Содержание
- 2. What is consulting? Engaged in the business of giving expert advice to people working in a
- 3. List of Management Consulting firms
- 4. What they do: They advise enterprise businesses on their most critical issues and opportunities: strategy operations
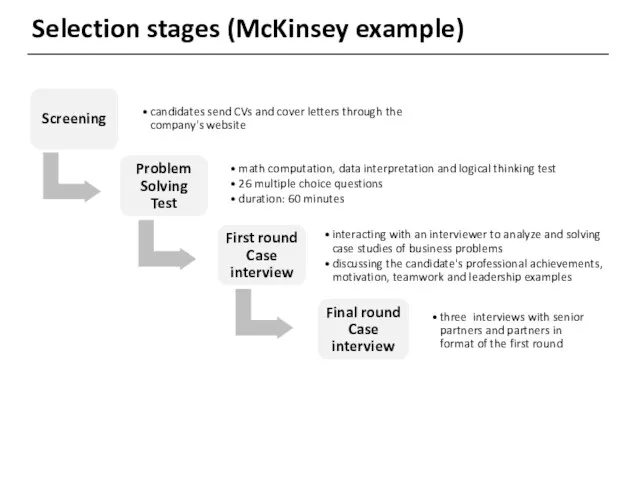
- 5. Selection stages (McKinsey example)
- 6. NU CC Outline Types of Cases Problem-Solving Tools Problem Identifying Structuring Drill-down analysis Synthesis Case-Solving Part
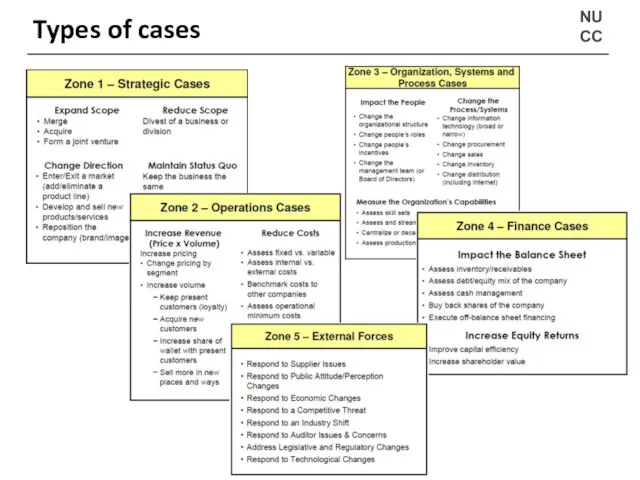
- 7. NU CC Types of cases
- 8. NU CC Types of cases The most likely scenario – Strategy and Operations Maximize profit (“Help!
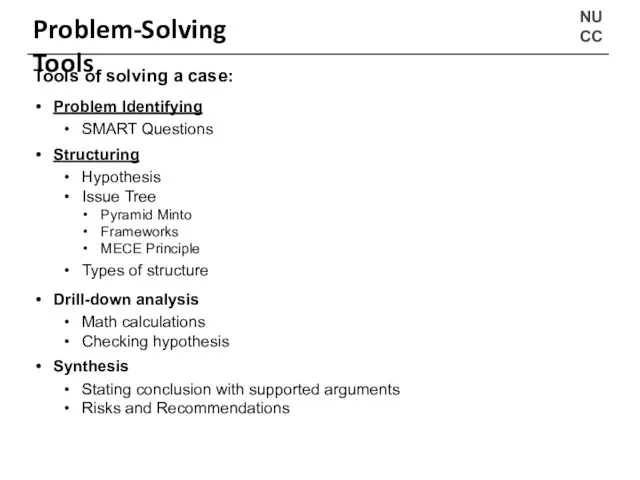
- 9. NU CC Problem-Solving Tools Tools of solving a case: Problem Identifying SMART Questions Structuring Hypothesis Issue
- 10. NU CC Problem Identifying Main Steps: Summarize the question to avoid answering a wrong question to
- 11. NU CC Problem Identifying SMART principle: Specific What? Who? Why? Where? Which? Measurable What indicators will
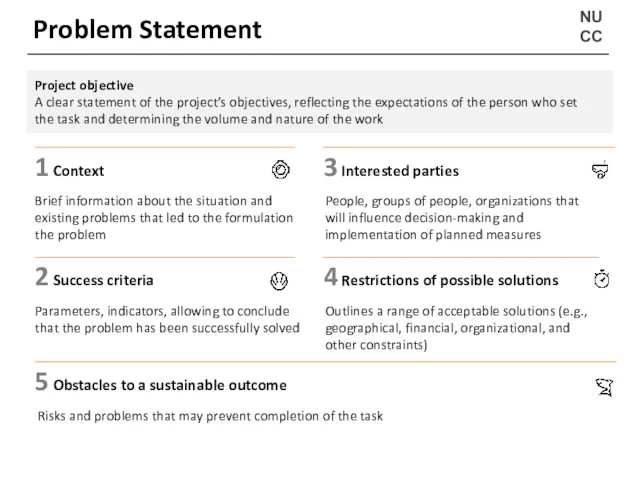
- 12. NU CC Problem statement Just a fact Too broad Not disputable Much better, but contains unnecessary
- 13. NU CC Problem Statement Risks and problems that may prevent completion of the task
- 14. NU CC Structuring a problem These three steps of the science – hypothesis, experiment, and conclusion
- 15. NU CC Structuring a problem Hypothesis Your idea which you need to test Client doesn`t need
- 16. NU CC Structuring a problem Hypothesis Let`s say a client asks, “Should I enter the XYZ
- 17. NU CC Structuring a problem Types of structure Formula based Value chain/customer journey Qualitative issue tree
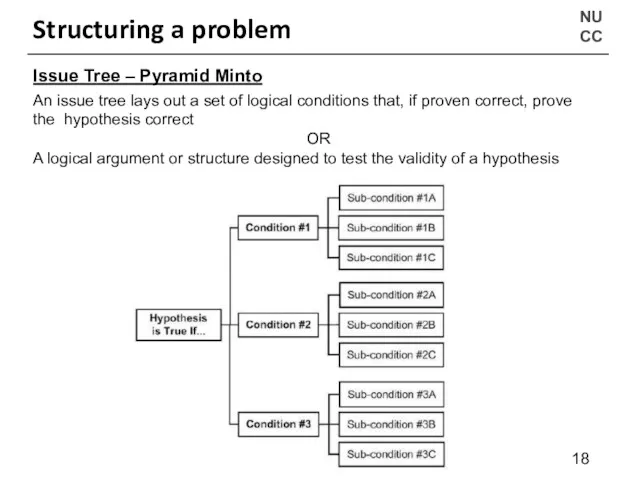
- 18. NU CC Structuring a problem Issue Tree – Pyramid Minto An issue tree lays out a
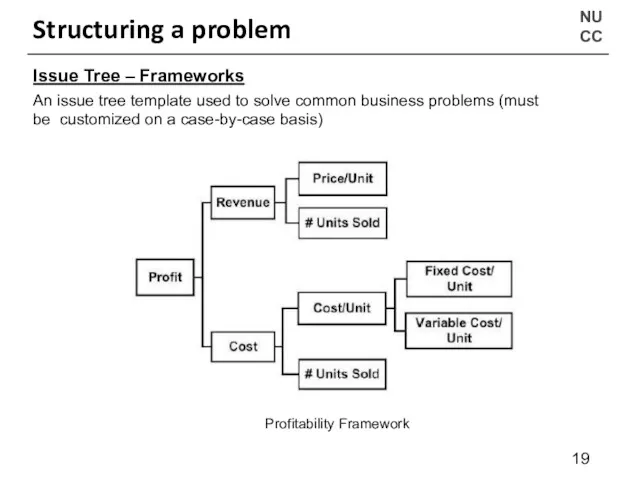
- 19. NU CC Structuring a problem Issue Tree – Frameworks An issue tree template used to solve
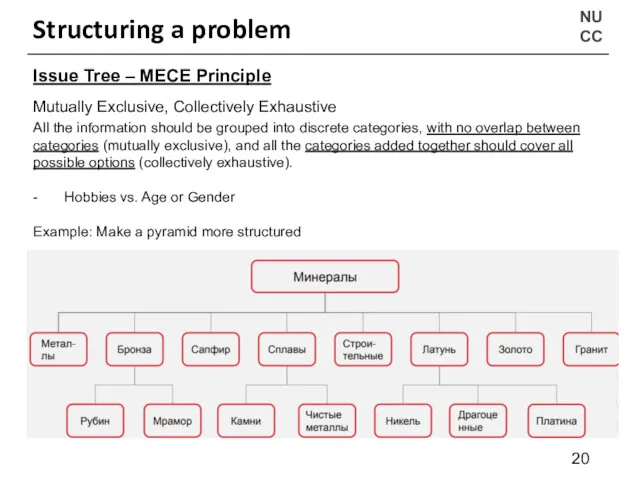
- 20. NU CC Structuring a problem Issue Tree – MECE Principle Mutually Exclusive, Collectively Exhaustive All the
- 21. NU CC Structuring a problem Issue Tree Previous Example: “Should I enter the XYZ market?” Make
- 22. NU CC Structuring a problem Issue Tree We have a framework as: Customer, Competitor, Company and
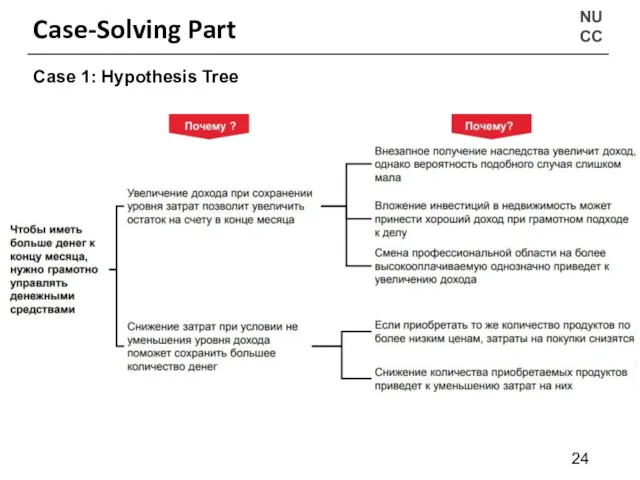
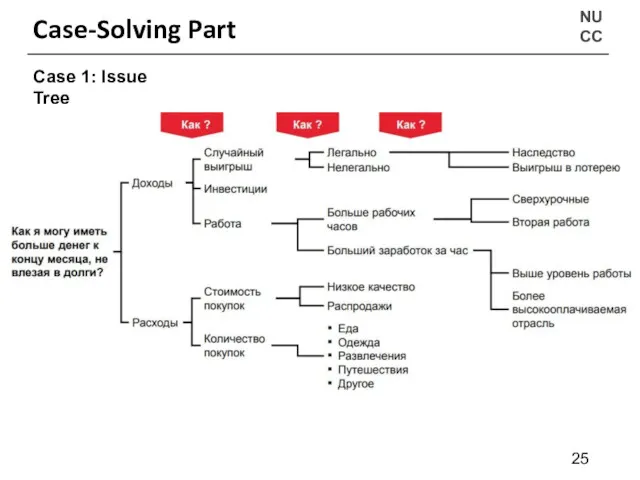
- 23. NU CC Case-Solving Part Case 1: “Как я могу иметь больше денег к концу месяца, не
- 24. NU CC Case-Solving Part Case 1: Hypothesis Tree
- 25. NU CC Case-Solving Part Case 1: Issue Tree
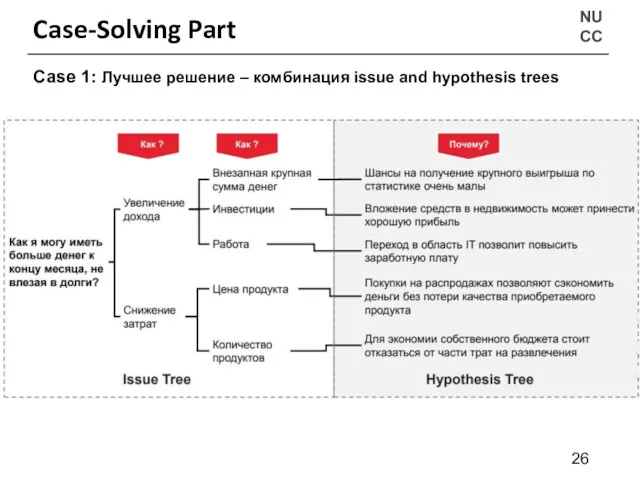
- 26. NU CC Case-Solving Part Case 1: Лучшее решение – комбинация issue and hypothesis trees
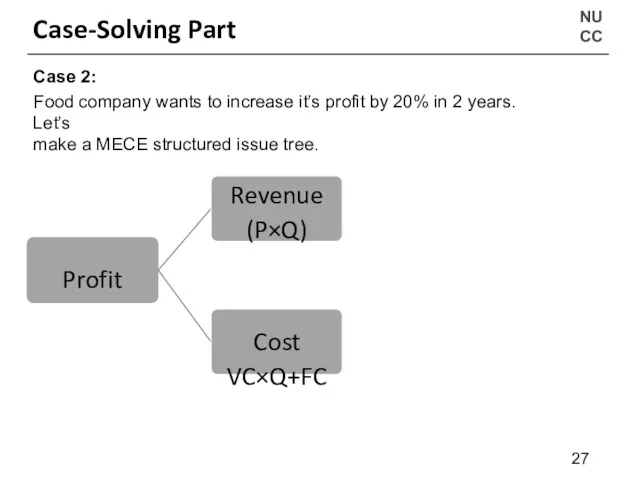
- 27. NU CC Case-Solving Part Case 2: Food company wants to increase it’s profit by 20% in
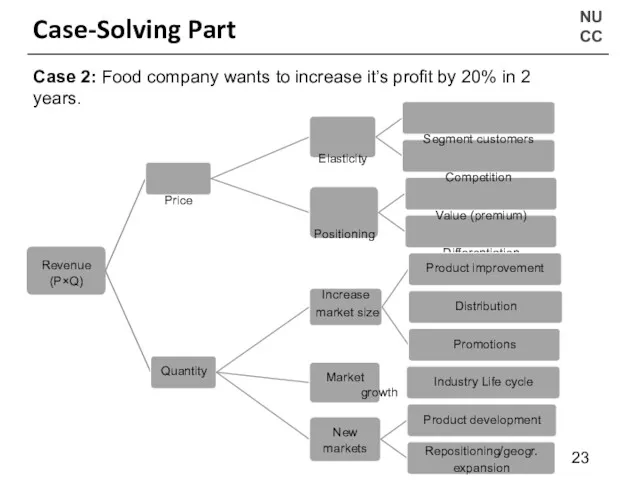
- 28. NU CC Case-Solving Part Revenue (P×Q) Case 2: Food company wants to increase it’s profit by
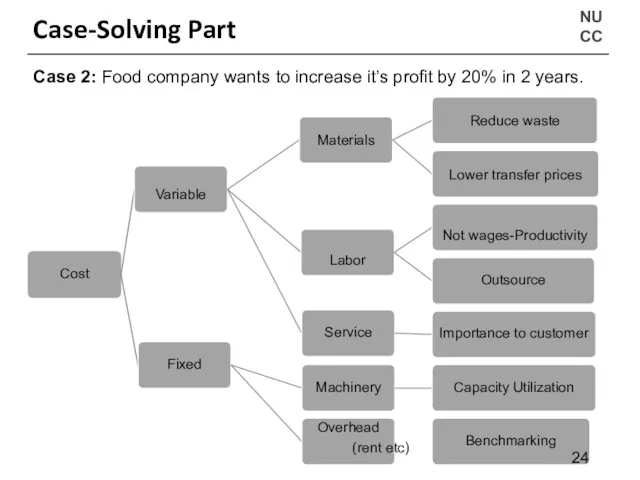
- 29. NU CC Case-Solving Part Cost Case 2: Food company wants to increase it’s profit by 20%
- 31. Скачать презентацию














 The past form of become is
The past form of become is Определение перевода. Предмет и объект теории перевода
Определение перевода. Предмет и объект теории перевода Вариант схемы для background. Nord Stream 2
Вариант схемы для background. Nord Stream 2 You are going to give a talk about travelling
You are going to give a talk about travelling Education system in the USSR
Education system in the USSR Infinitive. Irregular verbs. Past simple. Matching game
Infinitive. Irregular verbs. Past simple. Matching game United States of America
United States of America Turkey (Republic of Turkey)
Turkey (Republic of Turkey) Happy Easter. Cultural learning
Happy Easter. Cultural learning Word formation. Game
Word formation. Game Language & style. (Lecture 1)
Language & style. (Lecture 1) Animals. What letters are missing
Animals. What letters are missing Choose much or many
Choose much or many Rainbow english
Rainbow english Present Tenses Present Simple + Present Continuous
Present Tenses Present Simple + Present Continuous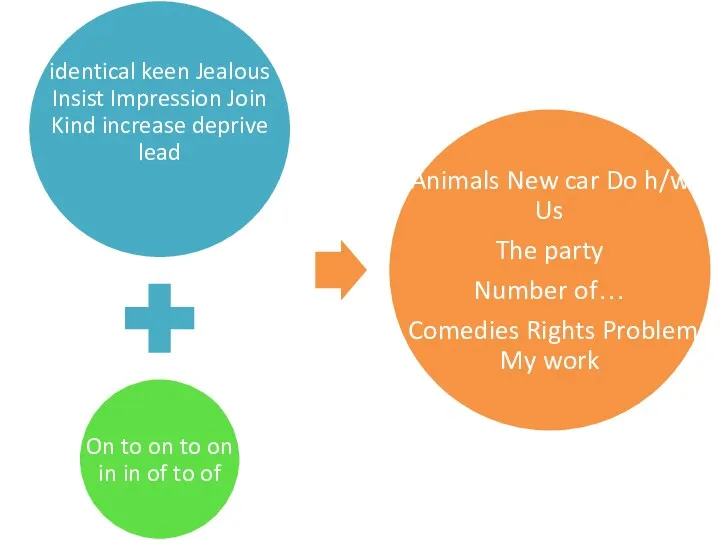 Request Will Can Could Would
Request Will Can Could Would Question forms
Question forms Additional information about the subject. Questions
Additional information about the subject. Questions My future profession
My future profession Подготовка к контрольной работе за триместр
Подготовка к контрольной работе за триместр My favourite artist
My favourite artist Социализация личности учащихся в процессе изучения английского языка
Социализация личности учащихся в процессе изучения английского языка Intralinguistic relations of words
Intralinguistic relations of words Family review
Family review Talking about a photo
Talking about a photo Travelling Across Great Britain
Travelling Across Great Britain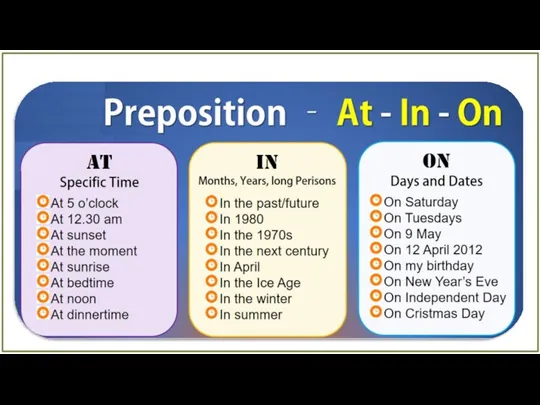 How about..? Vocabulary. TV programmes
How about..? Vocabulary. TV programmes Toys. Lego set
Toys. Lego set