Содержание
- 2. C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 Our Political
- 3. Chapter 2, Section 1 S E C T I O N 1 Our Political Beginnings What
- 4. The English colonists in America brought with them three main concepts: Basic Concepts of Government The
- 5. Important English Documents The way our government works today can be traced to important documents in
- 6. The Thirteen Colonies Chapter 2, Section 1 There were three types of colonies in North America:
- 7. Section 1 Review 1. All of the following are basic concepts of government brought to the
- 8. S E C T I O N 2 The Coming of Independence What were Britain’s colonial
- 9. Chapter 2, Section 2 3 4 1 5 British Colonial Policies Until the mid-1700s, the colonies
- 10. Growing Colonial Unity Early Attempts In 1643, several New England settlements formed the New England Confederation.
- 11. The Continental Congresses Chapter 2, Section 2 3 4 1 5 First Continental Congress The colonists
- 12. American Independence On July 4, 1776, the Second Continental Congress adopted the Declaration of Independence. Between
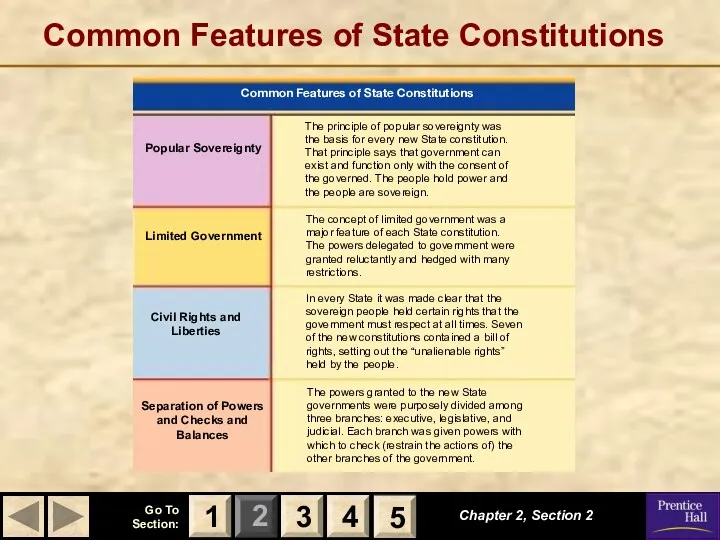
- 13. Common Features of State Constitutions Chapter 2, Section 2 3 4 1 5 The principle of
- 14. Section 2 Review 1. The Declaration of Independence was signed in (a) 1765. (b) 1776. (c)
- 15. Chapter 2, Section 3 S E C T I O N 3 The Critical Period What
- 16. The Articles of Confederation The Articles of Confederation established “a firm league of friendship” among the
- 17. Weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation Chapter 2, Section 3 2 4 1 5
- 18. A Call for a Stronger Government Chapter 2, Section 3 2 4 1 5 Representatives from
- 19. Section 3 Review 1. The government set up by the Articles of Confederation had (a) the
- 20. S E C T I O N 4 Creating the Constitution Who were the Framers of
- 21. Framers of the Constitution Chapter 2, Section 4 2 3 1 5
- 22. Framers of the Constitution
- 23. Framers of the Constitution
- 24. Chapter 2, Section 4 2 3 1 5 Different Constitutional Plans The Virginia Plan Three branches
- 25. Constitutional Compromises The Connecticut Compromise Delegates agreed on a bicameral Congress, one segment with equal representation
- 26. Influences on and Reactions to the New Constitution Influences The Framers were familiar with the political
- 27. Section 4 Review 1. The first national government for the United States was (a) the First
- 28. Chapter 2, Section 1 S E C T I O N 5 Ratifying the Constitution Who
- 29. The Federalists and Anti-Federalists The Constitution was very controversial at first, with some groups supporting it,
- 30. The Constitution is Ratified Chapter 2, Section 5 3 4 1 2 Nine States ratified the
- 31. Inaugurating the Government Chapter 2, Section 5 2 4 1 3 The new Congress met for
- 33. Скачать презентацию




























 Знай свои права! Направление: Экстремизм
Знай свои права! Направление: Экстремизм Регулирование естественных монополий
Регулирование естественных монополий Всероссийский цикл семинаров по охране труда. Риск-ориентированный подход
Всероссийский цикл семинаров по охране труда. Риск-ориентированный подход Правовые основы организации муниципального управления
Правовые основы организации муниципального управления Права, обязанности и ответственность граждан в области пожарной безопасности
Права, обязанности и ответственность граждан в области пожарной безопасности Коррупция и антикоррупционная политика в современной России
Коррупция и антикоррупционная политика в современной России Формирование стипендиального фонда
Формирование стипендиального фонда Практические проблемы реализации муниципально-правовой ответственности
Практические проблемы реализации муниципально-правовой ответственности О перспективах развития гражданской обороны Российской фФедерации
О перспективах развития гражданской обороны Российской фФедерации Обеспечение информационной безопасности России
Обеспечение информационной безопасности России Субъекты оценочной деятельности
Субъекты оценочной деятельности prezentatsia_lektsia_1
prezentatsia_lektsia_1 Тәртіпке бағынған ел құл болмайды. Тәртіпсіздік неден басталады? Құқықбұзушылық, қылмыс жақсылыққа апармайды
Тәртіпке бағынған ел құл болмайды. Тәртіпсіздік неден басталады? Құқықбұзушылық, қылмыс жақсылыққа апармайды Объективная сторона преступления
Объективная сторона преступления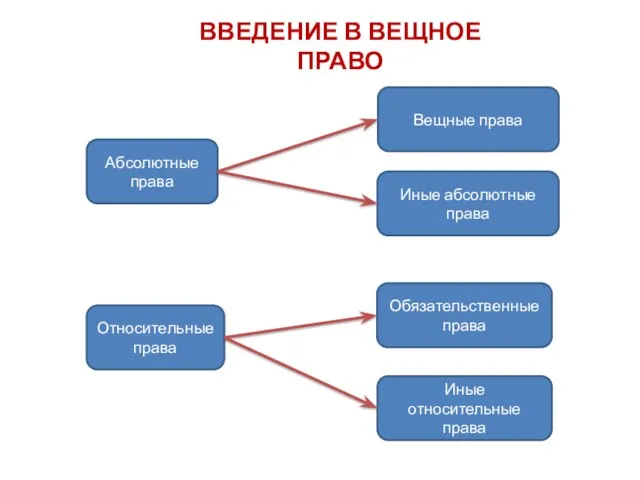 Введение в вещное право
Введение в вещное право System Informacyjny Schengen
System Informacyjny Schengen Авиакомпания РусЛайн. Программа развития маршрутной сети из г. Курска на 2020 г
Авиакомпания РусЛайн. Программа развития маршрутной сети из г. Курска на 2020 г Сontracts. Definition
Сontracts. Definition Материальная поддержка обучающихся: теория и практика
Материальная поддержка обучающихся: теория и практика О законодательстве в схемах. Акты президента Российской Федерации
О законодательстве в схемах. Акты президента Российской Федерации Об утверждении методических указаний по расчету размера платы за ТО ВДГО в МКД, а также за то ВДГО в ЖД
Об утверждении методических указаний по расчету размера платы за ТО ВДГО в МКД, а также за то ВДГО в ЖД Электронный листок нетрудоспособности в 1С. Взаимодействие с ФСС
Электронный листок нетрудоспособности в 1С. Взаимодействие с ФСС Юридична відповідальність за екологічні правопорушення
Юридична відповідальність за екологічні правопорушення Основы административного права
Основы административного права Уголовное право. Общая часть
Уголовное право. Общая часть Институт парламентского контроля в России
Институт парламентского контроля в России Захист права власності в цивільному судочинстві
Захист права власності в цивільному судочинстві Коррупция в России
Коррупция в России