Содержание
- 2. The English language is the sea which receives tributaries from every region under heaven Ralph Waldo
- 3. A borrowing (a loan word) is a word taken over from another language and modified in
- 4. Up to 80 per cent of the English vocabulary consists of borrowed words. For more than
- 5. The Normans bestowed on English words such us duchess, city, mansion, and palace. The Anglo-Saxon gave
- 6. In English, a material culture word rouge was borrowed from French, a social culture word republic
- 7. Original spelling, pronunciation and foreign identity: rendezvous, coup, gourmet, détente (French); status quo, ego, curriculum vitae,
- 8. Different types of borrowing: (1) when the two languages represent different social, economic, and political units
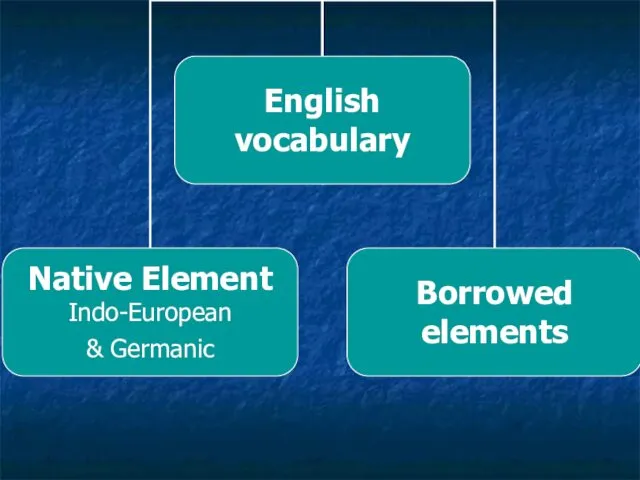
- 11. Native Element – words that are not borrowed from other languages. A native word is a
- 12. Indo-European Element words expressing family relations: brother, daughter, father, mother, son; names of parts of the
- 13. Common Germanic nouns: hand, life, sea, ship, meal, winter, ground, coal, goat; adjectives: heavy, deep, free,
- 14. 3 periods of Latin borrowings in OE: 1. Latin-Continental borrowings. 2. Latin-Celtic borrowings (port, fountain, mountain).
- 15. To the first period belong military terms (wall, street, etc.), trade terms (pound, inch), names of
- 16. Such words as port, fountain and mountain were borrowed from Latin through Celtic. With the Adoption
- 17. Many words from Greek came into English by way of French and Latin. Directly or indirectly,
- 18. French had most influence on the EVoc; it also influenced its spelling. government terms: to govern,
- 19. During the 17th century English took lots of words to do with cooking, the arts, and
- 20. Scandinavian Borrowings are connected with the Scandinavian Conquest of the British Isles (the end of the
- 21. Over 120 lang-s are on record as sources of the EVoc Arabic: algebra, algorithm, fakir, giraffe,
- 22. Borrowed words can be classified according to the aspect which is borrowed: phonetic borrowings (table, chair,
- 23. Assimilation of borrowed words is their adaptation to the system of the receiving language in pronunciation,
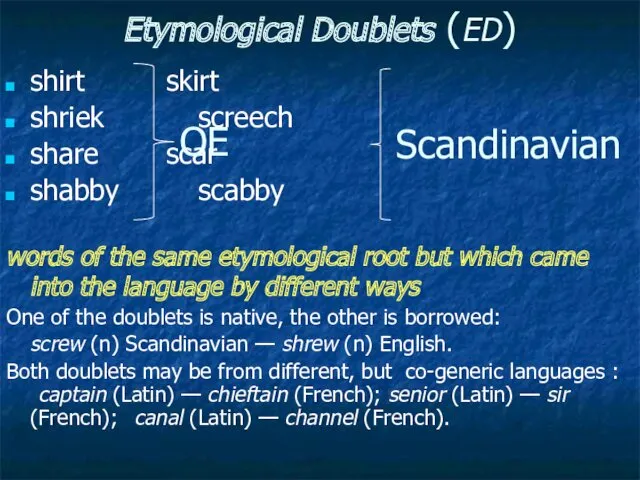
- 24. Etymological Doublets (ED) shirt skirt shriek screech share scar shabby scabby words of the same etymological
- 25. ED-s may be borrowed from the same language but in different historical periods: travel (Norman borrowing)
- 26. International Words words of identical origin that occur in several languages as a result of simultaneous
- 28. Скачать презентацию























 Australia
Australia Informatics – Class 3. IT Infrastructure and Support Systems
Informatics – Class 3. IT Infrastructure and Support Systems Ireland - Dublin
Ireland - Dublin My winter holidays
My winter holidays Literary calendar. February
Literary calendar. February Вопросительные слова и относительные местоимения. 6 класс
Вопросительные слова и относительные местоимения. 6 класс Description of housing
Description of housing Reading skills presa
Reading skills presa It's a wonderful world we live in. But now human beings are killing our planet
It's a wonderful world we live in. But now human beings are killing our planet Reported speech
Reported speech История. Философия. Своя игра. Шаблон
История. Философия. Своя игра. Шаблон Герундий The gerund
Герундий The gerund Поговорим о прошлом
Поговорим о прошлом Past Continuous
Past Continuous ЕГЭ. Английский язык (устный)
ЕГЭ. Английский язык (устный) London is the capital city of England
London is the capital city of England Saint Petersburg in brief
Saint Petersburg in brief Making pairs and groups. Keeping pair work and group work interesting
Making pairs and groups. Keeping pair work and group work interesting Spotlight 5. Module 2. That's me
Spotlight 5. Module 2. That's me Culture vulture. Unit 1.1
Culture vulture. Unit 1.1 Герундий. Глагольные свойства герундия
Герундий. Глагольные свойства герундия The United States of America
The United States of America My Family
My Family Dvizh. Spotlight 11. Mod 5a
Dvizh. Spotlight 11. Mod 5a Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal Companies
Companies Past simple. Regular verbs
Past simple. Regular verbs Present Perfect. Настоящее завершенное время
Present Perfect. Настоящее завершенное время