Содержание
- 2. 1. Тhe construction and composition of DNA 2. Тhe history of DNA studies 3. Difference of
- 3. DNA (or deoxyribonucleic acid) is the molecule that carries the genetic information in all cellular forms
- 4. Within cells, DNA is organized into long structures called chromosomes. During cell division these chromosomes are
- 6. The structure of the DNA double helix was proposed by Francis Crick and James Watson in
- 7. Френсис Крик Джеймс Уотсон
- 8. Strand of polynucleotides DNA's ability to store - and transmit - information lies in the fact
- 13. Скачать презентацию
Слайд 2
1. Тhe construction and composition of DNA
2. Тhe history of DNA
1. Тhe construction and composition of DNA
2. Тhe history of DNA
studies
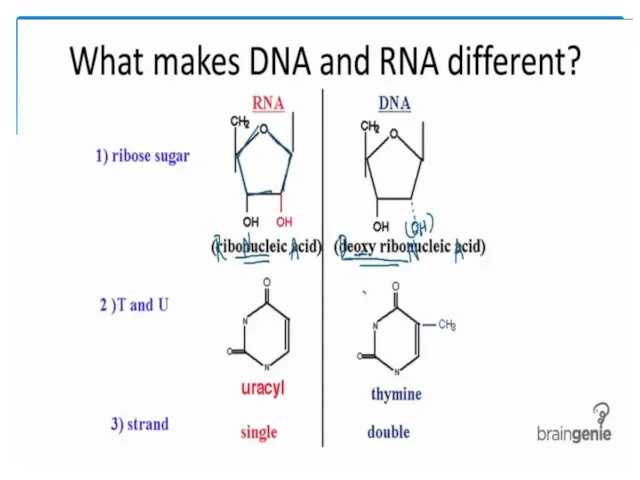
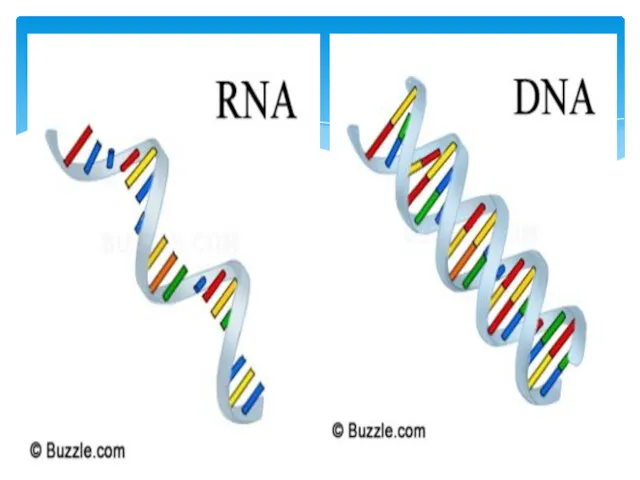
3. Difference of RNA from DNA
4. Conclusion
3. Difference of RNA from DNA
4. Conclusion
Cоntents
Слайд 3
DNA (or deoxyribonucleic acid) is the molecule that carries the genetic
DNA (or deoxyribonucleic acid) is the molecule that carries the genetic
information in all cellular forms of life and some viruses. It belongs to a class of molecules called the nucleic acids, which are polynucleotides - that is, long chains of nucleotides.
Each nucleotide consists of three components:
•a nitrogenous base: cytosine (C), guanine (G), adenine (A) or thymine (T)
•a five-carbon sugar molecule (deoxyribose in the case of DNA)
•a phosphate molecule
Each nucleotide consists of three components:
•a nitrogenous base: cytosine (C), guanine (G), adenine (A) or thymine (T)
•a five-carbon sugar molecule (deoxyribose in the case of DNA)
•a phosphate molecule
Слайд 4
Within cells, DNA is organized into long structures called chromosomes. During
Within cells, DNA is organized into long structures called chromosomes. During
cell division these chromosomes are duplicated in the process of DNA replication, providing each cell its own complete set of chromosomes. Eukaryotic organisms (animals, plants, Gribova protists) store most of their DNA inside the cell nucleus and some of their DNA in organelles, such as mitochondria or chloroplasts.In contrast, prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea) store their DNA only in the cytoplasm. In chromosomes, chromatin proteins such as histones compact and organize DNA. These compact structures guide the interactions between DNA and other proteins, helping control which parts of DNA are transcribed.
Слайд 5
Слайд 6
The structure of the DNA double helix was proposed by Francis
The structure of the DNA double helix was proposed by Francis
Crick and James Watson in 1953, on the basis of x-ray diffraction data obtained by Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin, and "rules of Chargaff", according to which each DNA molecule adhered to a strict ratio linking the number of nitrogenous bases of different types. Later proposed by Watson and Crick model of DNA structure was proven, and their work awarded with the Nobel prize in physiology or medicine 1962 was Among the winners was not died by that time from cancer Rosalind Franklin, as the prize is not awarded posthumously.
Слайд 7
Френсис Крик Джеймс Уотсон
Френсис Крик Джеймс Уотсон
Слайд 8
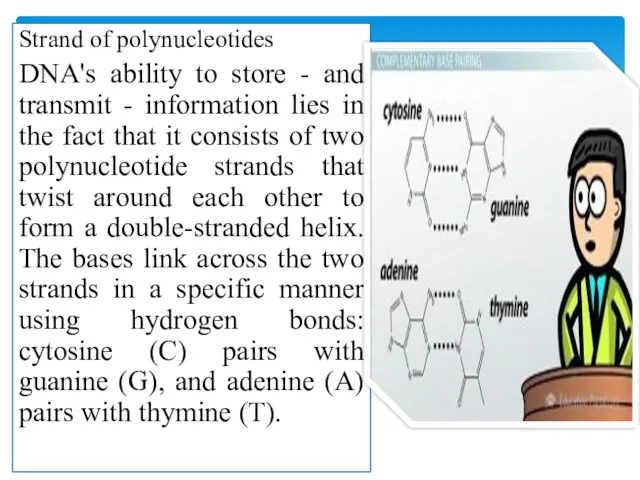
Strand of polynucleotides
DNA's ability to store - and transmit - information
Strand of polynucleotides
DNA's ability to store - and transmit - information
lies in the fact that it consists of two polynucleotide strands that twist around each other to form a double-stranded helix. The bases link across the two strands in a specific manner using hydrogen bonds: cytosine (C) pairs with guanine (G), and adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T).
Слайд 9
Слайд 10
Слайд 11
- Предыдущая
Зернові культури світуСледующая -
Bacterial Growth and Metabolism Lecture






 Жасушалардың қартаюы және сомалық жасушалардың жасушалық өлу түрлері
Жасушалардың қартаюы және сомалық жасушалардың жасушалық өлу түрлері Рациональное питание - залог здоровья
Рациональное питание - залог здоровья Лист. Внешнее и внутреннее строение
Лист. Внешнее и внутреннее строение Общие свойства сенсорных систем. Болевая сенсорная система
Общие свойства сенсорных систем. Болевая сенсорная система Животные морей
Животные морей Углеводный обмен. Глюкоза крови
Углеводный обмен. Глюкоза крови Презентация Популяция как единица эволюции
Презентация Популяция как единица эволюции Класс Пресмыкающиеся
Класс Пресмыкающиеся Интегрированный урок по русскому языку и биологии в 9 классеГлобальные экологические проблемы современности.
Интегрированный урок по русскому языку и биологии в 9 классеГлобальные экологические проблемы современности. Тип Плоские черви
Тип Плоские черви Строение центральной нервной системы человека
Строение центральной нервной системы человека Онтогенез нервной системы
Онтогенез нервной системы Кожа. Защитная функция кожи
Кожа. Защитная функция кожи 20190208_mollsyuski_
20190208_mollsyuski_ Необычные рыбы
Необычные рыбы Влияние человека на растительный и животный мир
Влияние человека на растительный и животный мир презентации к циклу уроков по природоведению в 5 классе Кто чем питается по программе Природа.Введение в биологию и экологию Т.С. Сухова, В.И. Строганов
презентации к циклу уроков по природоведению в 5 классе Кто чем питается по программе Природа.Введение в биологию и экологию Т.С. Сухова, В.И. Строганов Генная инженерия
Генная инженерия Пам’ять та научіння у тварин
Пам’ять та научіння у тварин Фотосинтез. 9 класс
Фотосинтез. 9 класс Жапырақ тақтасының пішіні
Жапырақ тақтасының пішіні Белковый обмен. Обмен нуклеопротеинов
Белковый обмен. Обмен нуклеопротеинов Наследование признаков при взаимодействии генов
Наследование признаков при взаимодействии генов Обеспечение клеток энергией. Фотосинтез
Обеспечение клеток энергией. Фотосинтез Тест. Как правильно
Тест. Как правильно Липиды - жиры и жироподобные органические соединения, практически нерастворимые в воде
Липиды - жиры и жироподобные органические соединения, практически нерастворимые в воде ВКР: Толерантность гибридов кукурузы к условиям Орловской области
ВКР: Толерантность гибридов кукурузы к условиям Орловской области Настройка лазерного сканирующего конфокального микроскопа
Настройка лазерного сканирующего конфокального микроскопа