Содержание
- 2. Success Criteria Aim To know about volcanoes and where in the world they can be found.
- 3. Have you ever thought about why volcanoes are actually called 'volcanoes'? Can you think of a
- 4. Roman mythology says that Vulcan lived in a volcano. As well as being the god of
- 5. What Is Our Earth Made Of? Click on the circles to reveal the information. + +
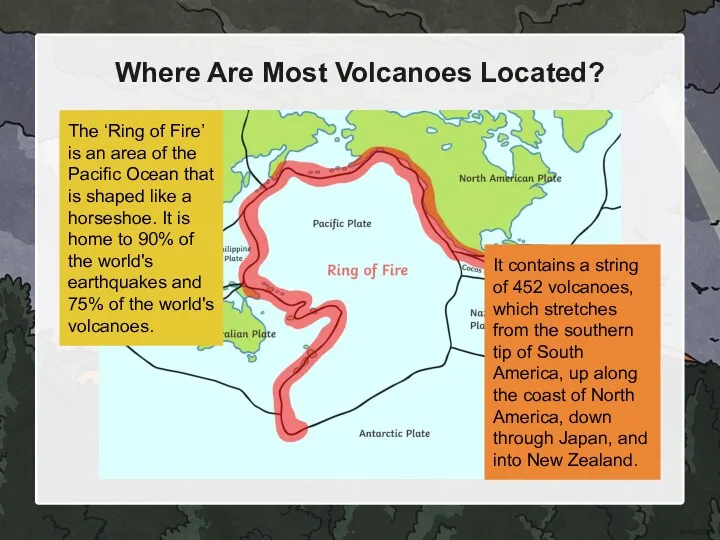
- 6. Where Are Most Volcanoes Located? The ‘Ring of Fire’ is an area of the Pacific Ocean
- 7. How Are Volcanoes Formed? Deep in the earth, it is extremely hot. It is so hot,
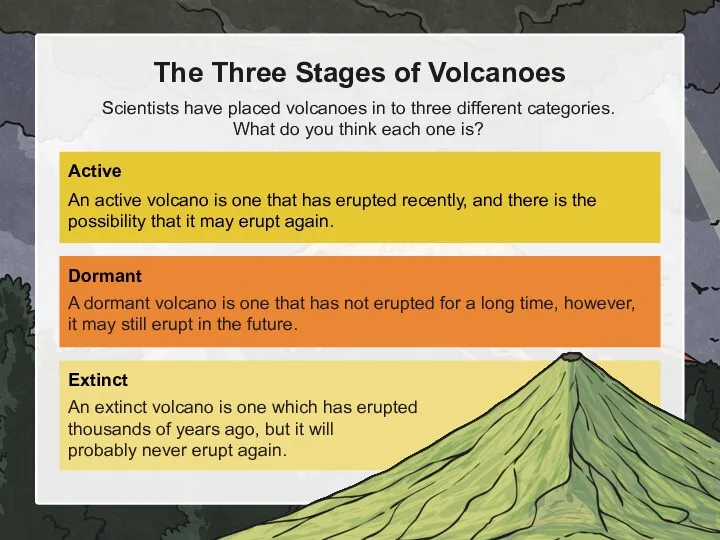
- 8. The Three Stages of Volcanoes Scientists have placed volcanoes in to three different categories. What do
- 9. Why Do Volcanoes Erupt? We know that the earth's crust is made up of huge slabs
- 10. What Are the Different Parts of a Volcano? Click on each label to find out more.
- 11. How Many Volcanoes Are There? There are more than 1500 active volcanoes on Earth. There are
- 12. What Types of Volcano Are There? Composite Volcanoes These volcanoes are steep-sided volcanoes and are made
- 13. What Types of Volcano Are There? Cinder Cones Cinder cones are circular or oval cones. They
- 14. What Types of Volcano Are There? Shield Volcanoes Shield volcanoes are bowl or shield-shaped in the
- 15. More Volcano Facts What is the difference between magma and lava? Magma is liquid rock inside
- 16. What Is the Largest Active Volcano? The largest, active volcano in the world is Mauna Loa
- 17. 2 1 Volcanoes of the World Mount St Helens Click on the numbers to reveal the
- 18. 2 1 Mount Vesuvius, Naples, Italy Click on the numbers to reveal the facts. 5 3
- 19. 2 1 Mount Fuji, Japan Click on the numbers to reveal the facts. 5 3 4
- 20. 2 1 Popocatépetl, Mexico Click on the numbers to reveal the facts. 4 3 Volcanoes of
- 21. Are There Volcanoes on Other Planets? Earth is not the only planet to have volcanoes, although
- 22. Glossary Forged: to have made or shaped a metal object using a fire or furnace. Molten:
- 24. Скачать презентацию



















 Valentine's day in Velikobritanii
Valentine's day in Velikobritanii Evolution of youth Groups in Russia
Evolution of youth Groups in Russia Answer the questions
Answer the questions Exotic festivals
Exotic festivals See to believe it. In search of Nessie
See to believe it. In search of Nessie Локализация игровых текстов
Локализация игровых текстов In the jungle
In the jungle Открытые и закрытые слоги
Открытые и закрытые слоги London
London Shopping. Поход по магазинам
Shopping. Поход по магазинам English-speaking countries
English-speaking countries 12 months make a year
12 months make a year English food
English food The UNESCO world heritage of USA
The UNESCO world heritage of USA Maslenitsa
Maslenitsa Sport in France
Sport in France Hobbies
Hobbies Check your phrasal verbs (speaking)
Check your phrasal verbs (speaking) Coils deformation. Wire rod mill. (Team 3)
Coils deformation. Wire rod mill. (Team 3) Present perfect
Present perfect What´s in my schoolbag?
What´s in my schoolbag? Possessive ‘s
Possessive ‘s Salty dough products
Salty dough products Historical perspectives. Popular methodology
Historical perspectives. Popular methodology The Past Simple Tense Adverbs and expressions of frequency
The Past Simple Tense Adverbs and expressions of frequency St. Paul's Cathedral in London
St. Paul's Cathedral in London The advantages and disadvantages of doing a sport
The advantages and disadvantages of doing a sport Inversion and conditionals
Inversion and conditionals