Содержание
- 2. B.G. Ananiev: “Lack of assessment ... is the worst kind of assessment, because this impact is
- 3. What is assessment? The process of gathering evidence Then use defined criteria to judge performance based
- 4. Who is involved in, affected by or interested in assessment? Who are the stakeholders? Learners Parents
- 5. Types of assessment Formative assessment of learners during teaching and learning Summative assessment of learning Diagnostic
- 6. Assessment: What for is assessment necessary? What is criteria-based assessment? What is the purpose of criteria-based
- 7. The term “criteria-based assessment” was first used by Robert Eugene Glazer (1963) and characterized as the
- 8. Criteria-based Assessment Assessment, which is measured against general, specific criteria General, all learners are assessed against
- 9. The purpose of the criteria-based assessment is to obtain objective information on learning achievements of learners
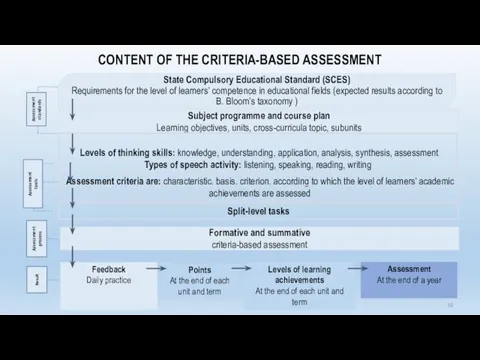
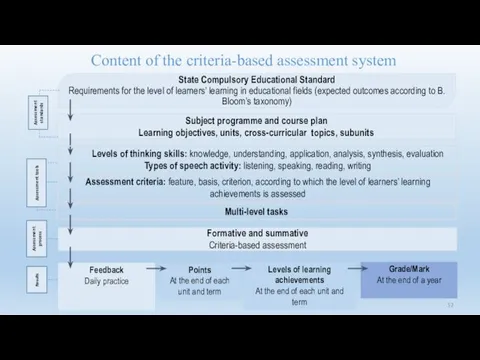
- 10. State Compulsory Educational Standard (SCES) Requirements for the level of learners’ competence in educational fields (expected
- 11. Instructive and methodological documents State Compulsory Educational Standard (Primary, Secondary, High); Subject programme (by subject); Course
- 12. Principles of criteria-based assessment What is the relationship between learning and assessment? What is good assessment?
- 13. Assessment Assessment of learning achievements is the process of establishing the level of accordance between the
- 14. Principles of criteria-based assessment Interrelation of learning and assessment. Assessment is an integral part of learning,
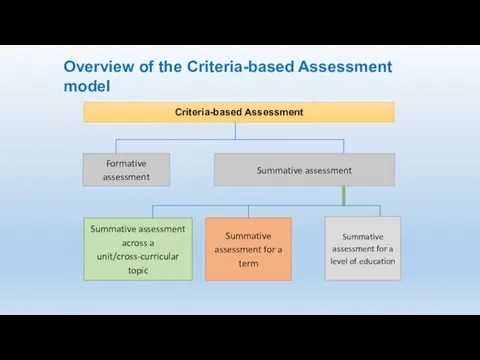
- 15. Overview of the Criteria-based Assessment model Criteria-based Assessment model Formative assessment Summative assessment
- 16. Formative Assessment Task: Discuss questions in groups and write down your answers on the flipcharts. 1.
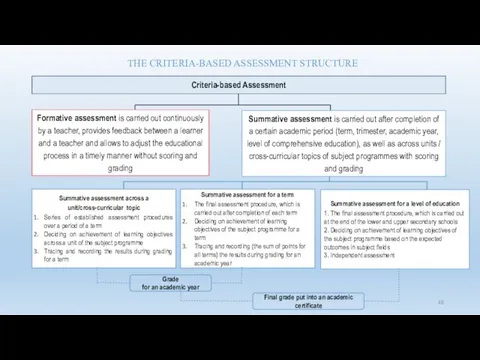
- 17. Formative Assessment (FA) - is a type of assessment that provides feedback between learners and teachers
- 18. FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT Is carried by Inform Role of a learner A teacher during the term learners
- 19. These are the important elements of effective formative assessment: Formative assessment Learning objectives (from curriculum) Assessment
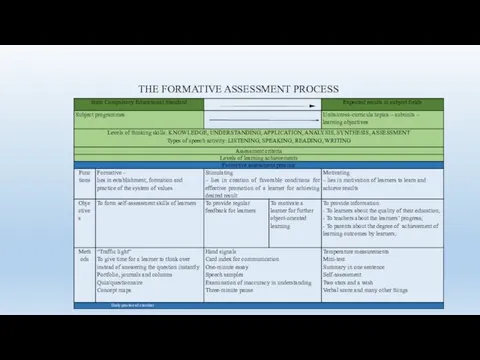
- 20. THE FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT PROCESS
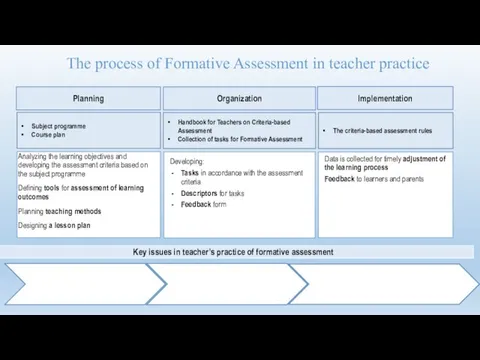
- 21. Formative assessment: Daily practice of a teacher Planning and organizing formative assessment; Selecting formative assessment methods;
- 22. Formative assessment Task: It is necessary to carry out a formative assessment depending on the following
- 23. Formative assessment
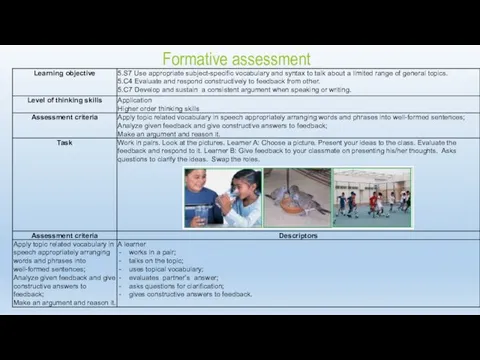
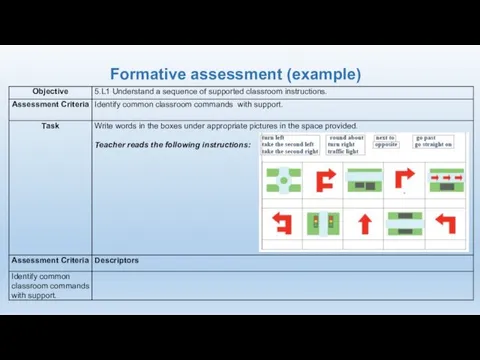
- 24. Formative assessment (example)
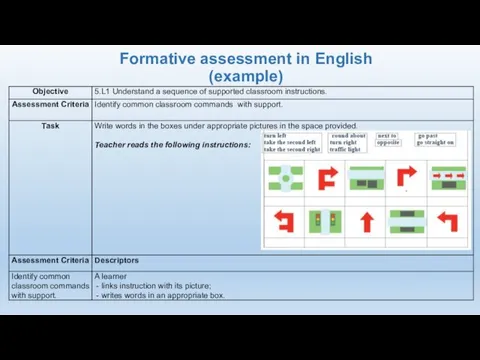
- 25. Formative assessment in English (example)
- 26. TASK FOR FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT IN ENGLISH FOR GRADE 5 Work in pairs. Ask your partner questions
- 27. TASK FOR FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT IN ENGLISH FOR GRADE 5 Work in pairs. Ask your partner questions
- 28. TASK FOR FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT IN ENGLISH FOR GRADE 5 Read the text. Once a deer, a
- 29. TASK FOR FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT IN ENGLISH FOR GRADE 5 Read the text. Once a deer, a
- 30. State Compulsory Educational Standard of the Republic of Kazakhstan State Compulsory Educational Standard Requirements for the
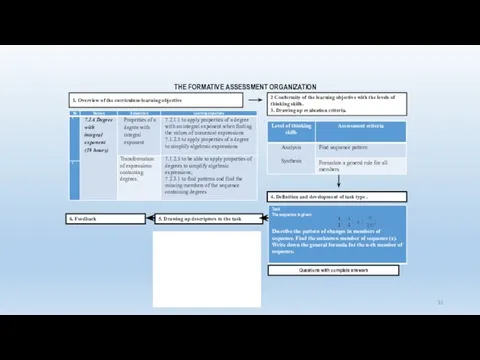
- 31. 5. Drawing up descriptors to the task 1. Overview of the curriculum-learning objective 2 Conformity of
- 32. Features of the model: Integration
- 33. The main documents: Subject programme + Course plans + Assessment materials
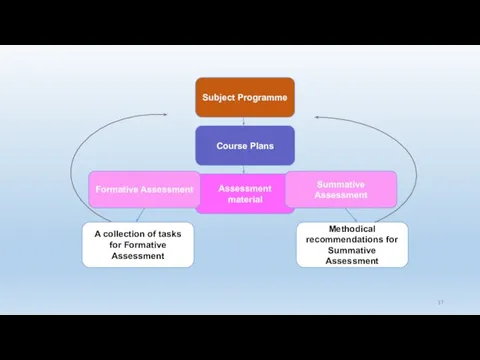
- 34. Subject Programme Course Plans 33
- 35. Subject Programme Course Plans Assessment material 34
- 36. Subject Programme Course Plans Assessment material Formative Assessment Summative Assessment 35
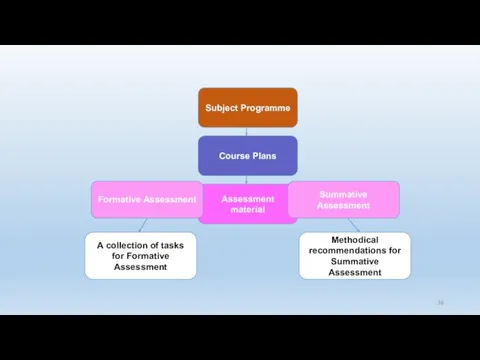
- 37. Subject Programme Course Plans Assessment material Formative Assessment Summative Assessment A collection of tasks for Formative
- 38. Subject Programme Course Plans Assessment material Formative Assessment Summative Assessment A collection of tasks for Formative
- 39. Key skills for the 21st century Discuss what skills are relevant for today’s learner Do you
- 40. Features of the model: 21st-century skills Enquiry Problem solving Critical thinking Collaboration Independent learning Creating and
- 41. Criterion-referencing Norm-referencing: compares a learner’s performance to the rest of the group either locally, nationally or
- 42. The criteria-based assessment Generates variety of approaches Enhances involvement and motivation Integrates the 21th century skills
- 43. FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT: PART OF DAILY TEACHING Learning objectives (skills and content) Planning of the learning and
- 44. ‘A criteria-based assessment model compares learners’ achievements with clearly defined, collectively developed criteria, which are known
- 45. ‘Criteria-based assessment is fairer to learners than the traditional method applied in Kazakhstan.’ 44
- 46. Overview of the Criteria-based Assessment model Criteria-based Assessment model Formative assessment Summative assessment
- 47. SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT Type of assessment, which is carried out after completion of a certain academic period
- 48. Overview of the Criteria-based Assessment model Criteria-based Assessment Formative assessment Summative assessment across a unit/cross-curricular topic
- 49. THE CRITERIA-BASED ASSESSMENT STRUCTURE
- 50. The process of Formative Assessment in teacher practice Key issues in teacher’s practice of formative assessment
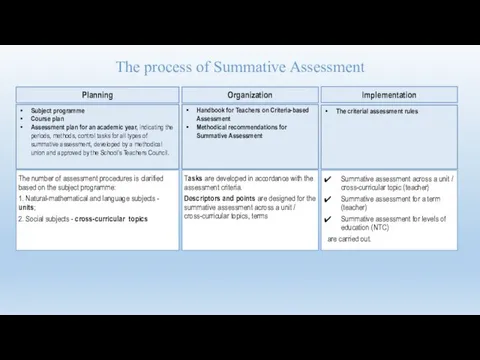
- 51. The process of Summative Assessment
- 52. State Compulsory Educational Standard Requirements for the level of learners’ learning in educational fields (expected outcomes
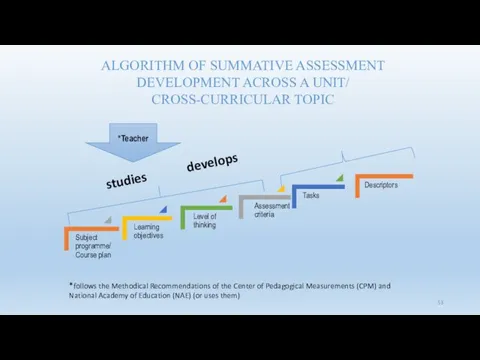
- 53. ALGORITHM OF SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT DEVELOPMENT ACROSS A UNIT/ CROSS-CURRICULAR TOPIC *Teacher studies develops *follows the Methodical
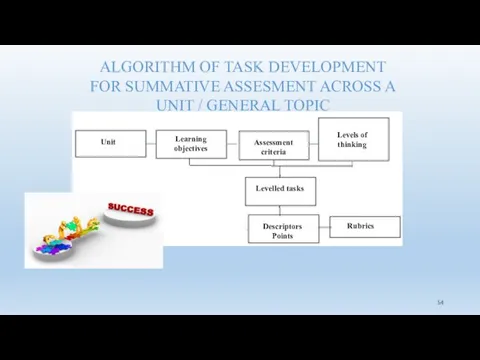
- 54. ALGORITHM OF TASK DEVELOPMENT FOR SUMMATIVE ASSESMENT ACROSS A UNIT / GENERAL TOPIC Unit Learning objectives
- 55. Two approaches:
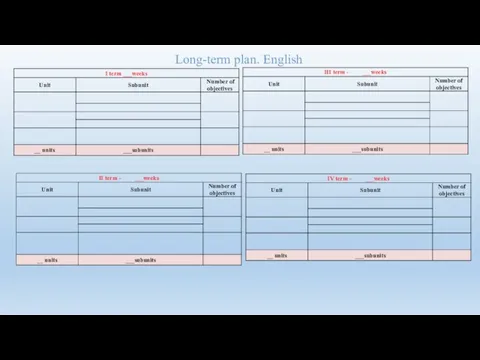
- 56. Long-term plan. English
- 59. Rubrics for providing results on Summative assessment for a unit / cross-curricular topic Rubrics is a
- 60. SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT ACROSS A UNIT/CROSS-CURRICULAR TOPIC Summative assessment is carried out: across units (natural and mathematical
- 61. SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT FOR A TERM Summative assessment for a term is carried out at the end
- 62. SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT FOR A TERM For whom are the tasks intended? How much time is allowed
- 63. SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT ACROSS A UNIT / CROSS-CURRICULAR TOPIC Tasks for Summative assessment across a unit /
- 64. Task: Identify the similarities and differences between the summative assessment for a unit / cross-curricular topic
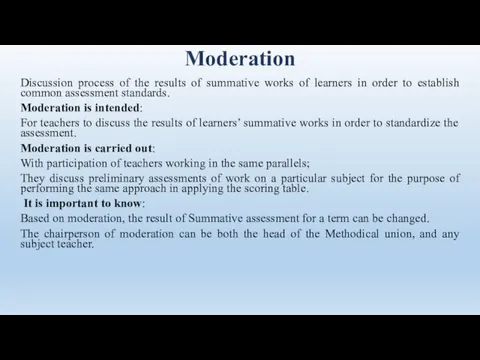
- 65. Moderation Discussion process of the results of summative works of learners in order to establish common
- 66. Moderation Teacher’s role
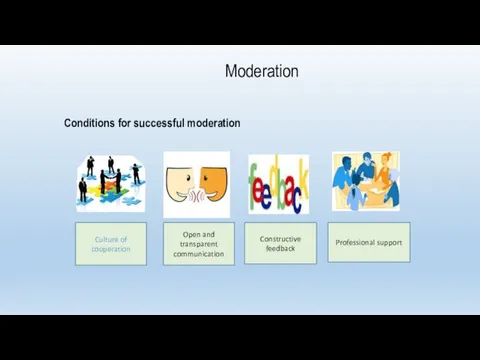
- 67. Conditions for successful moderation Culture of cooperation Open and transparent communication Constructive feedback Professional support Moderation
- 73. Скачать презентацию



















































 Animals on the farm
Animals on the farm What is network security?
What is network security? Complete the conversation
Complete the conversation Qatar education
Qatar education Words to renember verbs
Words to renember verbs Literary and cultural heritage
Literary and cultural heritage Newspapers: broadsheets and tabloids
Newspapers: broadsheets and tabloids Causative
Causative Can you do it?
Can you do it?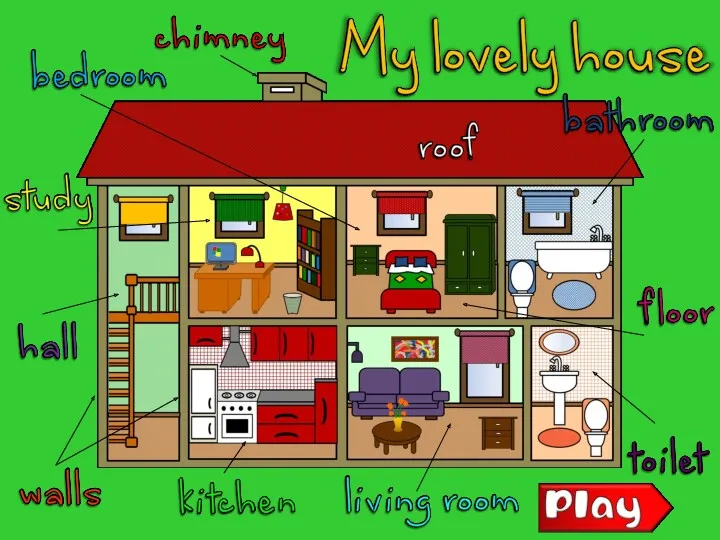 House parts
House parts Модальный глагол can
Модальный глагол can St. Valentine's
St. Valentine's Parts of the house
Parts of the house Exam classroom language
Exam classroom language This is Lew. He is two. This is Guy. He is five. This is Kevin. He is seven
This is Lew. He is two. This is Guy. He is five. This is Kevin. He is seven Subculture is the Way to Express Your Individuality
Subculture is the Way to Express Your Individuality Лексика и грамматика в формате ЕГЭ
Лексика и грамматика в формате ЕГЭ Actual problems in electrical equipment
Actual problems in electrical equipment Английский для начинающих
Английский для начинающих Местоимения some any no
Местоимения some any no Новая Зеландия
Новая Зеландия Фонетика английского языка
Фонетика английского языка Теоретическая грамматика английского языка
Теоретическая грамматика английского языка We are in London
We are in London The seasons
The seasons Conditionals. Типы условных предложений
Conditionals. Типы условных предложений Притяжательный падеж существительных
Притяжательный падеж существительных Horror Film
Horror Film