Содержание
- 2. Lesson plan: Language and speech; Types of speech
- 3. Speech is the vocal form of human communication.
- 4. Speech or speaking may also refer to: Spoken language Animal language, forms of animal communication that
- 6. Production In linguistics (articulatory phonetics), manner of articulation describes how the tongue, lips, jaw, vocal cords,
- 8. Problems involving speech There are several organic and psychological factors that can affect speech. Among these
- 9. Hearing problems, such as otitis media with effusion, and listening problems, auditory processing disorders, can lead
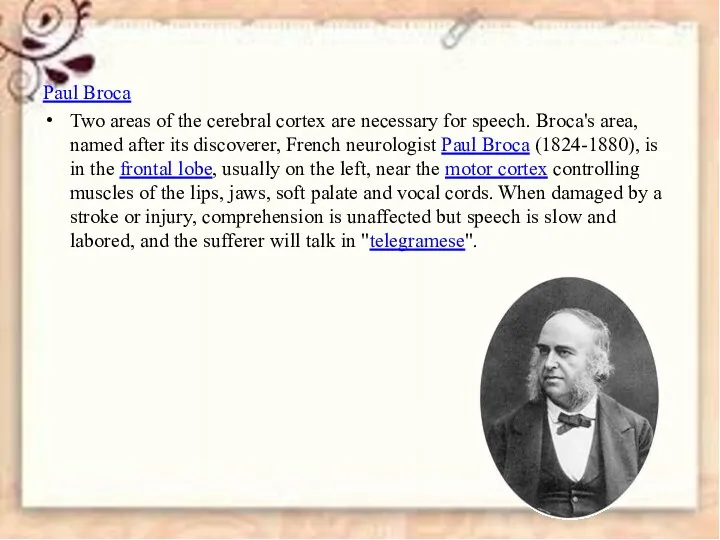
- 10. Paul Broca Two areas of the cerebral cortex are necessary for speech. Broca's area, named after
- 11. Speech is a form of communication that was established historically in the process of the material
- 12. External speech includes oral (dialogical and monologic) and written. Dialogue is the direct communication of two
- 13. Monologic speech is a long, consistent, coherent exposition of the system of thoughts, knowledge by one
- 14. Written speech is a kind of monologic speech. It is more developed than oral monologic speech.
- 15. Inner speech is a special kind of speech activity. It acts as a planning phase in
- 16. Speech consists of the following: Articulation How speech sounds are made (e.g., children must learn how
- 17. Voice Use of the vocal folds and breathing to produce sound (e.g., the voice can be
- 18. Fluency The rhythm of speech (e.g., hesitations or stuttering can affect fluency).
- 19. In summary: Speech is the verbal means of communicating.
- 21. Скачать презентацию

















 Unusual holidays of the world
Unusual holidays of the world Great Britain: the hiStory, information & territories
Great Britain: the hiStory, information & territories Expressing numbers in english
Expressing numbers in english Ways to express future tense. My summer holidays plans
Ways to express future tense. My summer holidays plans Direct speech
Direct speech Making news. Unit 9.1
Making news. Unit 9.1 Как написать письмо? Почтовая открытка: задание
Как написать письмо? Почтовая открытка: задание Lost and found
Lost and found Hey, hey, for Halloween
Hey, hey, for Halloween Exam practice (part 2). Tasks 1-2-3-4
Exam practice (part 2). Tasks 1-2-3-4 English. Чтение буквосочетаний!. 2 класс
English. Чтение буквосочетаний!. 2 класс Story about us
Story about us Jobs of the future
Jobs of the future My favorite book
My favorite book My favourite sportsman Gabdrakhmanov Ilmir
My favourite sportsman Gabdrakhmanov Ilmir Hippies
Hippies Middle english. Lecture 3
Middle english. Lecture 3 Wednesday’s life. Possessive pronouns
Wednesday’s life. Possessive pronouns News stories
News stories Landslides
Landslides Времена действительного залога в английском языке
Времена действительного залога в английском языке Prepositions
Prepositions Эмоционально-художественные технологии в изучении английского языка
Эмоционально-художественные технологии в изучении английского языка Крути барабан. Нажимай на картинки, чтобы услышать, как это будет по-английски
Крути барабан. Нажимай на картинки, чтобы услышать, как это будет по-английски Guess the word
Guess the word The kingdom of riddles fun activities games
The kingdom of riddles fun activities games English speaking countries
English speaking countries Russian traditions
Russian traditions