Содержание
- 2. AGENDA Features of contemporary enterprises Information assymetry Agency theory Accounting as an element of corporate’s information
- 3. 1. Features of contemporary enterprises value-oriented (highlighting the value category in the structure of the objectives
- 4. 2. Information asymmetry Information asymmetry may concern: - hidden action, so-called the temptation of abuse (moral
- 5. 3. Agency theory
- 6. 4. Accounting as an element of corporate’s information system Accounting is the main element of a
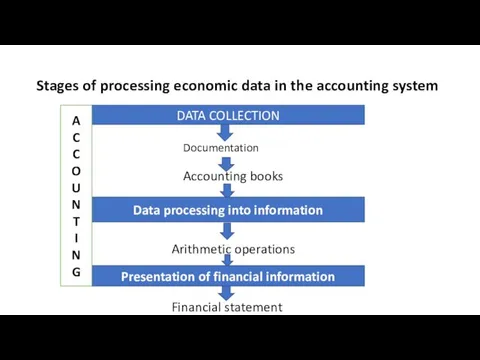
- 7. Stages of processing economic data in the accounting system DATA COLLECTION Documentation Accounting books Data processing
- 8. 5. Subject of accounting Subject of accounting Assets and sources of their financing Economic processes (revenues,
- 9. 6. Functions of accounting information control reporting analytical-interpretative statistical function
- 10. 7. Principles of accounting memorial - consists in including in the period of all economic transactions
- 11. 8. National and international accounting regulations Accounting Act International Accounting Standards (IASs) International Financial Reporting Standards
- 12. 9. Decision areas of modern enterprises operational decisions - decisions regarding the basic activity of the
- 13. 10. What is a company ? A company can be as a collection: • funds (capital)
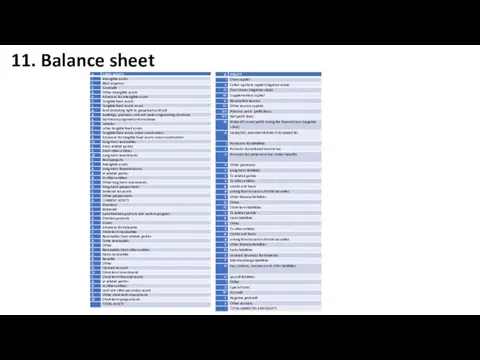
- 14. 11. Balance sheet
- 15. SIMPLIFIED BALANCE SHEET increasing liquidity increasing level of maturity
- 16. A. FIXED ASSETS economic life of more than one I. Intangible assets
- 17. A. FIXED ASSETS I. Intangible assets patents, licenses, trademark, know-how, goodwill
- 18. A. FIXED ASSETS I. Intangible assets II. Tangible fixed assets land, buildings, premises, vehicles, technical equipment
- 19. A. FIXED ASSETS I. Intangible assets II. Tangible fixed assets III. Long-term receivables III. Long-term investment
- 20. A. FIXED ASSETS I. Intangible assets II. Tangible fixed assets III. Long-term receivables III. Long-term investment
- 22. Скачать презентацию

















 Seasons and Weather
Seasons and Weather Inventions and inventors
Inventions and inventors Our family went on a campaign…
Our family went on a campaign… What do the posters (A-F) advertise? Spotlight 5
What do the posters (A-F) advertise? Spotlight 5 Многозначность слов в английском языке
Многозначность слов в английском языке Present Perfect
Present Perfect Условные предложения в английском языке
Условные предложения в английском языке Describing people
Describing people Celebrating spring
Celebrating spring Parts of the body game
Parts of the body game Урок-презентация по теме Еда
Урок-презентация по теме Еда Syntactical stylistic devices and expressive means
Syntactical stylistic devices and expressive means Конструкции “There is / are”: утверждение, вопрос, отрицание
Конструкции “There is / are”: утверждение, вопрос, отрицание The Peculiarities of Upbringing work in the Organization of Working in Groups and Teams
The Peculiarities of Upbringing work in the Organization of Working in Groups and Teams Customs and traditions of celebrating Christmas in different countries
Customs and traditions of celebrating Christmas in different countries Словообразование при помощи суффиксов в английском языке. 9 класс
Словообразование при помощи суффиксов в английском языке. 9 класс A system of courts of law for the administration of justice. (Unit 10)
A system of courts of law for the administration of justice. (Unit 10) Past simple. Простое прошедшее время
Past simple. Простое прошедшее время Welcome to Аlicante
Welcome to Аlicante The Lorax by Dr. Seuss
The Lorax by Dr. Seuss Упражнение времена группы past
Упражнение времена группы past English club. Topic ITALY
English club. Topic ITALY Zhambyl region, city of Taraz
Zhambyl region, city of Taraz The main features of Constructivism
The main features of Constructivism Структура английского предложения
Структура английского предложения Places of interests in Syktyvkar
Places of interests in Syktyvkar Equity theory
Equity theory Tag-questions. Тест по английскому языку
Tag-questions. Тест по английскому языку