Содержание
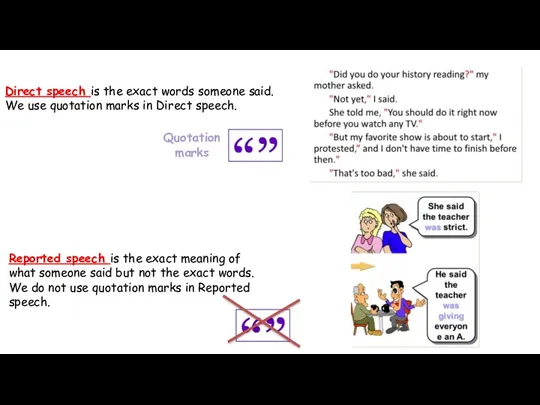
- 2. Direct speech is the exact words someone said. We use quotation marks in Direct speech. Quotation
- 3. She said to me, “I am very tired.” She told me that she was very tired.
- 4. Learn these expressions: Say good morning etc Say something Say one’s prayers Say so Tell the
- 5. Say “say” or “tell” ... sb one’s name Tell sb one’s name … the truth Tell
- 6. Fill in “say” or “tell” in the correct form. 1. The policeman …………… that the man
- 7. Fill in “say” or “tell” in the correct form. 7. Stop ………………… lies! 8. Could you
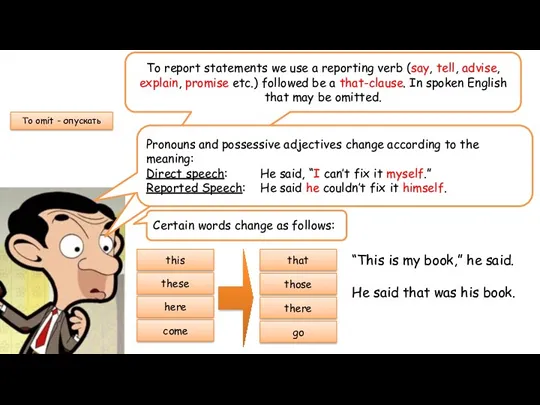
- 8. To report statements we use a reporting verb (say, tell, advise, explain, promise etc.) followed be
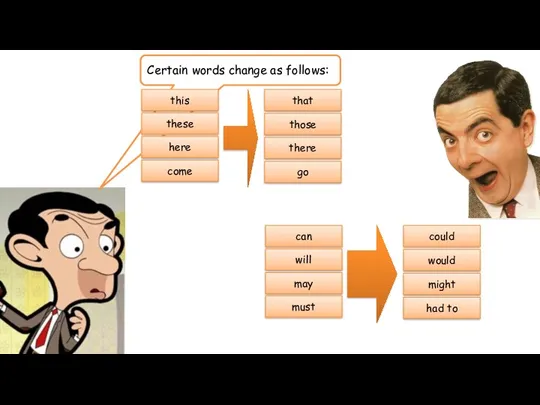
- 9. RULES! Certain words change as follows: this that these those here there come go can could
- 10. When the reporting verb is in the Past the verb tenses change as follows: Direct speech
- 11. When the reporting verb is in the Past the verb tenses change as follows: Direct speech
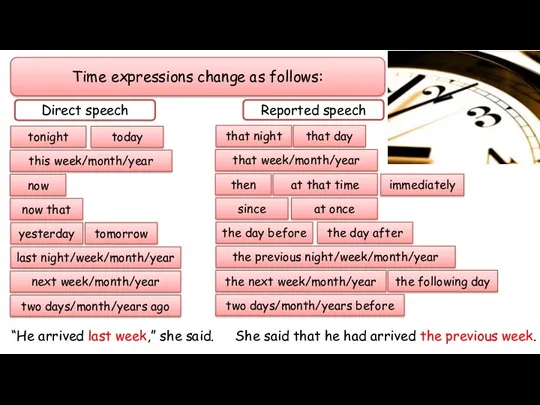
- 12. Time expressions change as follows: Direct speech Reported speech tonight today this week/month/year now now that
- 13. There are no changes in verb tenses when the reporting verb is in the Present, Future
- 14. Certain modal verbs do not change in Reported speech. These are: would, could, might, should, ought
- 15. 1. They’ll make a lovely couple. (Miss Moore) 2. They’re going to live in Brighton. (Mr
- 16. Reported Questions In Reported questions we use affirmative word order and the question mark is omitted.
- 17. Report the police-officer’s questions to the shop owner. 1. What’s your name? 2. Did you see
- 18. Reported Commands / Requests / Suggestions To report commands, requests, suggestions etc we use a reporting
- 20. Скачать презентацию













 Pitch Deck for Start-up
Pitch Deck for Start-up The preservation and restoration of forests
The preservation and restoration of forests Medical education in the USA
Medical education in the USA Тема 2. Актуальное членение предложения. Эмфаза и логическое ударение
Тема 2. Актуальное членение предложения. Эмфаза и логическое ударение Jobs, what do you do
Jobs, what do you do System of education
System of education Phrasal verbs
Phrasal verbs Wild animals. Game
Wild animals. Game Fantasy films and its history
Fantasy films and its history Present Tenses
Present Tenses My favourite hobby
My favourite hobby Summer course. Lesson 4
Summer course. Lesson 4 Hobbies and free time activities
Hobbies and free time activities Subculture is the way to express. Your individuality
Subculture is the way to express. Your individuality Условные предложения
Условные предложения The transportation system in Ottawa
The transportation system in Ottawa Spain. Madrid
Spain. Madrid Halloween
Halloween Fruit, drink, eat, teatime,
Fruit, drink, eat, teatime, Halloween game
Halloween game Happy Halloween
Happy Halloween Speaking Lessons for English learners
Speaking Lessons for English learners Reported speech. Intermediate level
Reported speech. Intermediate level Местоимение. Древнеанглийский период
Местоимение. Древнеанглийский период Would you like to take a trip round the world
Would you like to take a trip round the world Conditionals. Spotlight 9. Module 7 C
Conditionals. Spotlight 9. Module 7 C “Easter”.(Великдень)
“Easter”.(Великдень) Present perfect vs past simple. Teacher switcher
Present perfect vs past simple. Teacher switcher