Содержание
- 2. Basic Cost Management Concepts CHAPTER 2
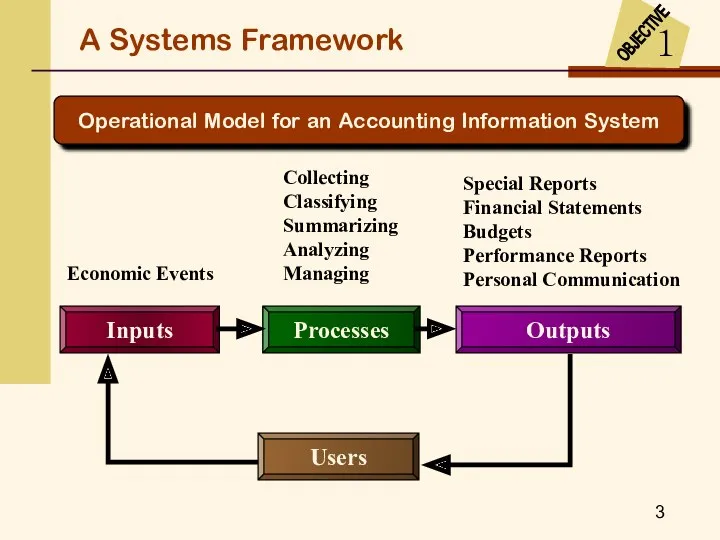
- 3. A Systems Framework OBJECTIVE 1 Operational Model for an Accounting Information System Collecting Classifying Summarizing Analyzing
- 4. Financial Accounting Information System Inputs: well-specified economic events Processes: rules and conventions established by the SEC
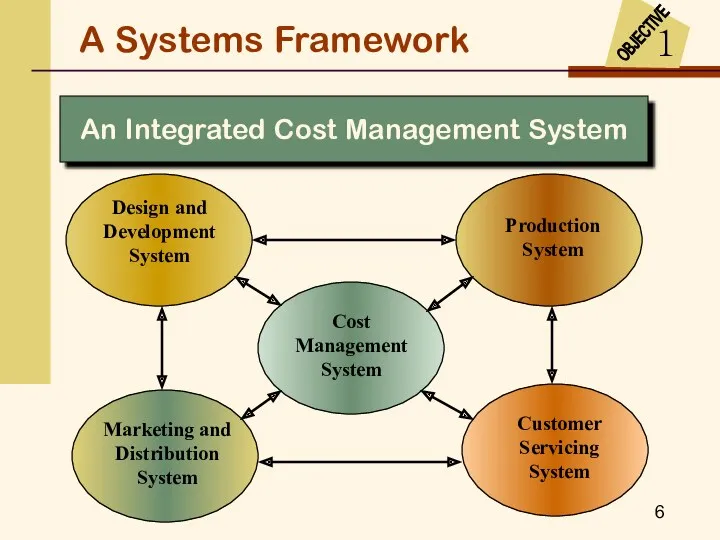
- 5. A Systems Framework The cost management information system has three broad objectives that provide information for--
- 6. An Integrated Cost Management System Design and Development System Customer Servicing System Marketing and Distribution System
- 7. A Systems Framework 1 OBJECTIVE The Subsystems of the Accounting Information System Accounting Information System Assigns
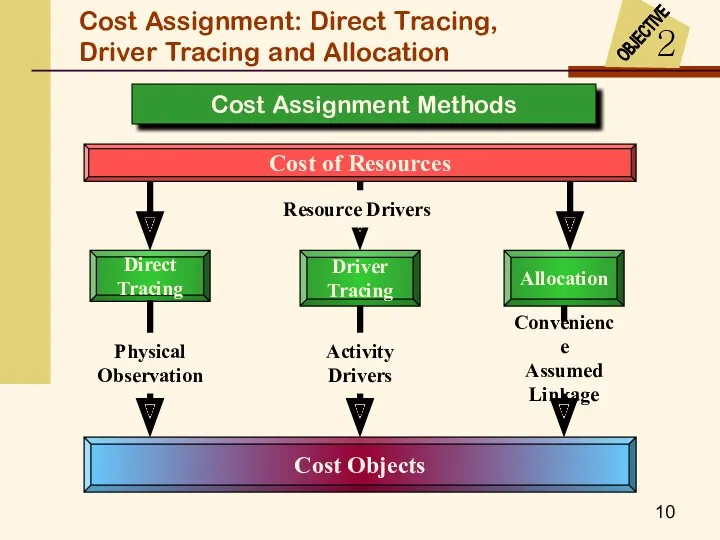
- 8. Cost Assignment: Direct Tracing, Driver Tracing and Allocation 2 OBJECTIVE A cost object is any item,
- 9. Cost Assignment: Direct Tracing, Driver Tracing and Allocation 2 OBJECTIVE Traceability means that costs can be
- 10. Cost Assignment Methods Cost Assignment: Direct Tracing, Driver Tracing and Allocation
- 11. Cost Assignment Methods Cost Assignment: Direct Tracing, Driver Tracing and Allocation
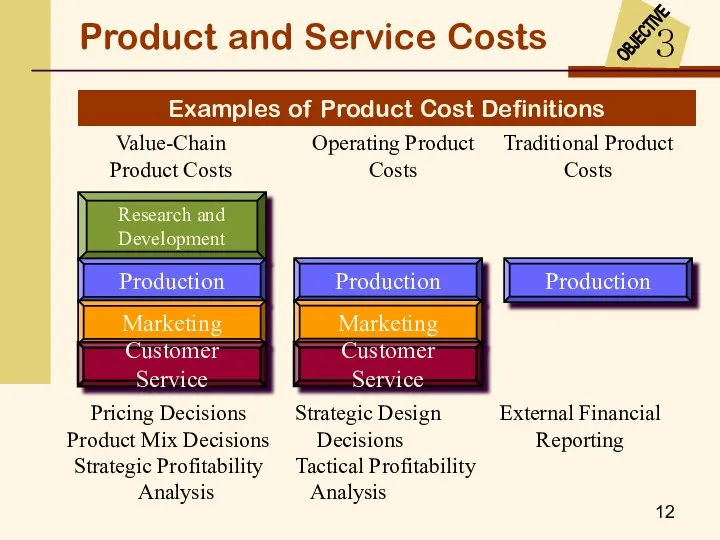
- 12. Examples of Product Cost Definitions Pricing Decisions Product Mix Decisions Strategic Profitability Analysis Strategic Design Decisions
- 13. Direct materials are those materials that are directly traceable to the goods or services being produced.
- 14. Product and Service Costs Manufacturing costs are assigned to products and carried in inventories until the
- 15. Marketing (selling) costs are the costs necessary to market, distribute, and service a product or service.
- 16. Product and Service Costs For external financial reporting, marketing and administrative costs are not inventoried. They
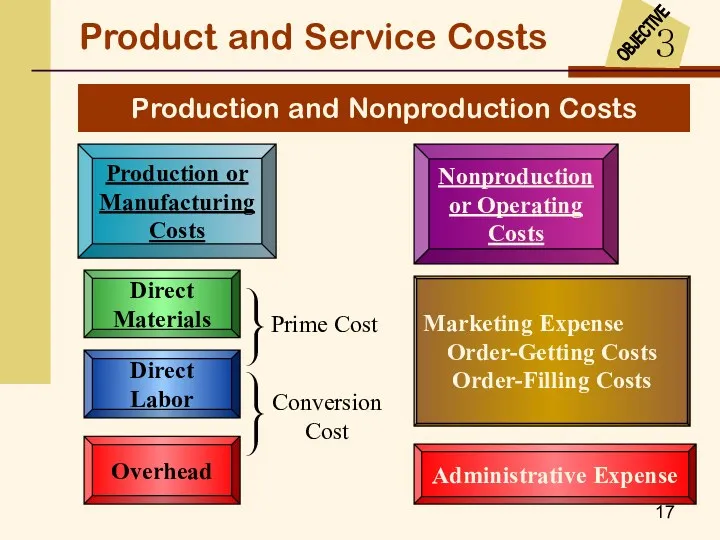
- 17. Production or Manufacturing Costs Nonproduction or Operating Costs Product and Service Costs Production and Nonproduction Costs
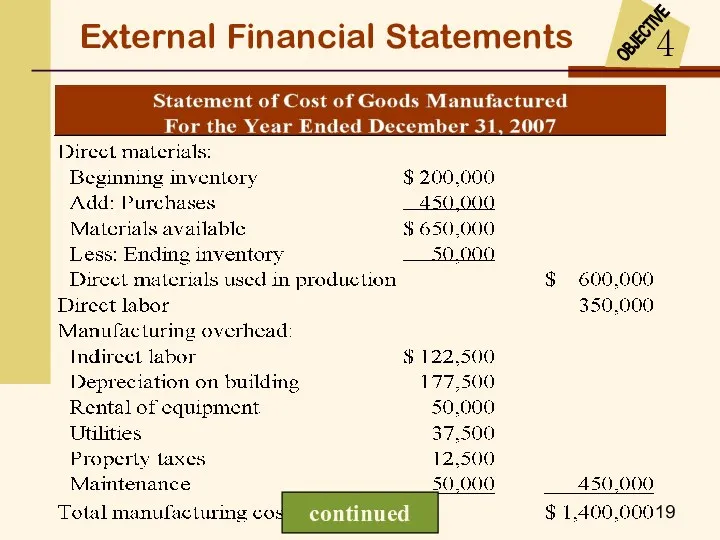
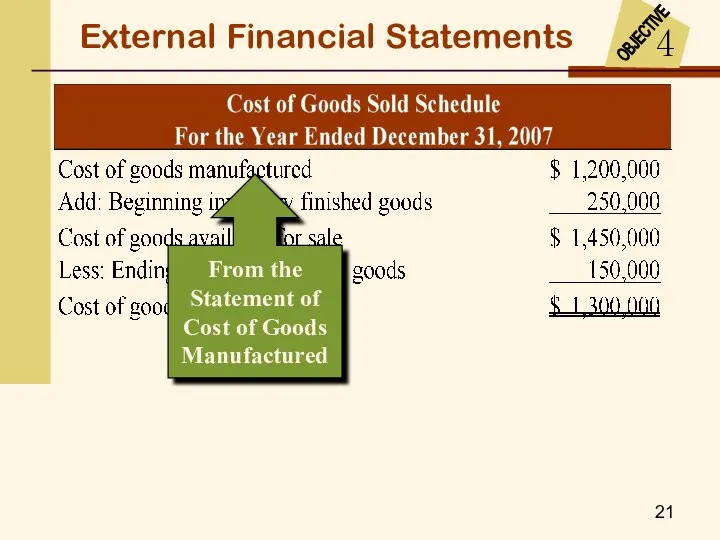
- 18. External Financial Statements From the Cost of Goods Sold Schedule
- 19. External Financial Statements continued
- 20. External Financial Statements
- 21. External Financial Statements From the Statement of Cost of Goods Manufactured
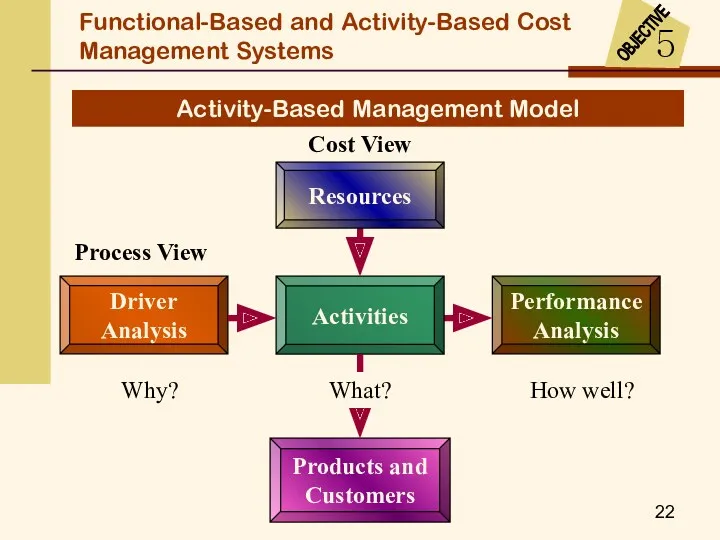
- 22. Activity-Based Management Model Cost View Driver Analysis Process View Why? What? How well? Resources Functional-Based and
- 23. 1. Unit-based drivers 2. Allocation-intensive 3. Narrow and rigid product costing 4. Focus on managing costs
- 24. Activity-Based 1. Unit- and nonunit-based drivers 2. Tracing intensive 3. Broad, flexible product costing 4. Focus
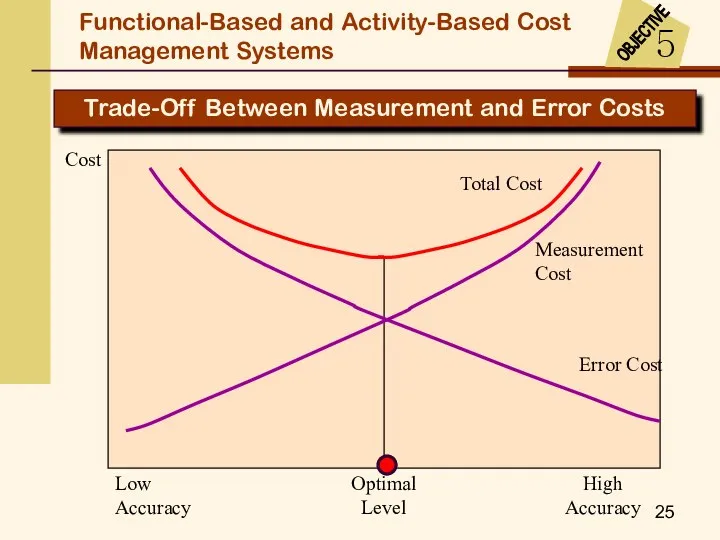
- 25. Low Accuracy High Accuracy Optimal Level Measurement Cost Cost Error Cost Total Cost Trade-Off Between Measurement
- 26. Low High Accuracy New Measurement Cost Cost Old Error Cost Shifting Costs Old Optimum Old Measurement
- 28. Скачать презентацию
















 Holidays in Great Britain
Holidays in Great Britain Lecture 5 Categories and types of present-day English and Ukrainian word-formation (part 2)
Lecture 5 Categories and types of present-day English and Ukrainian word-formation (part 2) My favorite sportsman
My favorite sportsman Higher education in the USA
Higher education in the USA A hobby is something you like to do in your free time
A hobby is something you like to do in your free time Update K10 to android 8.1 process
Update K10 to android 8.1 process Memory Game 08 (Body parts)
Memory Game 08 (Body parts) Verbs. What is a verb
Verbs. What is a verb Introduction to the Practice of Medicine - II
Introduction to the Practice of Medicine - II Guess the Countries and Nationalities with profession
Guess the Countries and Nationalities with profession Reported Speech
Reported Speech Betty Schrampfer Azar. Teacher Resource Disc
Betty Schrampfer Azar. Teacher Resource Disc My friends and me
My friends and me Jeopardy game Christmas
Jeopardy game Christmas Companies
Companies Television. For and agains
Television. For and agains Моя семья. Spotlight (5 класс)
Моя семья. Spotlight (5 класс) Participle II
Participle II Тренажёр ОГЭ / ЕГЭ. Pronunciation ABC
Тренажёр ОГЭ / ЕГЭ. Pronunciation ABC Is the Internet the most important part of our life or not
Is the Internet the most important part of our life or not Seasons and the weather
Seasons and the weather Can you remember some types of personalities?
Can you remember some types of personalities? Oxford and Cambridge Universities
Oxford and Cambridge Universities Электронное письмо. ОГЭ - 2020
Электронное письмо. ОГЭ - 2020 Living plants
Living plants Choose this, that, these or those
Choose this, that, these or those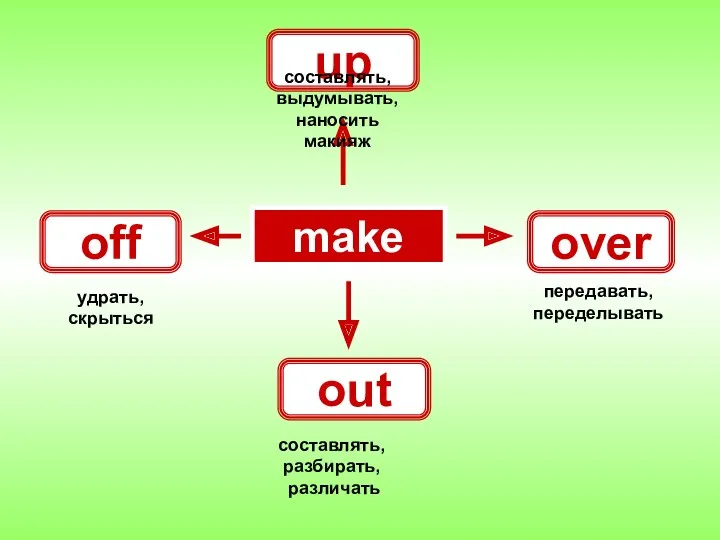 Глаголы
Глаголы What kind of country i want to visit
What kind of country i want to visit