Содержание
- 2. Stylistic analysis 1. Summarize the plot (a one-sentence description) 2. Identify the message 3. Setting 4.
- 3. Setting the time in which the action takes place The specific characteristics of location - building,
- 4. Setting can help in the portrayal of characters. “I write this sitting in the kitchen sink.
- 5. Setting can establish the atmosphere of a work. It was a dark and stormy night…
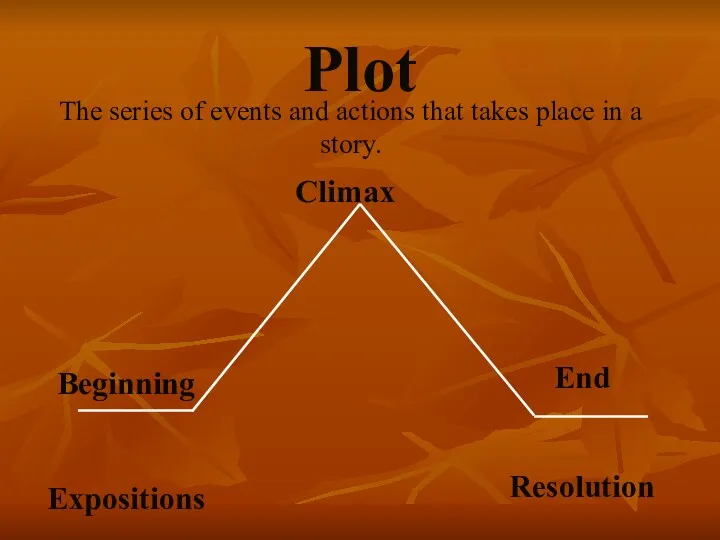
- 6. Plot The series of events and actions that takes place in a story. Beginning Expositions Climax
- 7. Elements of Plot Conflict Man VS Man Man VS Nature Man VS Society Man VS Himself
- 8. The Theme / Message . is the central idea, the purpose of a work some insight
- 9. Narration Author’s narrative: omniscient (= all-knowing) point of view Entrusted narrative: a) the story is told
- 10. Fiction Elements Dialogue (speech characteristics) Interior monologue Stream-of-consciousness Author’s remarks
- 11. Fiction Elements: Structure Foreshadowing: early clues about what will happen later in a piece of fiction
- 12. Style: Level of Complexity mostly simple sentence structure or varies the sentence structures (simple, compound, complex
- 13. TONE is the author’s attitude toward the subject. can be recognized by the language/word choices the
- 14. TONE Bitter Serious Witty Playful Tender Mysterious Suspenseful Nonchalant Angry Detached Poignant Compassionate Sympathetic Humorous
- 15. Tone : “A Gift in His Shoes” Donovan and Larry were early for baseball practice. They
- 16. Tone: “A Gift in His Shoes” How would you describe the tone of this passage? Angry
- 17. MOOD MOOD is the overall feelings or emotions that are created IN THE READER. Authors “move”
- 18. MOOD Cheerful Relieved Gloomy Bleak Uncertain Bittersweet Relaxed Confused Hopeless Tense
- 19. MOOD EXAMPLE During the holidays, my mother's house glittered with decorations and hummed with preparations. We
- 20. MOOD EXAMPLE After New Year's the time came to put all the decorations away and settle
- 21. Types of Characters Round Character: convincing, true to life and have many character traits. Dynamic Character:
- 22. Characters Protagonist -the main character in a literary work (usually positive). Antagonist - the character who
- 23. Methods of Characterization direct- “he was an old man…” characters’ thoughts, words, and actions reactions/comments of
- 24. Symbolism A symbol represents an idea, quality, or concept larger than itself. A Journey can symbolize
- 26. Скачать презентацию






















 European day of languages. Famous faces. Quiz
European day of languages. Famous faces. Quiz Plants and Flowers
Plants and Flowers Present perfect words
Present perfect words Modal Verbs
Modal Verbs Canadian English
Canadian English Degrees of Comparison
Degrees of Comparison Разница между have got и has got
Разница между have got и has got Sledding in Yakutia in Russia
Sledding in Yakutia in Russia Past Simple (простое прошедшее). Когда употребляем?
Past Simple (простое прошедшее). Когда употребляем? Musical instrument cello
Musical instrument cello Пунктуация в английском языке. (7 класс)
Пунктуация в английском языке. (7 класс) Summer holidays oral practice
Summer holidays oral practice I'm a teacher
I'm a teacher Types of questions in English
Types of questions in English Present simple tense. Настоящее простое время
Present simple tense. Настоящее простое время Турнир знатоков английского языка
Турнир знатоков английского языка How did you spend your holidays
How did you spend your holidays Practice of lexical and grammar skills
Practice of lexical and grammar skills Phone fun Unit 3.3
Phone fun Unit 3.3 The Plurals. Exceptions.
The Plurals. Exceptions. Peter’s family
Peter’s family Hobbies and Leisure Consolidation game for lesson 11
Hobbies and Leisure Consolidation game for lesson 11 Krasnoyarsk english class – speaking guide lecture and workshop
Krasnoyarsk english class – speaking guide lecture and workshop Heading to Corsica
Heading to Corsica История. Философия. Своя игра. Шаблон
История. Философия. Своя игра. Шаблон Развитие глагола в истории английского языка
Развитие глагола в истории английского языка Учимся читать
Учимся читать Daily routines
Daily routines