Содержание
- 2. Agenda for the lecture What is sociology? Sociology and common sens. The beginnings of sociology. Major
- 3. What is sociology? Individual perspective
- 4. What is sociology? Broad perspective
- 5. What is sociology? „A systematic study of human society” (Plummer 2002) But it is not only
- 6. Definition „Sociology is the scientific study of social behavior, including its origins, development, organization, and institutions.[1]
- 7. Common sens vs Sociological thinking Common sens Based on own experience Familiar routines of daily life
- 8. Sociological thinking Benefits Thanks to sociological awerness and critical thinking we can assest the truth about
- 9. August Comte 1798 - 1857 1838 – Sociology Phases of social evolution: the theological stage the
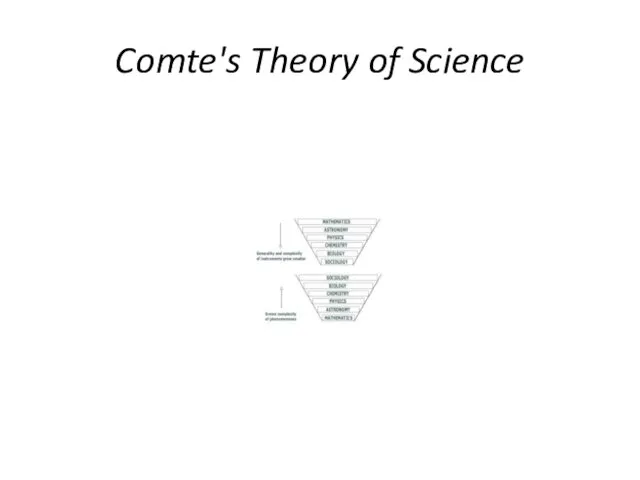
- 10. Comte's Theory of Science
- 11. Theoretical perspective A basic image that guides thinking and research. Research Fact Veryfication
- 12. The functionalist perspective Functionalism is a framework for building theory that envisages society as a complex
- 13. The conflict perspective is a framework for building theory that envisages society as an arena of
- 14. Social action perspective A focus on social interaction in a specific situation (Plummer 2002:26) How social
- 15. Agenda for the semester What is sociology? Sociology and common sense. The beginnings of sociology. Major
- 16. Agenda for the semester 3. Socialization. Social control. Conformity. Social roles. The social collectivity and the
- 17. Agenda for the semester 5. Interactions.Communication. Mass media. The information society. 6. Population and urbanization 7.
- 19. Скачать презентацию















 Новые правила грамматики английского языка
Новые правила грамматики английского языка London attractions
London attractions Infinitive. The negative infinitive. The present infinitive
Infinitive. The negative infinitive. The present infinitive Интерактивные методы обучения как способ формирования коммуникативной компетенции учащихся при изучении английского языка
Интерактивные методы обучения как способ формирования коммуникативной компетенции учащихся при изучении английского языка The Beatles music
The Beatles music Future Tenses
Future Tenses Косвенная речь
Косвенная речь All about volcanoes
All about volcanoes Present Continuous mine
Present Continuous mine Неопределенный артикль, 5 класс
Неопределенный артикль, 5 класс Language and culture
Language and culture We are having a great time!
We are having a great time! Body parts
Body parts Everyday products
Everyday products Wh-questions vk interactive english
Wh-questions vk interactive english Using games in a foreign language classroom
Using games in a foreign language classroom The impact of discrimination on culture
The impact of discrimination on culture The Verb
The Verb Present Simple
Present Simple Leisure and entertainment
Leisure and entertainment Big Ben
Big Ben Hello, kids! Hello September
Hello, kids! Hello September Игра-викторина по английскому языку
Игра-викторина по английскому языку Rotordynamics
Rotordynamics Leisure Activities. Vocabulary
Leisure Activities. Vocabulary Причастие – неличная форма глагола, сочетающая свойства глагола, прилагательного и наречия
Причастие – неличная форма глагола, сочетающая свойства глагола, прилагательного и наречия Трудности перевода терминов
Трудности перевода терминов Distinctive features of the functional styles. Lecture 10
Distinctive features of the functional styles. Lecture 10