Содержание
- 2. Magister Manajemen 1. COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE The company occupies some positions where the competitors cannot copy its
- 3. Competitive Advantage (Barney, 1991); Company has low cost compared to other competitors. The quality of products/services
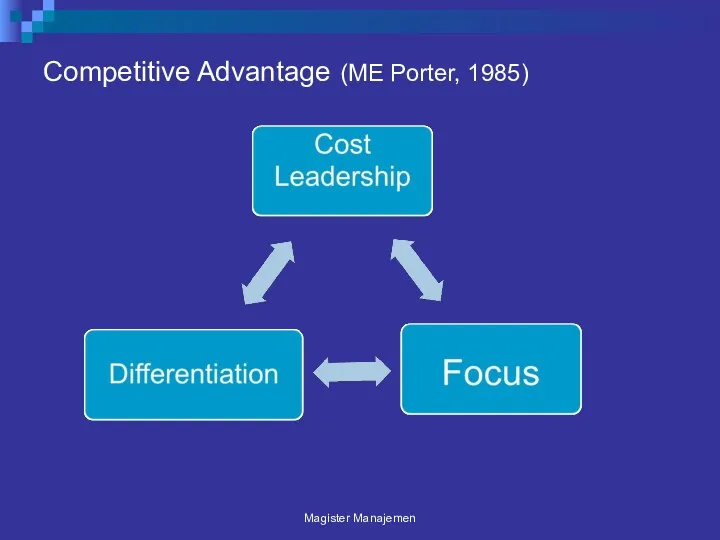
- 4. Competitive Advantage (ME Porter, 1985) Magister Manajemen
- 5. Competitive Advantage in the Public Sector (Popa dkk; Theoretical and Empiribal Researchers in Urban Management, Vol.1
- 6. The source CA of an organization: Available of quantity/quality superior financial, physical and HR Possession of
- 7. Sources of CA in the public sector: Emergence of a new service Introduction of new management
- 8. The key questions to gains CA: Do distinctive element actually meet the needs, interest and expectation
- 9. The information revolution: Change the structure of industries and the rules competition Gives companies the chance
- 10. Particularly of CA in the public sector: Important; the CA has to be perceived by stakeholders
- 11. Innovative business models a factor for CA of the companies (Stoilkovska dkk; UTMS journal of economics
- 12. Elaborate as sources of CA; Selection of a target market Contemporary information and communication technologies The
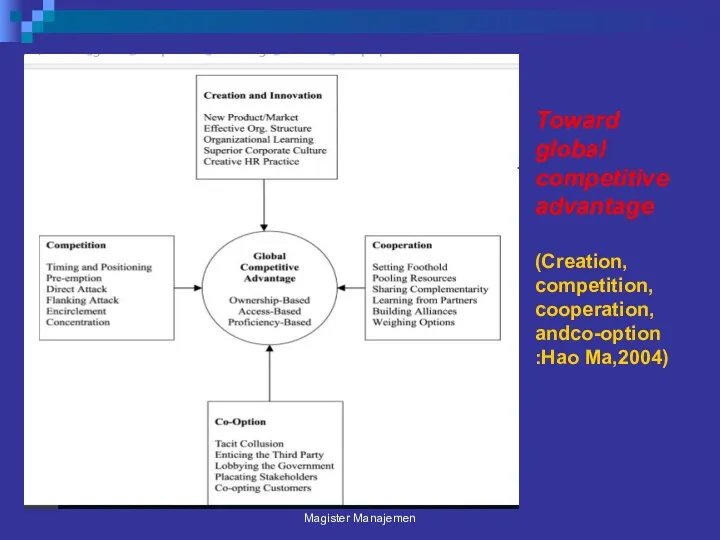
- 13. Toward global competitive advantage (Creation, competition, cooperation, andco-option :Hao Ma,2004) Magister Manajemen
- 14. 2. GLOBALISASI Perkembangan ekonomi dimana perusahaan-perusahaan dari negara industri (Eropa,Jepang, Amerika Utara) mendominasi pasar dunia. (Amerika
- 15. NICs (Korea, Singapura dan Taiwan) Growing wealth from supplying technologically sophisticated product and services, like software
- 16. Manajer : Serving customer world wide with regional manufacturing and product feature, but with many common
- 17. 3. ENVIRONMENTAL NEW INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION (Berry & Rondinelli, 1998) GREEN CUSTOMER GREEN PRODUCT GREEN PROCESS GREEN
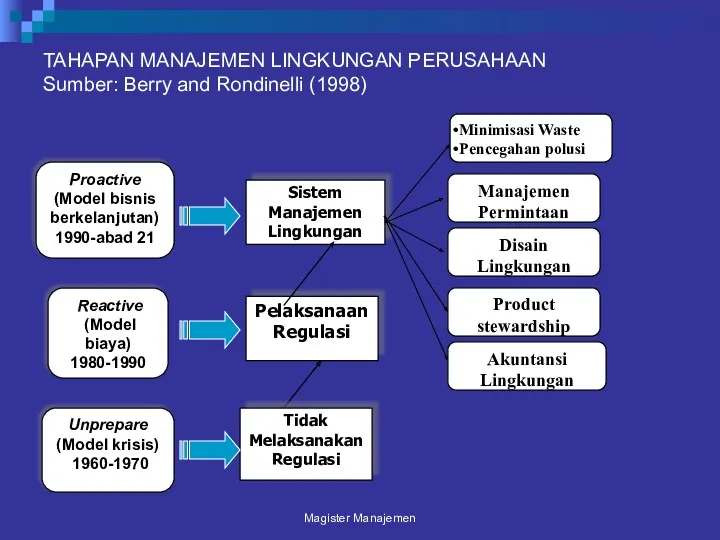
- 18. TAHAPAN MANAJEMEN LINGKUNGAN PERUSAHAAN Sumber: Berry and Rondinelli (1998) Magister Manajemen Sistem Manajemen Lingkungan Pelaksanaan Regulasi
- 19. 4. CORPORATE SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY (CSR) CSR represent action that appears to further some social good, extends
- 20. Definisi CSR Vos (2003); As the obligations or duties of an organization to a specific systems
- 21. CSR of public sector company: a case study of BHEL (Khatik,2016; International business ethics in developing
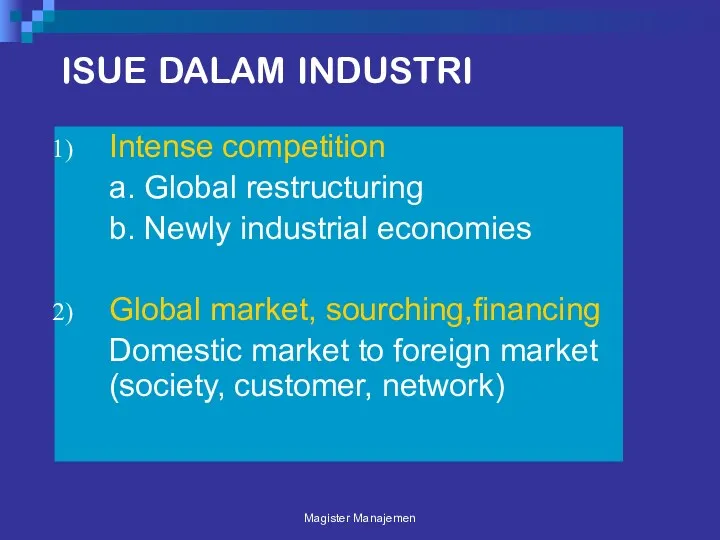
- 22. ISUE DALAM INDUSTRI Intense competition a. Global restructuring b. Newly industrial economies Global market, sourching,financing Domestic
- 23. Lanjutan…… Product variety & mass customization PLC continue to decrease Emphasis on quality Zero defect will
- 24. Lanjutan……. Advance in technology Information tech. change dramatically Worker involvement Ability to create, utilize knowledge as
- 25. FACILITY LAYOUT Magister Manajemen
- 26. Managerial Issues Recognizing that many factors must be considered in choosing how to layout a facility.
- 27. Facilities Layout The configuration of departments, work centers, and equipment, with particular emphasis on movement of
- 28. Implication Layout: Reaching quality, productivity, and competitiveness of a firm. How efficient workers can do their
- 29. Objective of Layout Design Facilitate attainment of product or service quality Use workers and space efficiently
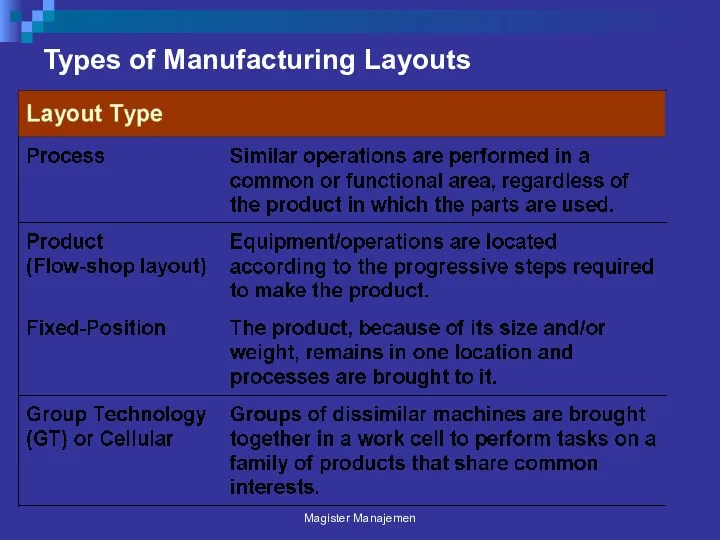
- 30. Types of Manufacturing Layouts Magister Manajemen
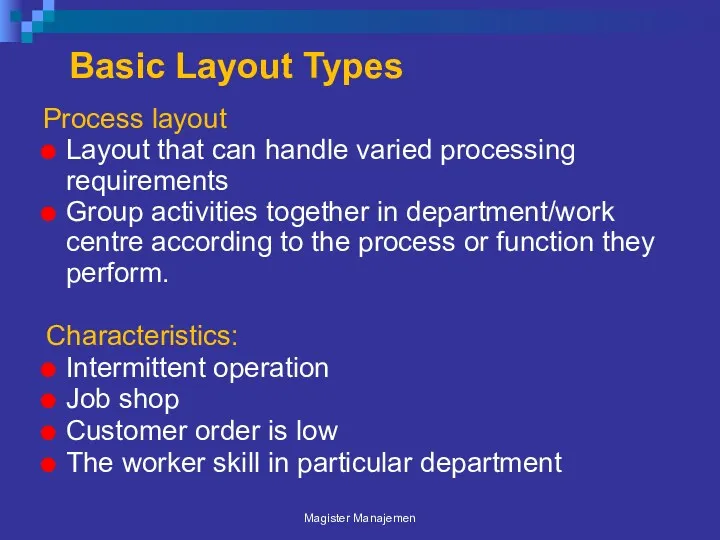
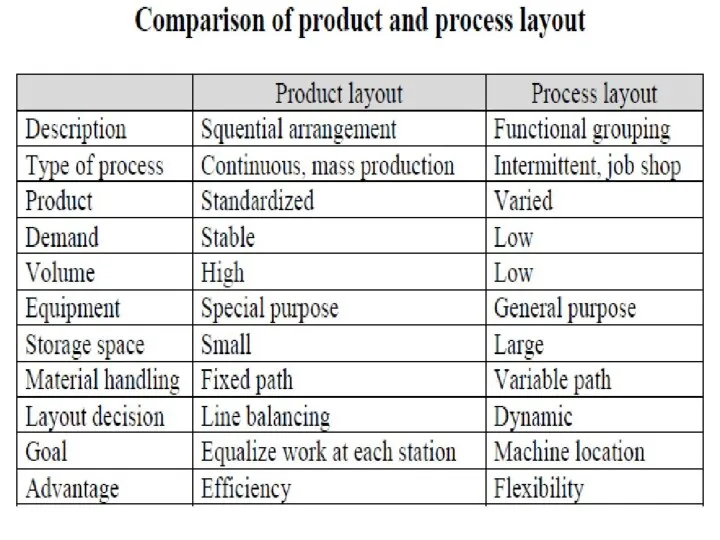
- 31. Basic Layout Types Process layout Layout that can handle varied processing requirements Group activities together in
- 32. Can handle a variety of processing requirements Not particularly vulnerable to equipment failures Equipment used is
- 33. In-process inventory costs can be high Challenging routing and scheduling Equipment utilization rates are low Material
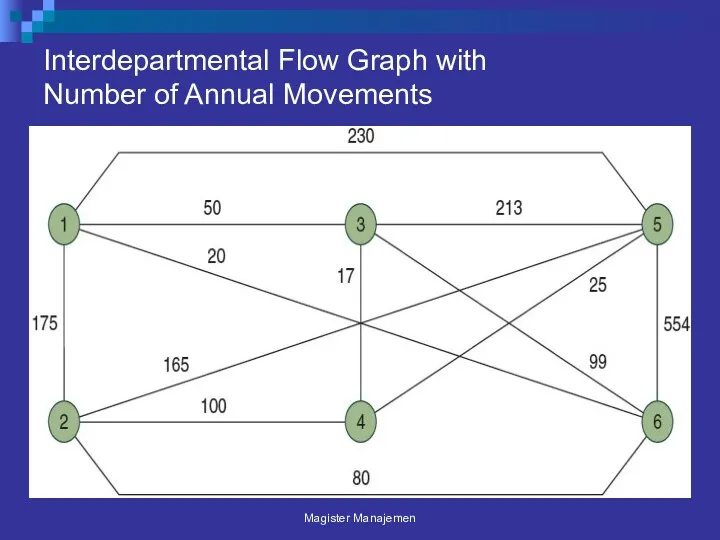
- 34. Interdepartmental Flow Graph with Number of Annual Movements Magister Manajemen
- 35. Steps for Process Layout Loading department to department Non-adjacent load Re-layout Steps for Process Layout Magister
- 36. Product Layout Layout that uses standardized processing operations to achieve smooth, rapid, high-volume flow. Arrange activities
- 37. High rate of output Low unit cost Labor specialization Low material handling cost High utilization of
- 38. Creates dull, repetitive jobs Poorly skilled workers may not maintain equipment or quality of output Fairly
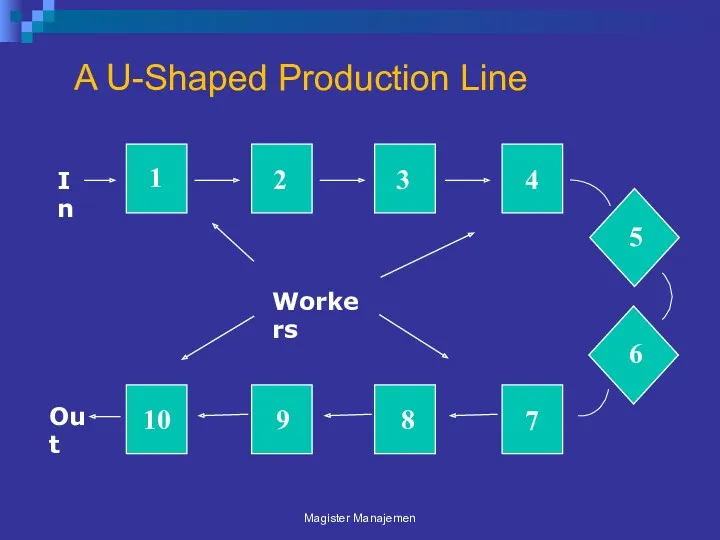
- 39. A U-Shaped Production Line Magister Manajemen
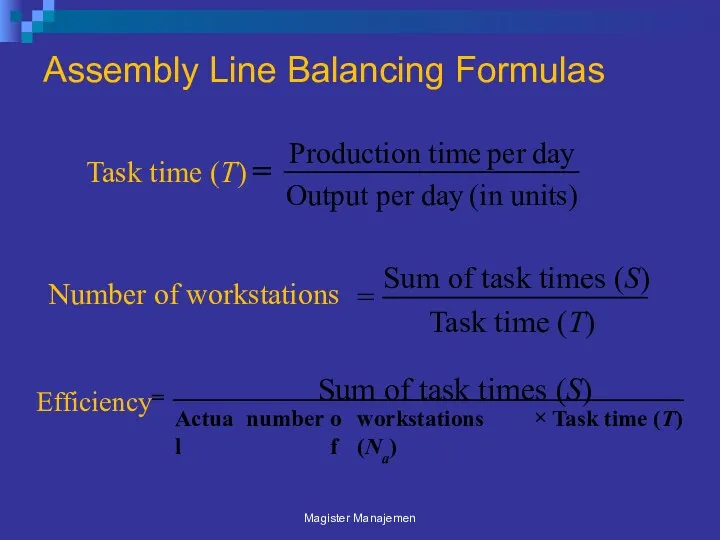
- 40. Assembly Line Balancing Formulas Magister Manajemen
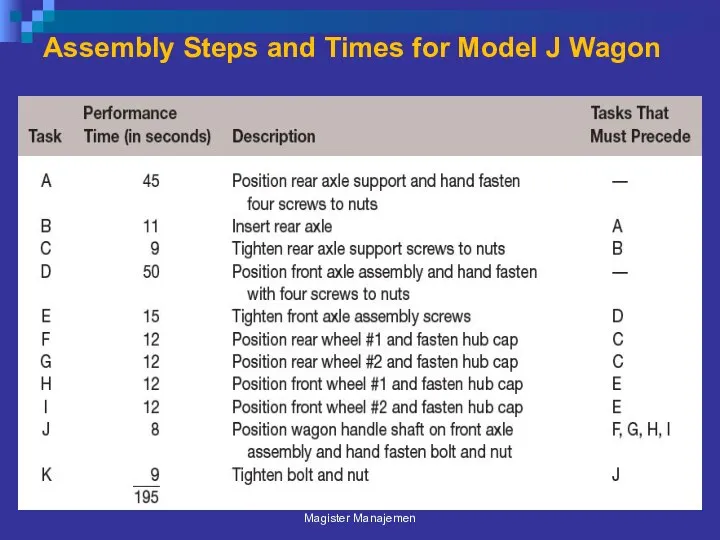
- 41. Assembly Steps and Times for Model J Wagon Magister Manajemen
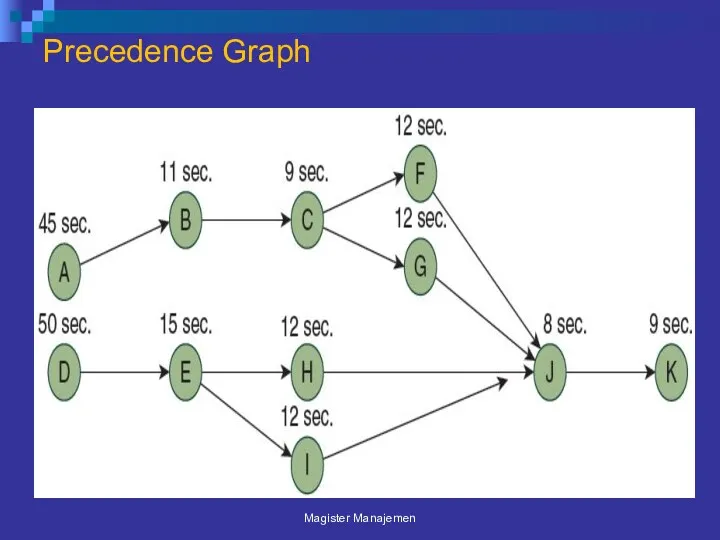
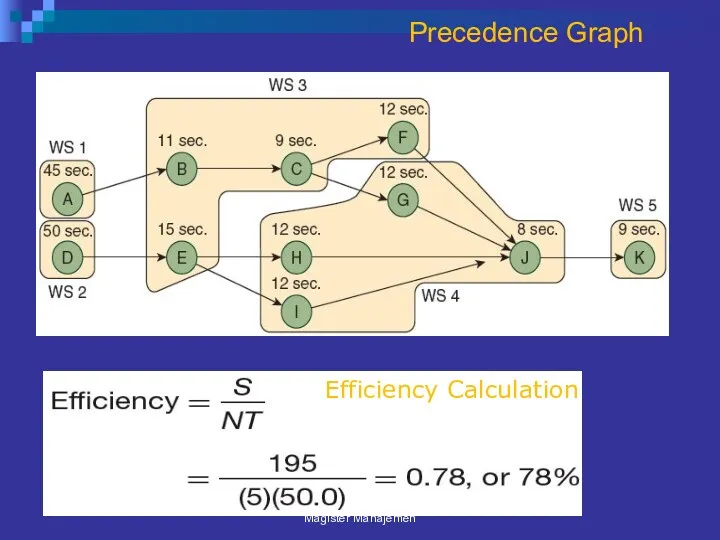
- 42. Precedence Graph Magister Manajemen
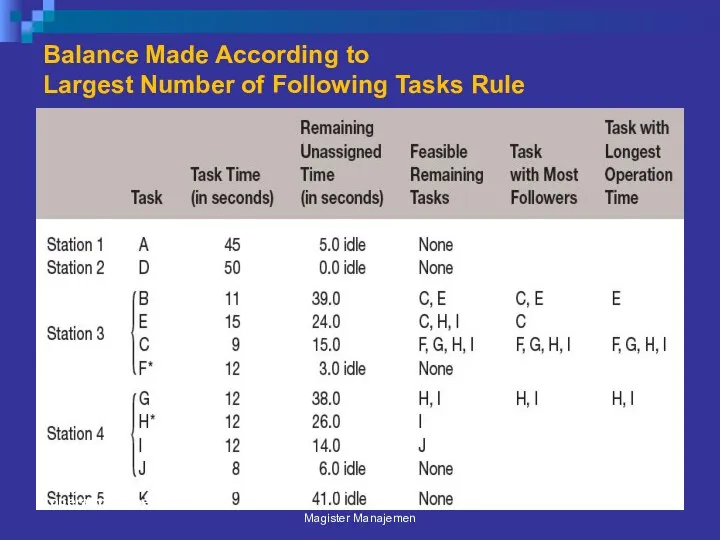
- 43. Balance Made According to Largest Number of Following Tasks Rule *Denotes task arbitrarily selected where there
- 44. Precedence Graph Efficiency Calculation Magister Manajemen
- 45. Magister Manajemen
- 46. JUST-IN TIME (JIT) Magister Manajemen
- 47. Managerial Issues The natural tension between effectiveness (satisfying customers) and efficiency (using resources well). The evolution
- 48. JUST-IN TIME (JIT) IS A PHILOSOPHY OF IMPROVEMENT THROUGH AGGRESSIVELY DISCOVERING AND RESOLVING ANY PROBLEMS OR
- 49. Magister Manajemen Waste is ‘anything other than the minimum amount of equipment, materials, parts, space, and
- 50. Management philosophy of continuous and forced problem solving Supplies and components are ‘pulled’ through system to
- 51. Lean Production; Lean Production supplies customers with exactly what the customer wants, when the customer wants,
- 52. Attacks waste Anything not adding value to the product From the customer’s perspective Exposes problems and
- 53. Magister Manajemen Overproduction Waiting Transportation Inefficient processing Inventory Unnecessary motion Product defects Types of Waste
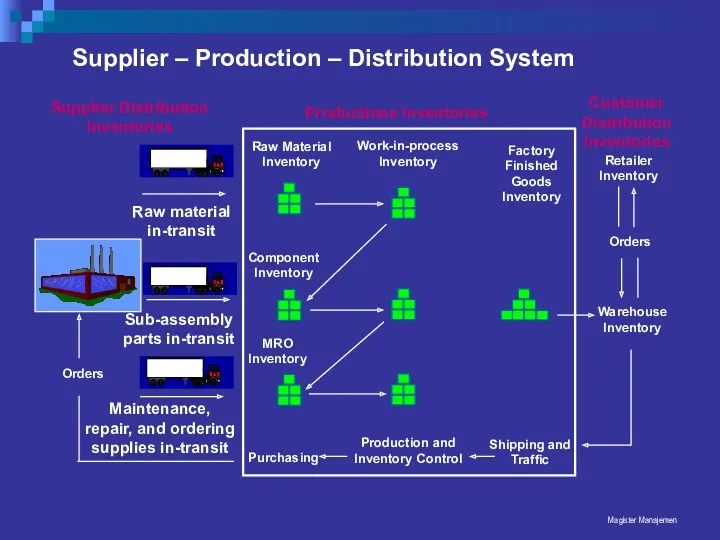
- 54. Magister Manajemen Supplier – Production – Distribution System
- 55. Suppliers reduced number of vendors supportive supplier relationships quality deliveries on time Layout work-cell layouts with
- 56. Magister Manajemen Inventory small lot sizes low setup times specialized bins for holding set number of
- 57. Magister Manajemen JIT Contribution to Competitive Advantage – continued…….. Preventive Maintenance scheduled daily routine operator involvement
- 58. Magister Manajemen JIT Contribution to Competitive Advantage – continued…….. Employee Empowerment empowered and cross-trained employees few
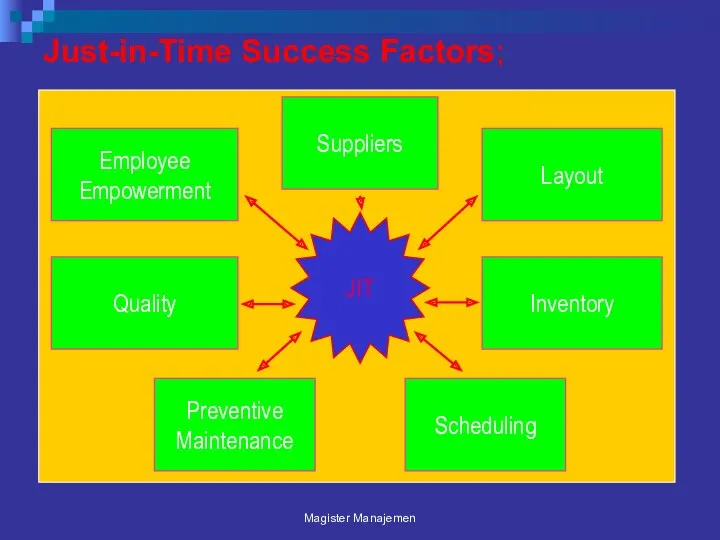
- 59. Just-in-Time Success Factors; Magister Manajemen
- 60. KOMPONEN JIT PEOPLE INVOLVEMENT 1. Team Work. 2. Disiplin. 3. Supplier Partnership. Magister Manajemen
- 61. TOTAL QUALITY CONTROL (TQC) 1. Quality is every body job 2. The Immediate customer 3. Quality
- 62. IMPLEMENTASI JIT Pendidikan dan kepemimpinan bagi seluruh level manajemen. Partisipasi dan keterlibatan karyawan. Pengendalian mutu terpadu.
- 63. BENEFIT JIT Reduce Inventory. Improve Quality. Lower Cost. Shorter Lead Time. Increase Productivity. Greater Flexibility. Better
- 64. Yielding Faster response to the customer at lower cost and higher quality A competitive advantage! Magister
- 65. JIT (TOYOTA) Sejarah berdirinya Toyota: Magister Manajemen
- 66. Lanjutan...... Magister Manajemen
- 67. Toyota Production System (TPS) Filosofi Bisnis Toyota (Toyota WAY) 2 Pilar TPS Just-In Time Barang yang
- 68. Apakah Just-in Time itu ? Kumpulkan hanya barang yang tepat, diwaktu yang tepat, dalam jumlah yang
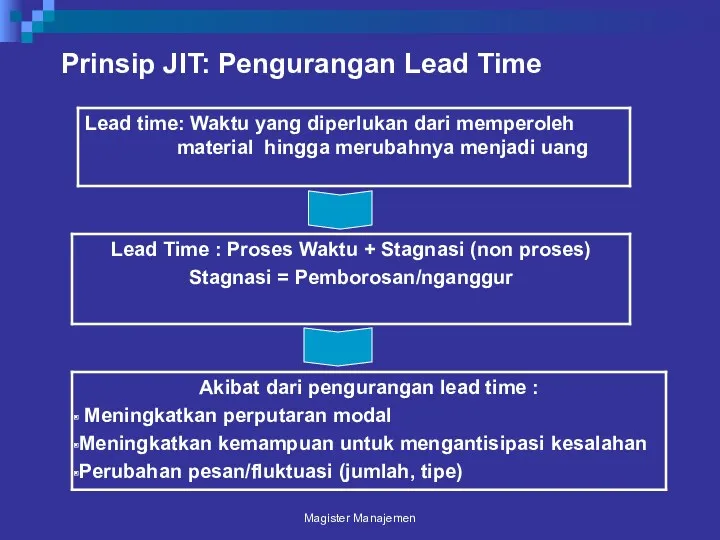
- 69. Prinsip JIT: Pengurangan Lead Time Magister Manajemen
- 70. Yang tidak boleh terjadi (Muda) 7 muda : Over production Menunggu Transportasi Over proses/kualitas Stock (dana
- 71. Bagaimana menjadi kompetitif ? Meningkatkan produktivitas kerja adalah penting Produktivitas Peralatan Produktivitas Material Produktivitas Kerja Magister
- 72. SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT (SCM) Magister Manajemen
- 73. Managerial Issues Concentration of resources on the firm’s core competencies such as supply chain management. Increasing
- 74. VALUE CHAIN AND COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE Competitive adv. Cannot be understand by looking at a firm as
- 75. Gossman (1977) “Competition is no longer company to company, but supply chain to supply chain” Dalam
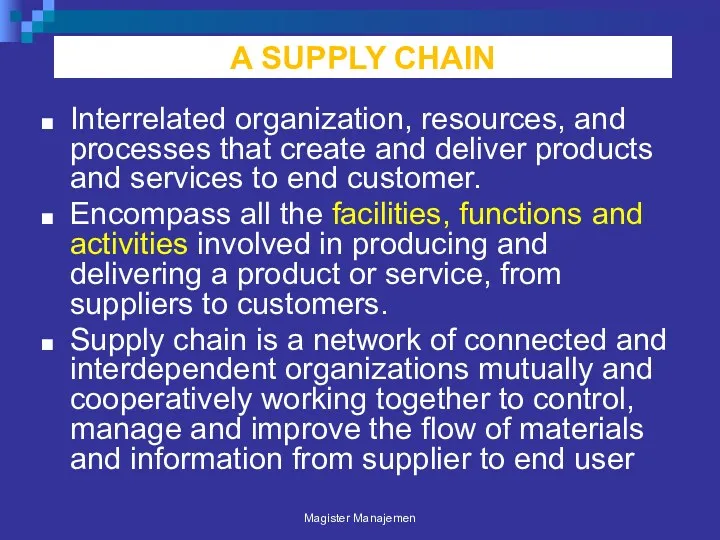
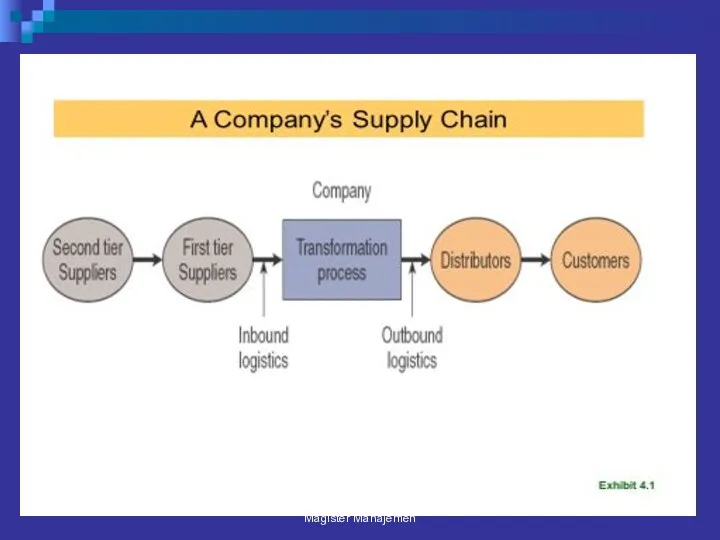
- 76. A SUPPLY CHAIN Interrelated organization, resources, and processes that create and deliver products and services to
- 77. Facilities Warehouses Factories Processing centers Distribution centers Retail outlets Offices Magister Manajemen
- 78. Functions and Activities Forecasting Purchasing Inventory management Information management Quality assurance Scheduling Production and delivery Customer
- 79. SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT (SCM) Coordinate all these activities so that customers can be provide with prompt
- 80. continued……. Suatu jaringan bisnis yang otonom, atau semiotonom, terintegrasi dan bertanggung jawab terhadap penyediaan, pemrosesan dan
- 81. continued…… Supply Chain Management The long-term relationship between a firm and its suppliers to ensure the
- 82. Logistics Inbound Logistics The delivery of goods and services that are purchased from suppliers and/or their
- 83. Magister Manajemen
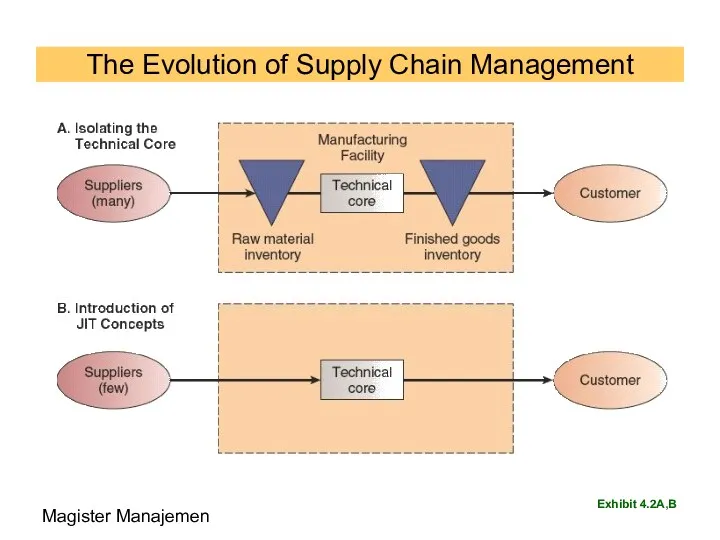
- 84. The Evolution of Supply Chain Management Exhibit 4.2A,B Magister Manajemen
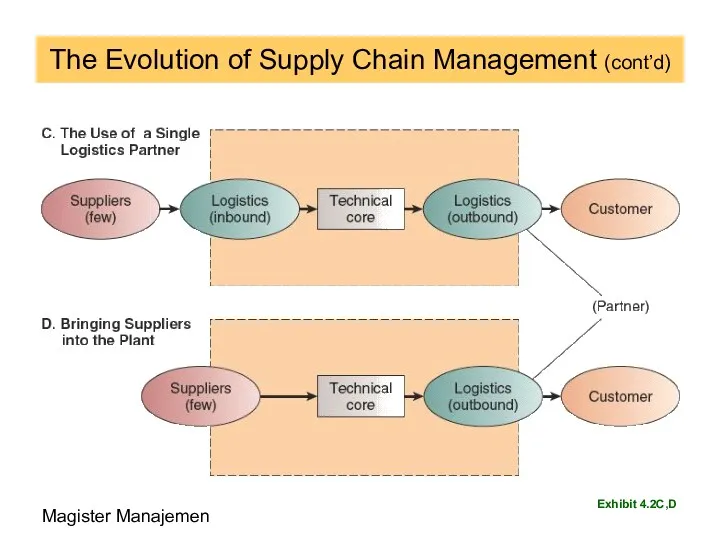
- 85. The Evolution of Supply Chain Management (cont’d) Exhibit 4.2C,D Magister Manajemen
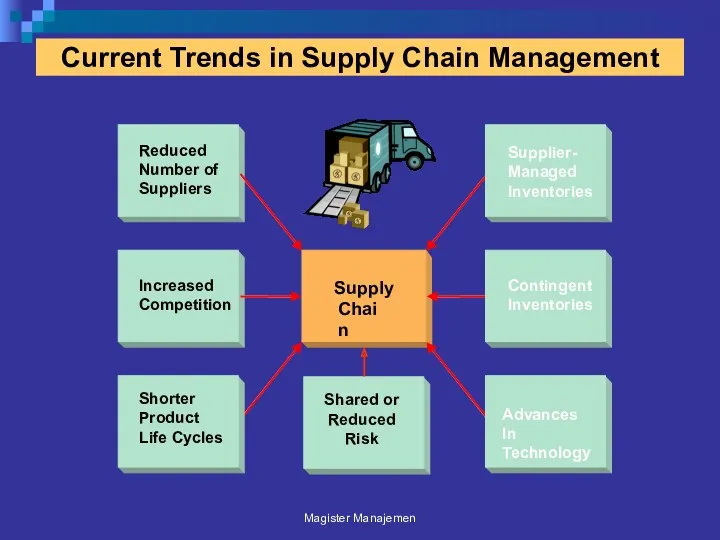
- 86. Current Trends in Supply Chain Management Magister Manajemen
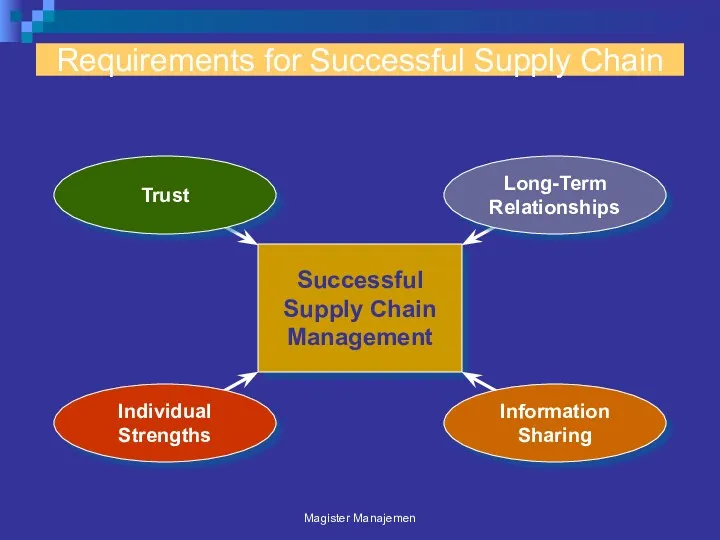
- 87. Requirements for Successful Supply Chain Successful Supply Chain Management Magister Manajemen
- 88. OBJECTIVE SCM To coordinate all the different activities, or “links” of the chain, so that goods
- 89. Tujuan SCM: Penyerahan produk secara tepat waktu untuk memuaskan konsumen. Mengurangi biaya Meningkatkan value dari seluruh
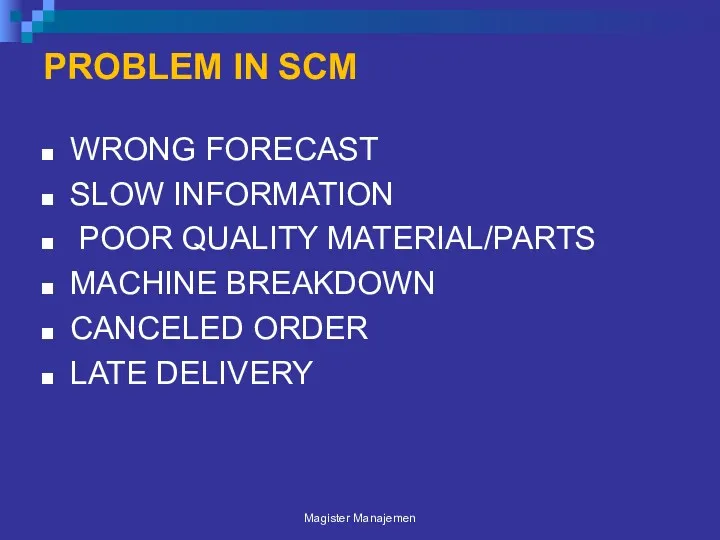
- 90. PROBLEM IN SCM WRONG FORECAST SLOW INFORMATION POOR QUALITY MATERIAL/PARTS MACHINE BREAKDOWN CANCELED ORDER LATE DELIVERY
- 91. Faktor Pendorong SCM Consumer demand Globalisasi Competition Teknologi informasi dan komunikasi Government regulation Environment Magister Manajemen
- 92. EFFECTIVE SCM Require that suppliers and customers work together in a coordinated manner by sharing and
- 93. TWO PRIMARY ELEMEN SCM Structure Include org. units that interact within the supply chain such as
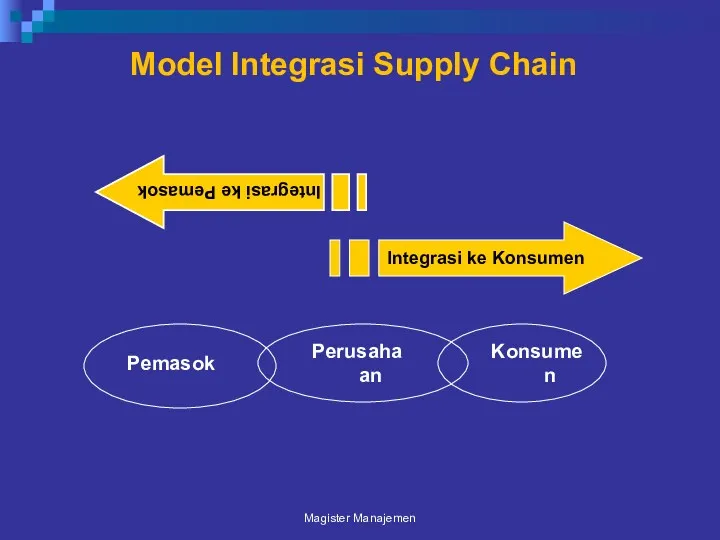
- 94. Model Integrasi Supply Chain Magister Manajemen Integrasi ke Konsumen Integrasi ke Pemasok Pemasok Perusahaan Konsumen
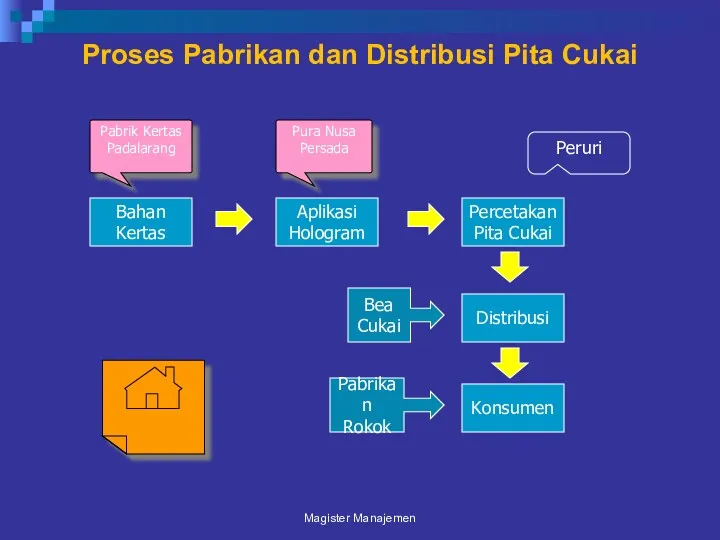
- 95. Proses Pabrikan dan Distribusi Pita Cukai Magister Manajemen Aplikasi Hologram Percetakan Pita Cukai Distribusi Konsumen Bahan
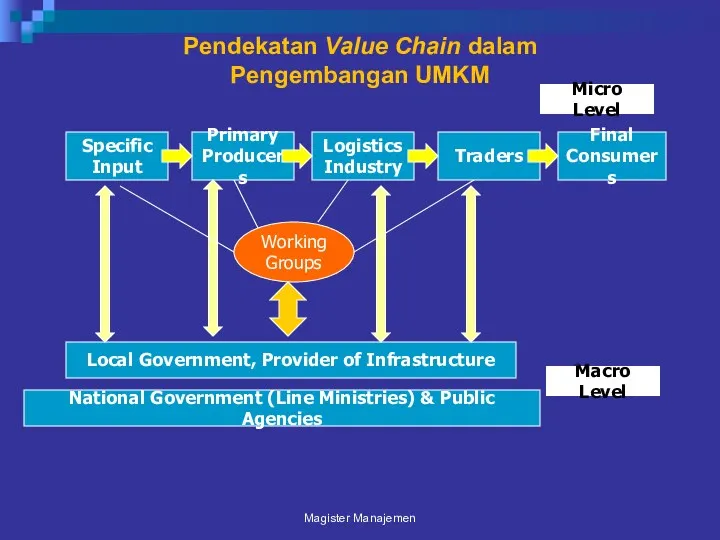
- 96. Pendekatan Value Chain dalam Pengembangan UMKM Magister Manajemen Primary Producers Logistics Industry Traders Micro Level Specific
- 97. Fleksibilitas SCM Kemampuan organisasi secara efektif beradaptasi atau merespon berbagai perubahan. (Gerwin, 1993) Fleksibilitas yang secara
- 98. Product flexibility: Kemampuan memenuhi produk non-standar (feature, warna, desain dll) Volume flexibility: Kemampuan perusahaan scr efektif
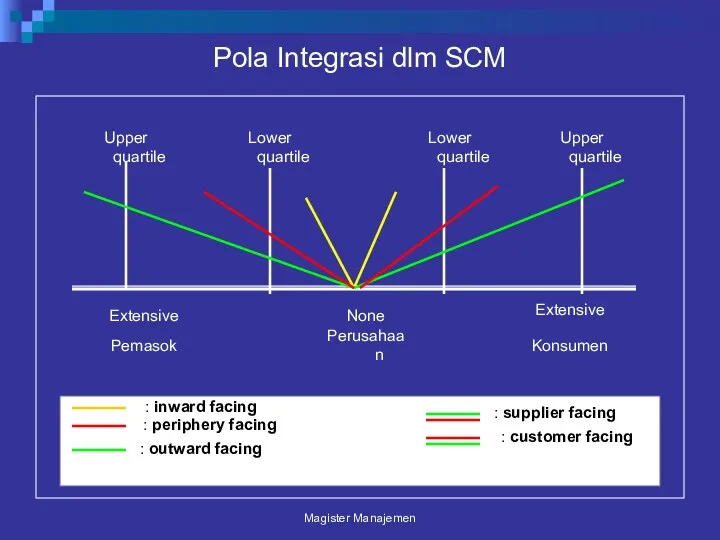
- 99. Pola Integrasi dlm SCM Magister Manajemen Upper quartile Perusahaan Konsumen Extensive None Pemasok Extensive Lower quartile
- 100. Magister Manajemen QUALITY MANAGEMENT
- 101. Managerial Issues Defining quality from the customer’s perspective. Constant increases in the level of quality of
- 102. Magister Manajemen
- 103. Magister Manajemen
- 104. What is Quality ? A degree or level of excellence (Oxford American dictionary) 2.The totally of
- 105. The Quality Gurus Quality Gurus Individuals who have been identified as making a significant contribution to
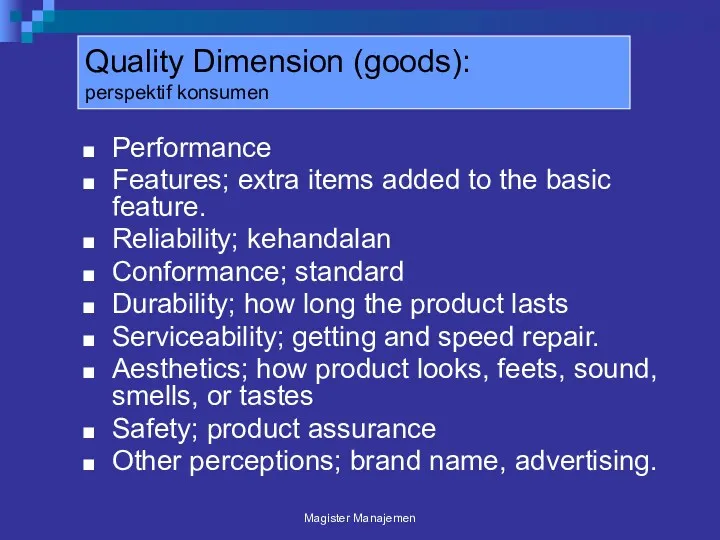
- 106. Quality Dimension (goods): perspektif konsumen Performance Features; extra items added to the basic feature. Reliability; kehandalan
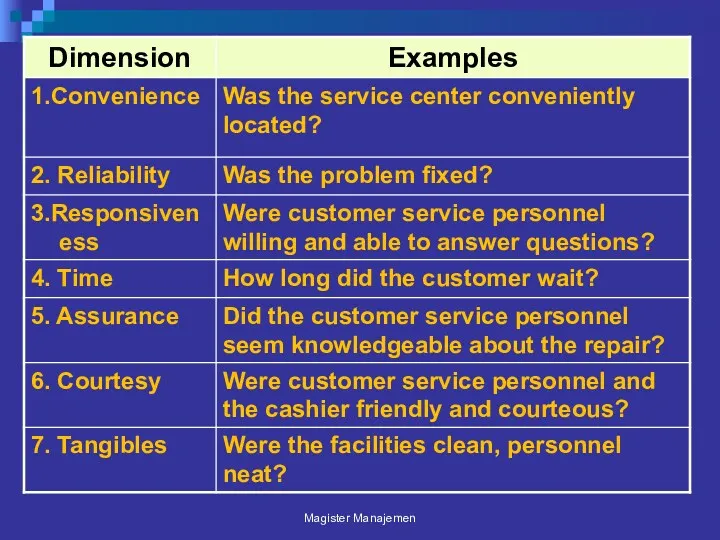
- 107. Quality Dimension(services): perspektif konsumen Time and timeliness Completeness Courtesy; how customers are treated by employees Consistency
- 108. Magister Manajemen
- 109. Quality (perspektif produsen) Conform to specification Quality is free (Philip Crosby) Dipengaruhi oleh: Desain proses produksi
- 110. Management Quality Awards International Standard Organization (ISO)-9000, 14000 Standard Nasional Indonesia (SNI) Akreditasi Museum Rekor Indonesia
- 111. 3 Mitos dalam MBNQA The Baldrige Award requires large expenditures on the application and preparation for
- 112. MBNQA Items (1000 points) Leadership (100 point) Information and Analysis (70 point) Strategic Quality Planning (60
- 113. Quality Certification ISO 9000 Set of international standards on quality management and quality assurance, critical to
- 114. ISO 9000 Quality Management Principles Customer focus Leadership People involvement Process approach A systems approach to
- 115. ISO 14000 ISO 14000: a set of international standards for assessing a company’s environmental performance Standards
- 116. ISO 14000 Management systems Systems development and integration of environmental responsibilities into business planning Operations Consumption
- 117. TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT (TQM) The management of quality in every facet of the business and the
- 118. PRINCIPLES OF TQM The customer defines quality, and the customer needs are the top priority. Top
- 119. KEY TQM CONCEPTS Long term perspective Upper management commitment Employ a system approach Training and tools
- 120. 5 reason for resistance to change Fear of losing something (authority, pay, status or job) Poor
- 121. KAIZEN Usaha perbaikan terus menerus dan tidak pernah berhenti untuk mencapai keadaan atau kondisi yang lebih
- 122. Bentuk Aplikasi Kaizen Jishuken Suatu aplikasi kaizen yang dilakukan di area dimana proses kerja berlangsung dengan
- 123. Tujuan Kaizen Memberikan sumbangan untuk perbaikan dan pengembangan perusahaan. Menghormati harkat manusia di dalam usahanya untuk
- 124. Sasaran Kaizen: Lebih baik (kualitas meningkat, produktivitas) Lebih murah (pengurangan biaya yang tidak perlu). Lebih aman
- 125. Kaizen diciptakan untuk menghilangkan : Muda (pemborosan); menunggu, gerakan, persediaan, pengiriman, proses, peduksi, dan repair. Mura
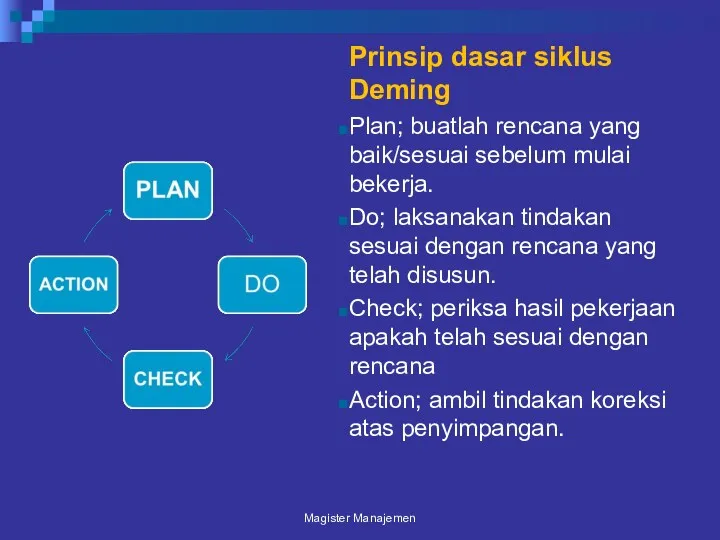
- 126. Prinsip dasar siklus Deming Plan; buatlah rencana yang baik/sesuai sebelum mulai bekerja. Do; laksanakan tindakan sesuai
- 127. STATISTICAL QUALITY CONTROL (SQC) Magister Manajemen
- 128. LATAR BELAKANG Global Competition Pergeseran level persaingan (state-corporate-product) Improve Quality Increase customer satisfaction and competitiveness Magister
- 129. STATISTICAL PROCESS CONTROL (SPC) A statistical procedure using control chart to see if any part of
- 130. CONTROL CHART Is a graph that establishes the control limits of a process. Fungsi Control Chart
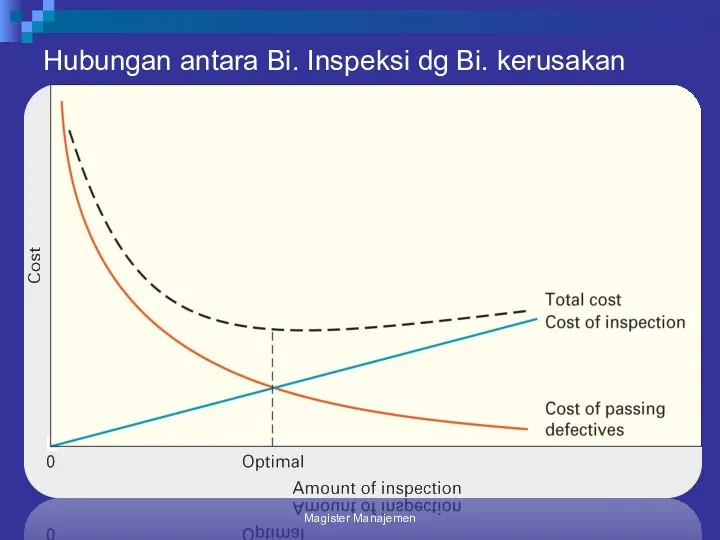
- 131. Hubungan antara Bi. Inspeksi dg Bi. kerusakan Magister Manajemen
- 132. Cost of Quality Appraisal Costs Costs of activities designed to ensure quality or uncover defects Prevention
- 133. SPC Applied to Service Hospital: quickness of care, staff responses, accuracy of lab tests, cleanliness. Grocery
- 134. Why use sampling ? Sampling often is faster Some test require that the product be damaged
- 136. Скачать презентацию





































































































 Merida Board Game
Merida Board Game Environment, weather and climate
Environment, weather and climate The Monument to Peter I in Maple Alley
The Monument to Peter I in Maple Alley Comparative and superlative adjectives. Grammar
Comparative and superlative adjectives. Grammar Виды письменного перевода
Виды письменного перевода English houses
English houses Степени сравнения прилагательных. 4 класс
Степени сравнения прилагательных. 4 класс Dtscribing a house
Dtscribing a house More esl games: DE&AL DE&AL https://vk.com/deandal
More esl games: DE&AL DE&AL https://vk.com/deandal The Gerund Герундий 9 класс
The Gerund Герундий 9 класс In my lunch box
In my lunch box The gerund. Герундий в английском языке
The gerund. Герундий в английском языке Present simple and continuous контакт
Present simple and continuous контакт Shopping for clothes
Shopping for clothes насекомые
насекомые Исторические изменения в грамматическом строе, грамматикализация на примере русского и английского языков
Исторические изменения в грамматическом строе, грамматикализация на примере русского и английского языков Was or were. Game
Was or were. Game This, that, these, those
This, that, these, those Demonstrative pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns The Great British Quiz
The Great British Quiz Переклад англомовного тексту українською мовою. “Злочин лорда Артура Севіля та інші оповідання” Оскара Уайльда
Переклад англомовного тексту українською мовою. “Злочин лорда Артура Севіля та інші оповідання” Оскара Уайльда Sights of Donbass. Welcome to Donetsk
Sights of Donbass. Welcome to Donetsk How I Spent My Summer
How I Spent My Summer Professions
Professions The toys
The toys Guess how many toys
Guess how many toys Grammar: -ing form or infinitive Part I
Grammar: -ing form or infinitive Part I Who want to be a millionaire. The game
Who want to be a millionaire. The game