Содержание
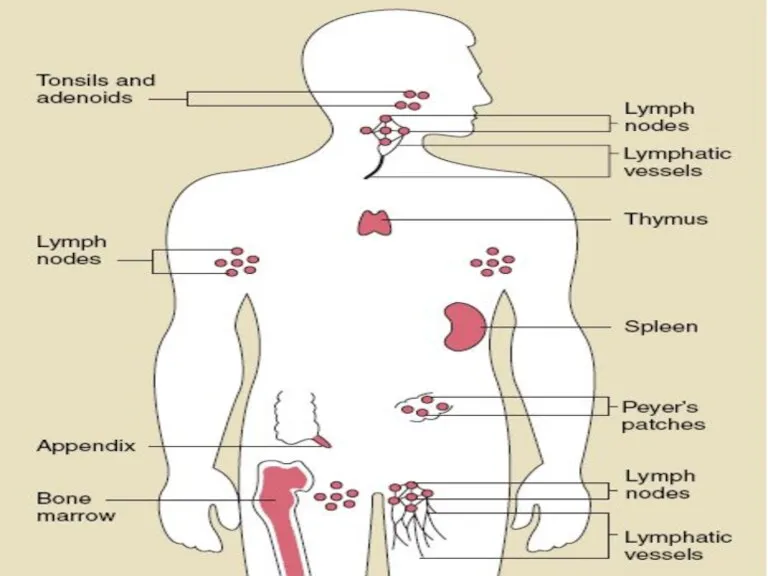
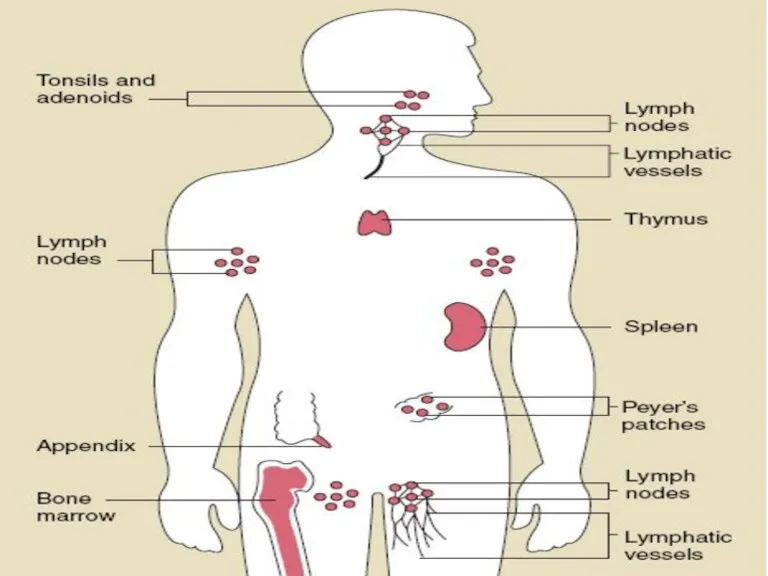
- 4. The major organs of the immune system are: Central: Bone marrow Thymus Peripheral: Spleen Lymph nodes
- 6. In central organs antigen-independent production of uncommitted T lymphocyte (thymus) or B lymphocyte (bone marrow) precursors
- 7. Bone Marrow is a soft tissue occupying the medullary cavity of a long bone There are
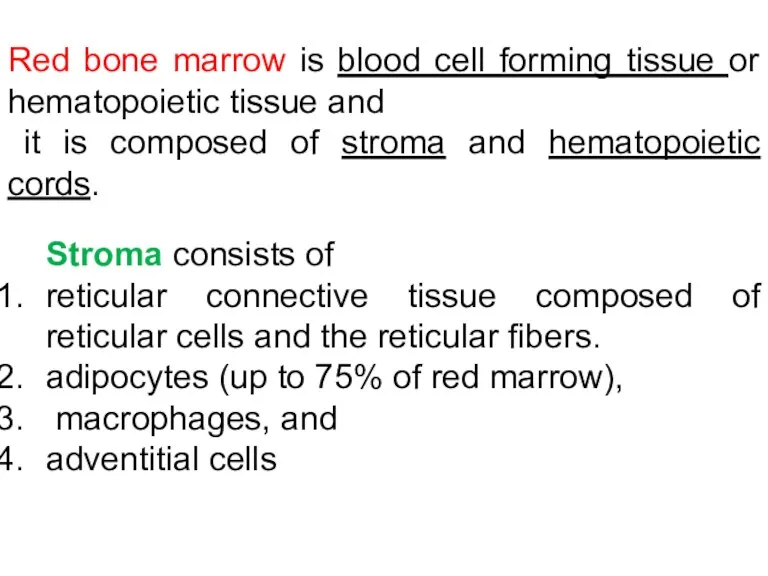
- 8. Red bone marrow is blood cell forming tissue and it is composed of stroma (reticular tissue)
- 9. Red bone marrow is blood cell forming tissue or hematopoietic tissue and it is composed of
- 10. Erythroblastic islands are clusters of developing erythrocytes surrounding macrophages and receiving iron from them. Sinusoids (capillaries)
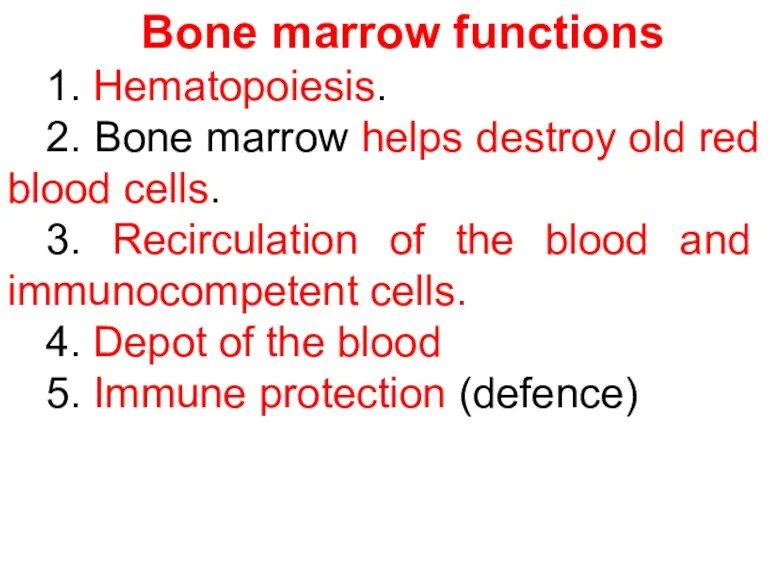
- 11. Bone marrow functions 1. Hematopoiesis. 2. Bone marrow helps destroy old red blood cells. 3. Recirculation
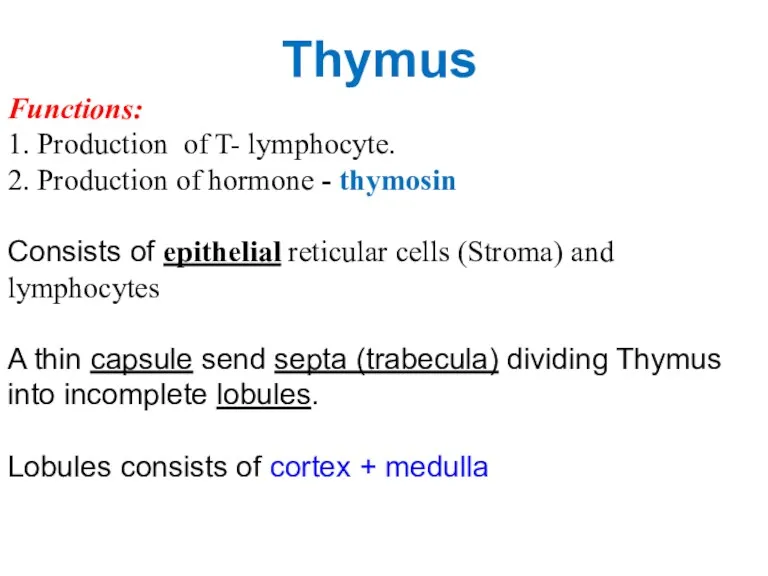
- 13. Thymus Functions: 1. Production of T- lymphocyte. 2. Production of hormone - thymosin Consists of epithelial
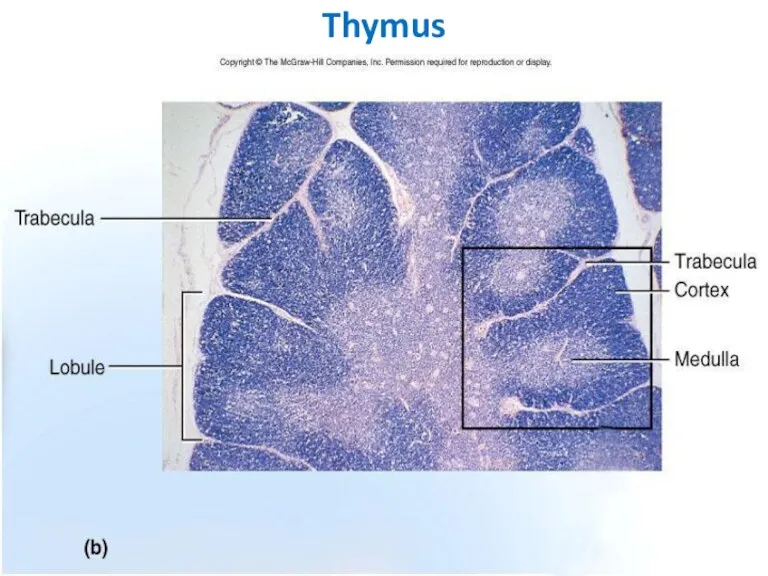
- 14. Thymus
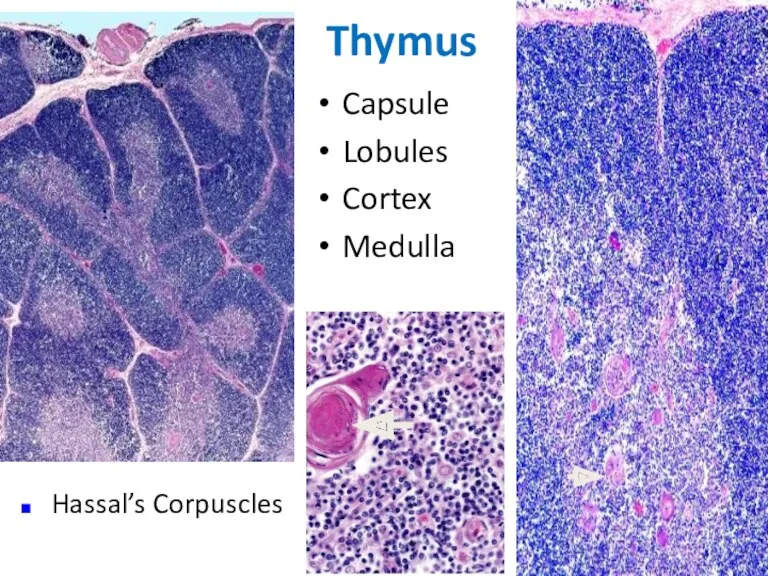
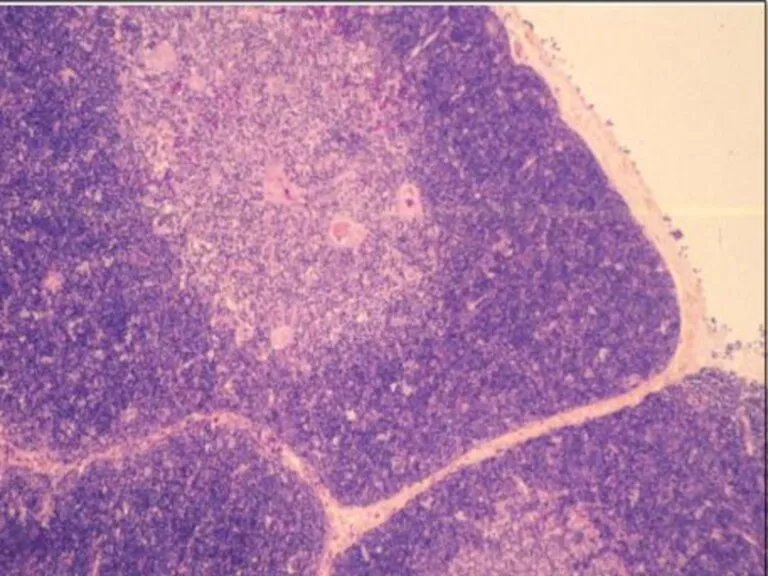
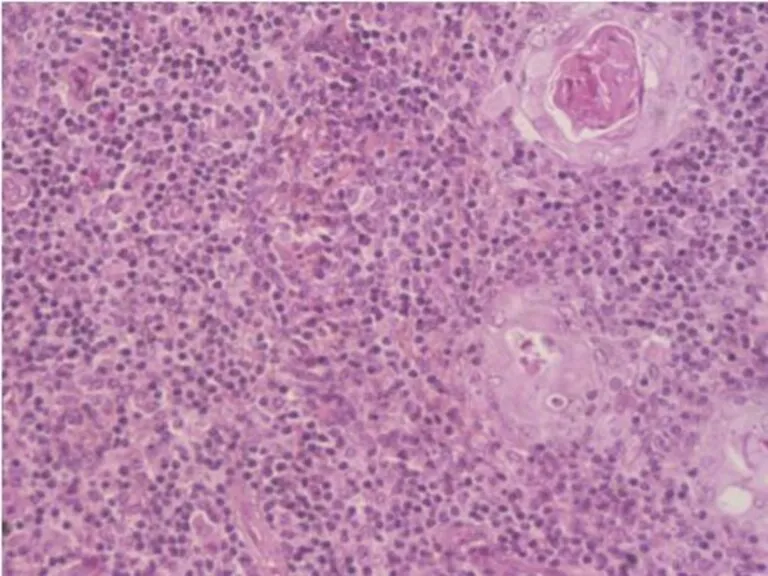
- 15. Thymus Capsule Lobules Cortex Medulla Hassal’s Corpuscles
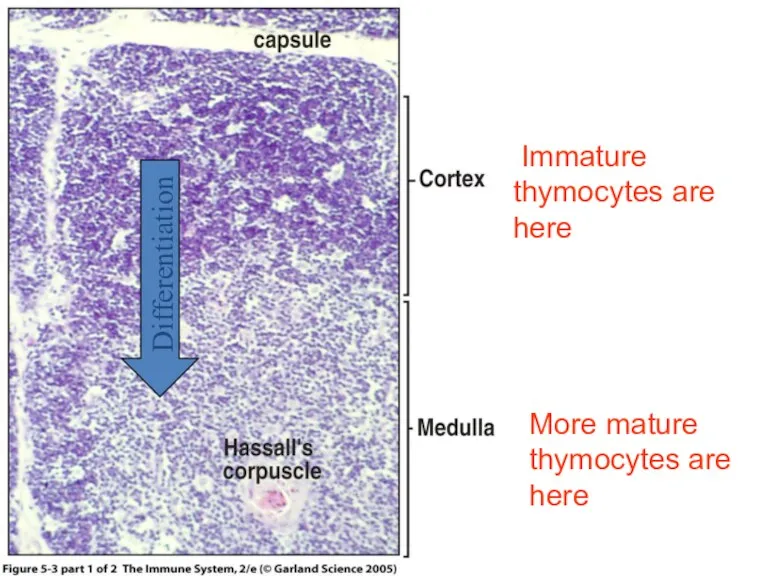
- 16. Cortex--- dark-staining periphery of each lobule. Small lymphocytes predominate Medulla is the light core of each
- 17. Figure 5-3 part 1 of 2 Differentiation Immature thymocytes are here More mature thymocytes are here
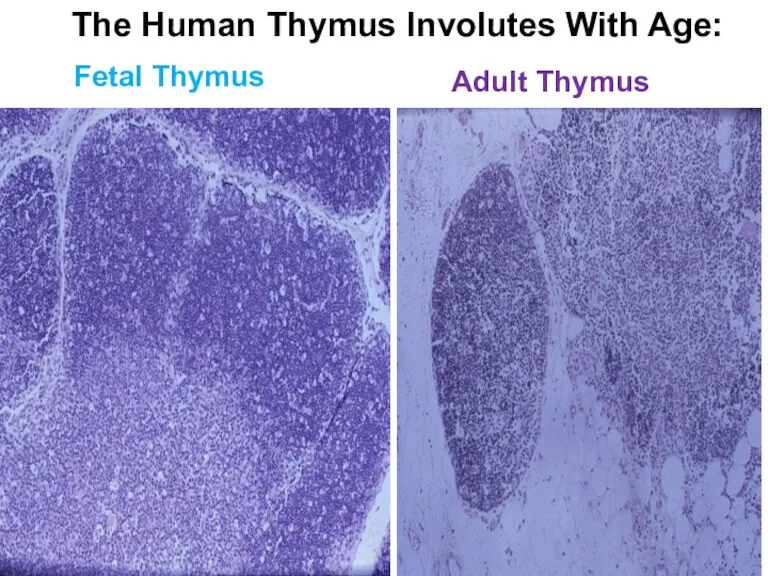
- 20. Adult Thymus Fetal Thymus The Human Thymus Involutes With Age:
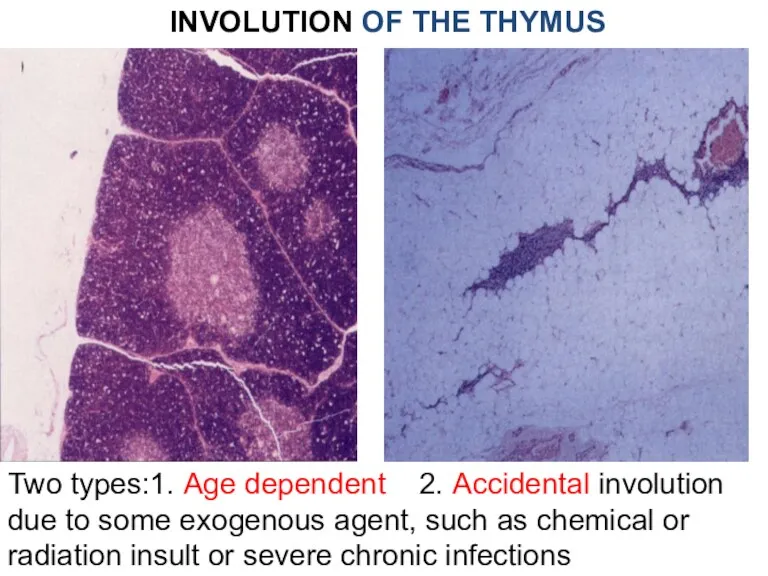
- 21. INVOLUTION OF THE THYMUS Two types:1. Age dependent 2. Accidental involution due to some exogenous agent,
- 22. Peripheral part of I. S.
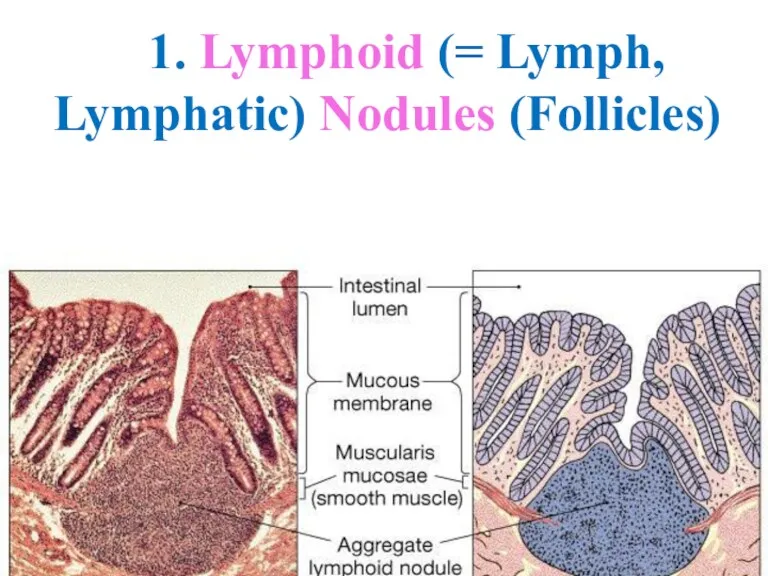
- 23. 1. Lymphoid (= Lymph, Lymphatic) Nodules (Follicles)
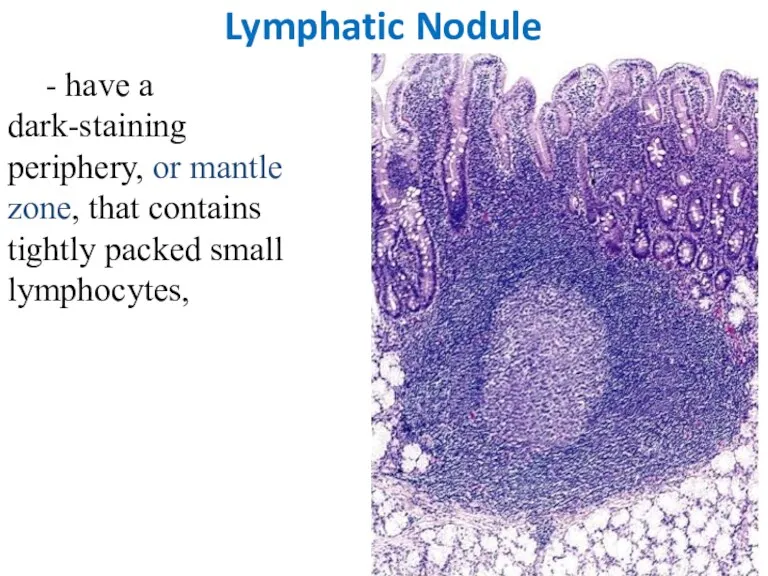
- 24. Lymphatic Nodule - have a dark-staining periphery, or mantle zone, that contains tightly packed small lymphocytes,
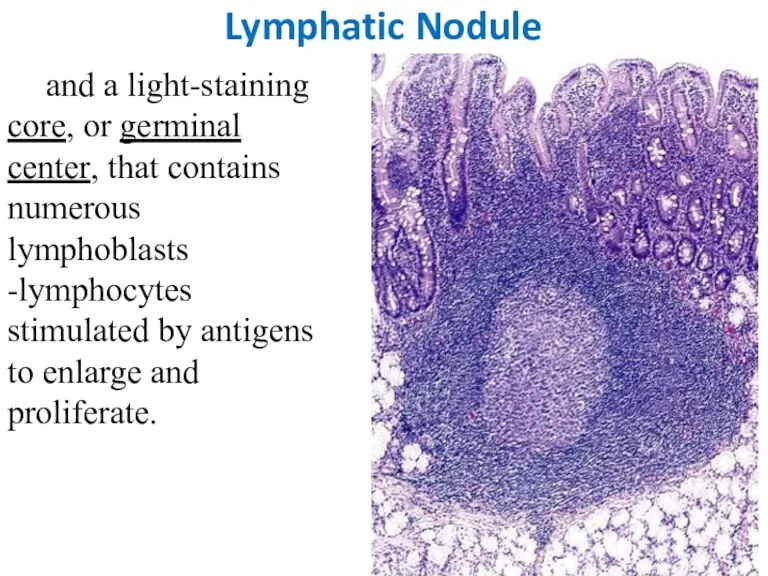
- 25. Lymphatic Nodule and a light-staining core, or germinal center, that contains numerous lymphoblasts -lymphocytes stimulated by
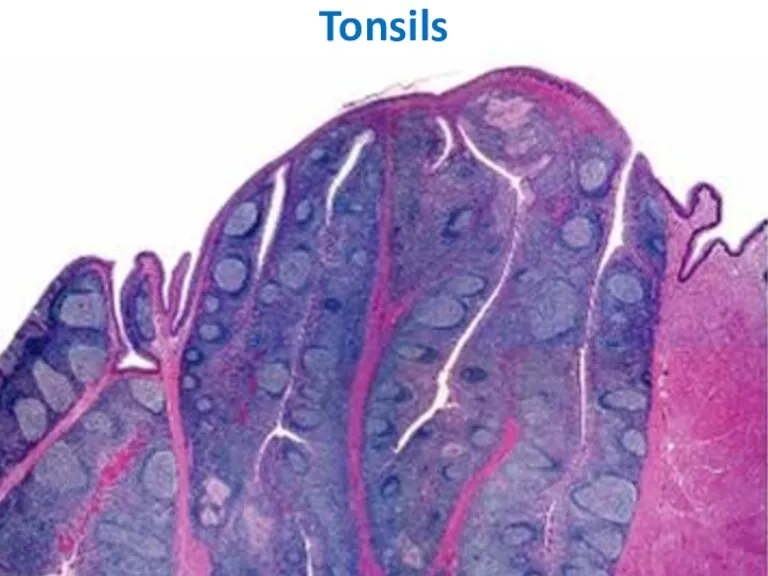
- 26. TONSILS underlie the epithelial lining of the mouth and pharynx. palatine tonsils (2), pharyngeal tonsil (1),
- 27. Tonsils
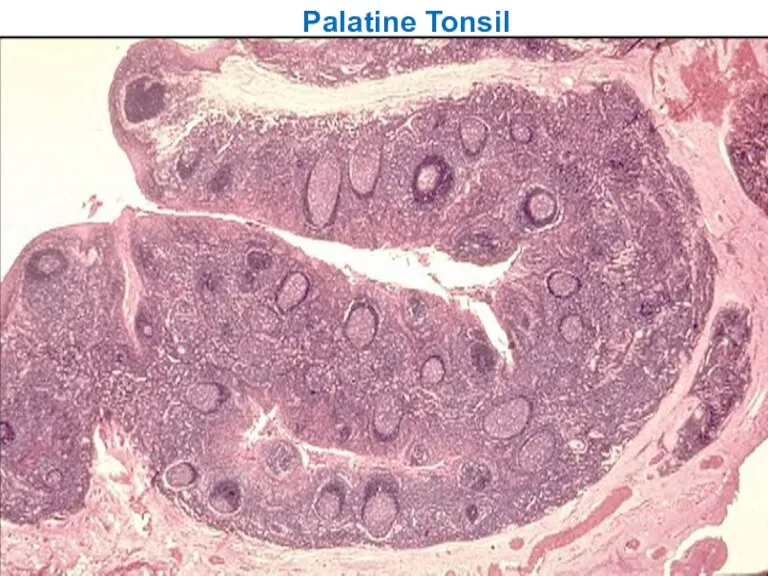
- 28. Palatine Tonsil
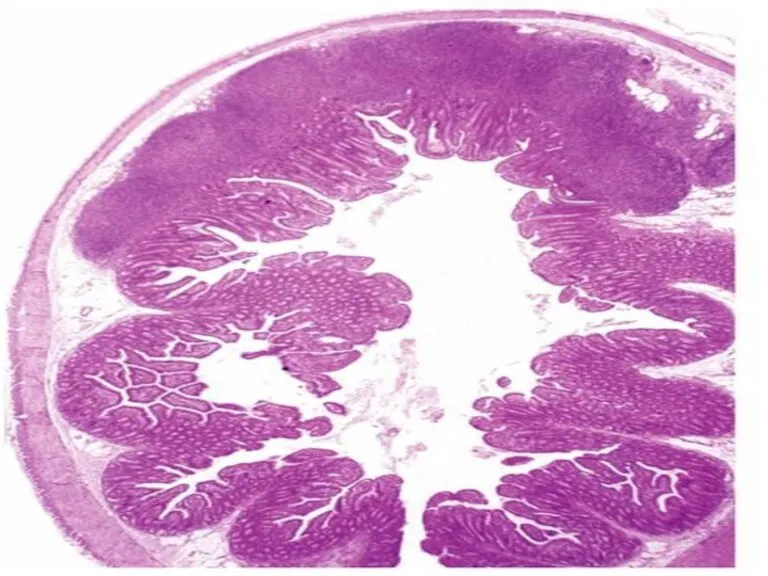
- 29. Peyer’s Patches Smaller aggregates present under mucous membrane: “Mucosa Associated Lymphoid Tissue” or MALT (in Digestive
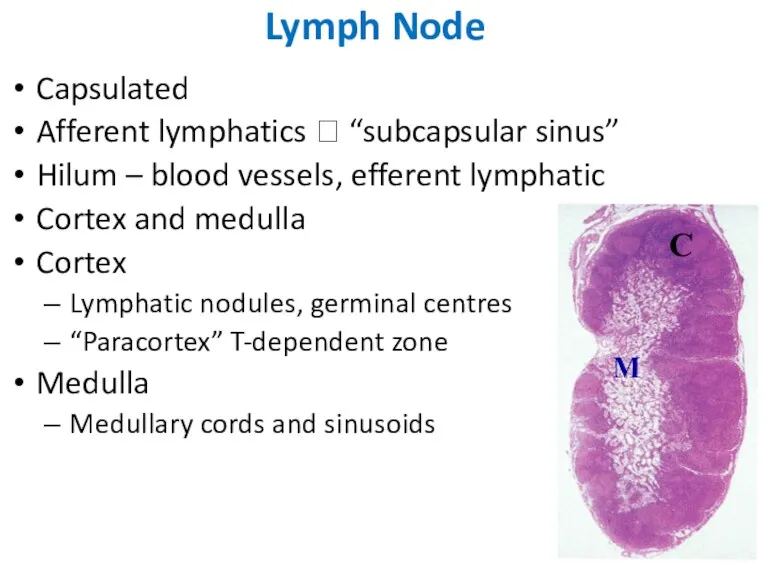
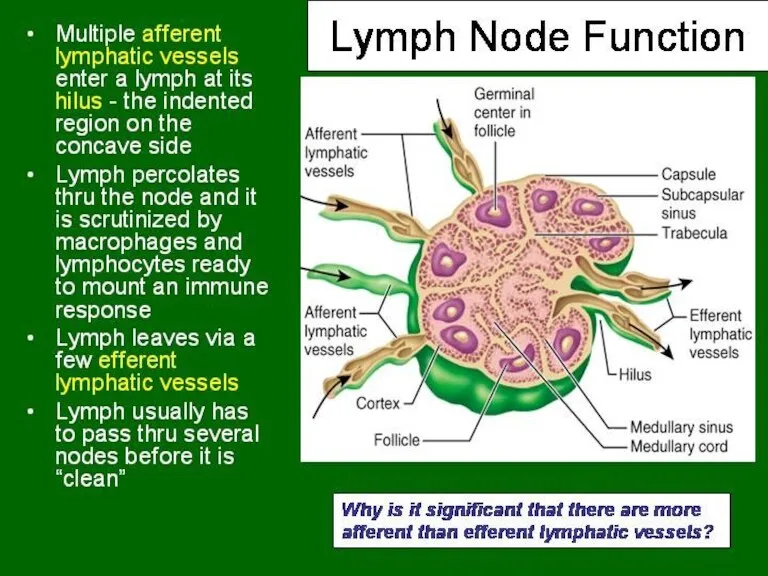
- 31. Capsulated Afferent lymphatics ? “subcapsular sinus” Hilum – blood vessels, efferent lymphatic Cortex and medulla Cortex
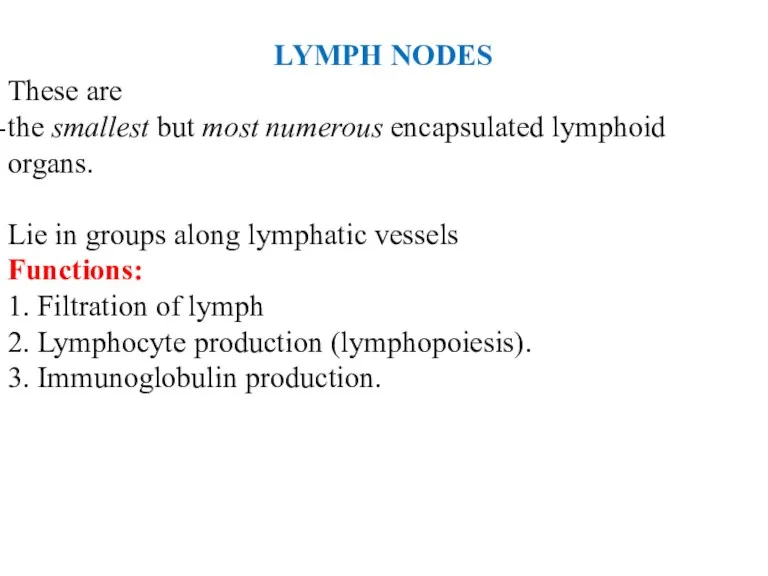
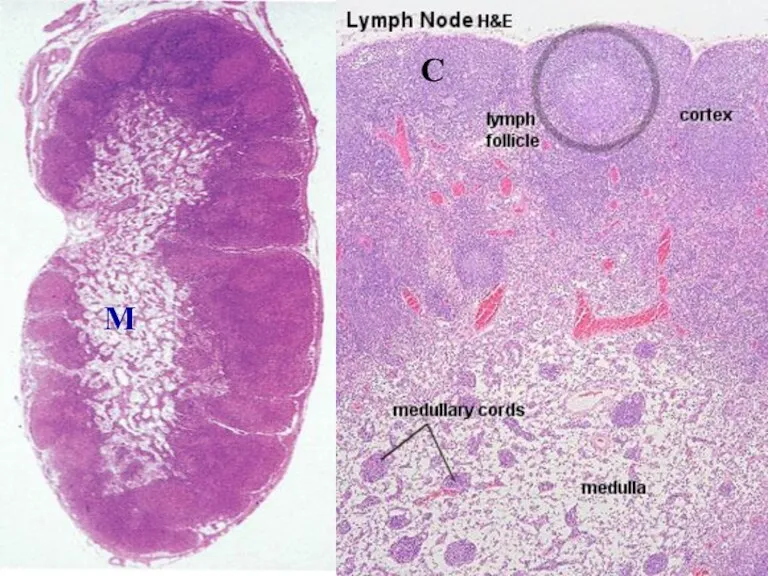
- 32. LYMPH NODES These are the smallest but most numerous encapsulated lymphoid organs. Lie in groups along
- 33. C M
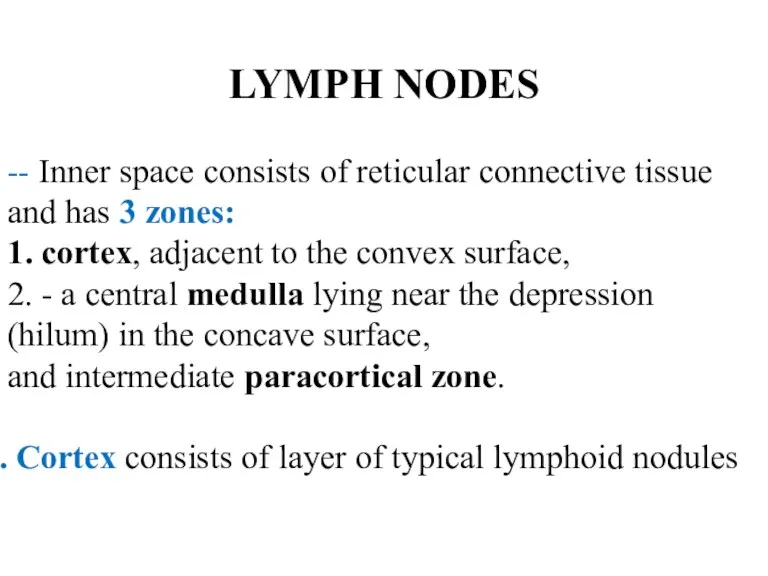
- 34. LYMPH NODES -- Inner space consists of reticular connective tissue and has 3 zones: 1. cortex,
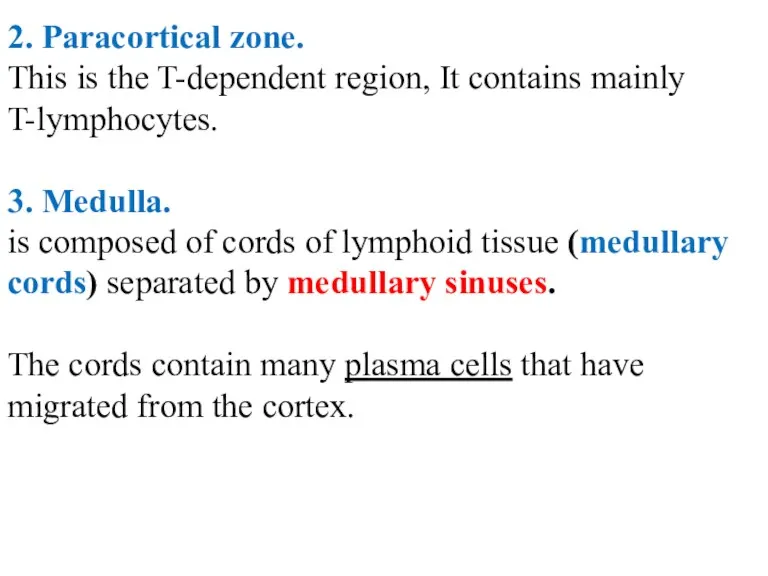
- 35. 2. Paracortical zone. This is the T-dependent region, It contains mainly T-lymphocytes. 3. Medulla. is composed
- 36. Lymphatic vessels inside LN are Sinuses. Types: subcapsular, peritrabecular, medullary
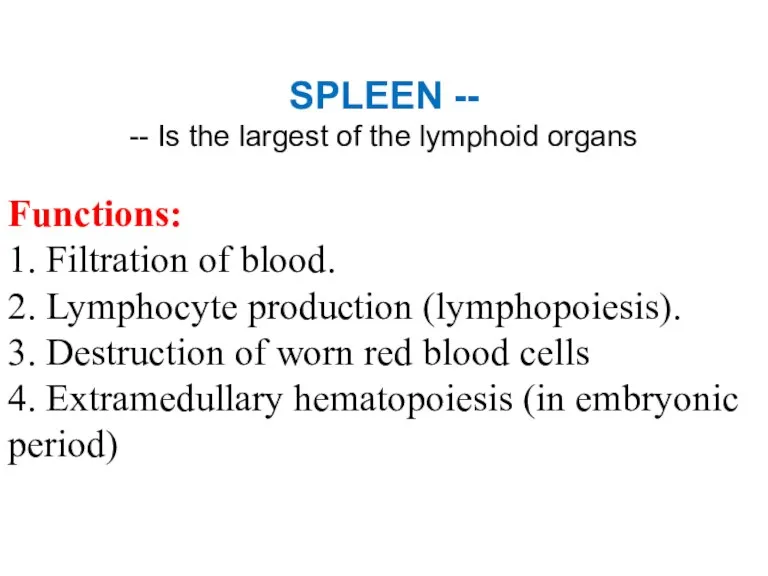
- 39. SPLEEN -- -- Is the largest of the lymphoid organs Functions: 1. Filtration of blood. 2.
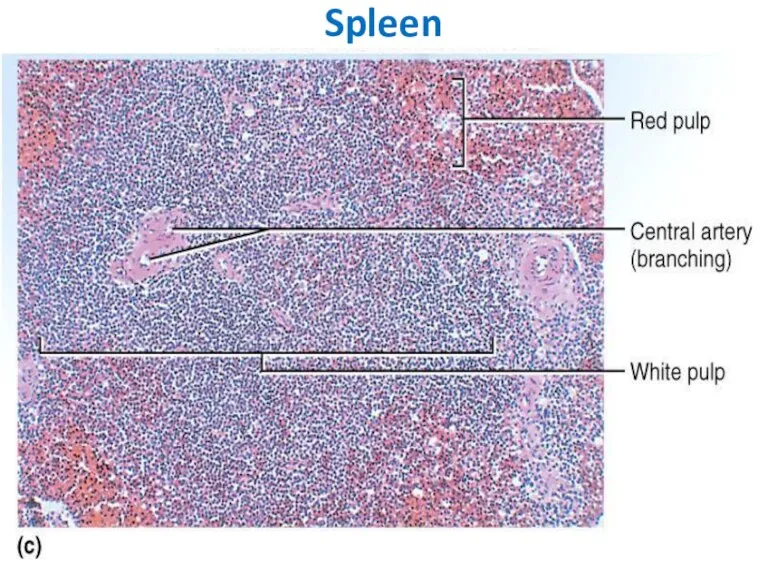
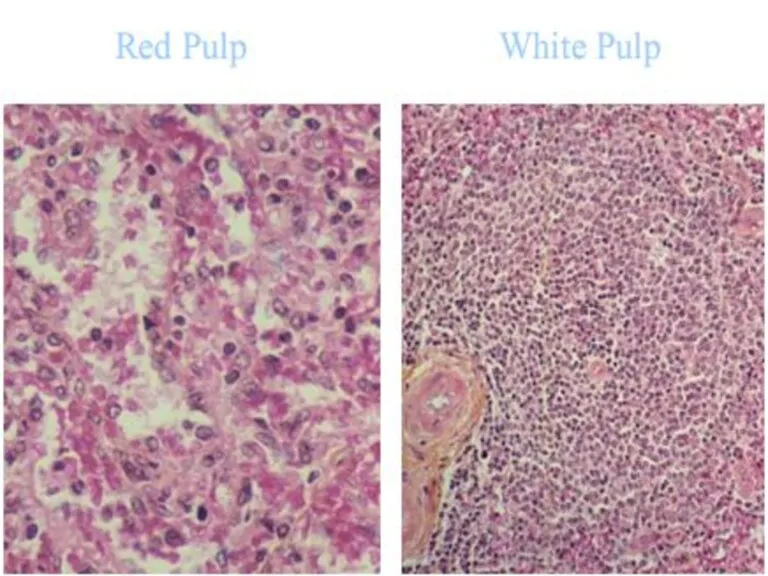
- 40. Inner space -- Splenic pulp -- is composed of: reticular tissue consisting of reticular cells and
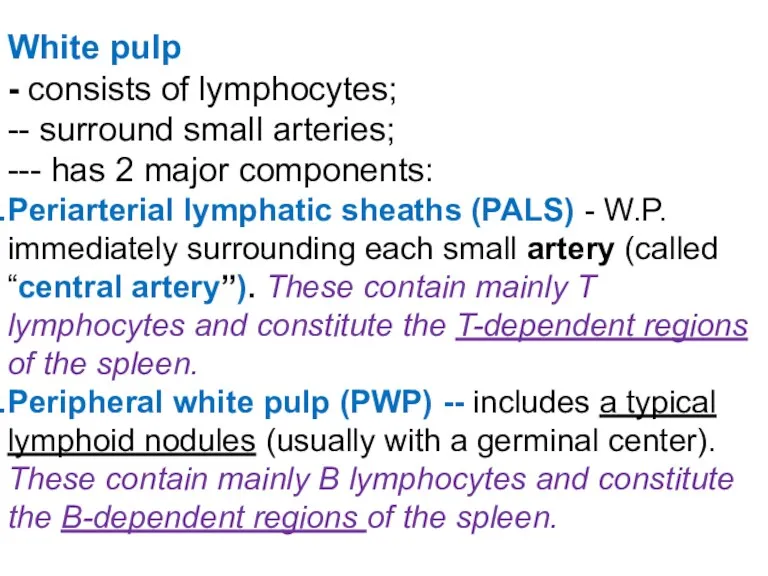
- 41. White pulp - consists of lymphocytes; -- surround small arteries; --- has 2 major components: Periarterial
- 42. Red pulp -- collects blood and makes up most of the spleen and also has 2
- 43. Red pulp -- collects blood and makes up most of the spleen and also has 2
- 44. Splenic sinusoids differ from common capillaries: - the lumen is wider and more irregular; - small
- 45. Spleen
- 48. Скачать презентацию

















 Строение стебля
Строение стебля Лекция № 1 Наука экология биосфера
Лекция № 1 Наука экология биосфера Размножение мхов
Размножение мхов Регуляция экспрессии генов
Регуляция экспрессии генов Классификация гормонов
Классификация гормонов Незаконное истребление животных
Незаконное истребление животных Питание и пищеварение
Питание и пищеварение Строение нервной системы
Строение нервной системы Эмбриональное развитие организмов
Эмбриональное развитие организмов Вендские жители Земли
Вендские жители Земли Движение крови в организме
Движение крови в организме Історія відкриття вітамінів
Історія відкриття вітамінів Вегетативное размножение покрытосеменных растений
Вегетативное размножение покрытосеменных растений Chromosomes. (Chapter 6.1)
Chromosomes. (Chapter 6.1) Регуляция пищеварения. Заболевания органов пищеварения и их предупреждение. Биология 8 кл (Пасечник)
Регуляция пищеварения. Заболевания органов пищеварения и их предупреждение. Биология 8 кл (Пасечник) Органы выделения у животных
Органы выделения у животных Голосовой аппарат
Голосовой аппарат Биология как наука. Экосистемы. Факультатив по биологии 10 -11 классы
Биология как наука. Экосистемы. Факультатив по биологии 10 -11 классы Живые клетки
Живые клетки Разбор заданий ВПР 5 класс
Разбор заданий ВПР 5 класс Борьба за существование
Борьба за существование Роль покрытосеменных в жизни человека
Роль покрытосеменных в жизни человека Введение в биохимию. Структура и функции белков
Введение в биохимию. Структура и функции белков Система двигательных действий и организация управления ими
Система двигательных действий и организация управления ими Цитогенетические основы размножения
Цитогенетические основы размножения Работа мышц
Работа мышц Животные саванн и полупустынь Южной Америки
Животные саванн и полупустынь Южной Америки Бионика. Биология – техника
Бионика. Биология – техника