Содержание
- 2. Plan: 1. Notion of a report. 2. Types of reports. 3. Structure of a report.
- 3. 1. Notion of a Report. A report is an orderly and objective presentation of information that
- 4. Report Aims:
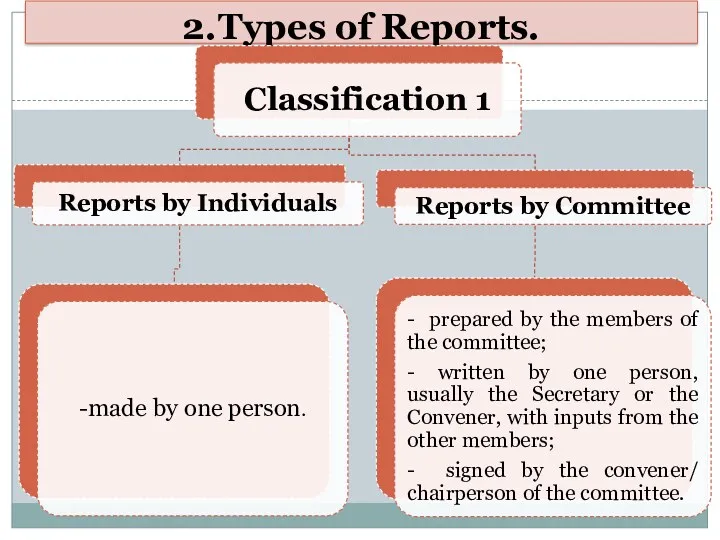
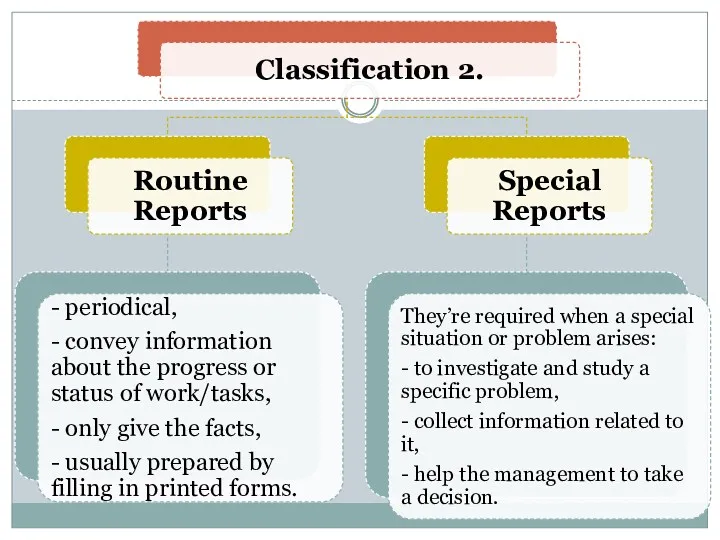
- 5. 2. Types of Reports.
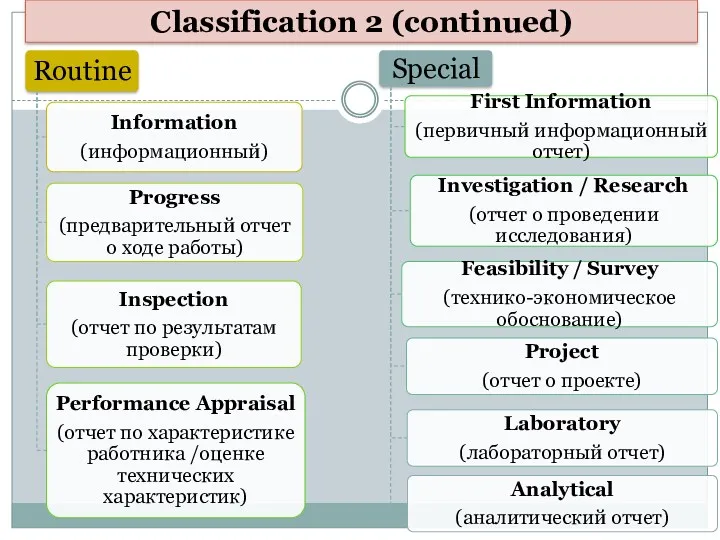
- 7. Classification 2 (continued)
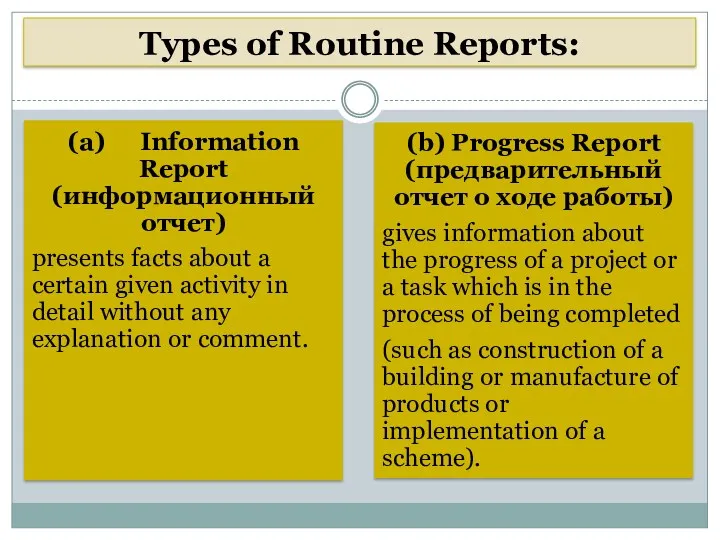
- 8. Types of Routine Reports:
- 10. (d) Performance Appraisal Report (отчёт по характеристике работника/оценке технических характеристик) is meant for assessing and recording
- 11. Types of Special Reports: (a) First Information Report (первичный информационный отчет) - is required when there
- 12. (b) Investigation/Research Report (отчет о результатах исследования) - is written after making a thorough study and
- 13. c) Feasibility / Survey Report (технико-экономическое обоснование) is required when an organization intends to -launch a
- 14. (d) Project Report (отчет о проекте) - describes the project in the future and expected results;
- 15. (e) Laboratory Report (лабораторный отчет) is written -to record observations made in a laboratory test and
- 16. (f) Analytical Report (аналитический отчет) contains: -the narration of facts, -collected data and information, -classified and
- 17. 3. Structure of a Report 1 Letter of transmittal 2 Title page 3 Table of contents
- 18. 1. Letter of Transmittal is a letter addressed to the person who commissioned the report. The
- 19. Example: Dear Mr. Pitt, Please accept the accompanying Work Term Report entitled "Colour Sonar Imaging Tool
- 20. 2. Title Page includes: • the name of the organization • the title • details of
- 21. Title Page (Example)
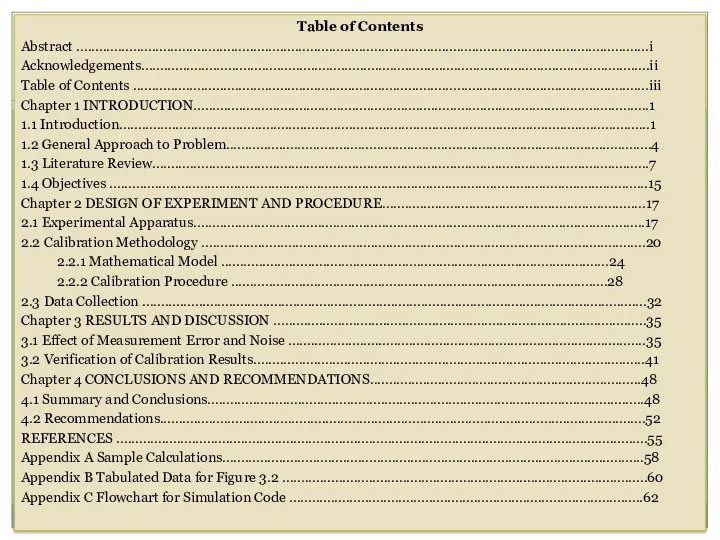
- 22. 3. Table of Contents shows 1. The full list of sections within the report (including any
- 23. Table of Contents Abstract ........................................................................................................................................................i Acknowledgements.......................................................................................................................................ii Table of Contents .........................................................................................................................................iii Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION.........................................................................................................................1 1.1 Introduction.............................................................................................................................................1 1.2
- 24. 4. List of Abbreviations and/or Glossary If the report includes abbreviations which may not be known
- 25. If there are many technical terms, a glossary is also provided. A glossary is an alphabetical
- 26. 5. Acknowledgements This is the appreciation to persons who helped the writer of the report with
- 27. 6. Summary The summary contains the overview of the most important aspects of a report. It
- 28. 7. Introduction The introduction shows the points that will be looked at. It can include: •
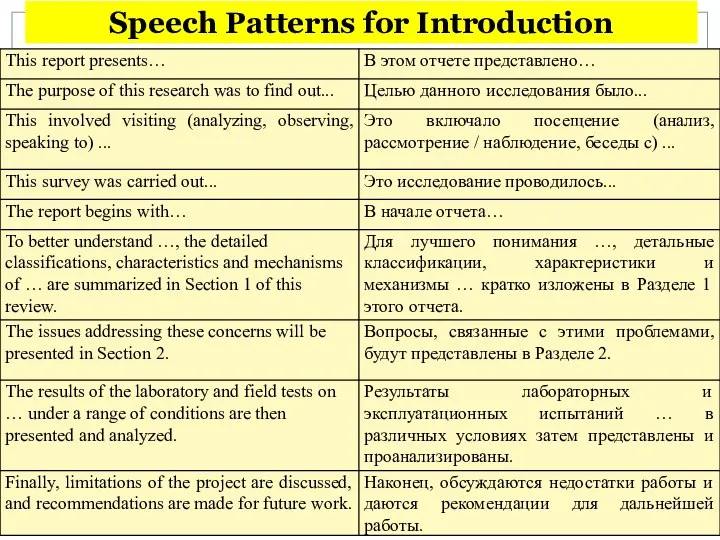
- 29. Speech Patterns for Introduction
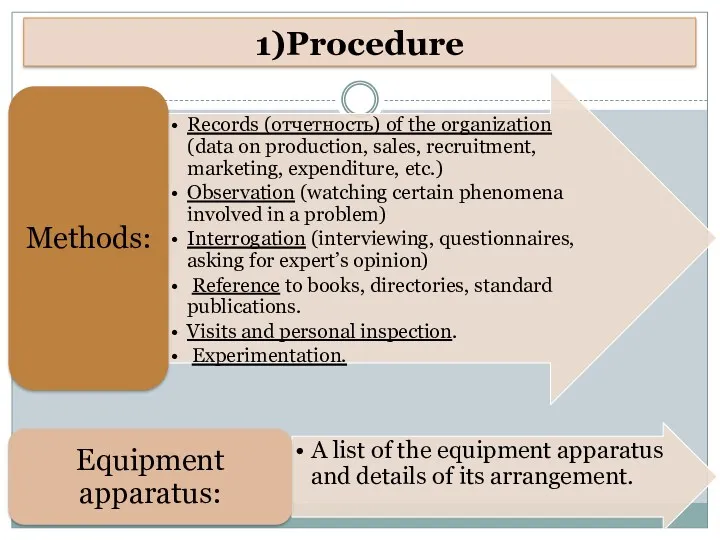
- 31. 1)Procedure
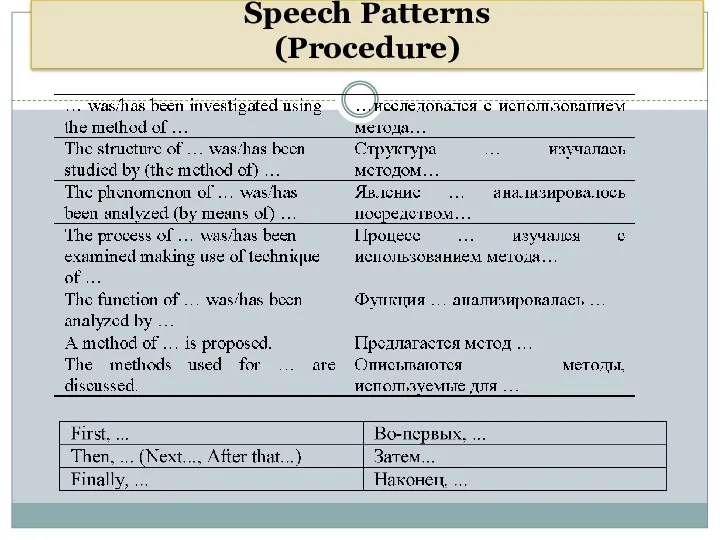
- 32. Speech Patterns (Procedure)
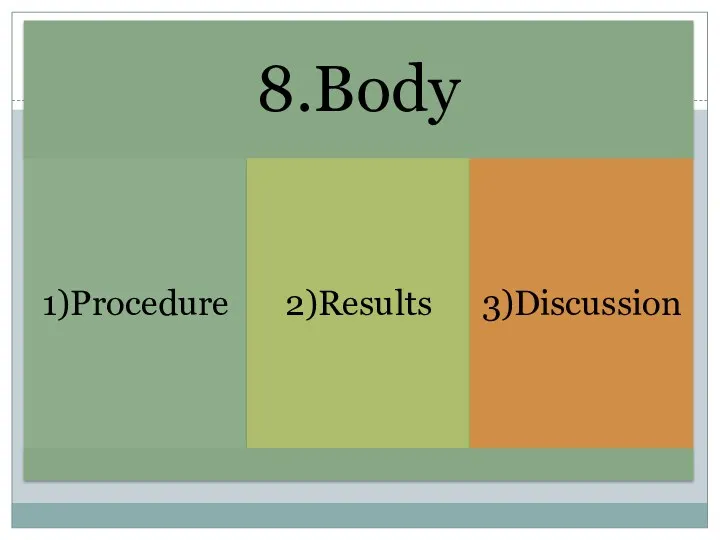
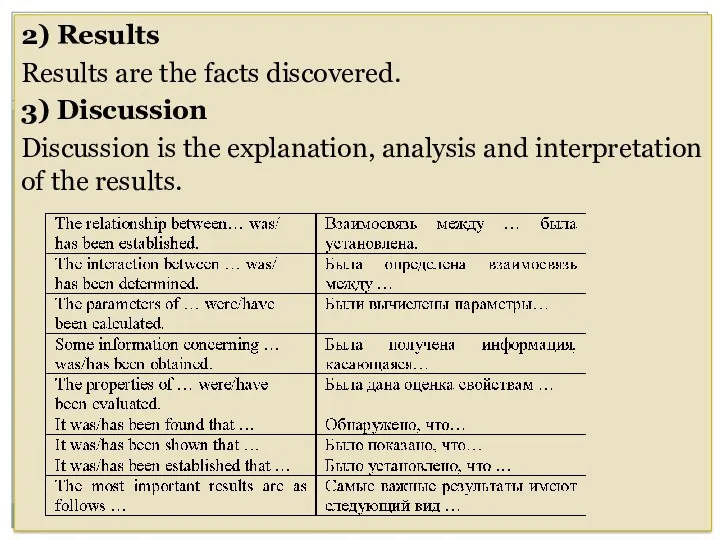
- 33. 2) Results Results are the facts discovered. 3) Discussion Discussion is the explanation, analysis and interpretation
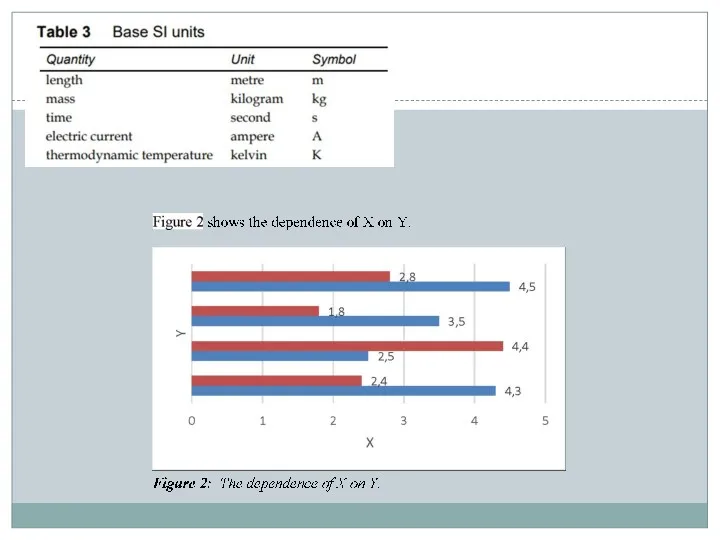
- 34. Use of Illustrations 1) A report becomes much more readable, clear and effective if the findings
- 36. 9. Conclusion The conclusion is where you sum up the general conclusion(s) you have reached. It
- 37. 10. Recommendations Recommendations suggest actions to be taken in response to the findings of a report.
- 38. 11. References (Bibliography) (References) Bibliography is the list of books, articles and other sources used by
- 39. 12. Appendices (Приложения) Appendix (plural: appendices or appendixes) is supplementary material given at the end of
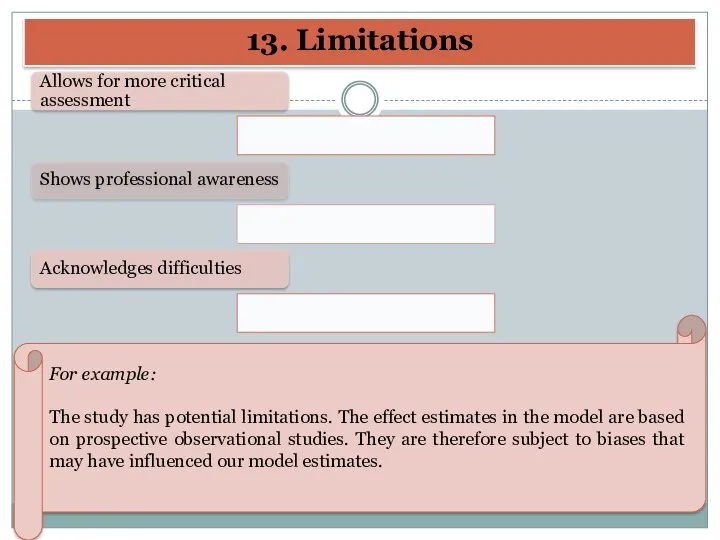
- 40. 13. Limitations Allows for more critical assessment Shows professional awareness Acknowledges difficulties For example: The study
- 42. Скачать презентацию



























 Christmas and New Year in Great Britain
Christmas and New Year in Great Britain Present simple
Present simple Who wants to be a millionaire. Sport game
Who wants to be a millionaire. Sport game Great scientist
Great scientist Местоимения SOME и ANY. 7 класс
Местоимения SOME и ANY. 7 класс Условные предложения. Conditional sentences
Условные предложения. Conditional sentences Answer the questions
Answer the questions Hello! I am Harry Potter! Let’s go to Hogwarts!
Hello! I am Harry Potter! Let’s go to Hogwarts! Modal Verbs
Modal Verbs Comparatives and Superlatives
Comparatives and Superlatives Present continuous
Present continuous Etymology of english words. Native and borrowed words in english
Etymology of english words. Native and borrowed words in english Неправильные глаголы Эффективный способ запоминания
Неправильные глаголы Эффективный способ запоминания Idioms
Idioms Ethical decision making
Ethical decision making Эффективные способы изучения английских слов
Эффективные способы изучения английских слов Past Simple (Прошедшее простое время)
Past Simple (Прошедшее простое время) Horror Film
Horror Film My Last shopping
My Last shopping “Functional styles”. Lecture 13
“Functional styles”. Lecture 13 Smiles. 4 класс 1 урок
Smiles. 4 класс 1 урок Quiz. The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
Quiz. The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland Irregular verbs
Irregular verbs Great Britain
Great Britain The Republic of Kenya
The Republic of Kenya A quantum computer
A quantum computer Легочный туберкулез. Страдательный залог. Настоящие и прошедшие времена страдательного залога
Легочный туберкулез. Страдательный залог. Настоящие и прошедшие времена страдательного залога Nouns countable
Nouns countable