ATP – Structure & Function/ Anaerobic and Aerobic Respiration Mitochondria Structure and Function презентация
Содержание
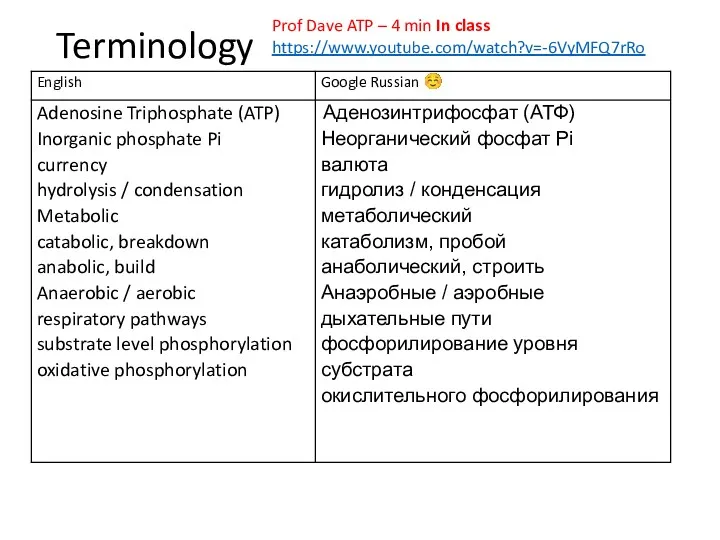
- 2. Terminology Prof Dave ATP – 4 min In class https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-6VyMFQ7rRo
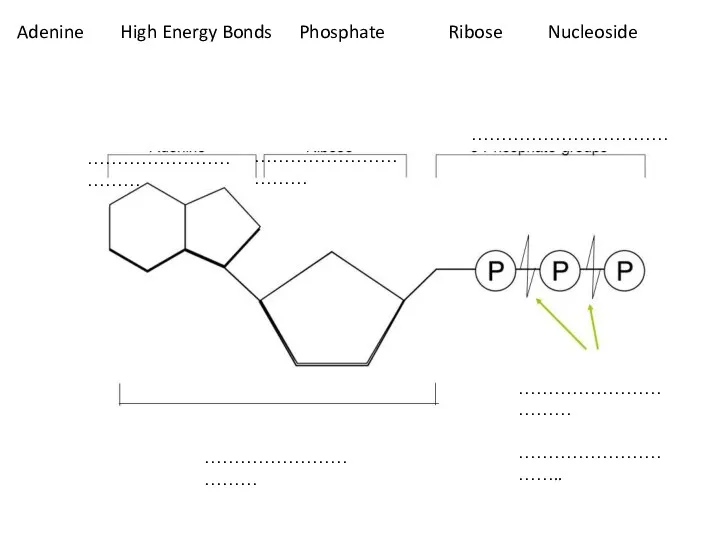
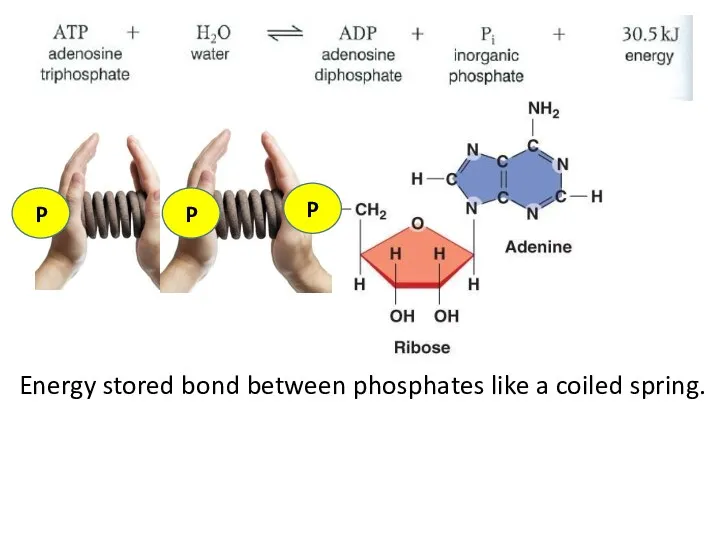
- 3. …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… ………………………….. Adenine High Energy Bonds Phosphate Ribose Nucleoside
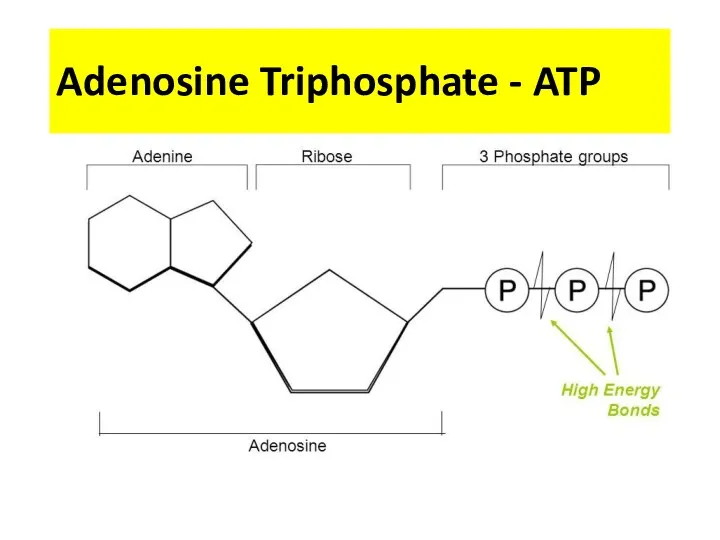
- 4. Adenosine Triphosphate - ATP
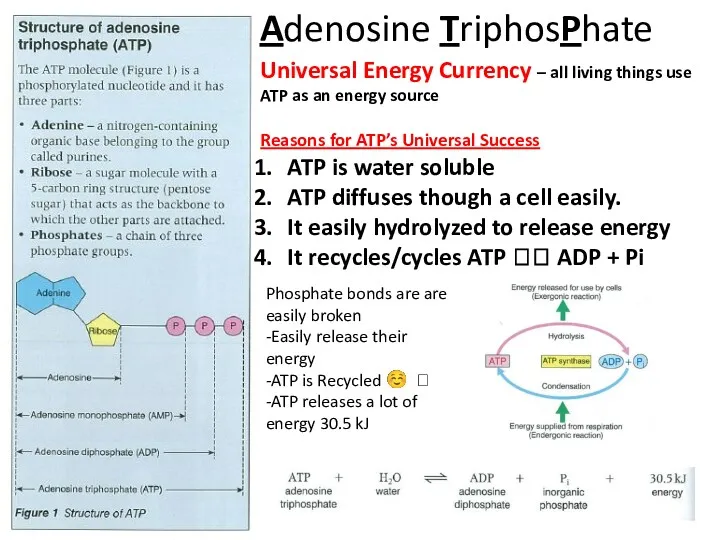
- 5. Adenosine TriphosPhate Universal Energy Currency – all living things use ATP as an energy source Reasons
- 6. P P P Energy stored bond between phosphates like a coiled spring.
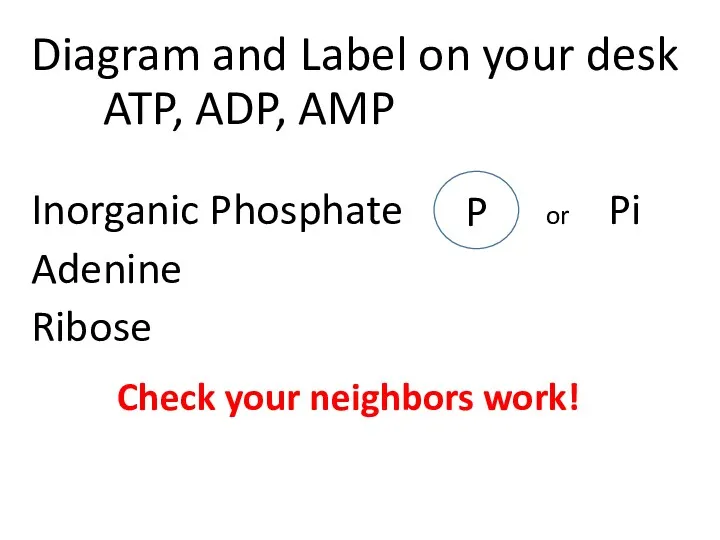
- 7. Diagram and Label on your desk ATP, ADP, AMP Inorganic Phosphate or Pi Adenine Ribose P
- 8. How do living things use ATP? List as many as you can on your desk ☺
- 9. DNA replication – growth and development Protein synthesis – growth, development, and important biological molecules (enzymes,
- 10. _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ + _
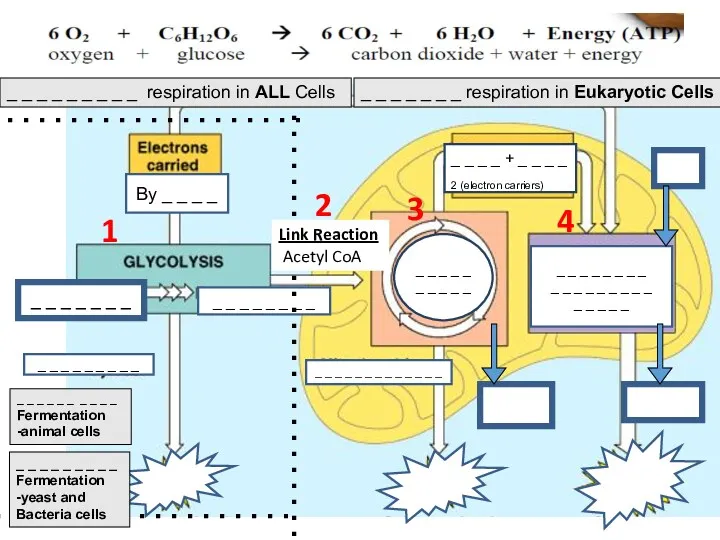
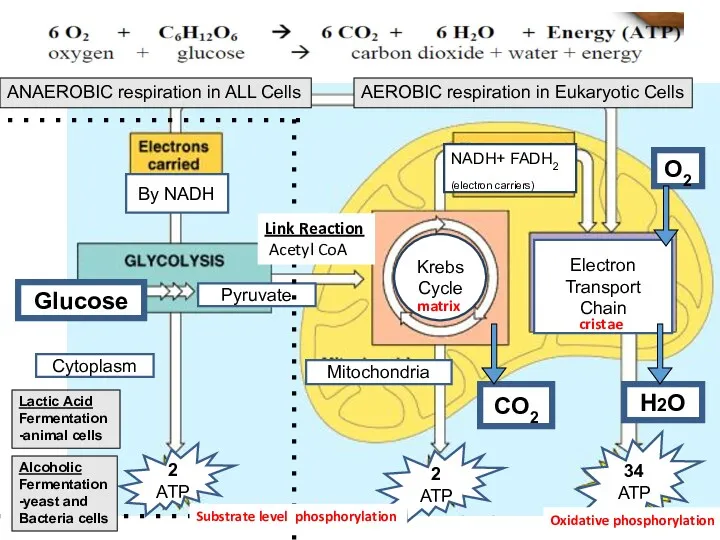
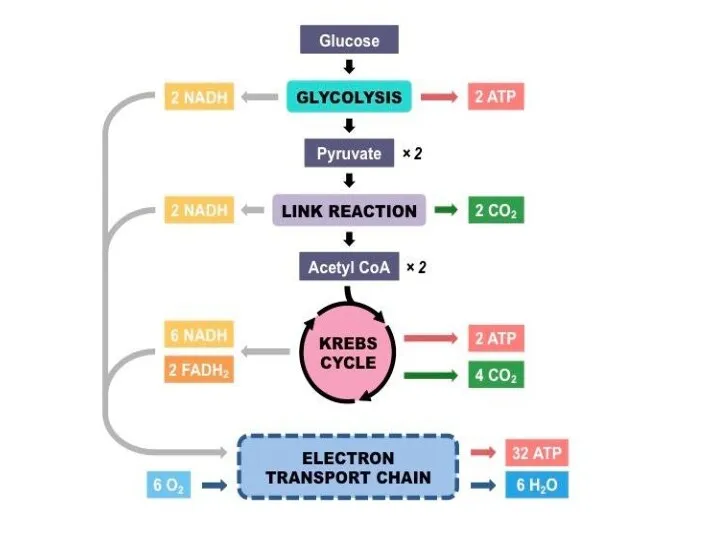
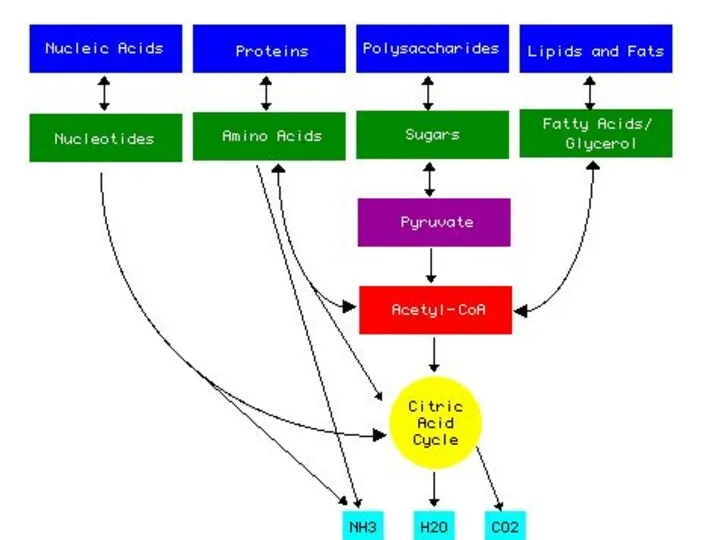
- 11. Krebs Cycle NADH+ FADH2 (electron carriers) Glucose Pyruvate By NADH Electron Transport Chain 2 ATP Mitochondria
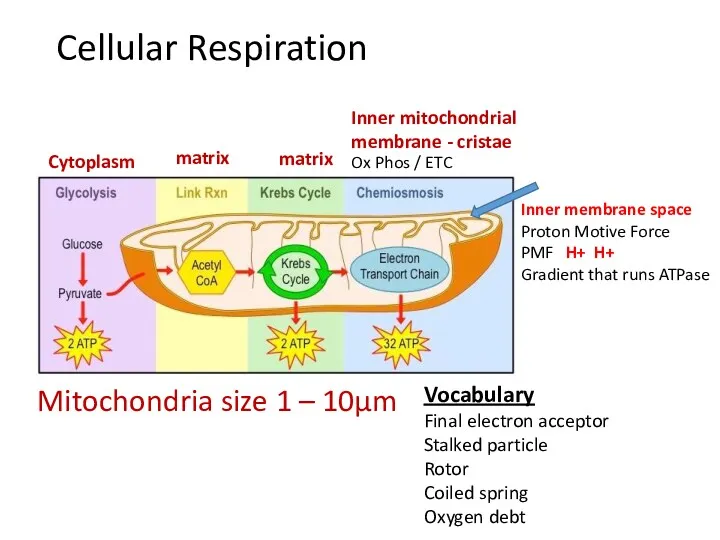
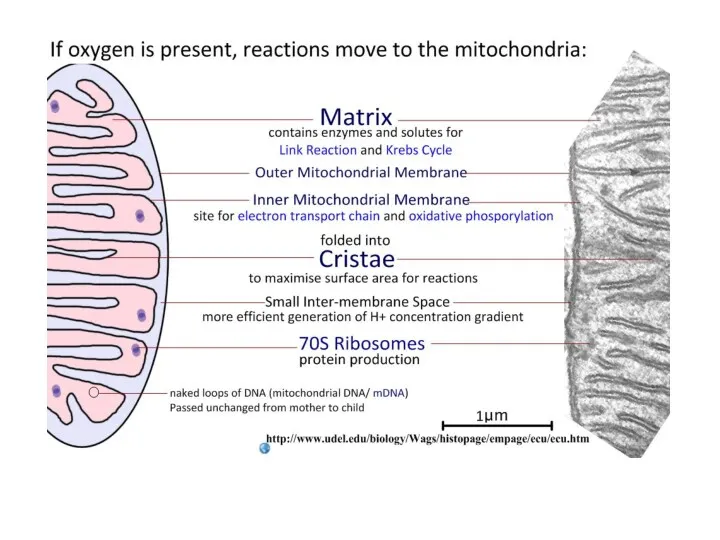
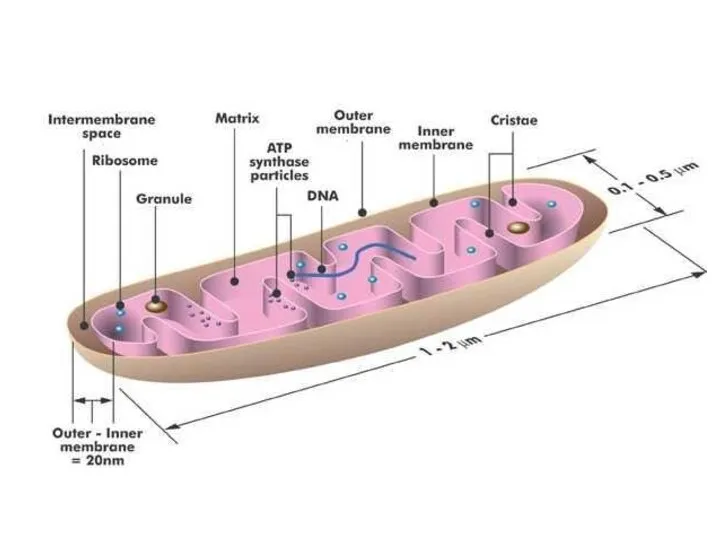
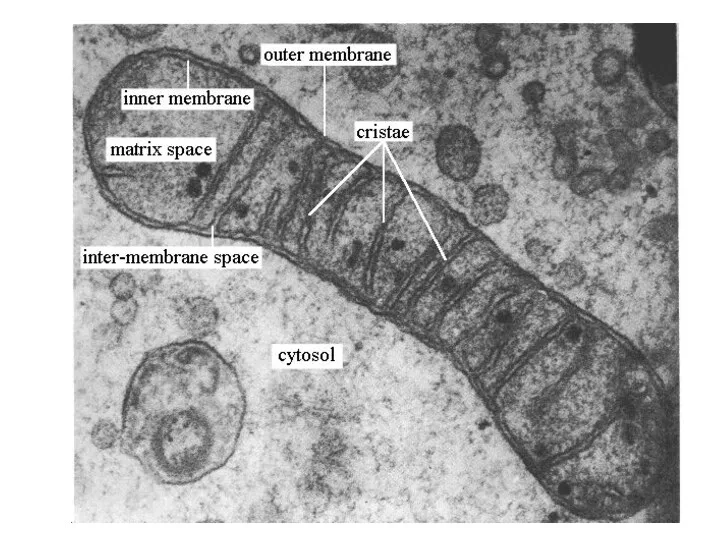
- 12. Cellular Respiration Mitochondria size 1 – 10μm matrix matrix Vocabulary Final electron acceptor Stalked particle Rotor
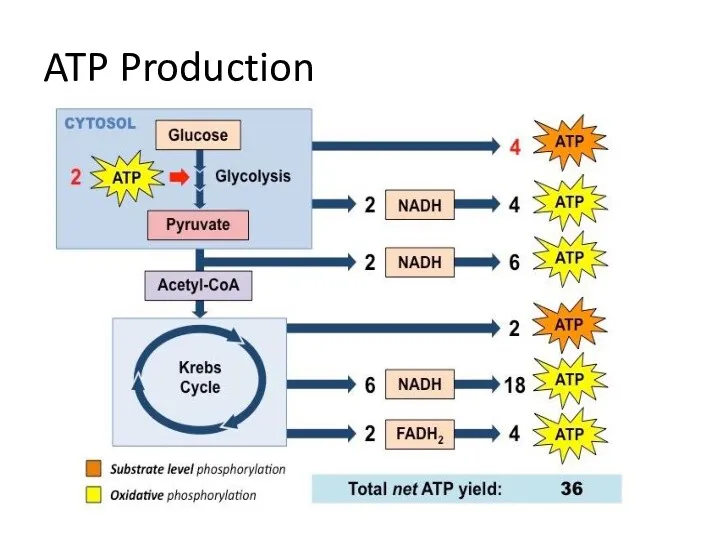
- 14. ATP Production
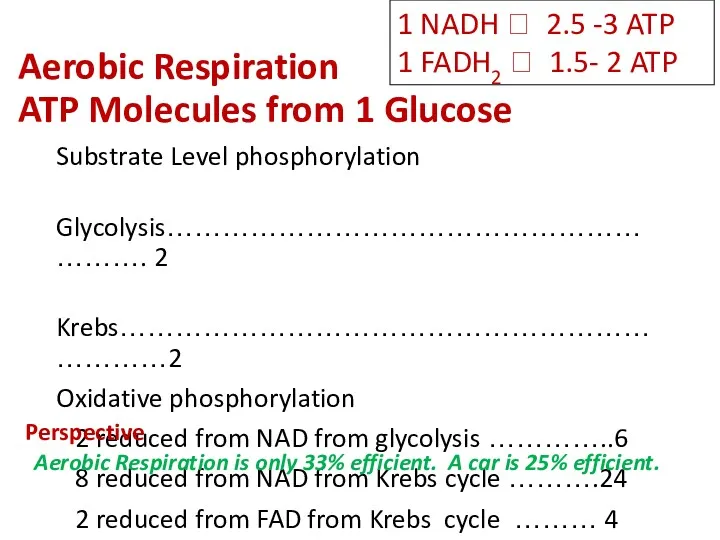
- 15. Aerobic Respiration ATP Molecules from 1 Glucose Substrate Level phosphorylation Glycolysis……………………………………………………. 2 Krebs……………………………………………………………2 Oxidative phosphorylation 2
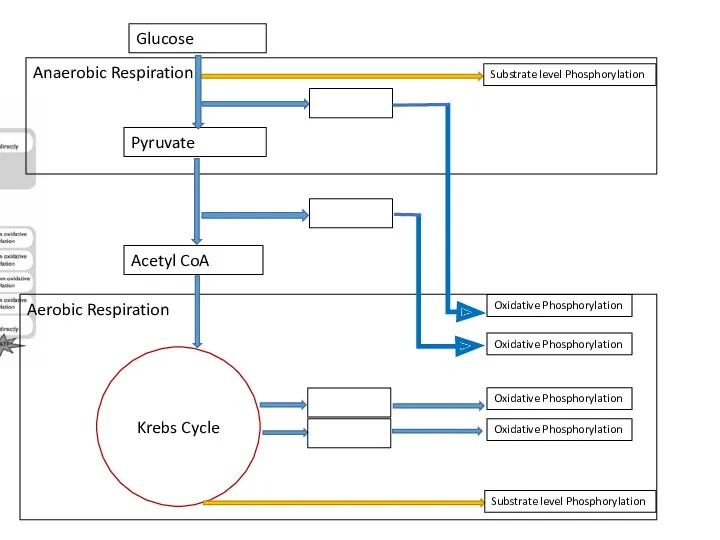
- 16. Anaerobic Respiration Aerobic Respiration Krebs Cycle Glucose Acetyl CoA Pyruvate Substrate level Phosphorylation Oxidative Phosphorylation Oxidative
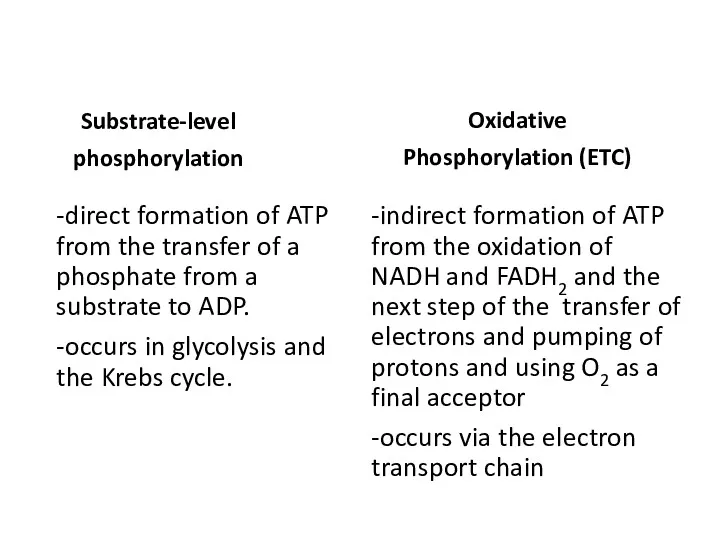
- 17. Substrate-level phosphorylation -direct formation of ATP from the transfer of a phosphate from a substrate to
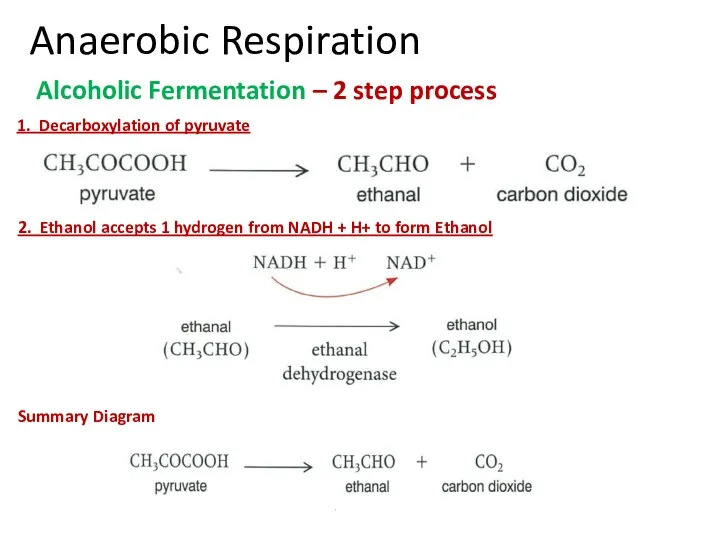
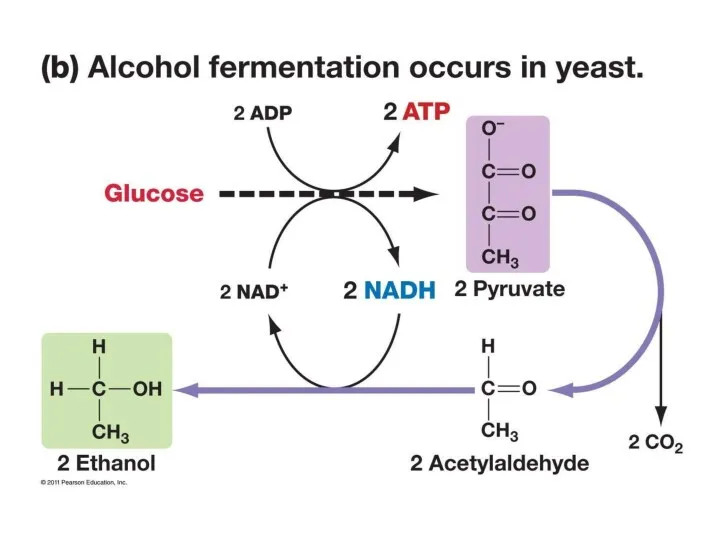
- 18. Anaerobic Respiration Alcoholic Fermentation – 2 step process 1. Decarboxylation of pyruvate 2. Ethanol accepts 1
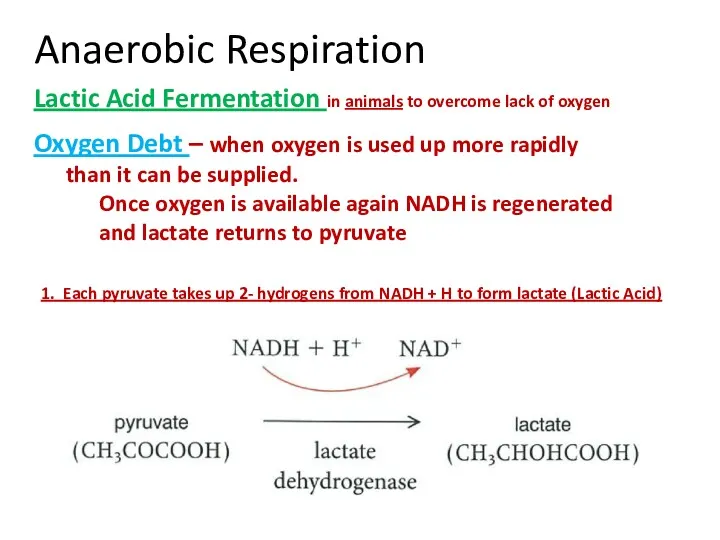
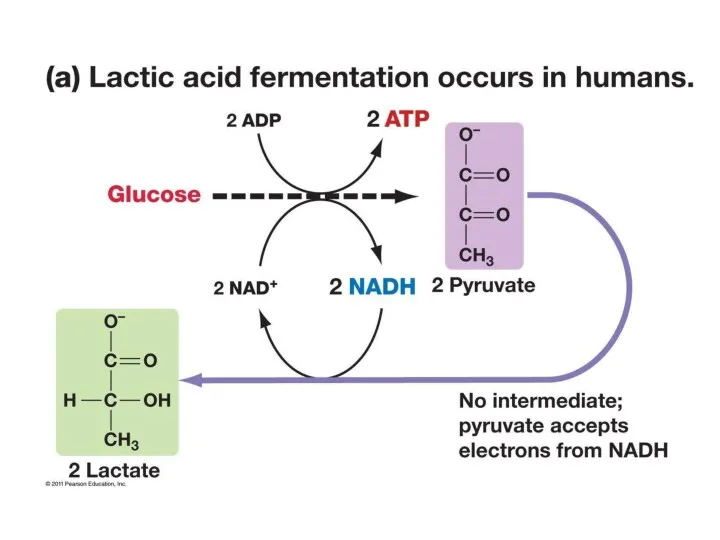
- 20. Anaerobic Respiration Lactic Acid Fermentation in animals to overcome lack of oxygen Oxygen Debt – when
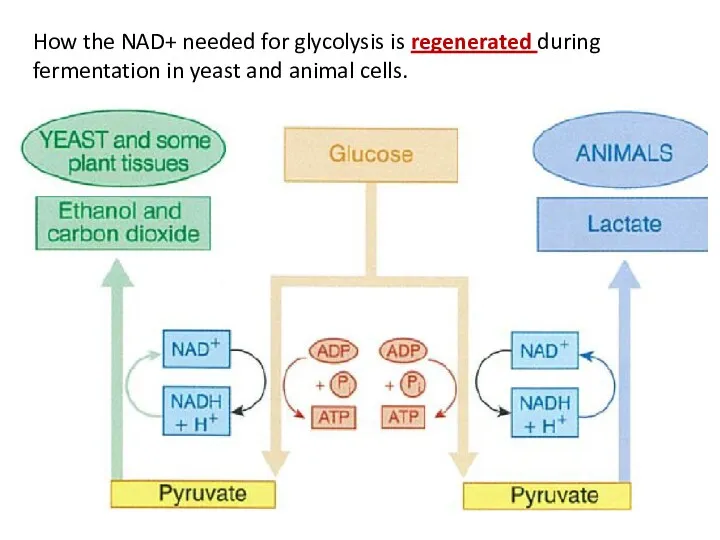
- 22. How the NAD+ needed for glycolysis is regenerated during fermentation in yeast and animal cells.
- 23. End
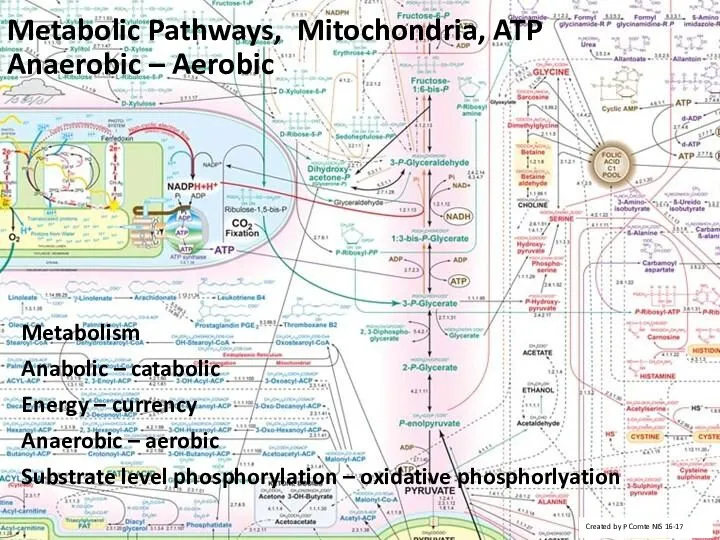
- 24. Metabolic Pathways, Mitochondria, ATP Anaerobic – Aerobic Metabolism Anabolic – catabolic Energy – currency Anaerobic –
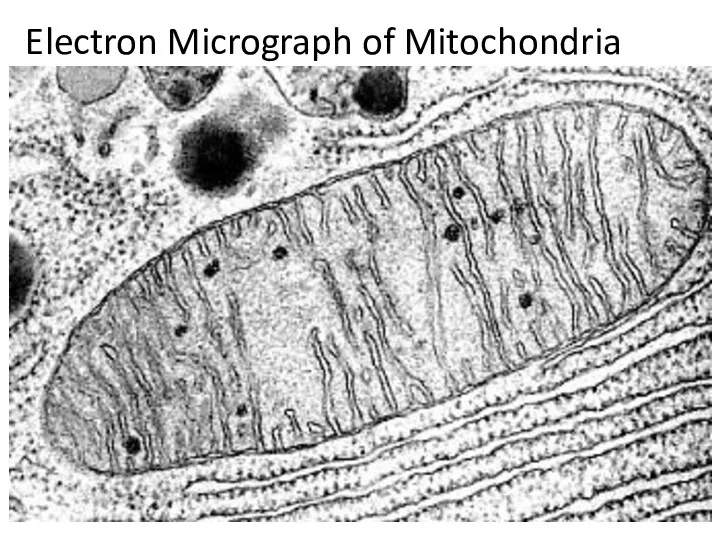
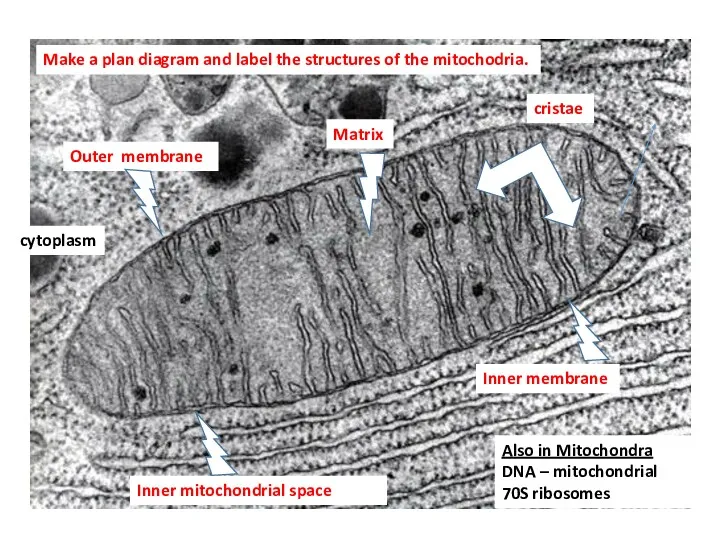
- 28. Electron Micrograph of Mitochondria
- 29. OUt Make a plan diagram and label the structures of the mitochodria. Outer membrane Inner membrane
- 32. Скачать презентацию



 Патогенное действие факторов внешней среды
Патогенное действие факторов внешней среды Natural selection of human population. Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection
Natural selection of human population. Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection Зачем в лесу грибы. Грибы –уникальные организмы
Зачем в лесу грибы. Грибы –уникальные организмы Строение живой клетки, химический состав и физико-химические свойства цитоплазмы
Строение живой клетки, химический состав и физико-химические свойства цитоплазмы Содержание и разведение организмов в ботанических садах
Содержание и разведение организмов в ботанических садах 20231130_8_klass_ptitsy._obshchie_priznaki._osobennosti_stroeniya._1
20231130_8_klass_ptitsy._obshchie_priznaki._osobennosti_stroeniya._1 Изменения в задании 27, ЕГЭ-2020 по биологии
Изменения в задании 27, ЕГЭ-2020 по биологии Development
Development Тканини тварин. Їх функції
Тканини тварин. Їх функції Влажные Экваториальные леса Африки
Влажные Экваториальные леса Африки Семейство Розоцветные
Семейство Розоцветные Культуры эукариотических клеток
Культуры эукариотических клеток Механизм мышечного сокращения
Механизм мышечного сокращения Незвичайні амфібії
Незвичайні амфібії Дистанционное обучение. Презентация: Законы Г. Менделя.
Дистанционное обучение. Презентация: Законы Г. Менделя. Хеморецепторні сенсорні системи. Органи нюху і смаку
Хеморецепторні сенсорні системи. Органи нюху і смаку Физология старения
Физология старения Пластикалық алмасу
Пластикалық алмасу Суган кабыгы ярысыннан препарат әзерләү һәм аны микроскоп аша карау
Суган кабыгы ярысыннан препарат әзерләү һәм аны микроскоп аша карау Животные и растения. Внеклассное мероприятие Почему их так назвали
Животные и растения. Внеклассное мероприятие Почему их так назвали Interstitial Lung Disease
Interstitial Lung Disease Клетки бактерий
Клетки бактерий Виды молочного сырья и показатели его качества
Виды молочного сырья и показатели его качества Биология 5 класс. Подготовка к ВПР
Биология 5 класс. Подготовка к ВПР Мир пернатых. Урок-соревнование
Мир пернатых. Урок-соревнование Экзотические плоды. Ягоды. Орехи
Экзотические плоды. Ягоды. Орехи Онтогенез и филогенез нервной системы
Онтогенез и филогенез нервной системы Исследования психофизиологических признаков
Исследования психофизиологических признаков