Types of norms
• Folkways refer to norms that protect common conventions.
Most people in a society follow traditional folkways but failure to conform to them is considered neither illegal nor immoral. Examples of common folkways found in the United States include having turkey for Thanksgiving dinner or mowing ones lawn.
• Mores refer to stronger norms with associated moral values. Examples of common mores found in the United States include prohibitions against murder, multiple spouses, or desecration of religious symbols.
• Taboos refer to the strongest types of mores. Taboos include the belief that certain activities, such cannibalism, are outside the bounds of cultural acceptance. Violations of mores and taboos tend to be treated with strong social disapproval or criminal consequences.









 The problem of teenagers
The problem of teenagers The house and flat we live in
The house and flat we live in Aubakir Ismailov
Aubakir Ismailov Personal letter
Personal letter Intellectual development, education of well-rounded person
Intellectual development, education of well-rounded person Daily routines
Daily routines The airport of Almaty
The airport of Almaty Toys game (3)
Toys game (3) Love is with music
Love is with music Opposites. Game
Opposites. Game Complex object. Сложное дополнение
Complex object. Сложное дополнение The seventh continent
The seventh continent Fox Past Simple ed
Fox Past Simple ed Describe a picture
Describe a picture Our ideal welfare state
Our ideal welfare state Diffusion welding
Diffusion welding Request Will Can Could Would
Request Will Can Could Would Can you....?
Can you....? Английский язык вне Англии
Английский язык вне Англии Some vs. Any. Game
Some vs. Any. Game Can it
Can it 10 great days this summer
10 great days this summer Модальные глаголы и их эквиваленты
Модальные глаголы и их эквиваленты UAV linear accelerometer мodule
UAV linear accelerometer мodule Английские цифры от 1 до 10
Английские цифры от 1 до 10 Английское наречие
Английское наречие Film genres quiz
Film genres quiz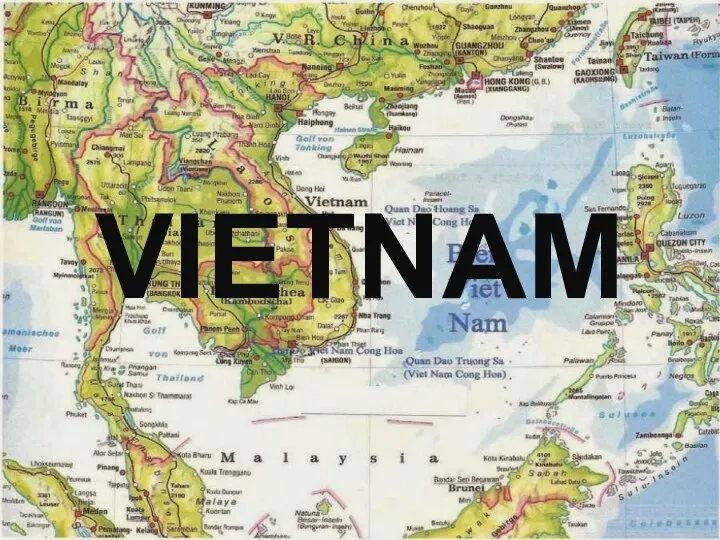 Socialist Republic of Vietnam
Socialist Republic of Vietnam