Содержание
- 3. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Mycobacterium leprae (uncommon) Mycobacterium avium-intracellulaire Complex (MAC) or (M. avium) Important Human Pathogens
- 4. Lipid-Rich Cell Wall of Mycobacterium CMN Group: Unusual cell wall lipids (mycolic acids,etc.) (Purified Protein Derivative)
- 5. Acid-Fast (Kinyoun) Stain of Mycobacterium NOTE: cord growth (serpentine arrangement) of virulent strains
- 6. Photochromogenic Mycobacterium kansasii on Middlebrook Agar NOTE: Mycobacteria pathogenic for humans can be differentiated (Runyon Groups)
- 7. Improved Mycobacterial Isolation Medium
- 8. Eight Week Growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis on Lowenstein-Jensen Agar
- 9. Pathogenic Mycobacterium spp. BCG AIDS patients
- 10. Mycobacterial Clinical Syndromes
- 11. Diagram of a Granuloma NOTE: ultimately a fibrin layer develops around granuloma (fibrosis), further “walling off”
- 12. Laboratory Diagnosis of Mycobacterial Disease
- 13. Differential Characteristics of Commonly Isolated Mycobacterium spp.
- 15. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- 16. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infections
- 17. Incidence of Tuberculosis in USA
- 18. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infections (cont.) BCG (bacille Calmette-Guerin) = attenuated M. bovis Positive PPD + Chest X-Ray
- 19. Pneumonia Granuloma formation with fibrosis Caseous necrosis Tissue becomes dry & amorphous (resembling cheese) Mixture of
- 20. PPD Tuberculosis Skin Test Criteria PPD = Purified Protein Derivative from M. tuberculosis
- 21. Chest X-Ray of Patient with Active Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- 22. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Stained with Fluorescent Dye
- 24. Mycobacterium leprae
- 25. Mycobacterium leprae Infections
- 26. Mycobacterium leprae Infections (cont.)
- 27. Tuberculoid vs. Lepromatous Leprosy Clinical Manifestations and Immunogenicity
- 28. Lepromatous vs. Tuberculoid Leprosy
- 29. Lepromatous Leprosy (Early/Late Stages)
- 30. Lepromatous Leprosy Pre- and Post-Treatment
- 31. Clinical Progression of Leprosy
- 32. Effect of Cell-Mediated Immunity on Leprosy Clinical Outcome
- 34. Mycobacterium avium-intracellulaire Complex (MAC)
- 35. Mycobacterium avium-intracellulaire Infections
- 36. Mycobacterium avium-intracellulaire Infections
- 37. M. avium-intracellulaire Complex (MAC) Progression vs. CD4 Count in AIDS Patients
- 38. Mycobacterium avium-intracellulaire in Tissue Specimens Low Magnification High Magnification
- 40. REVIEW of Mycobacterium
- 41. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Mycobacterium leprae (uncommon) Mycobacterium avium-intracellulaire Complex (MAC) or (M. avium) Important Human Pathogens REVIEW
- 42. Lipid-Rich Cell Wall of Mycobacterium CMN Group: Unusual cell wall lipids (mycolic acids,etc.) (Purified Protein Derivative)
- 43. Pathogenic Mycobacterium spp. BCG AIDS patients REVIEW
- 44. Mycobacterial Clinical Syndromes REVIEW
- 45. Diagram of a Granuloma NOTE: ultimately a fibrin layer develops around granuloma (fibrosis), further “walling off”
- 46. Review of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- 47. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infections REVIEW
- 48. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infections (cont.) BCG (bacille Calmette-Guerin) = attenuated M. bovis Positive PPD + Chest X-Ray
- 49. Pneumonia Granuloma formation with fibrosis Caseous necrosis Tissue becomes dry & amorphous (resembling cheese) Mixture of
- 50. Review of Mycobacterium leprae
- 51. Mycobacterium leprae Infections REVIEW
- 52. Mycobacterium leprae Infections (cont.) REVIEW
- 53. Lepromatous vs. Tuberculoid Leprosy REVIEW
- 54. Lepromatous Leprosy (Early/Late Stages) REVIEW
- 55. Clinical Progression of Leprosy REVIEW
- 56. Effect of Cell-Mediated Immunity on Leprosy Clinical Outcome REVIEW
- 57. Review of Mycobacterium avium-intracellulaire Complex (M. avium)
- 58. Mycobacterium avium-intracellulaire Infections REVIEW
- 59. Mycobacterium avium-intracellulaire Infections REVIEW
- 60. M. avium-intracellulaire Complex (MAC) Progression vs. CD4 Count in AIDS Patients REVIEW
- 62. Скачать презентацию
 Радіобіологія організму людини і тварин. Радіочутливість тканин і органів організму людини і тварин
Радіобіологія організму людини і тварин. Радіочутливість тканин і органів організму людини і тварин Органические удобрения
Органические удобрения Роль пчелы, как общественного насекомого
Роль пчелы, как общественного насекомого Белки - 2. Тканевой обмен аминокислот
Белки - 2. Тканевой обмен аминокислот Способы размножения растений
Способы размножения растений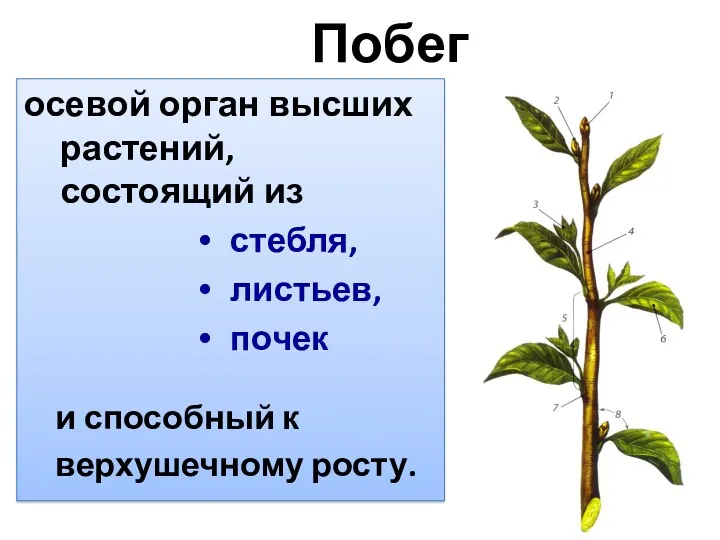 Побег - осевой орган высших растений
Побег - осевой орган высших растений Природа человека. 10 класс
Природа человека. 10 класс Як спілкуються тварини
Як спілкуються тварини Анатомо-физиологические особенности опорно-двигательной системы детей и подростков
Анатомо-физиологические особенности опорно-двигательной системы детей и подростков Организация наследственного аппарата в клетках человека в норме и при патологии. Мутации (геномные, хромосомные, генные)
Организация наследственного аппарата в клетках человека в норме и при патологии. Мутации (геномные, хромосомные, генные) Органы чувств человека
Органы чувств человека Презентация Рост и развитие растений.
Презентация Рост и развитие растений. Пищевая и биологическая ценность мяса. Санитарно-эпидемиологическое значение мяса
Пищевая и биологическая ценность мяса. Санитарно-эпидемиологическое значение мяса Тестовая работа по теме Корень. Строение корня, 6 класс.
Тестовая работа по теме Корень. Строение корня, 6 класс. Лекарственные растения Воронежской области
Лекарственные растения Воронежской области Квітка. Будова та різноманітність квіток
Квітка. Будова та різноманітність квіток Тема 12
Тема 12 f611e845-2141-4c61-a9b2-34e2049b0658
f611e845-2141-4c61-a9b2-34e2049b0658 Явление хемосинтеза
Явление хемосинтеза Психофизиология в системе наук о человеке. (Тема 1)
Психофизиология в системе наук о человеке. (Тема 1) Кошки и собаки
Кошки и собаки Строение и функции белков
Строение и функции белков Этапы онтогенеза человека. Генетическое определение пола
Этапы онтогенеза человека. Генетическое определение пола презентация по биологии 7 класс Плоские черви
презентация по биологии 7 класс Плоские черви Мал өсіру әдістері
Мал өсіру әдістері Физиология и экология диатомовых водорослей
Физиология и экология диатомовых водорослей Человек как результат биологической и социальной революции
Человек как результат биологической и социальной революции Продолговатый мозг. Ядра
Продолговатый мозг. Ядра