Содержание
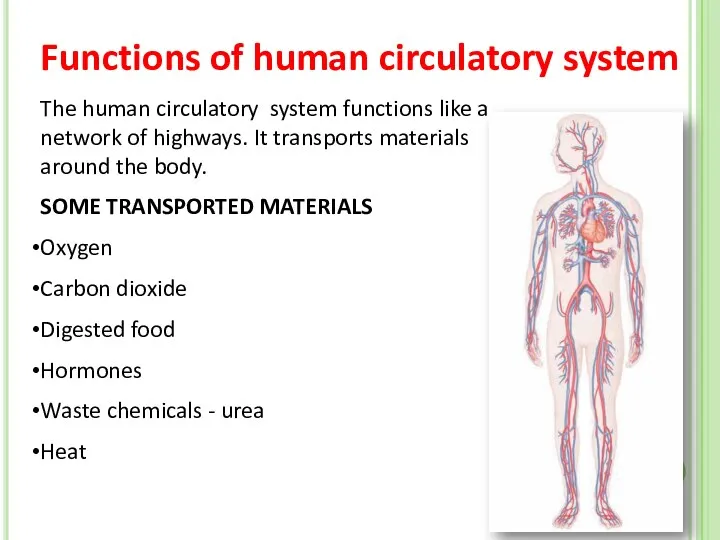
- 2. The human circulatory system functions like a network of highways. It transports materials around the body.
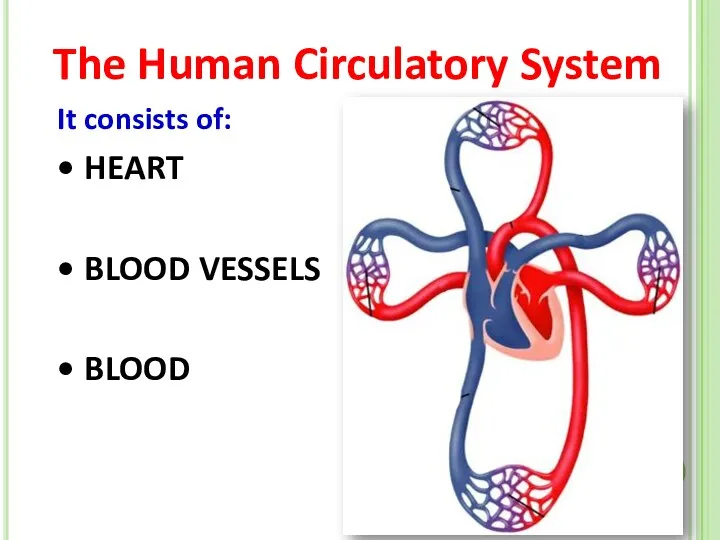
- 3. The Human Circulatory System It consists of: HEART BLOOD VESSELS BLOOD
- 4. The Heart
- 5. HEART FACTS: About 250-340 grams, In your life time, pumps about 300 million liter of blood,
- 6. Main structure of the heart The heart is made of a special type of muscle called
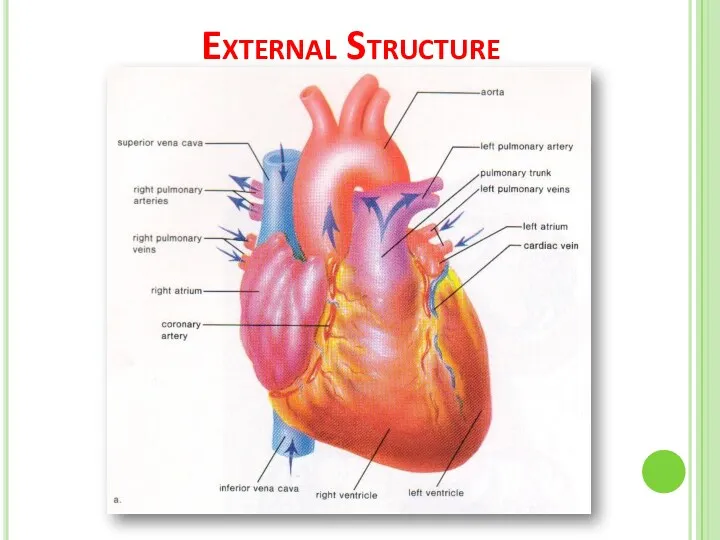
- 7. External Structure
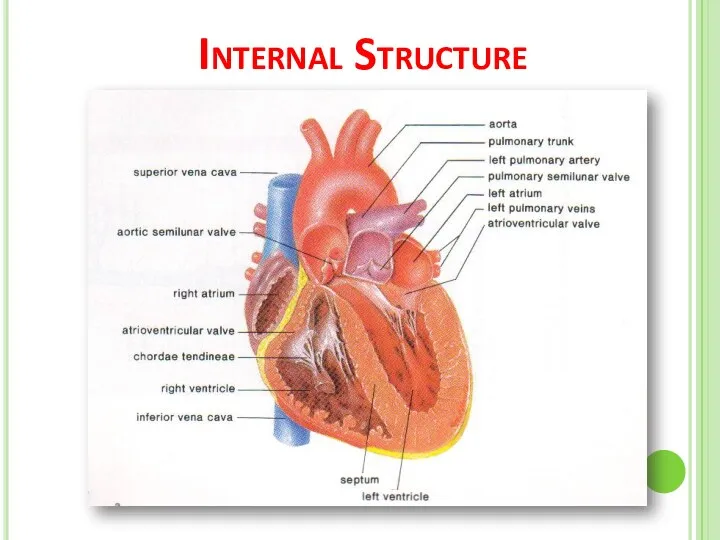
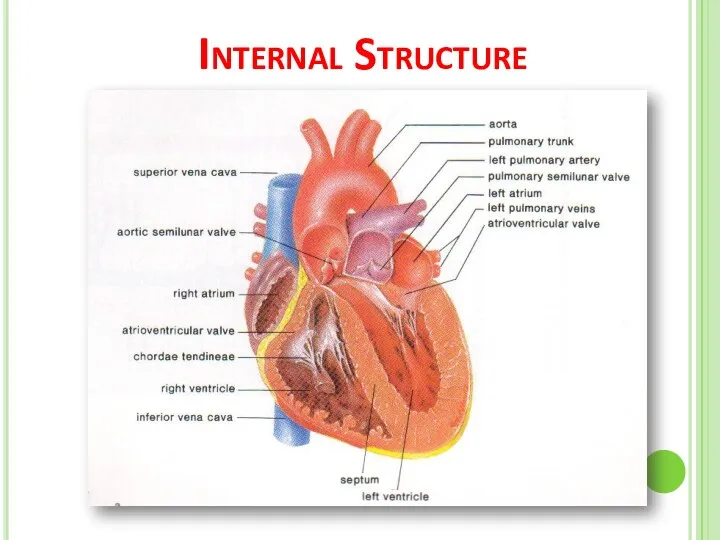
- 8. Internal Structure
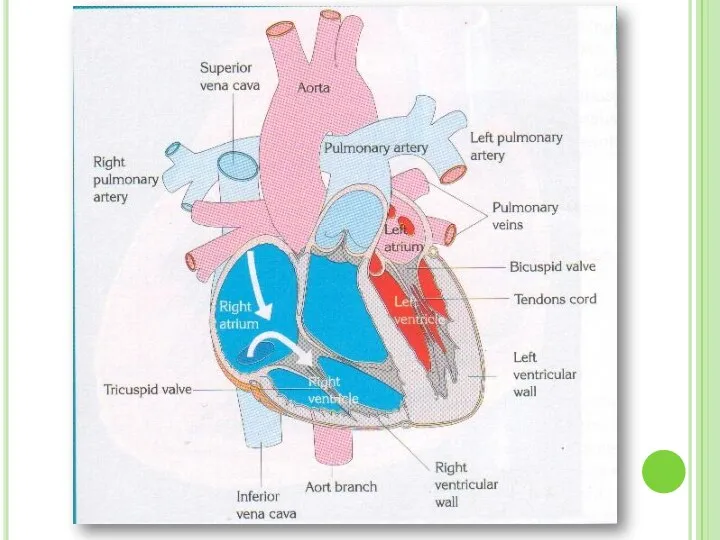
- 9. Internal Structure Of The Heart The heart consists of four chambers : The two upper chambers
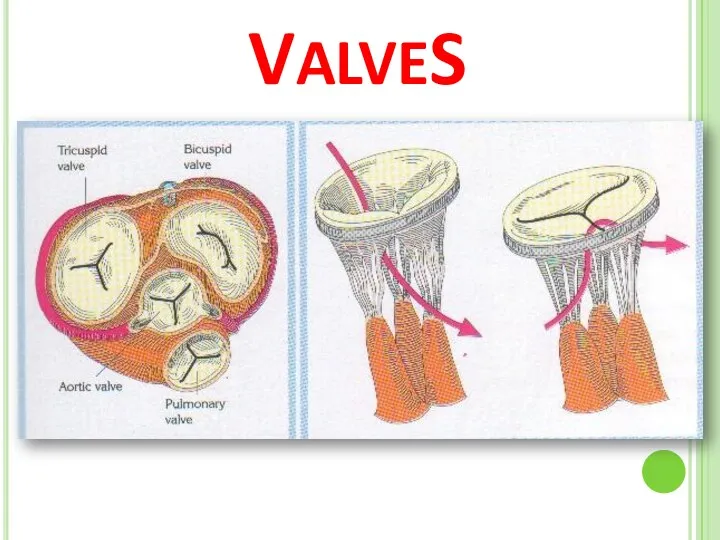
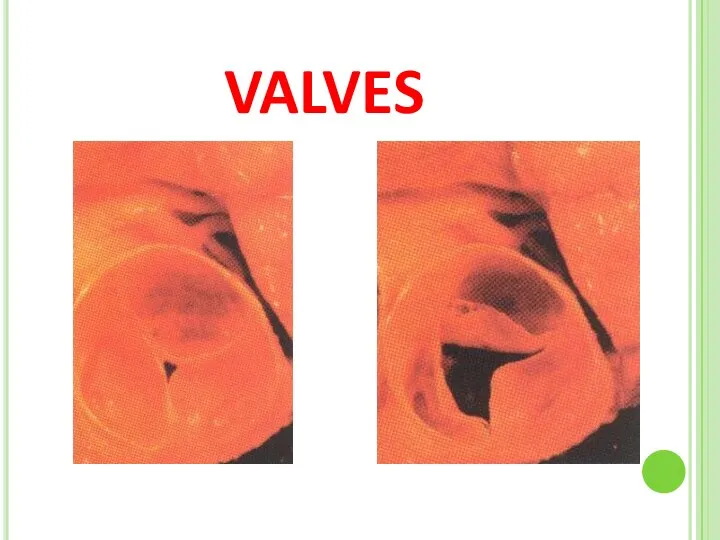
- 11. VALVES
- 12. Semilunar Valves Semilunar valves are found between the arteries and the ventricles. They prevent the blood
- 13. VALVES
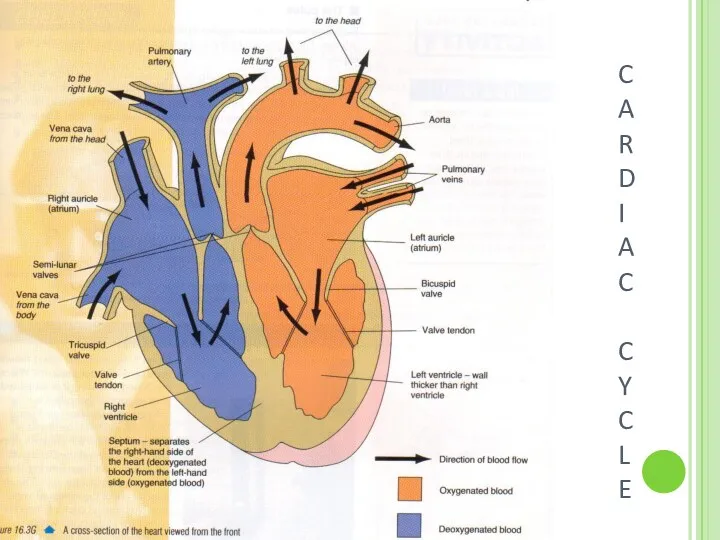
- 15. C A R D I A C C Y C L E
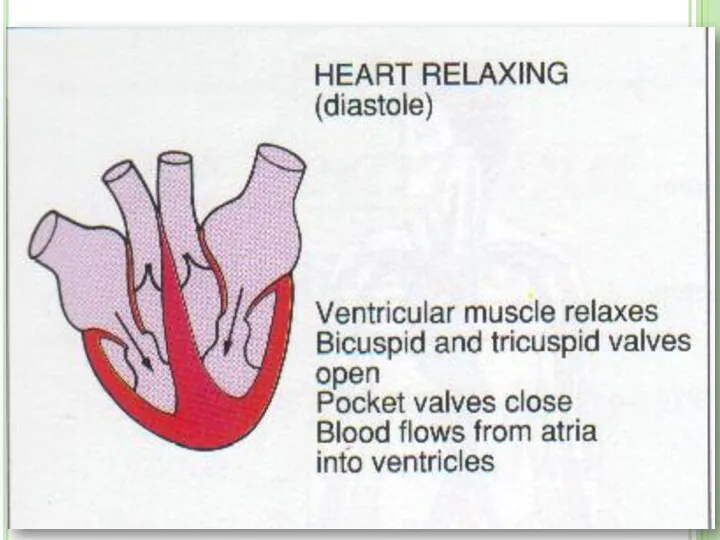
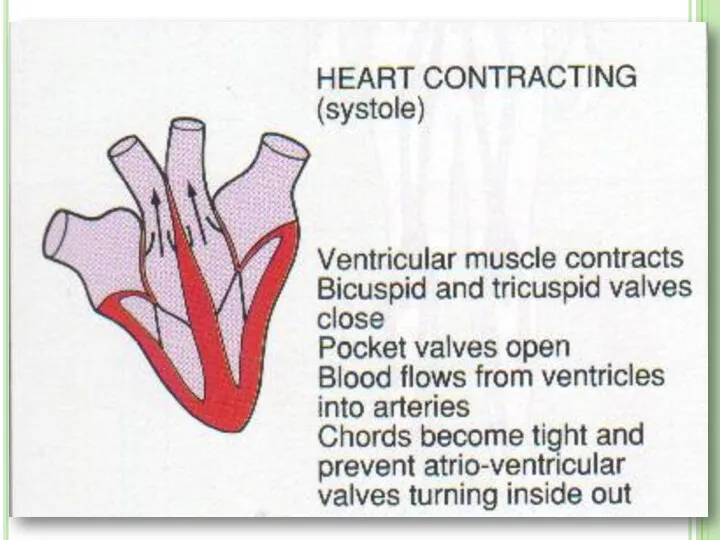
- 16. The heart pumps blood into the body. Relaxation of heart is known as diastole. Contraction of
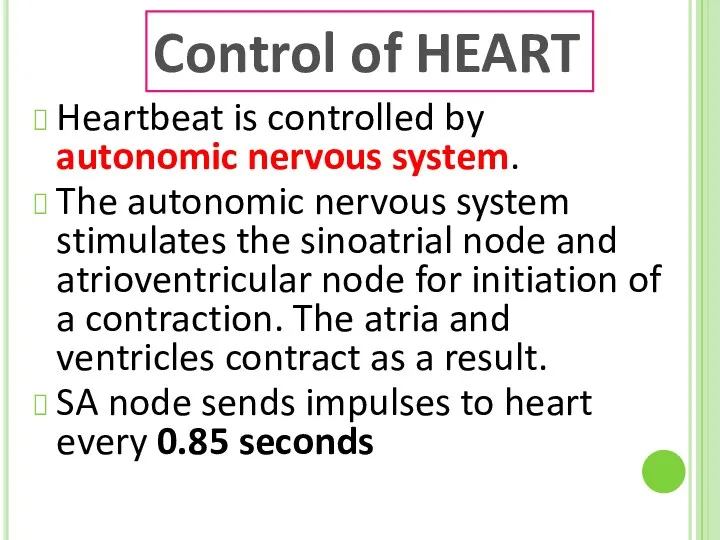
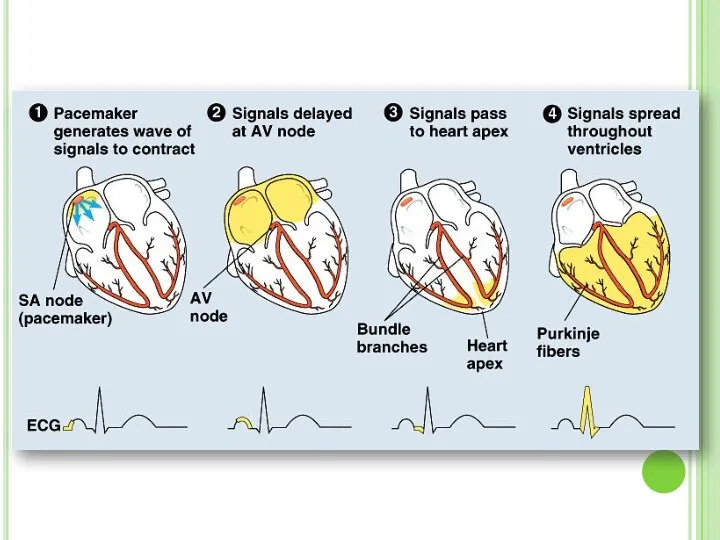
- 20. Heartbeat is controlled by autonomic nervous system. The autonomic nervous system stimulates the sinoatrial node and
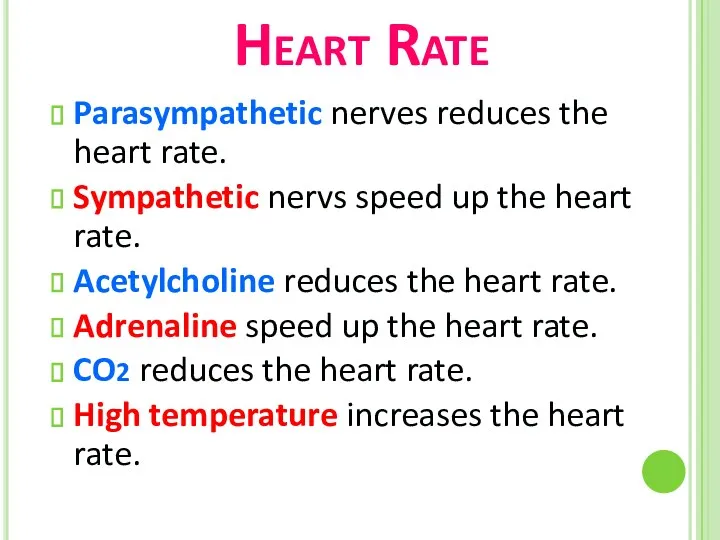
- 23. Heart Rate Parasympathetic nerves reduces the heart rate. Sympathetic nervs speed up the heart rate. Acetylcholine
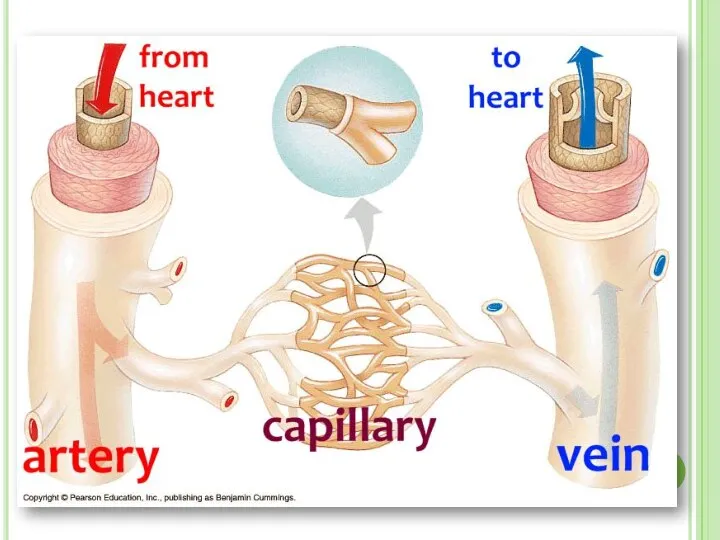
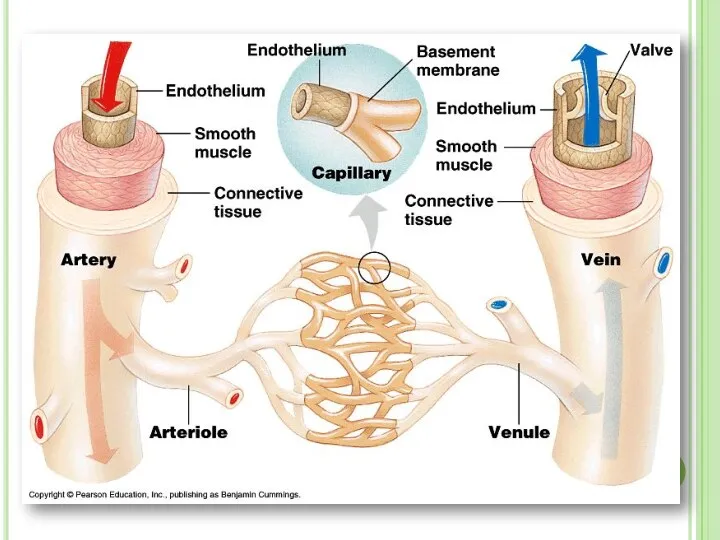
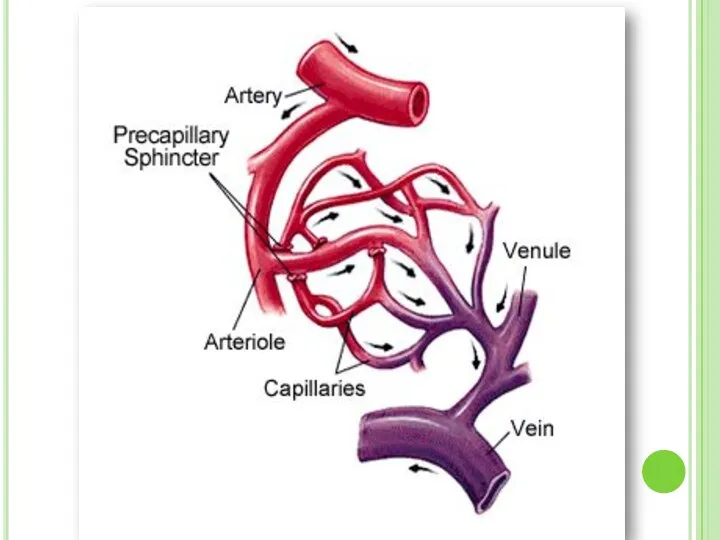
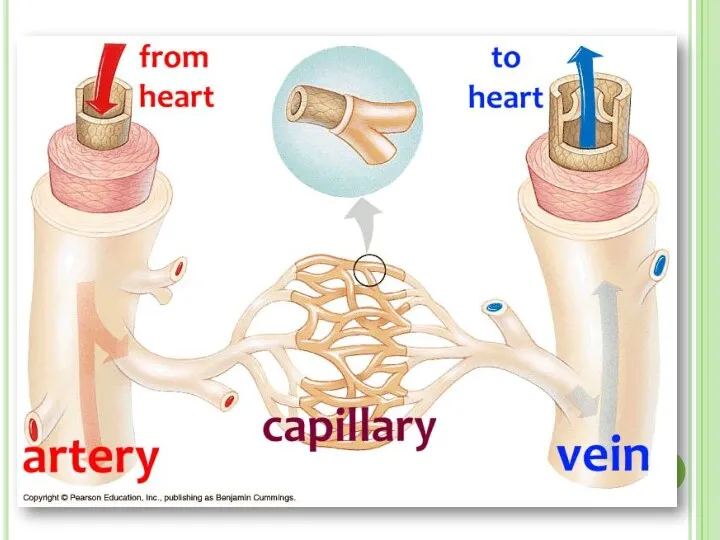
- 24. BLOOD VESSELS There are 3 types of vessels in our body. These are; ARTERIES VEINS CAPILLARIES
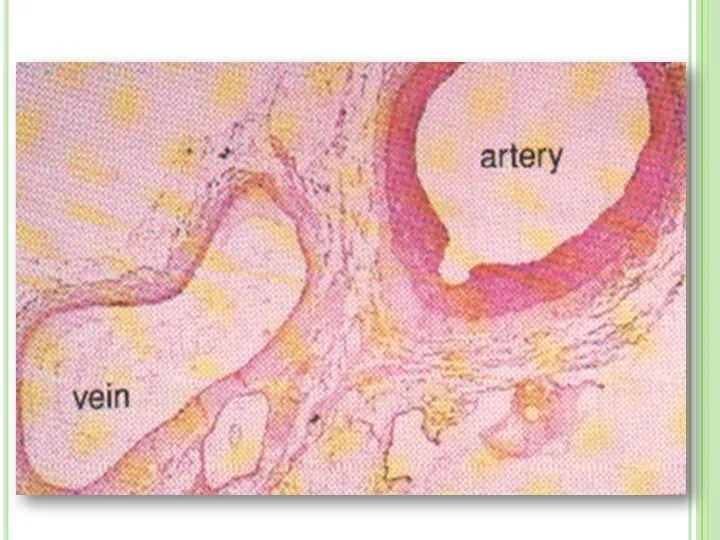
- 27. 1. Arteries Arteries carry blood away from heart to the different tissues of the body. Artery
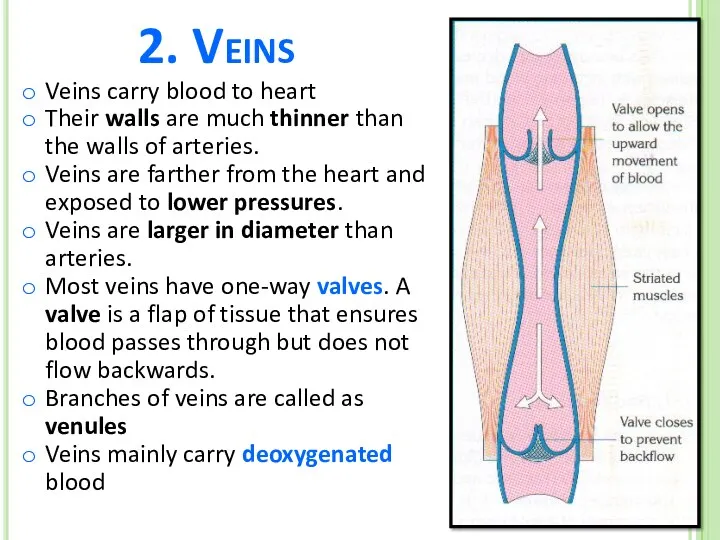
- 29. 2. Veins Veins carry blood to heart Their walls are much thinner than the walls of
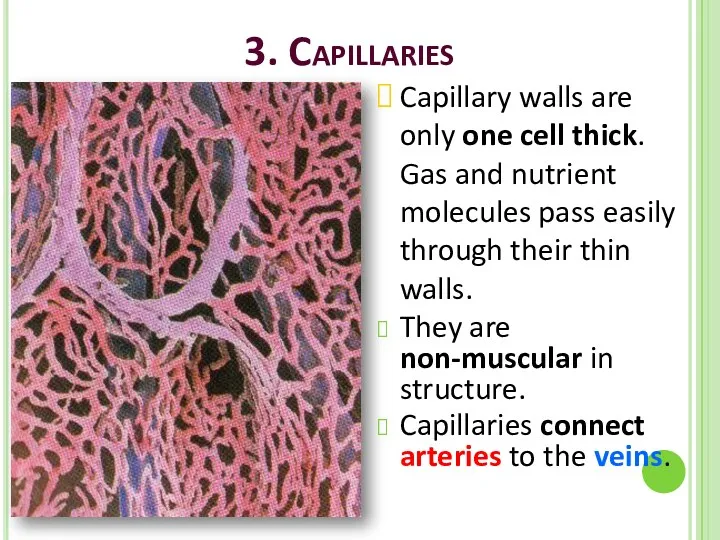
- 32. 3. Capillaries Capillary walls are only one cell thick. Gas and nutrient molecules pass easily through
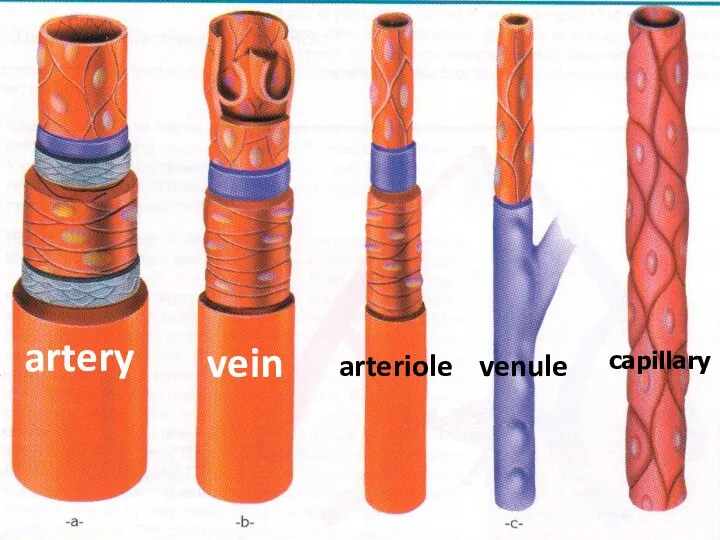
- 35. artery vein arteriole venule capillary
- 37. Blood Pressure Blood exerts pressure on the walls of vessels during circulation Blood pressure increases when
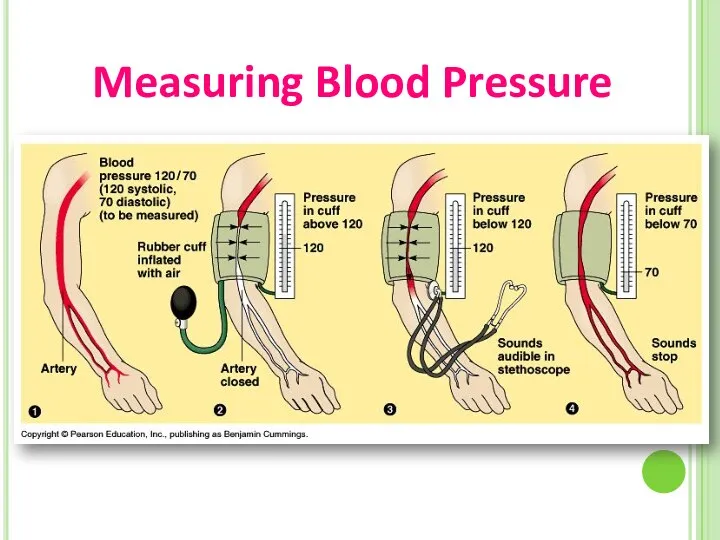
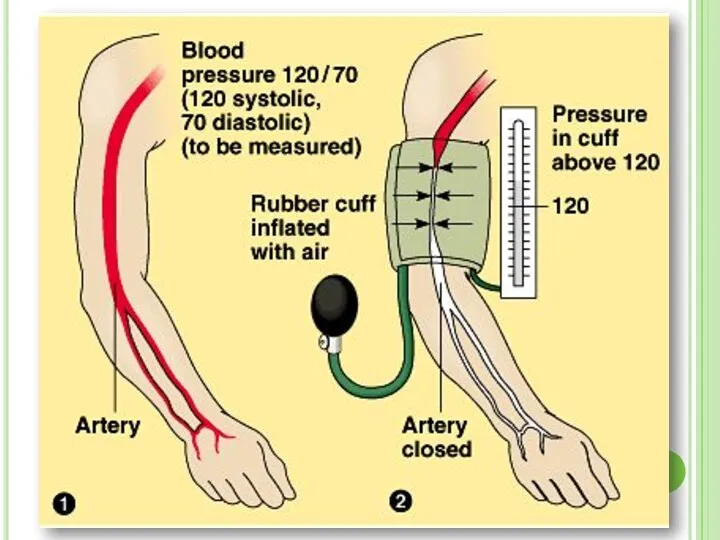
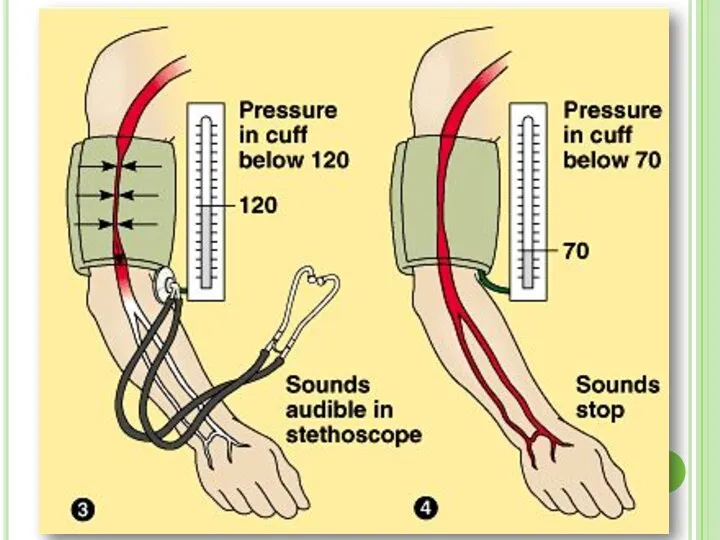
- 38. Measuring Blood Pressure
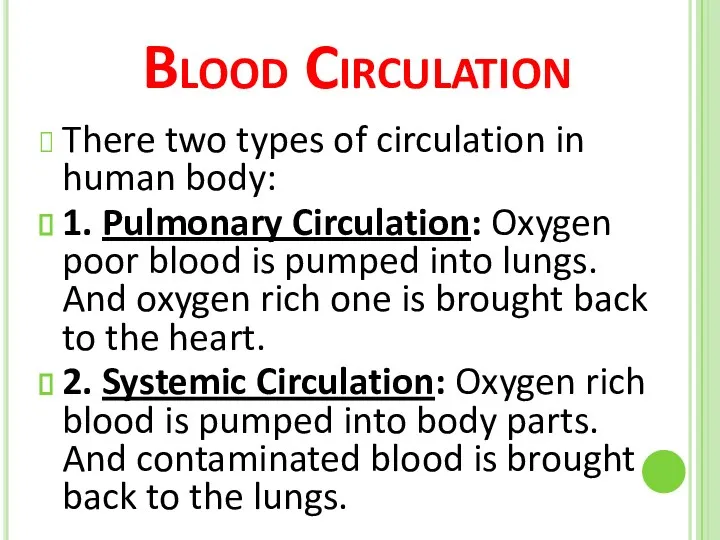
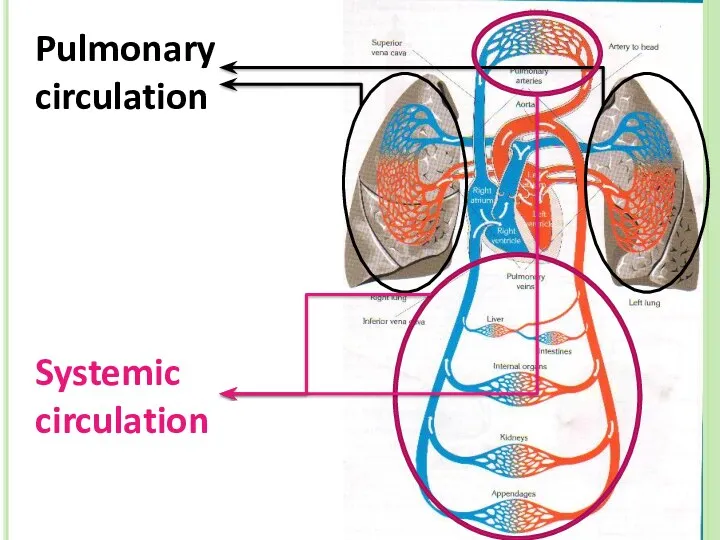
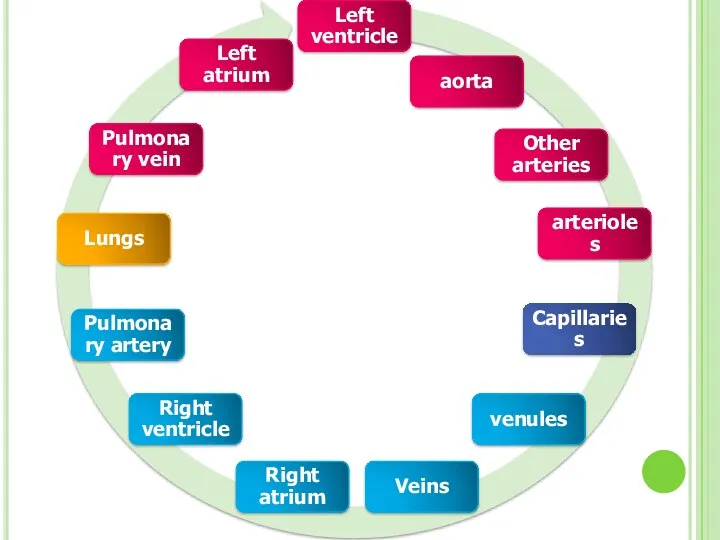
- 41. Blood Circulation There two types of circulation in human body: 1. Pulmonary Circulation: Oxygen poor blood
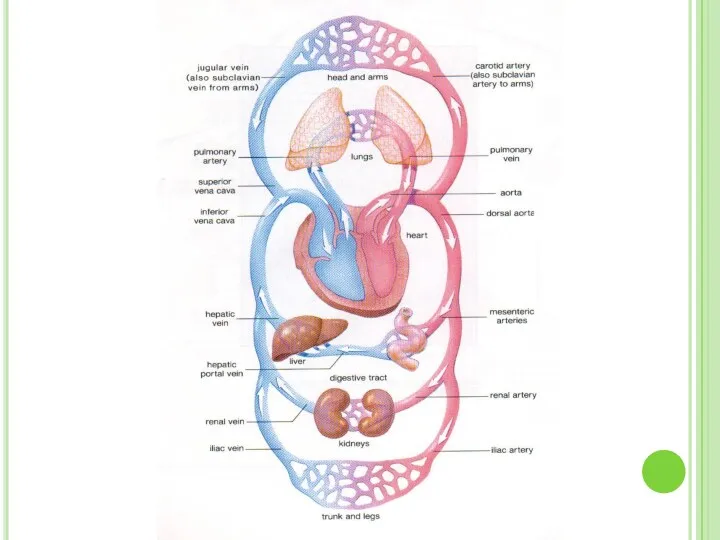
- 42. Pulmonary circulation Systemic circulation
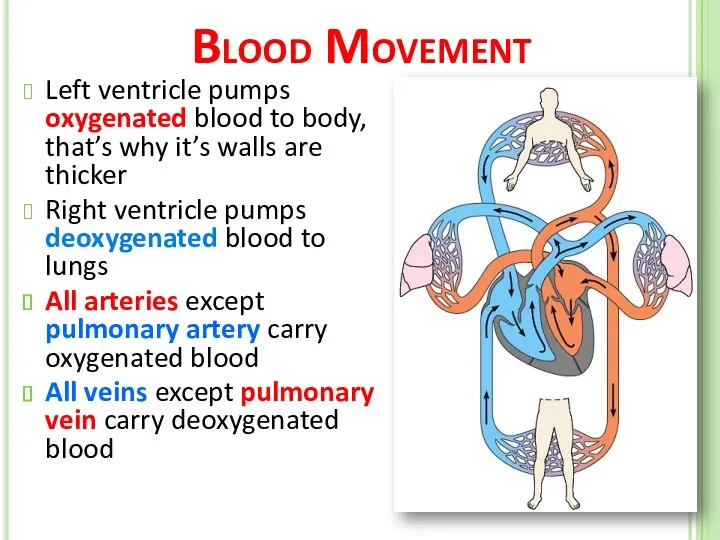
- 44. Blood Movement Left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to body, that’s why it’s walls are thicker Right
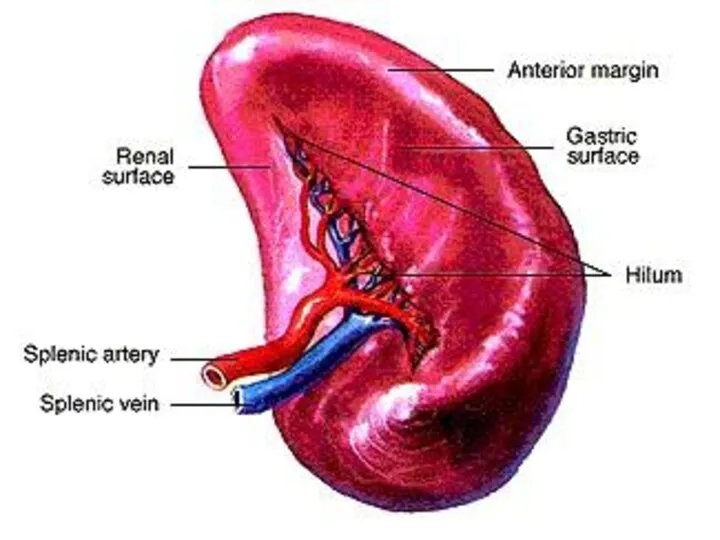
- 46. Internal Structure
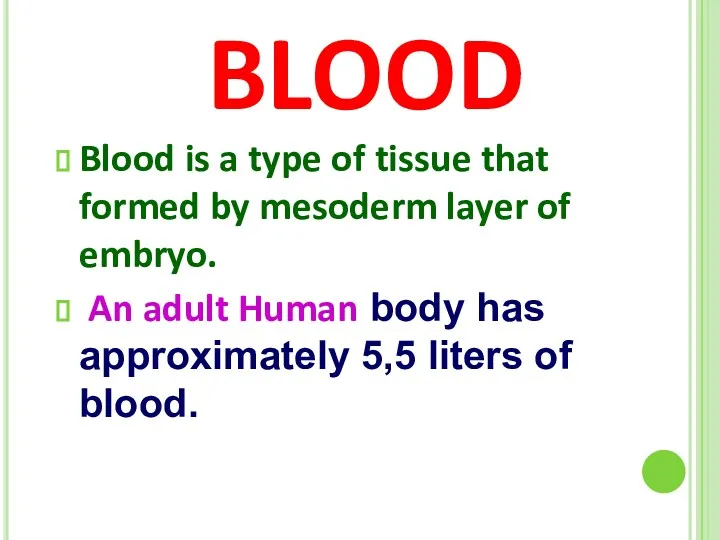
- 47. BLOOD Blood is a type of tissue that formed by mesoderm layer of embryo. An adult
- 48. FUNCTIONS OF BLOOD Transport of materials Hormone transport Homeostasis Immune response Blood Clotting
- 49. BLOOD COMPONENTS Blood contain 2 main parts. These are: Blood Plasma Blood cells
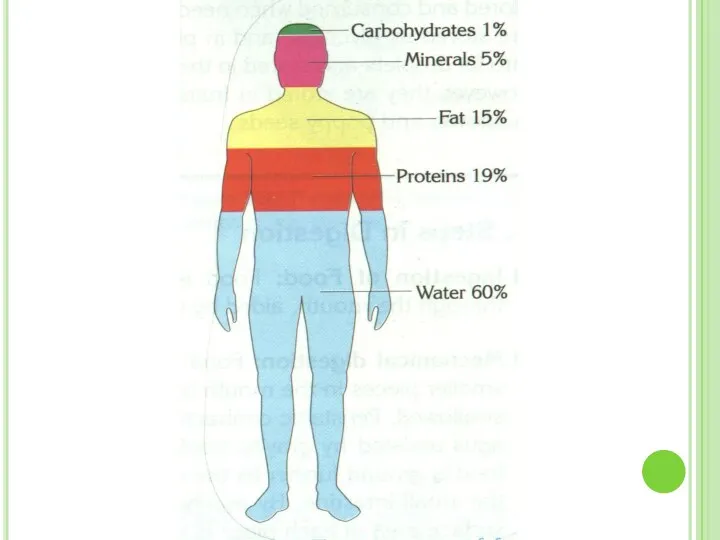
- 50. Blood Plasma Plasma is liquid part of blood. It includes water (90%) and dissolved proteins. It
- 52. Blood Cells There are three types of blood cells: Erythrocytes (=Red Blood Cells) Leucocytes (=White Blood
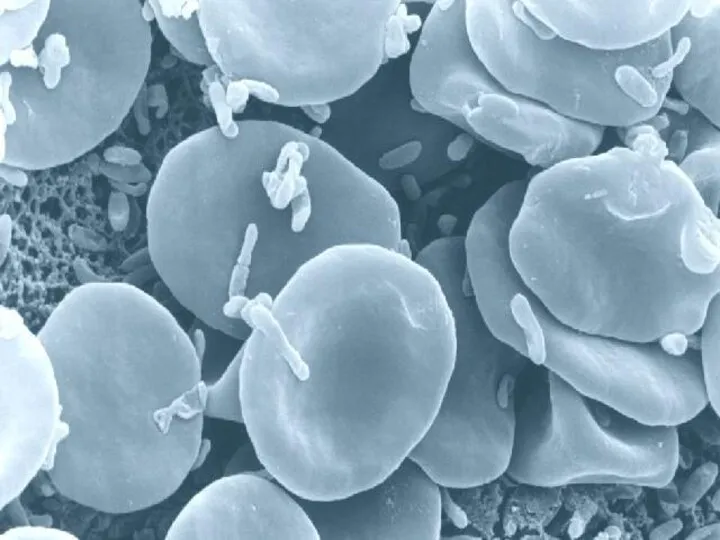
- 54. There are approximately 5 to 5,5 million of erythrocytes per cubic millimeter of blood. The major
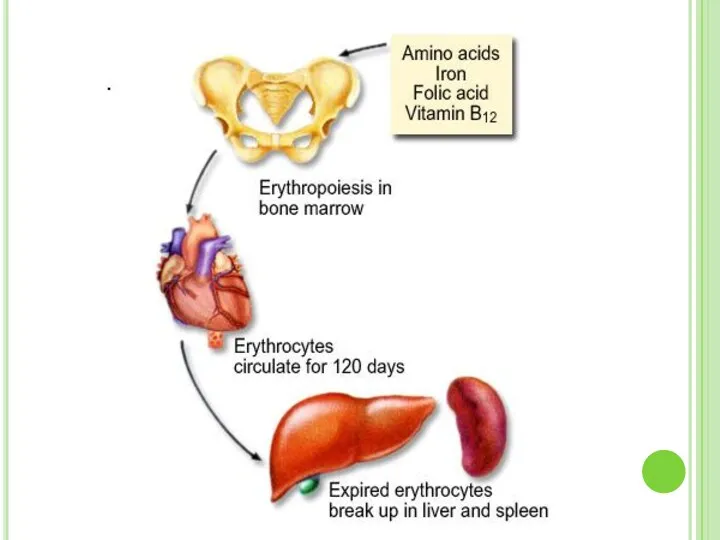
- 55. Mammalian erythrocytes have no nucleus at adult (maturation) stage. They are produced by red bone marrow.
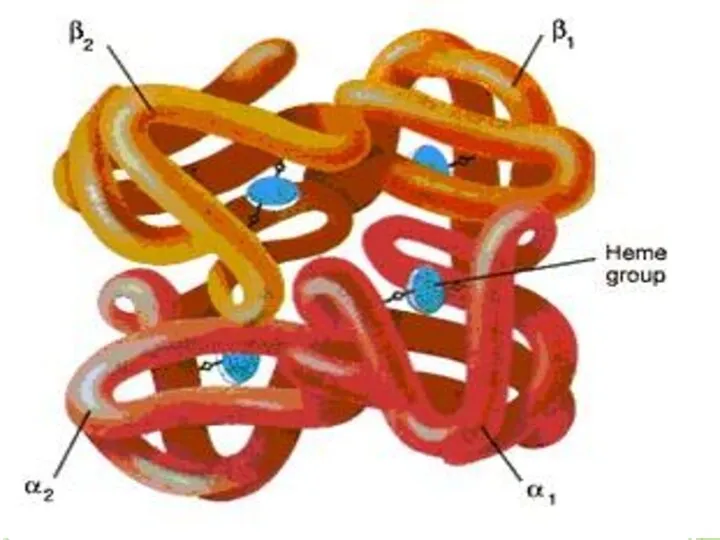
- 59. HEMOGLOBIN Erythrocytes are filled with hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is iron (Fe) containing pigment. It gives red color
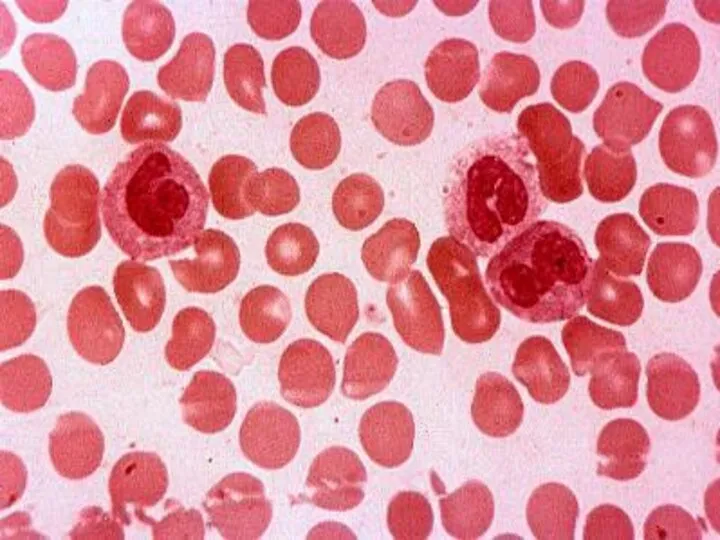
- 62. LEUCOCYTES Leucocytes protect the body from infections. They are produced by red bone marrow and lymph
- 63. Normally there are only 6000 to 8000 leucocytes per cubic millimeter of blood. When there is
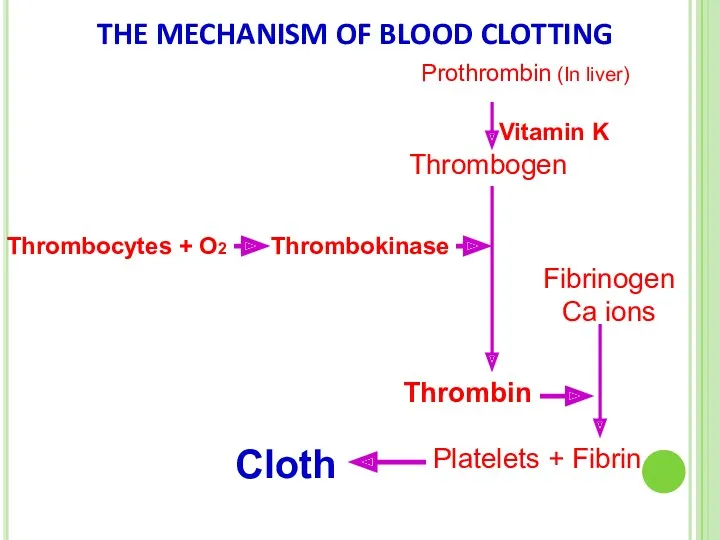
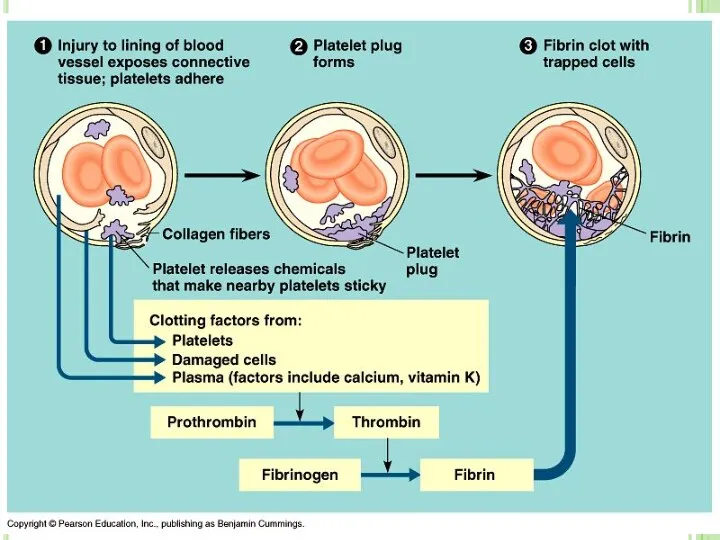
- 66. PLATELETS Platelets are produced by bone marrow. They play major role in blood clotting. Blood clotting
- 67. THE MECHANISM OF BLOOD CLOTTING Prothrombin (In liver) Vitamin K Thrombogen Thrombocytes + O2 Thrombokinase Thrombin
- 70. Diseases related to circulatory system Anemia Leukemia Arteriosclerosis
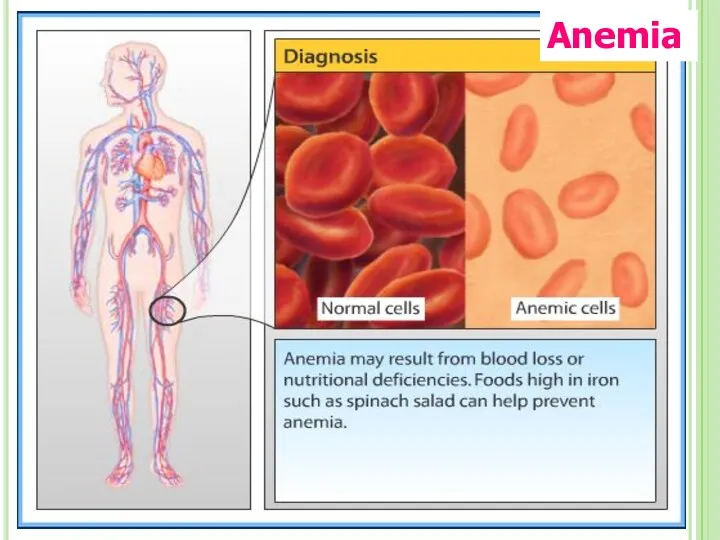
- 71. Anemia
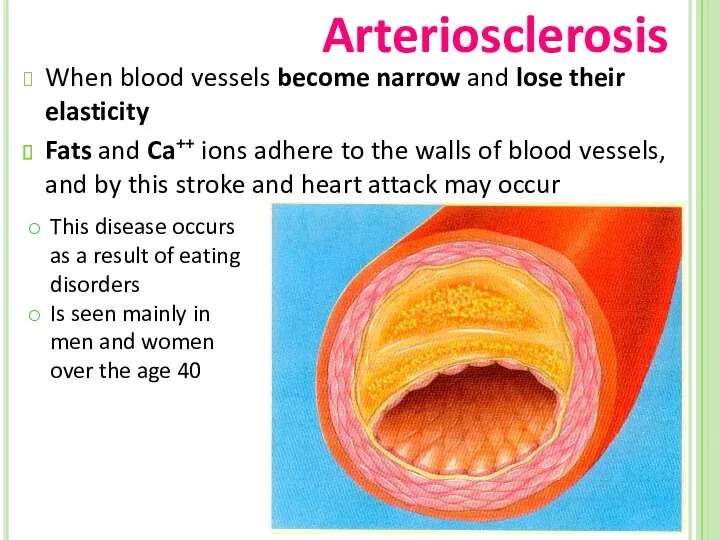
- 72. Arteriosclerosis When blood vessels become narrow and lose their elasticity Fats and Ca++ ions adhere to
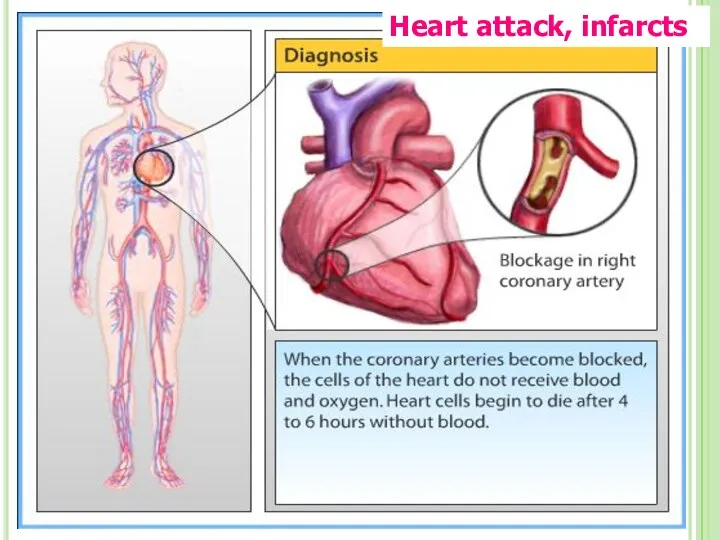
- 73. Heart attack, infarcts
- 75. Скачать презентацию
























 Рентгеноанатомия черепа. Обозначьте кости мозгового черепа
Рентгеноанатомия черепа. Обозначьте кости мозгового черепа Водорастворимые витамины
Водорастворимые витамины Птицы водоемов
Птицы водоемов Опора и движение. Опорно-двигательная система
Опора и движение. Опорно-двигательная система Мониезиоз жвачных животных. Разработка мер борьбы и профилактики
Мониезиоз жвачных животных. Разработка мер борьбы и профилактики Презентация В мире бактерий
Презентация В мире бактерий Перелётные птицы
Перелётные птицы Пространственная организация белков. Конформации полипептидной цепи. Карты Рамачандрана
Пространственная организация белков. Конформации полипептидной цепи. Карты Рамачандрана Всасывание. Роль печени. Функции толстого кишечника
Всасывание. Роль печени. Функции толстого кишечника Викторина. Тема Птицы.
Викторина. Тема Птицы. Функциональная асимметрия полушарий
Функциональная асимметрия полушарий Черты приспособленности организмов к среде обитания
Черты приспособленности организмов к среде обитания Ядовитые грибы и ягоды
Ядовитые грибы и ягоды Презентация Плоды
Презентация Плоды Урок по биологии в 7 классе по теме Семейство злаковые по программе Сонина Н.И. (содержит презентацию и текстовую разработку урока)
Урок по биологии в 7 классе по теме Семейство злаковые по программе Сонина Н.И. (содержит презентацию и текстовую разработку урока) Влияние двигательной активности на здоровье человека
Влияние двигательной активности на здоровье человека Біологічні науки, що вивчають організм людини
Біологічні науки, що вивчають організм людини Доклад на тему: Формирование универсальных умений и универсальных учебных действий учащихся в свете требований ФГОС на уроках биологии .
Доклад на тему: Формирование универсальных умений и универсальных учебных действий учащихся в свете требований ФГОС на уроках биологии .  Бактерии. История открытия. Строение бактерий
Бактерии. История открытия. Строение бактерий Проект Разнообразие природы родного края
Проект Разнообразие природы родного края Класс насекомые
Класс насекомые Викторина Анализаторы
Викторина Анализаторы История развития знаний о строении и функциях организма человека
История развития знаний о строении и функциях организма человека Класс Пресмыкающиеся, или Рептилии. Отряд Чешуйчатые
Класс Пресмыкающиеся, или Рептилии. Отряд Чешуйчатые Альбом по эмбриологии
Альбом по эмбриологии Социально-биологические основы физической культуры
Социально-биологические основы физической культуры Методика обучения биологии
Методика обучения биологии Кольчатые черви
Кольчатые черви