Содержание
- 2. INDEX Introduction. Population genetic. Genetic variation in natural population. i) Natural selection Type of natural selection
- 3. Population Genetics Chapter 8
- 4. Introduction 1. Population genetics is the study of change in the frequencies of allele and genotype
- 5. Gene – a discrete unit of hereditary information consisting of a specific nucleotide sequence in DNA.
- 6. Hardy Weinberg principle States that ; (p+q )² p² + 2pq + q² =1 Under the
- 7. Why Allele Frequencies Change Five evolutionary forces can significantly alter the allele frequencies of a population
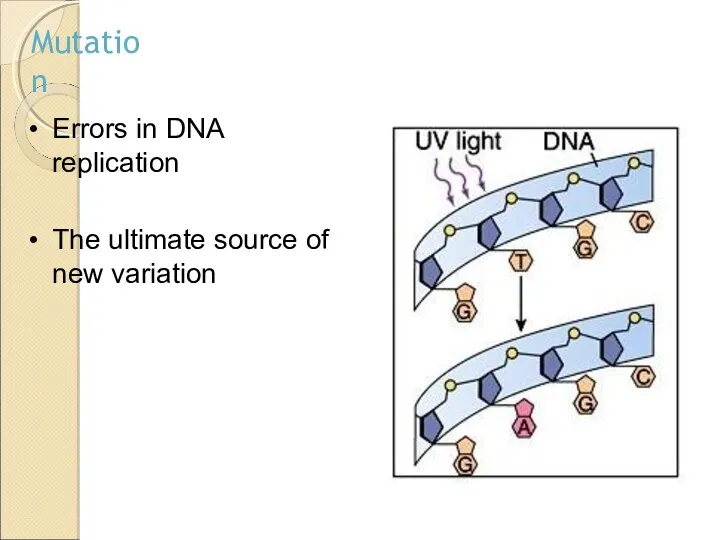
- 8. Errors in DNA replication The ultimate source of new variation Mutation
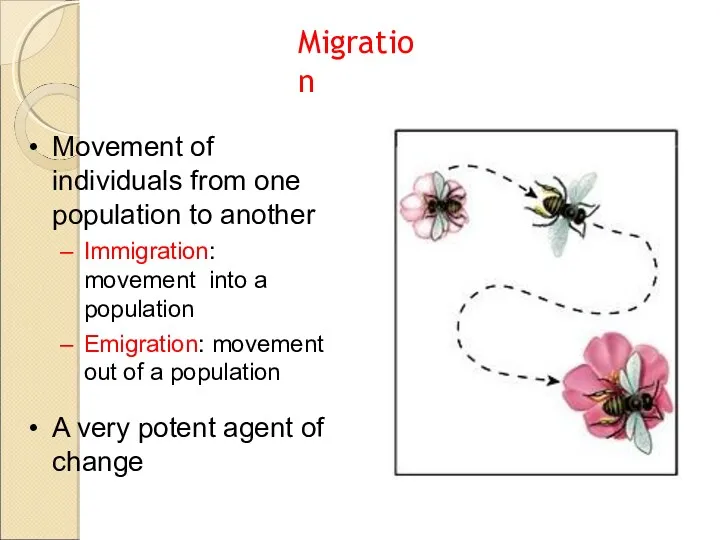
- 9. Movement of individuals from one population to another Immigration: movement into a population Emigration: movement out
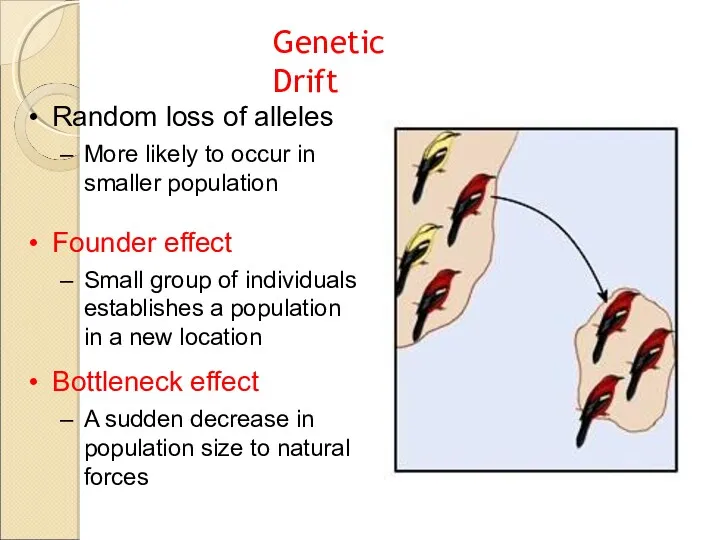
- 10. Genetic Drift Random loss of alleles More likely to occur in smaller population Founder effect Small
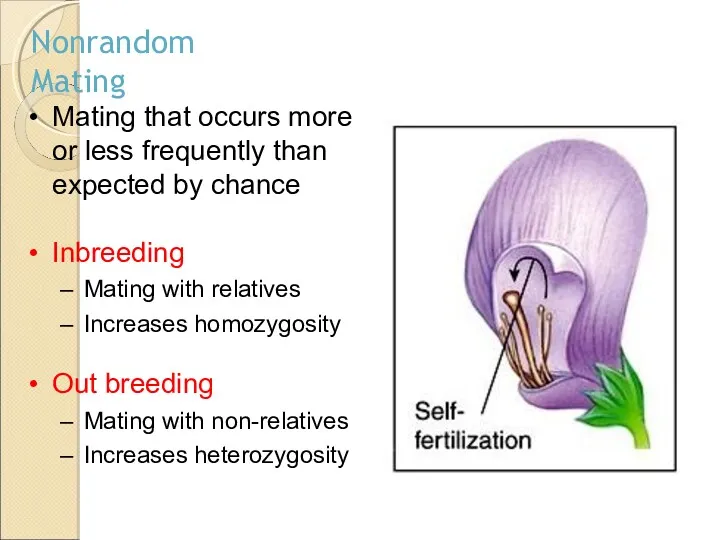
- 11. Nonrandom Mating Mating that occurs more or less frequently than expected by chance Inbreeding Mating with
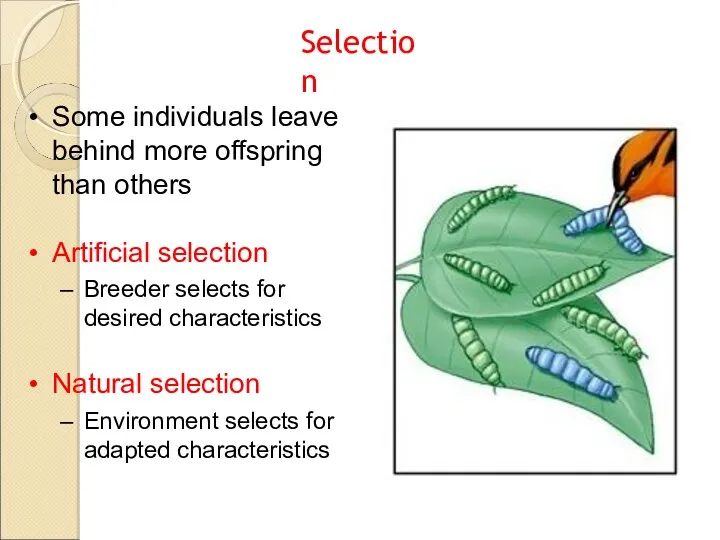
- 12. Some individuals leave behind more offspring than others Artificial selection Breeder selects for desired characteristics Natural
- 13. Genetic Variation in Natural Populations
- 14. Types of Variation Phenotypic variation: it’s a genetical basis morphological variation its some tie continuous and
- 15. Genetic variance: the variance that is due to variation among individuals in the alleles that they
- 16. Natural selection The natural selection is a process by which heritable traits that makes it more
- 17. Forms of Selection Three types of natural selection have been identified Stabilizing selection Acts to eliminate
- 18. Stabilizing Selection Its a type of natural selection in which genetic diversity decreases as the population
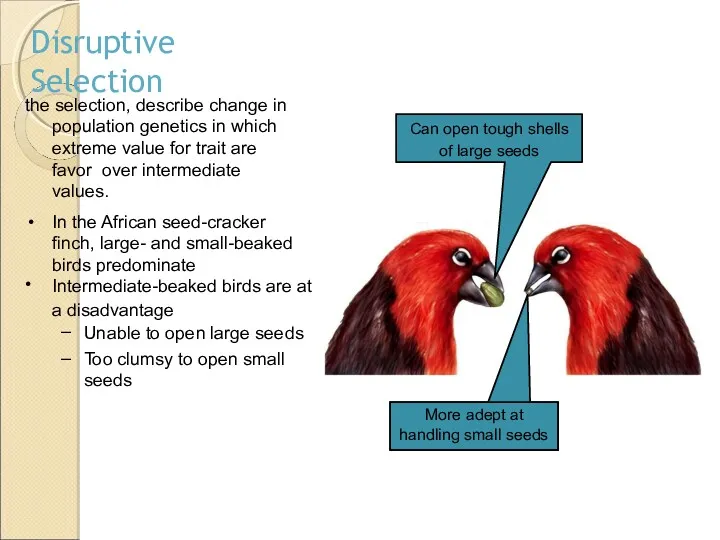
- 19. the selection, describe change in population genetics in which extreme value for trait are favor over
- 20. Direction selection is a mode of natural selection in which a single phenotype is favored, causing
- 21. Polymorphism . Naturalists have described phenotypic variation within many species. For example, , All these
- 22. Grove snail; , Cepaea nemoralis Grove snail The grove snail, Cepaea nemoralis, is famous for the
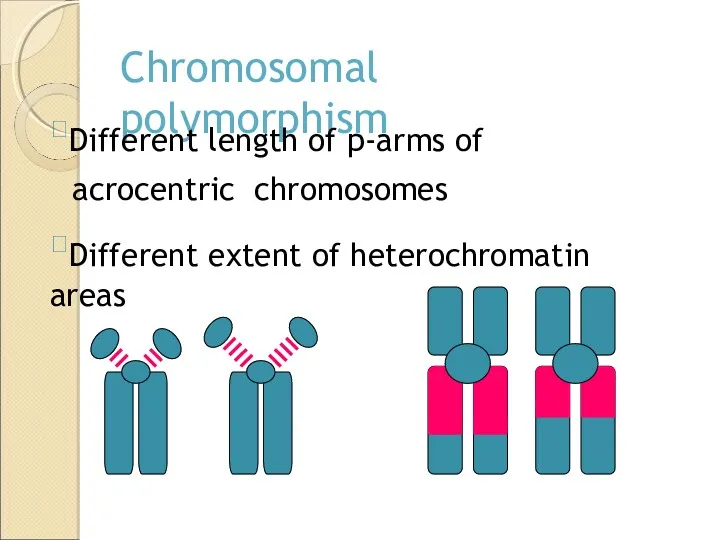
- 23. Chromosomal polymorphism Different length of p-arms of acrocentric chromosomes Different extent of heterochromatin areas
- 24. References Principle of genetics. By D. peter snustad. Genetics :robbert f.weaver www.worlofteaching.com www.vadlo.com www.google.co.in
- 26. Скачать презентацию













 Царства живой природы
Царства живой природы Работа и сила мышц. Строение сократительного аппарата поперечно-полосатой мышечной ткани
Работа и сила мышц. Строение сократительного аппарата поперечно-полосатой мышечной ткани Органы дыхания
Органы дыхания Гены и аллели. Аллельные взаимодействия
Гены и аллели. Аллельные взаимодействия Dinoflagellates
Dinoflagellates Торговий Дім АКТИВ-HARVEST. Добрива для позакореневого живлення
Торговий Дім АКТИВ-HARVEST. Добрива для позакореневого живлення Отряд Стрекозы
Отряд Стрекозы Рефлекторный принцип деятельности ЦНС. Возбуждение и торможение. Функции нейронов и нейроглии. Физиология рецепторов
Рефлекторный принцип деятельности ЦНС. Возбуждение и торможение. Функции нейронов и нейроглии. Физиология рецепторов Создание, исследование и испытание доступного биовегетария
Создание, исследование и испытание доступного биовегетария Асимметрия полушарий головного мозга человека
Асимметрия полушарий головного мозга человека Закон Менделя
Закон Менделя презентация к уроку Органические молекулы - углеводы
презентация к уроку Органические молекулы - углеводы Составление тренировочных программ для мужчин различных типов сложения
Составление тренировочных программ для мужчин различных типов сложения Репчатый лук
Репчатый лук Презентация Организация исследовательской работы
Презентация Организация исследовательской работы Презентация к уроку Эволюция строения и функций органов и их систем
Презентация к уроку Эволюция строения и функций органов и их систем Опорно-двигательная система человека
Опорно-двигательная система человека Репродукція клітин
Репродукція клітин Protein Structure and Function
Protein Structure and Function Инструменты для груминга
Инструменты для груминга klasss
klasss Подцарство одноклеточные
Подцарство одноклеточные Осьминоги. Головоногие моллюски
Осьминоги. Головоногие моллюски Особенности размножения рыб
Особенности размножения рыб Урок-игра Кровь и кровообращение
Урок-игра Кровь и кровообращение Для начинающих улитководов
Для начинающих улитководов Класс Земноводные, или Амфибии (Amphibia)
Класс Земноводные, или Амфибии (Amphibia) Вид. Критерии вида
Вид. Критерии вида