Содержание
- 2. Syllabus Lectures 20 hours Workshops 8 hours Supervised self-guided work (УСР) 6 hours TOTAL 34
- 3. RESOURSES Антрушина Г.Б. Лексикология английского языка: Учеб. пособие для студентов / Г.Б. Антрушина, О.В. Афанасьева, Н.Н.
- 4. LECTURE 1 The questions under consideration 1.What is lexicology? 1.1.The definition of lexicology 1.2.The object of
- 5. TEST 1 Name the type of lexicology which deals with the origin of various words, their
- 6. 2. Answer the following questions 1.What is the subject-matter of lexicology as a branch of linguistics?
- 7. 6.What are the points of interactions between lexicology and phonetics? 7. Morphological indicators can help to
- 8. 1.1. The definition of lexicology 1.2. The object of lexicology What is it - Modern English
- 9. The definition of lexicology Lexicology is the part of linguistics dealing with the vocabulary of the
- 10. The term lexicology lexicology lexis ‘word’ logos ‘learning’.
- 11. The object of lexicology a study and systematic description of vocabulary in respect to its origin,
- 12. The theoretical value of English lexicology forms the study of its vocabulary meets the demands of
- 13. Lexicology and a would-be teacher of languages it helps to stimulate a systematic approach to the
- 14. Lexicology and the general linguistic training of every philologist sums up the knowledge acquired during all
- 15. The practical value of English lexicology To study words is very important. Here's the proof. The
- 16. The proof 3.That the vocabulary of the average person almost stops growing by the middle twenties.
- 17. The results of a vocabulary test The participants 100 in the upper 10 per cent lower
- 18. Vocabulary and success the one and only common characteristic of outstandingly successful people is an extensive
- 19. What is vocabulary? One indication of intelligence Words are the tools of thinking Words are your
- 20. The basic task of lexicology a study and systematic description of vocabulary in respect to its
- 21. Different branches of Lexicology General lexicology Specia1 lexicology Etуmо1ogу Semasiology Onоmasiоlоgу Historical lexicology Desсriptive lexicology Cоntrastive
- 22. General lexicology is a part of general linguistics. It is concerned with the general study of
- 23. Specia1 lexicology is the lexicology of a particular language (e.g., English, Russian, French, etc.). It devotes
- 24. Etуmо1ogу is the branch of linguistics which studies the origin or derivation of words. In many
- 25. Semasiology is the branch of linguistics whose subject-matter is the study of word meaning. The term
- 26. Onоmasiоlоgу is the study of the principles of the signification of things and notions by lexical
- 27. Two different approaches in linguistic science to the study of language material the synchronic or descriptive
- 28. Desсriptive lexicology deals with the vocabulary of a given language at a given stage of its
- 29. Historical lexicology discusses the origin of various words, their change and development, the linguistic and extra
- 30. Cоntrastive and comparative lexicology This relatively new branch of study provides a theoretical basis on which
- 31. 1.4.The connection of lexicology with other branches of linguistics is closely connected with general linguistics, the
- 32. Lexicology and phonetics words acquire a different meaning because they are pronounced differently E.g., 'import, n,
- 33. lexicology and grammar Morphological indicators often help to differentiate the meanings of the words. E.g., plural
- 34. lexicology and grammar Syntactic position of a word does not only change its function but its
- 35. lexicology and grammar The grammatical form and function of the word affect its lexical meaning. E.g.
- 36. Lexicology and Stylistics Stylistics, although from a different angle, studies many problems treated in lexicology. These
- 37. Lexicology and Sосiо1inguistiсs Language is the reality of thought, and thought develops with the development of
- 38. Lexicology and Sосiо1inguistiсs The extra-linguistic factors influence usage and development of language. This influence is particularly
- 39. The new language of cyberspace (“cybervocabulary”). As computers gradually extended their influence, so did cyber-, as
- 40. Lexicology and Sосiо1inguistiсs PIN (1981) is an abbreviation of personal identification number, a number allocated by
- 41. Lexicology and Sосiо1inguistiсs E-mail (1982) is an abbreviation of electronic mail, which by the middle of
- 42. Lexicology and Sосiо1inguistiсs The power of English is not confined to the invention and manufacture of
- 43. Lexicology and Sосiо1inguistiсs Another example: the suffix — holic, -aholic, -oholoc (workaholic [1968]) describes "all-consuming obsessions",
- 44. Lexicology and Sосiо1inguistiсs Chocoholic, a compulsive eater of chocolate, appeared in 1976. Shopaholic, a compulsive shopper,
- 45. New words comprise various structural types: simple (cable, dude, rap); derived (buyout, to upchuck, animalist, synergy,
- 46. Lexicology and Sосiо1inguistiсs Over the years, many different meanings of cool have accumulated. Cool has meant
- 48. Скачать презентацию










































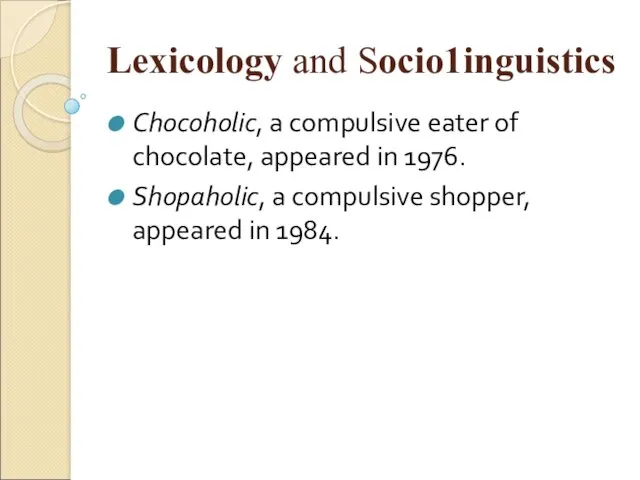

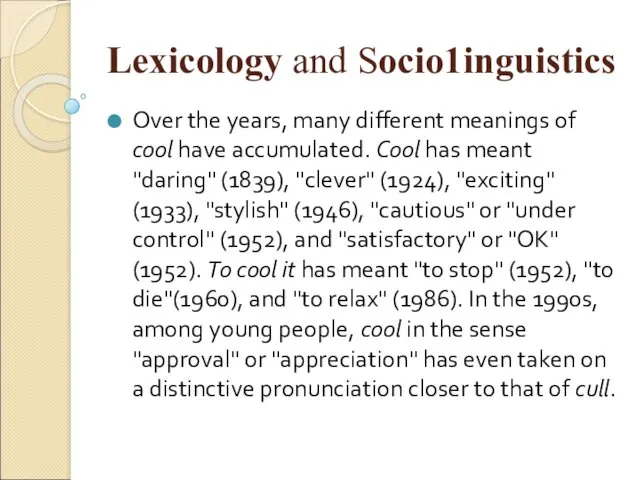
 Question forms
Question forms Environmental problems
Environmental problems Интересные факты об английском языке
Интересные факты об английском языке Vancouver Marathon by Slidesgo
Vancouver Marathon by Slidesgo Parts of body
Parts of body Переводческие трансформации. Виды трансформаций. Лексические и лексико-граматические переводческие трансформации. Лекция 2
Переводческие трансформации. Виды трансформаций. Лексические и лексико-граматические переводческие трансформации. Лекция 2 Comic Book Style Template-Playful
Comic Book Style Template-Playful Indirect (polite) questions
Indirect (polite) questions spelling bee things we do to our body fun activities
spelling bee things we do to our body fun activities SIS-3 Greenenergy
SIS-3 Greenenergy Present Tenses Practice
Present Tenses Practice American holidays-customs and traditions
American holidays-customs and traditions Questions and answers
Questions and answers Let's remember!
Let's remember! Report Writing. Term 6. Lecture 3
Report Writing. Term 6. Lecture 3 Using Virtual Reference Services to Embed the Library in the Academic Workflow
Using Virtual Reference Services to Embed the Library in the Academic Workflow School in Russia
School in Russia My dream holiday
My dream holiday Presentation on the topic: Wales
Presentation on the topic: Wales Extreme sport
Extreme sport Farm animals. Choose a tree
Farm animals. Choose a tree Relative Clauses (Относительные придаточные предложения)
Relative Clauses (Относительные придаточные предложения) Adjective (сын есім)
Adjective (сын есім) Television for youth
Television for youth Feedback
Feedback Plants and Flowers
Plants and Flowers Professions
Professions Kisel. traditional Russian dish
Kisel. traditional Russian dish