CO2Emissions. Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, U.S. Department of Energy, Oak Ridge, Tenn., U.S.A. doi 10.3334/CDIAC/00001_V2017.
Global carbon emissions from fossil fuels have significantly increased since 1900.
Since 1970, CO2 emissions have increased by about 90%, with emissions from fossil fuel combustion and industrial processes contributing about 78% of the total greenhouse gas emissions increase from 1970 to 2011.
Agriculture, deforestation, and other land-use changes have been the second-largest contributors.
 Prepositions
Prepositions Oscars
Oscars Учимся читать слова по транскрипции
Учимся читать слова по транскрипции Фразовые глаголы
Фразовые глаголы Ancient languages. Sanskrit
Ancient languages. Sanskrit Учим новую фразу. I like it
Учим новую фразу. I like it 90s fashion
90s fashion The Subjunctive Mood. Сослагательное наклонение в английском языке
The Subjunctive Mood. Сослагательное наклонение в английском языке Who is who
Who is who Shopping. Поход по магазинам
Shopping. Поход по магазинам Семья. Family
Семья. Family Angina pectoris. Sequence of tenses
Angina pectoris. Sequence of tenses Настоящее Простое время английского глагола (действия)
Настоящее Простое время английского глагола (действия) Англицизмы в современном русском языке
Англицизмы в современном русском языке Тренинг для начинающих изучать английский язык
Тренинг для начинающих изучать английский язык 10 reasons to visit Kazan
10 reasons to visit Kazan Higher education in the USA
Higher education in the USA Tourist Kazan
Tourist Kazan Goldilocks and the Three Bears
Goldilocks and the Three Bears Academy stars 3
Academy stars 3 Правила образования английских глаголов в форме простое прошедшее время
Правила образования английских глаголов в форме простое прошедшее время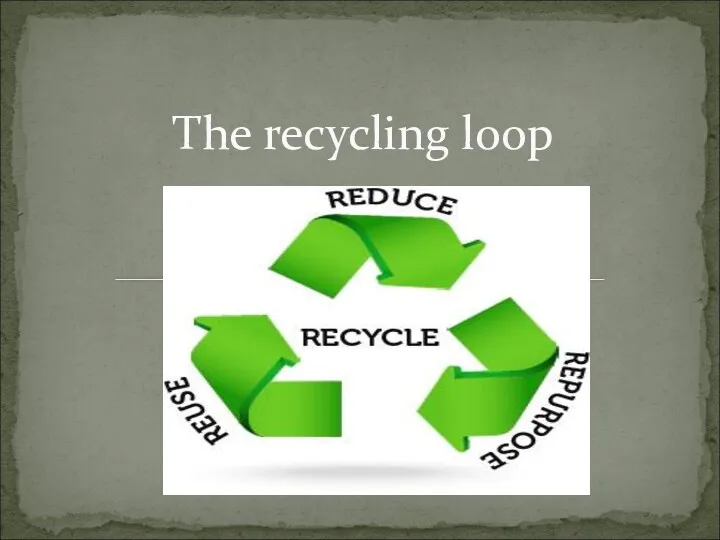 The recycling loop
The recycling loop Morphology is a branch of linguistics which studies the form and structure of words in a language
Morphology is a branch of linguistics which studies the form and structure of words in a language Halloween monsters fun activities games
Halloween monsters fun activities games Special day. Unit 7.3
Special day. Unit 7.3 The University of Mines in SaintPetersburg
The University of Mines in SaintPetersburg The rules of writing a personal letter
The rules of writing a personal letter Choose this, that, these or those
Choose this, that, these or those