Содержание
- 2. Consumer markets and consumer buyer behaviour Model of consumer behaviour Characteristics affecting consumer behaviour Types of
- 3. Consumer buyer behaviour: the buying behaviour of final consumers—individuals and households that buy goods and services
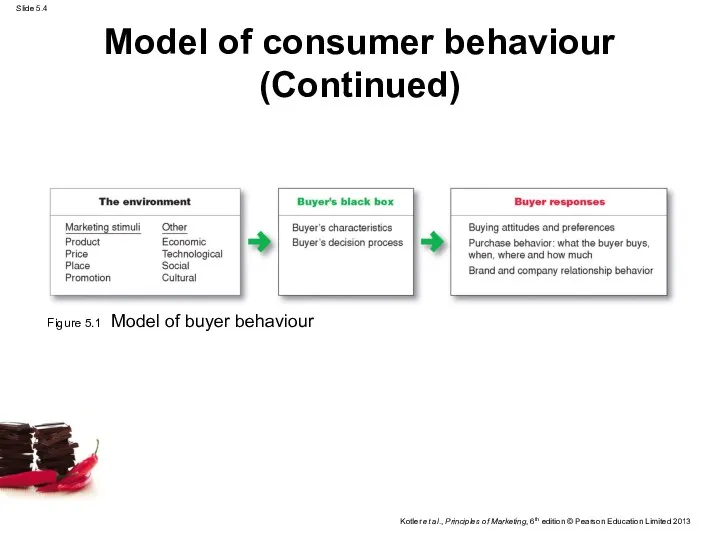
- 4. Model of consumer behaviour (Continued) Figure 5.1 Model of buyer behaviour
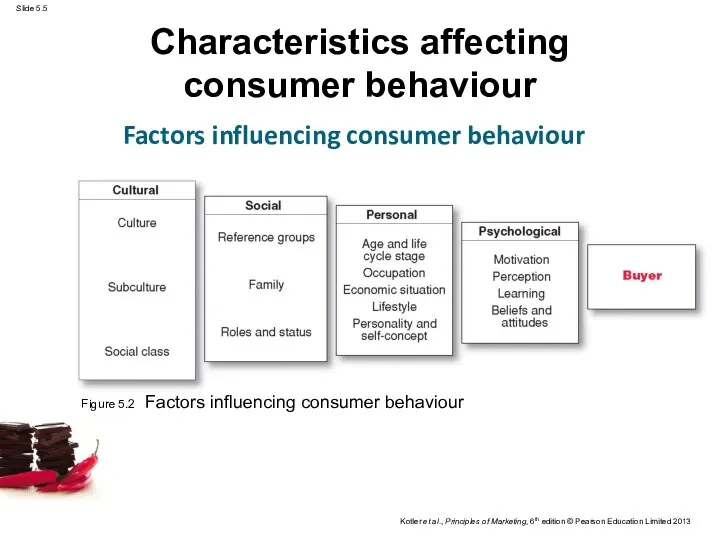
- 5. Characteristics affecting consumer behaviour Factors influencing consumer behaviour Figure 5.2 Factors influencing consumer behaviour
- 6. Culture is the learned values, perceptions, wants and behaviours from family and other important institutions. Characteristics
- 7. Characteristics affecting consumer behaviour (Continued) Subculture are groups of people within a culture with shared value
- 8. Social classes are relatively permanent and ordered divisions in a society whose members share similar values,
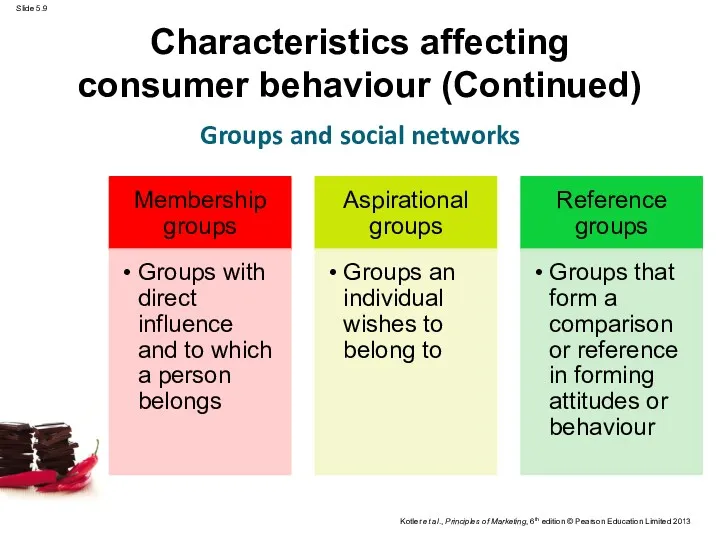
- 9. Characteristics affecting consumer behaviour (Continued) Groups and social networks
- 10. Characteristics affecting consumer behaviour (Continued) Word-of-mouth influence and buzz marketing Opinion leaders are people within a
- 11. Characteristics affecting consumer behaviour (Continued) Online social networks are online communities where people socialise or exchange
- 12. Characteristics affecting consumer behaviour (Continued) Family is the most important consumer-buying organisation in society. Social roles
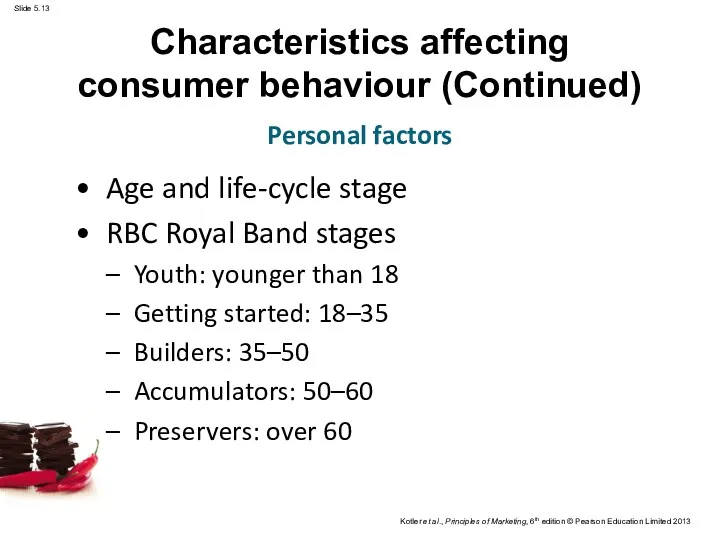
- 13. Characteristics affecting consumer behaviour (Continued) Age and life-cycle stage RBC Royal Band stages Youth: younger than
- 14. Characteristics affecting consumer behaviour (Continued) Occupation affects the goods and services bought by consumers. Economic situation
- 15. Characteristics affecting consumer behaviour (Continued) Lifestyle is a person’s pattern of living as expressed in his
- 16. Characteristics affecting consumer behaviour (Continued) Personality and self-concept Personality refers to the unique psychological characteristics that
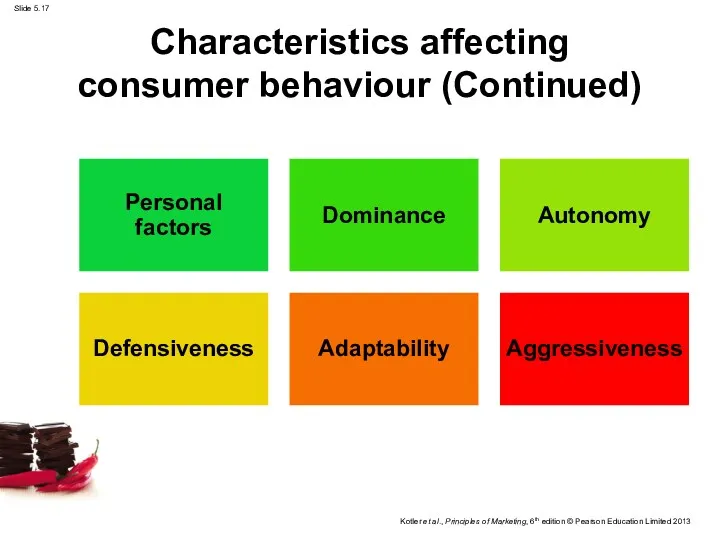
- 17. Characteristics affecting consumer behaviour (Continued)
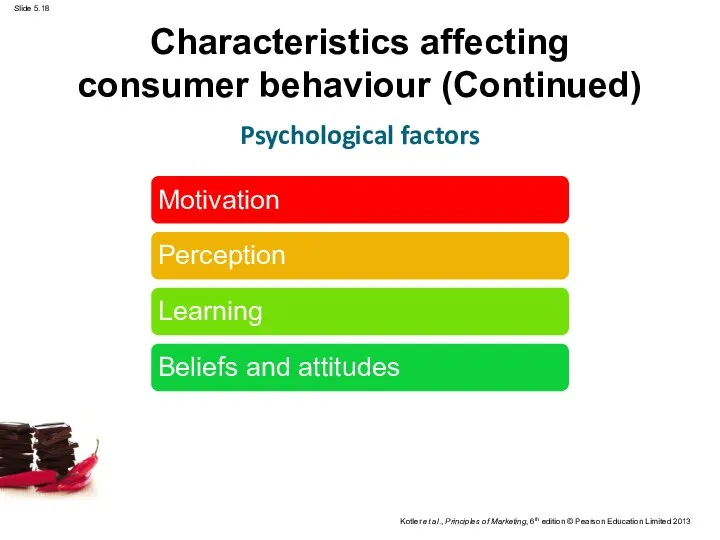
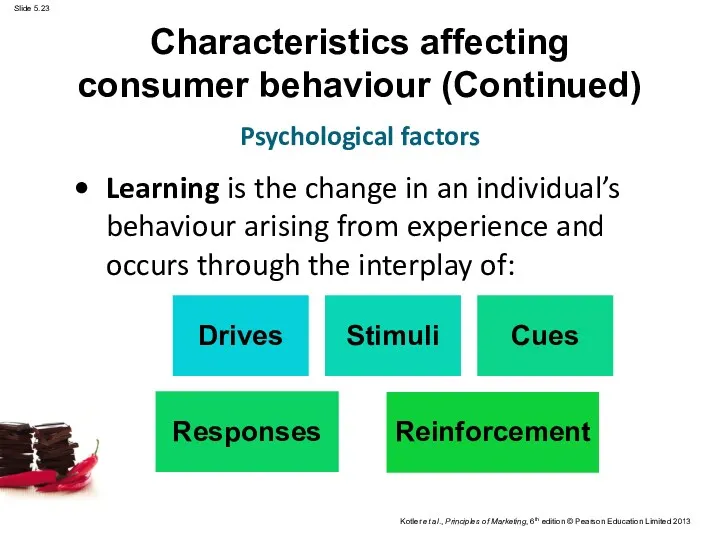
- 18. Characteristics affecting consumer behaviour (Continued) Psychological factors
- 19. Characteristics affecting consumer behaviour (Continued) A motive is a need that is sufficiently pressing to direct
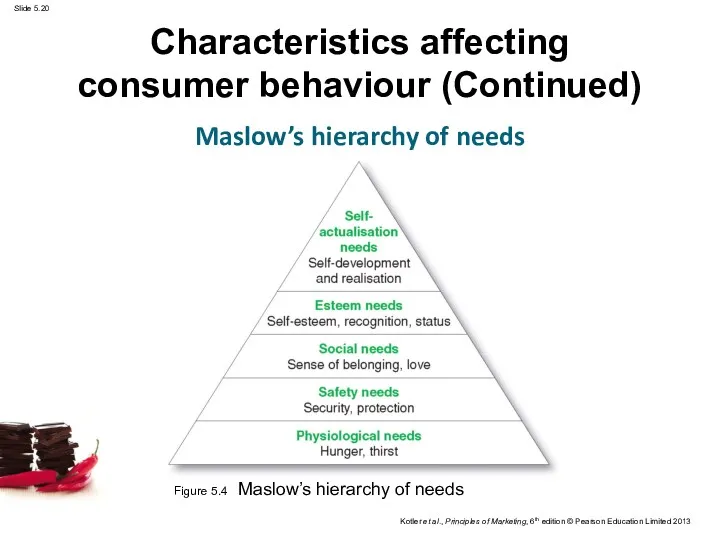
- 20. Characteristics affecting consumer behaviour (Continued) Maslow’s hierarchy of needs Figure 5.4 Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
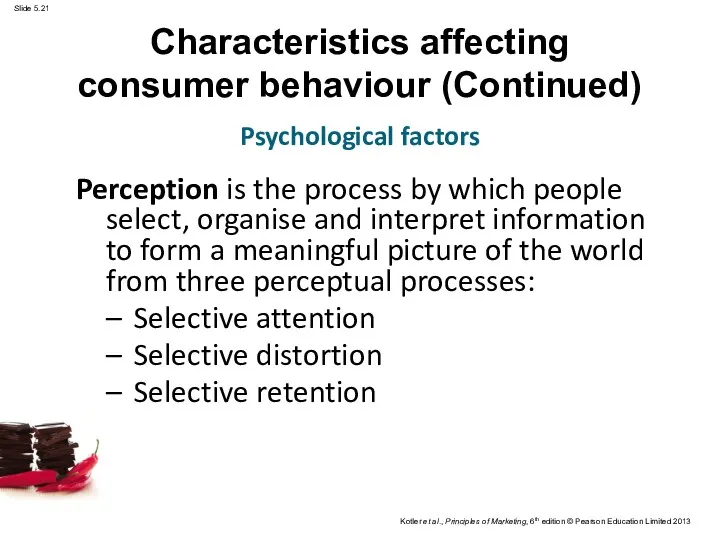
- 21. Characteristics affecting consumer behaviour (Continued) Perception is the process by which people select, organise and interpret
- 22. Characteristics affecting consumer behaviour (Continued) Selective attention is the tendency for people to screen out most
- 23. Characteristics affecting consumer behaviour (Continued) Learning is the change in an individual’s behaviour arising from experience
- 24. Characteristics affecting consumer behaviour (Continued) Belief is a descriptive thought that a person holds about something
- 25. Characteristics affecting consumer behaviour (Continued) Attitudes describe a person’s consistently favourable or unfavourable evaluations, feelings and
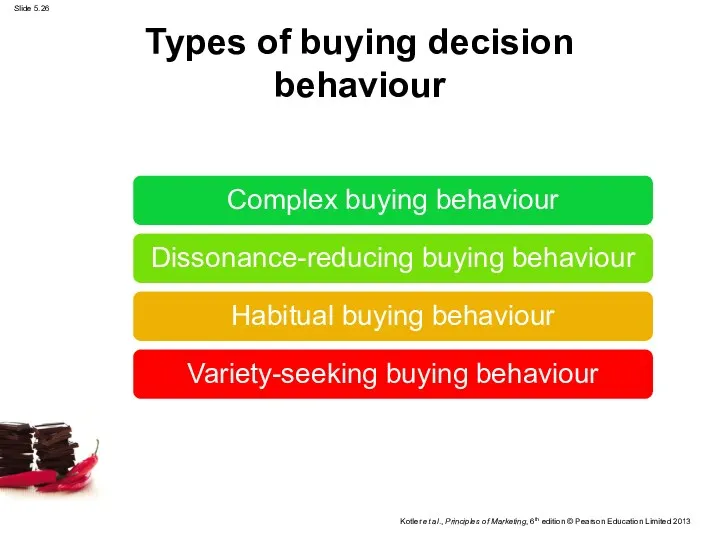
- 26. Types of buying decision behaviour
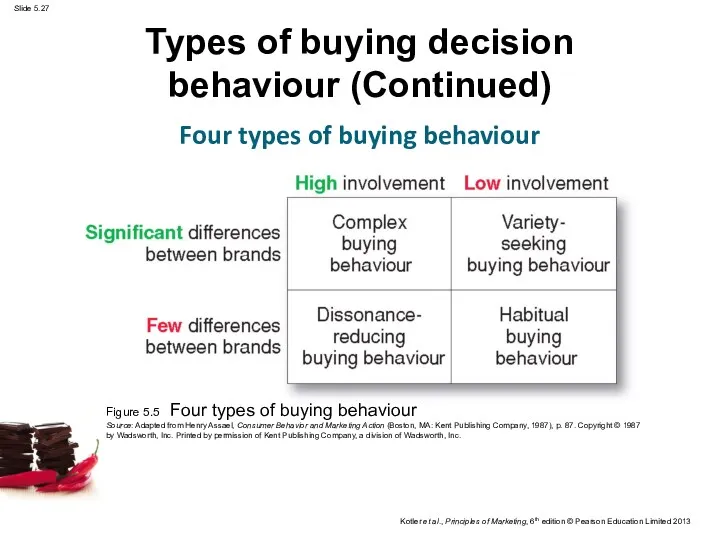
- 27. Types of buying decision behaviour (Continued) Four types of buying behaviour Figure 5.5 Four types of
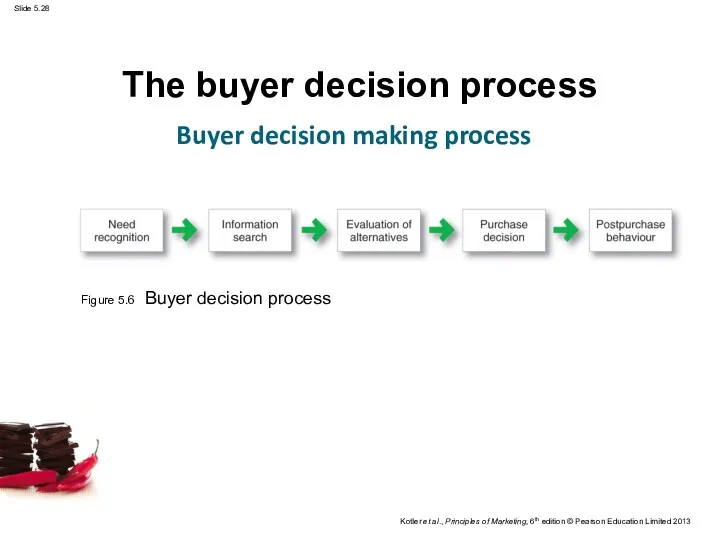
- 28. The buyer decision process Buyer decision making process Figure 5.6 Buyer decision process
- 29. The buyer decision process (Continued) Occurs when the buyer recognises a problem or need triggered by:
- 30. The buyer decision process (Continued) Personal sources—family and friends Commercial sources—advertising, Internet Public sources—mass media, consumer
- 31. The buyer decision process (Continued) How the consumer processes information to arrive at brand choices. Evaluation
- 32. The buyer decision process (Continued) The act by the consumer to buy the most preferred brand.
- 33. The buyer decision process (Continued) The satisfaction or dissatisfaction that the consumer feels about the purchase.
- 34. The buyer decision process (Continued) Customer satisfaction is a key to building profitable relationships with consumers—to
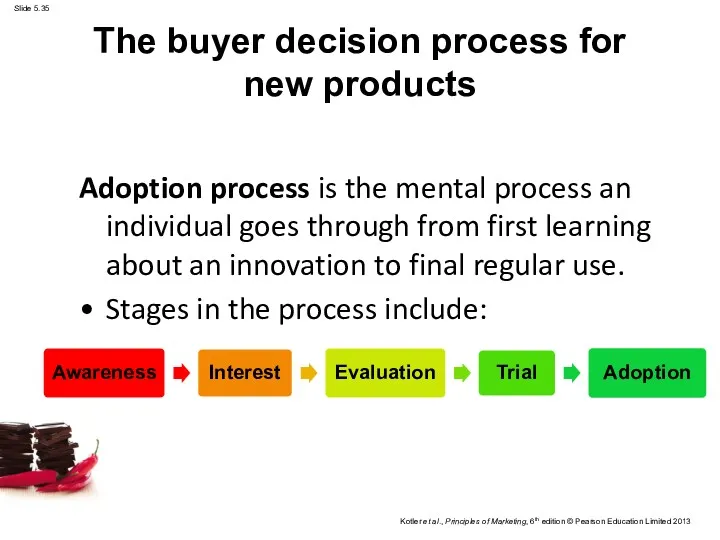
- 35. The buyer decision process for new products Adoption process is the mental process an individual goes
- 37. Скачать презентацию


















 Why is English so popular
Why is English so popular My summer vacation
My summer vacation Brief history of american music
Brief history of american music Времена в английском языке
Времена в английском языке Guess and express your opinion about my weekend
Guess and express your opinion about my weekend Изучение современного английского языка по песням
Изучение современного английского языка по песням The golden ring
The golden ring Possesives practice
Possesives practice “to be” in the past simple. (Урок 3)
“to be” in the past simple. (Урок 3) Деловая переписка. Структура делового письма
Деловая переписка. Структура делового письма Communication for Development in the Third World: Theory and Practice for Empowerment
Communication for Development in the Third World: Theory and Practice for Empowerment My future profession automation fitter
My future profession automation fitter Exciting Ukraine
Exciting Ukraine How I learn English
How I learn English Christmas celebrations in the Britain and the USA
Christmas celebrations in the Britain and the USA Английский язык в современном мире
Английский язык в современном мире Natural disasters
Natural disasters My native city Kovrov
My native city Kovrov Теоретическая грамматика английского языка. Глагол. (лекция 4)
Теоретическая грамматика английского языка. Глагол. (лекция 4) Medusa. The quest of Perseus
Medusa. The quest of Perseus How to shop properly
How to shop properly We count that lake Baikal need protect
We count that lake Baikal need protect Итоговый урок по английскому языку
Итоговый урок по английскому языку Sport in USA
Sport in USA Music in Our Life
Music in Our Life Причастие в английском языке
Причастие в английском языке Grammar
Grammar Spotlight 2 кл
Spotlight 2 кл