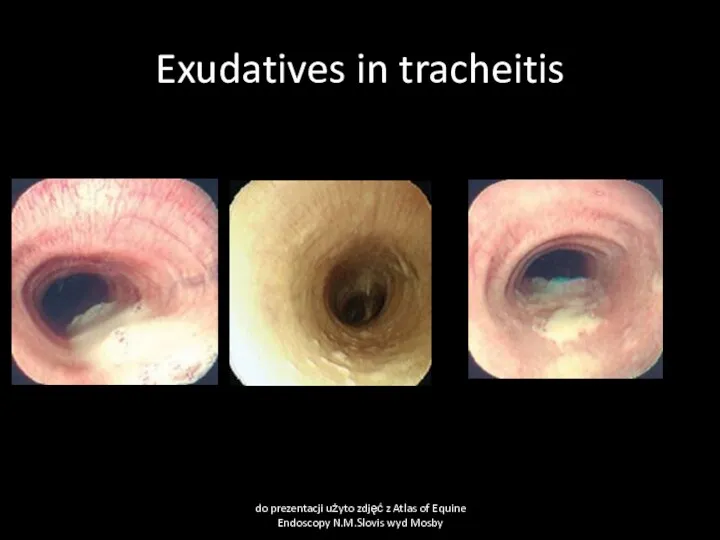
- 53. Exudatives in tracheitis do prezentacji użyto zdjęć z Atlas of Equine Endoscopy N.M.Slovis wyd Mosby
- 54. Tracheitis and bronchitis Clinical pathology bacteriological examination of tracheal wash or tharcheal aspirates, cytology, X-ray, thorax
- 55. Diseases of lungs Exercise-induced pulmonary hemorrhage Recurrect airway obstruction
- 56. Exercise-induced pulmonary hemorrhage Cause High pulmonary blood pressure during sternuous exercise cause rupture of pulmonary capillares.
- 57. Exercise-induced pulmonary hemorrhage Clinical signs: May be found in >80% racing horces but clinically observed in
- 58. Exercise-induced pulmonary hemorrhage Clinical pathology Macrophages with digested red blood cells (hemosiderin) in sample of tracheal
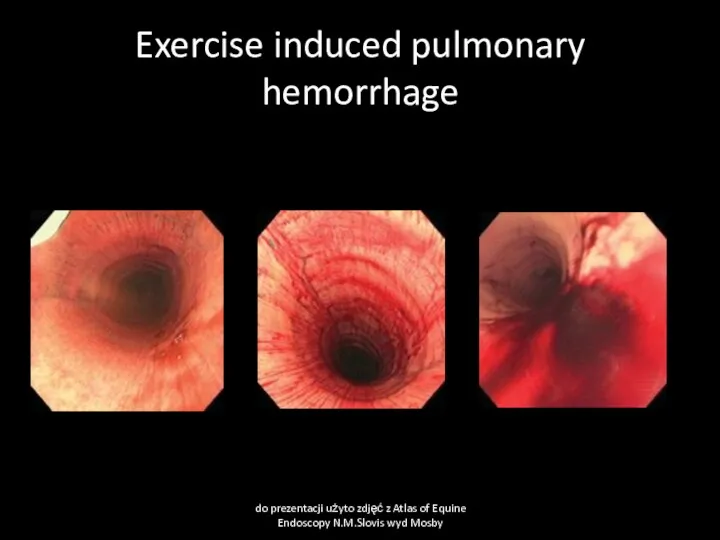
- 59. Exercise induced pulmonary hemorrhage do prezentacji użyto zdjęć z Atlas of Equine Endoscopy N.M.Slovis wyd Mosby
- 60. Exercise- induced pulmonary hemorrhage Treatment Rest, Treat respiratory disease if present. Furosemide before sternuous exercise may
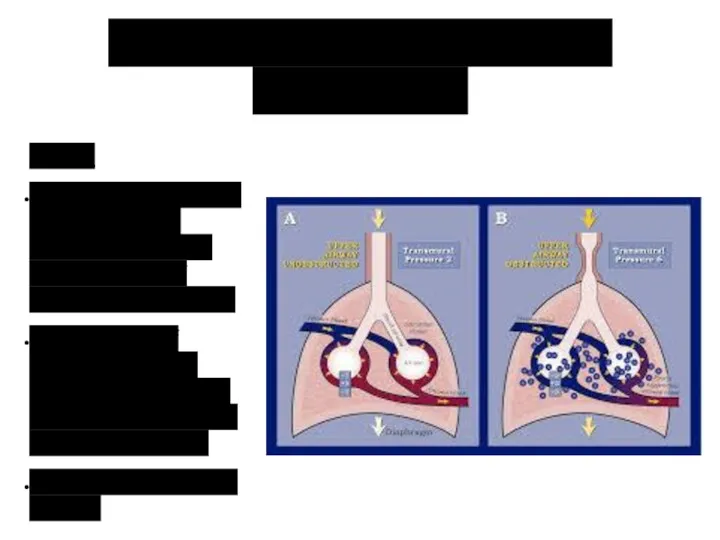
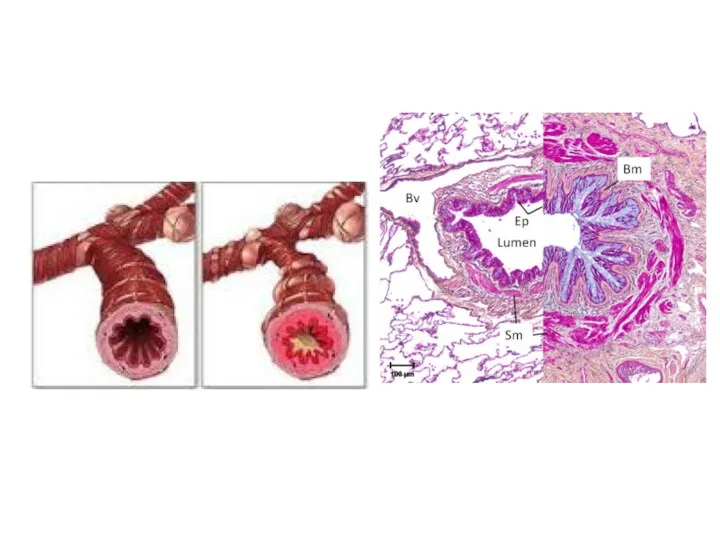
- 61. Recurrect Airway Obstruction (Heaves) Cause Dusty stable environment, viral infections, air pollution by Aspergillus fumigatus Actinomyces
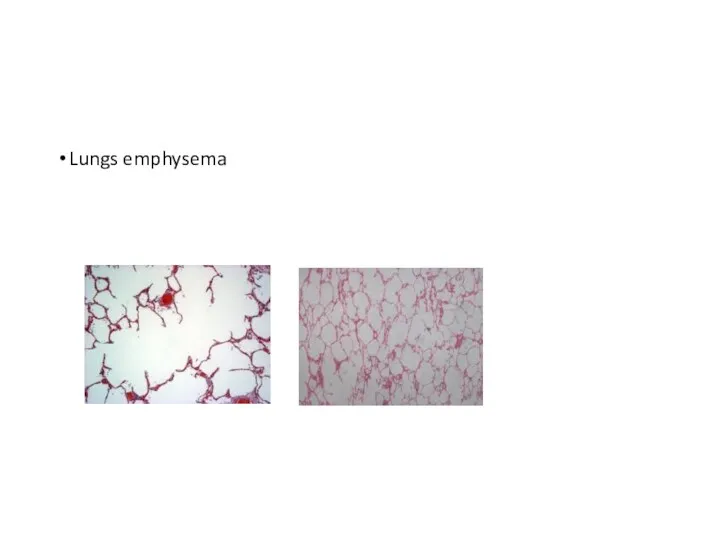
- 63. Lungs emphysema
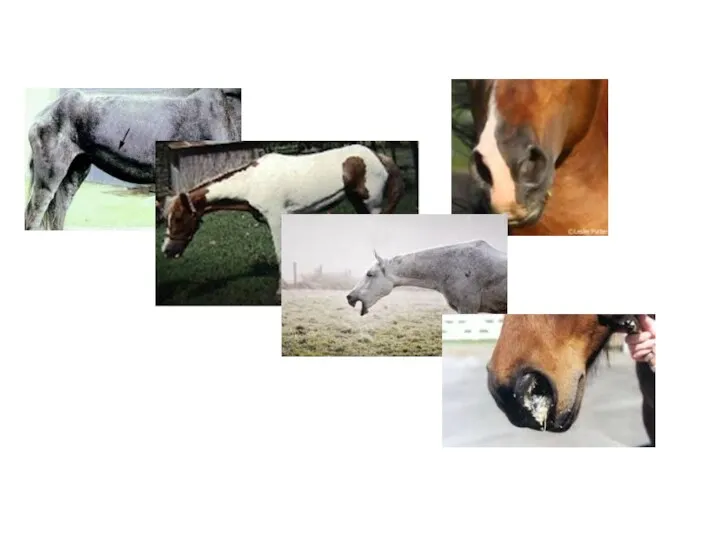
- 64. Recurrect Airway Obstruction (Heaves) Clinical signs: Older than 7 years horses most common affected. At the
- 66. Recurrect Airway Obstruction (Heaves) Clinical pathology Endoscopy examination ( chronic inflamation of bronchi and tracheal mucosa
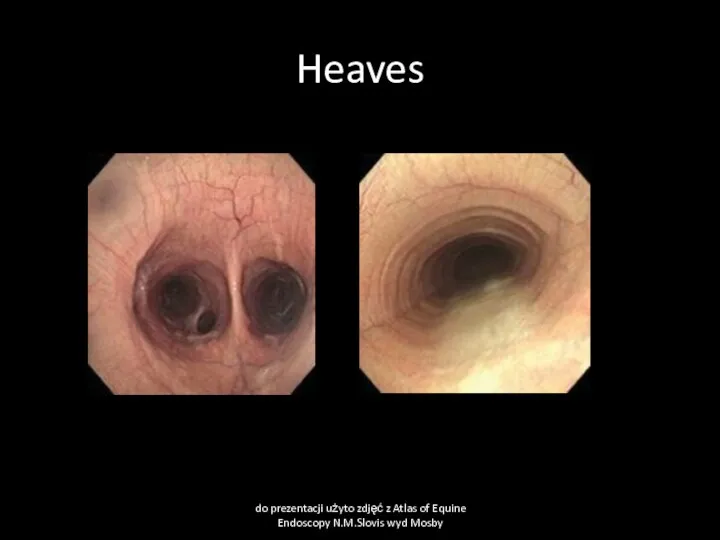
- 67. Heaves do prezentacji użyto zdjęć z Atlas of Equine Endoscopy N.M.Slovis wyd Mosby
- 69. Скачать презентацию



















 Święci i patroni
Święci i patroni Сказка о том, как Лягушонок научился гудеть, как пароход. Постановка и автоматизация звука [Ы]
Сказка о том, как Лягушонок научился гудеть, как пароход. Постановка и автоматизация звука [Ы] Inventronics. Информация о компании
Inventronics. Информация о компании Старинная ярмарка.
Старинная ярмарка. Схема геологического строения Верхнечонского месторождения
Схема геологического строения Верхнечонского месторождения Установка маркшейдерских и геодезических знаков и реперов
Установка маркшейдерских и геодезических знаков и реперов Глава над разделенным Телом. Марк Эфесский и православное понимание единства Церкви
Глава над разделенным Телом. Марк Эфесский и православное понимание единства Церкви Непредельные углеводороды. Алкены
Непредельные углеводороды. Алкены Аутоиммунный гепатит
Аутоиммунный гепатит Творчество Ф.М. Достоевского (1825-1881)
Творчество Ф.М. Достоевского (1825-1881) Как сочинить загадку
Как сочинить загадку Строение ядра клетки
Строение ядра клетки Мастерская Деда Мороза
Мастерская Деда Мороза документы SV
документы SV Северо-Восточная Русь в XII – начале XIII веков
Северо-Восточная Русь в XII – начале XIII веков Назначение и состав технологического оборудования стартового комплекса. Лекция 11
Назначение и состав технологического оборудования стартового комплекса. Лекция 11 Конституционные суды в системе правосудия РФ
Конституционные суды в системе правосудия РФ Токарные станки
Токарные станки Координаты векторов. Скалярное произведение векторов
Координаты векторов. Скалярное произведение векторов Туркестанская область
Туркестанская область Родительское собрание Подготовка в школе
Родительское собрание Подготовка в школе Механизация сельского хозяйства. Технология производства продукции растениеводства
Механизация сельского хозяйства. Технология производства продукции растениеводства Теория систем и системные исследования в энергетике
Теория систем и системные исследования в энергетике TPR метод в обучении иностранному языку
TPR метод в обучении иностранному языку Медициналық этика
Медициналық этика It takes many kinds to make the world
It takes many kinds to make the world Филогенез систем органов позвоночных животных
Филогенез систем органов позвоночных животных Форма организации труда. Средства производства строительных работ
Форма организации труда. Средства производства строительных работ