- Главная
- Юриспруденция
- Law Lesson

Содержание
- 2. A slide structure based on a lesson XL presentation, which you can easily adapt to your
- 3. COMMON LAW HISTORY OF COMMON LAW: The common law—so named because it was "common" to all
- 4. Common law, also called Anglo-American law, the body of customary law, based upon judicial decisions and
- 5. The common law is the law declared by judges, derived from custom and precedent. It originated
- 6. CIVIL LAW Civil law is a major branch of the law. The law relating to civil
- 7. LAW OF FRANCE HISTORY: Napoleon set out to reform the French legal system in accordance with
- 8. Legislation is seen as the primary source of French law. Unlike in common law jurisdictions, where
- 10. Lebanon Legal System From the time of the French mandate onward Lebanon gradually started to adopt
- 11. Judicial Foundation and Legal Codification The legal system of Lebanon is based on a combination of
- 12. Judicial Structure and Court System The judiciary is comprised of ordinary and exceptional courts. The ordinary
- 13. Judgments from the Courts of First Instance can be appealed to the Courts of Appeal, which
- 14. The Lebanese Judiciary The judiciary in Lebanon is divided horizontally into four main court systems, each
- 15. Is composed of three court levels of general jurisdiction. Original jurisdiction is normally found in the
- 16. 2-the administrative court system known as Majlis al-Shura, Is composed of administrative tribunals and the State
- 17. 3-the military court system is composed of a military court of cassation and a permanent military
- 19. Скачать презентацию
A slide structure based on a lesson XL presentation, which
A slide structure based on a lesson XL presentation, which
An assortment of pictures that are suitable for use in the presentation can be found in the alternative resources slide.
A thanks slide, which you must keep so that proper credits for our design are given.
A resources slide, where you’ll find links to all the elements used in the template.
Instructions for use.
Final slides with:
The fonts and colors used in the template.
A selection of illustrations. You can also customize and animate them as you wish with the online editor. Visit Storyset to find more.
More infographic resources, whose size and color can be edited.
Sets of customizable icons: general, business, avatar, creative process, education, help & support, medical, nature, performing arts, SEO & marketing, and teamwork.
CONTENTS
You can delete this slide when you’re done editing the presentation.
COMMON LAW
HISTORY OF COMMON LAW:
The common law—so named because it was
COMMON LAW
HISTORY OF COMMON LAW:
The common law—so named because it was
Common law, also called Anglo-American law, the body of customary law, based upon
Common law, also called Anglo-American law, the body of customary law, based upon
The common law is the law declared by judges, derived from custom and precedent. It
The common law is the law declared by judges, derived from custom and precedent. It
source of common law in england
CIVIL LAW
Civil law is a major branch of the law. The law relating to civil wrongs and
CIVIL LAW
Civil law is a major branch of the law. The law relating to civil wrongs and
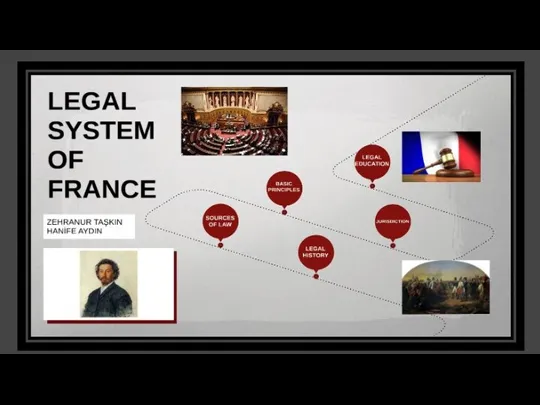
LAW OF FRANCE
HISTORY:
Napoleon set out to reform the French legal system
LAW OF FRANCE
HISTORY: Napoleon set out to reform the French legal system
STRUCTURE:
France is a civil law system which means it places a greater emphasis on statutes as found within various codes, instead of case law. ... France is a republic and is currently governed by the Constitution of the Fifth Republic, which was passed October 4, 1958.
Legislation is seen as the primary source of French law. Unlike in common law jurisdictions, where
Legislation is seen as the primary source of French law. Unlike in common law jurisdictions, where
SOURCE
Lebanon Legal System
From the time of the French mandate onward Lebanon
Lebanon Legal System
From the time of the French mandate onward Lebanon
Judicial Foundation and Legal Codification
The legal system of Lebanon is based
Judicial Foundation and Legal Codification
The legal system of Lebanon is based
The legal system is governed by a series of specialized codes of law. These include the Code of Obligations and Contracts of 1932, which is the primary source for civil law; the Code of Civil Procedure, contained in Decree Law No. 90 of 1983; the Code of Commerce of 1942; the Penal Code, originally formulated in Decree Law No. 340 of 1943; and the Code of Criminal Procedure.
Judicial Structure and Court System
The judiciary is comprised of ordinary and
Judicial Structure and Court System
The judiciary is comprised of ordinary and
Judgments from the Courts of First Instance can be appealed to
Judgments from the Courts of First Instance can be appealed to
The Lebanese Judiciary
The judiciary in Lebanon is divided horizontally into four
The Lebanese Judiciary
The judiciary in Lebanon is divided horizontally into four
the Judicial court system known as kadaa’ dli
the administrative court system known as Majlis al-Shura
the military court system
the religious court systems.
Is composed of three court levels of general jurisdiction. Original jurisdiction
Is composed of three court levels of general jurisdiction. Original jurisdiction
1-the Judicial court system known as kadaa’ dli,
2-the administrative court system known as Majlis al-Shura,
Is composed of administrative
2-the administrative court system known as Majlis al-Shura,
Is composed of administrative
3-the military court system
is composed of a military court of cassation
3-the military court system
is composed of a military court of cassation
4-the religious court systems.
is composed of the court systems of the 18 recognized denominations pertaining to the three main religions of Christianity, Islam and Judaism. The jurisdiction of these courts is limited to personal status and family law matters as authorized by law.















 Статус руботников прокуратуры в РФ
Статус руботников прокуратуры в РФ Дисциплина труда
Дисциплина труда Авторский надзор. Госэкспертиза. Технадзор
Авторский надзор. Госэкспертиза. Технадзор Правовой урок. Обязанности родителей (законных представителей)
Правовой урок. Обязанности родителей (законных представителей) Специальная оценка условий труда
Специальная оценка условий труда Интерактивная игра Выборы
Интерактивная игра Выборы Граждаско-правовой договор
Граждаско-правовой договор Международные преступления и ответственность за них
Международные преступления и ответственность за них Гражданство в Российской Федерации
Гражданство в Российской Федерации Величайшее поощрение преступления - безнаказанность
Величайшее поощрение преступления - безнаказанность Поняття, джерела та становлення Римського права
Поняття, джерела та становлення Римського права Проблема участия молодежи в выборах
Проблема участия молодежи в выборах Профессия полицейский
Профессия полицейский Право власності в міжнародному приватному праві
Право власності в міжнародному приватному праві Правовое положение латинов, перегринов, колонов
Правовое положение латинов, перегринов, колонов Преступность несовершеннолетних.
Преступность несовершеннолетних. Производство по делам об административных правонарушениях, посягающих на права граждан
Производство по делам об административных правонарушениях, посягающих на права граждан Права и обязанности учащихся
Права и обязанности учащихся Обязательства. Понятие и виды обязательств
Обязательства. Понятие и виды обязательств Организация и тактика действий правоохранительных органов при освобождении заложников
Организация и тактика действий правоохранительных органов при освобождении заложников Таможенные операции и лица их совершающие
Таможенные операции и лица их совершающие Деньги и их функции
Деньги и их функции Современная Россия. Основной закон России и права человека
Современная Россия. Основной закон России и права человека Сыбайлас жемқорлық - ғасыр індеті
Сыбайлас жемқорлық - ғасыр індеті  Система арбитражных судов
Система арбитражных судов Талқылауға арналған сұрақ. Инвестициялық қатынастарды мемлекеттік реттеу
Талқылауға арналған сұрақ. Инвестициялық қатынастарды мемлекеттік реттеу Всероссийский конкурс на лучшую работу по вопросам избирательного права и избирательного процесса
Всероссийский конкурс на лучшую работу по вопросам избирательного права и избирательного процесса Нормативная правовая база обеспечения БЖД
Нормативная правовая база обеспечения БЖД