Содержание
- 2. Lesson objectives: Establish the connection between DNA structure and its function; Describe the chemical structure of
- 3. Creating an information scheme that should describe the structure and function of DNA
- 4. Compare your schema with video info https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o_-6JXLYS-k
- 5. Why do we study DNA? We study DNA for many reasons, e.g., its central importance to
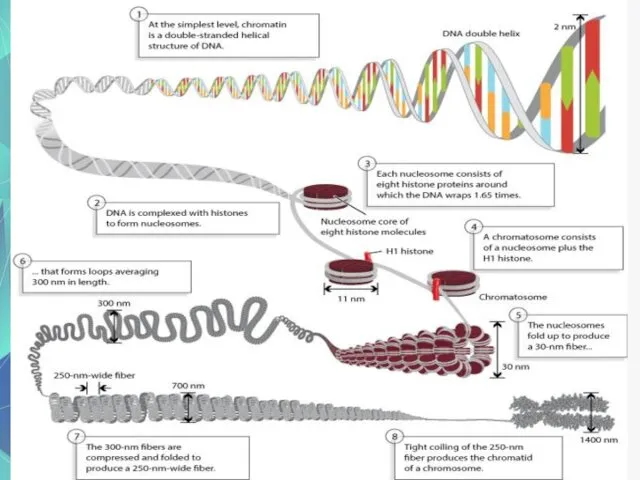
- 6. Chromosomes and DNA Our genes are on our chromosomes. Chromosomes are made up of a chemical
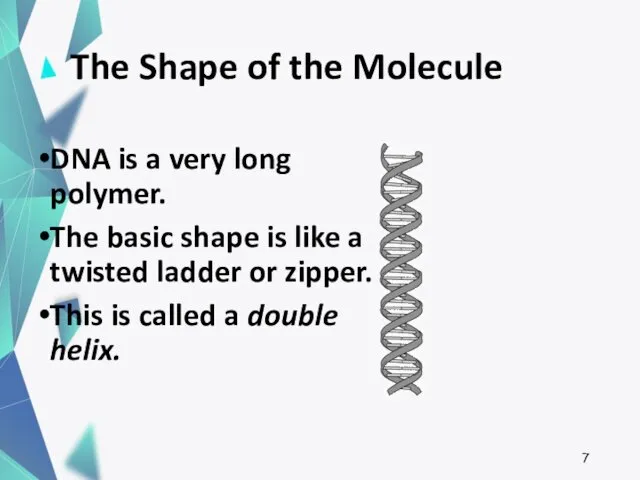
- 7. The Shape of the Molecule DNA is a very long polymer. The basic shape is like
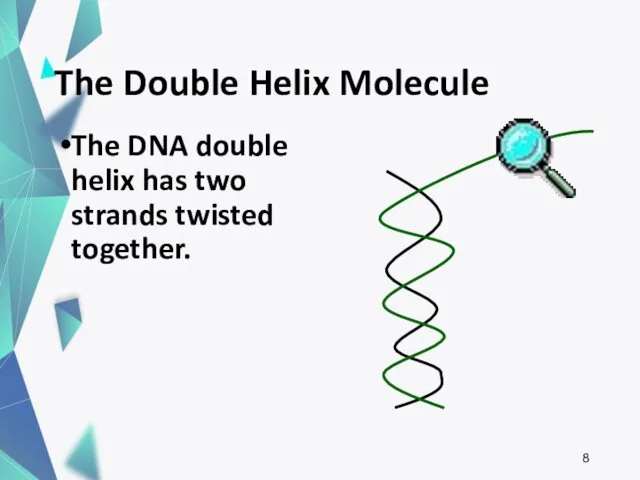
- 8. The Double Helix Molecule The DNA double helix has two strands twisted together.
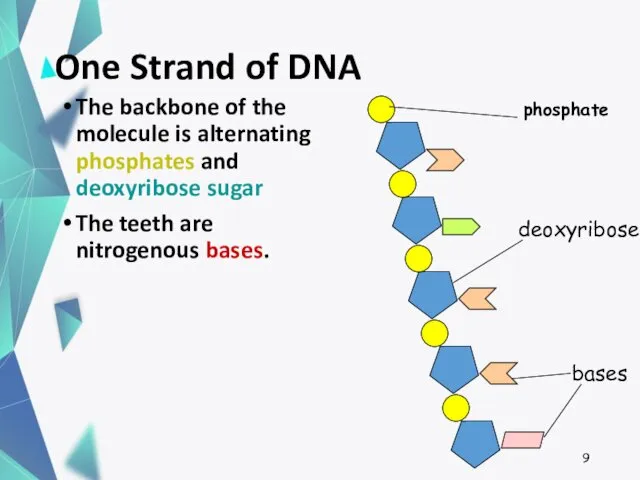
- 9. One Strand of DNA The backbone of the molecule is alternating phosphates and deoxyribose sugar The
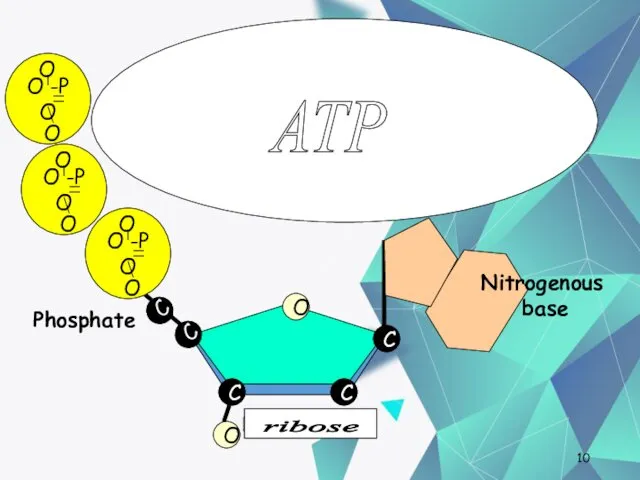
- 10. Nucleotides One deoxyribose together with its phosphate and base make a nucleotide. C C C O
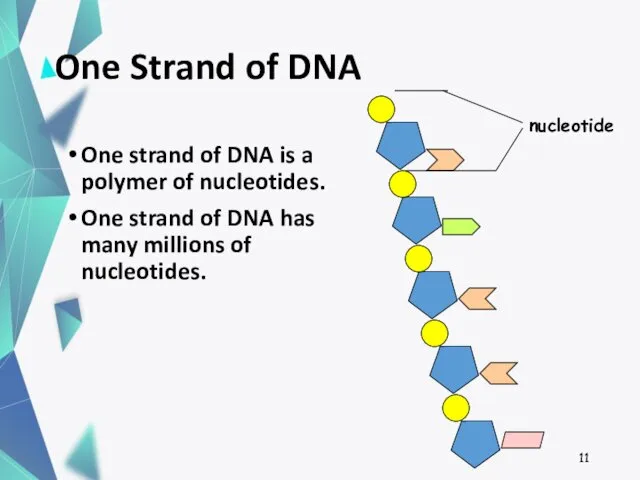
- 11. One Strand of DNA One strand of DNA is a polymer of nucleotides. One strand of
- 12. Four nitrogenous bases Cytosine C Thymine T Adenine A Guanine G DNA has four different bases:
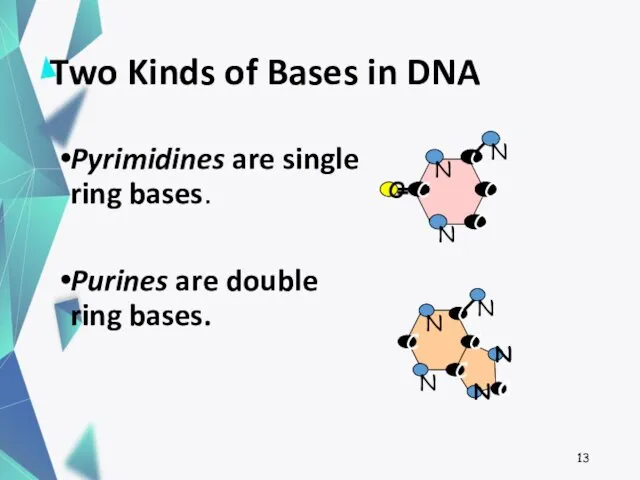
- 13. Two Kinds of Bases in DNA Pyrimidines are single ring bases. Purines are double ring bases.
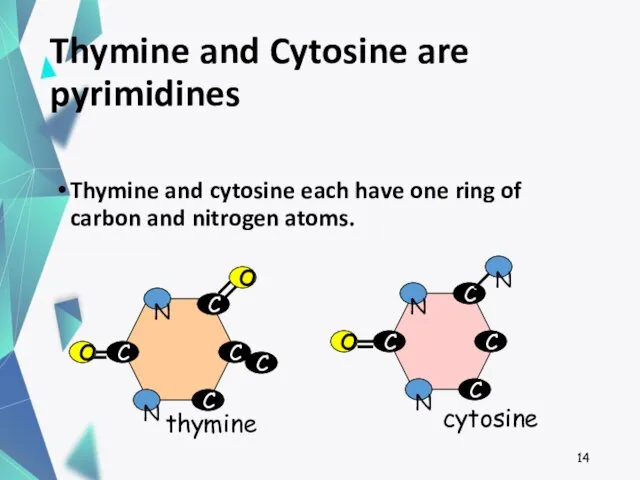
- 14. Thymine and Cytosine are pyrimidines Thymine and cytosine each have one ring of carbon and nitrogen
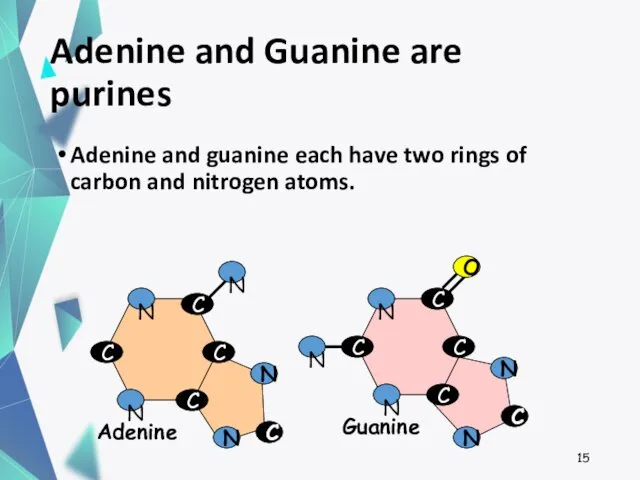
- 15. Adenine and Guanine are purines Adenine and guanine each have two rings of carbon and nitrogen
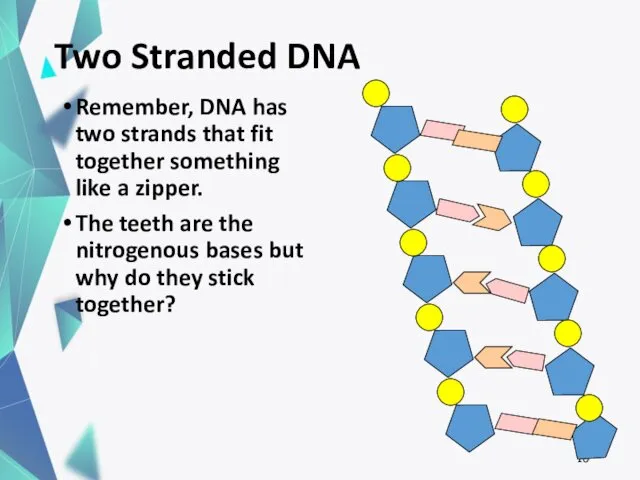
- 16. Two Stranded DNA Remember, DNA has two strands that fit together something like a zipper. The
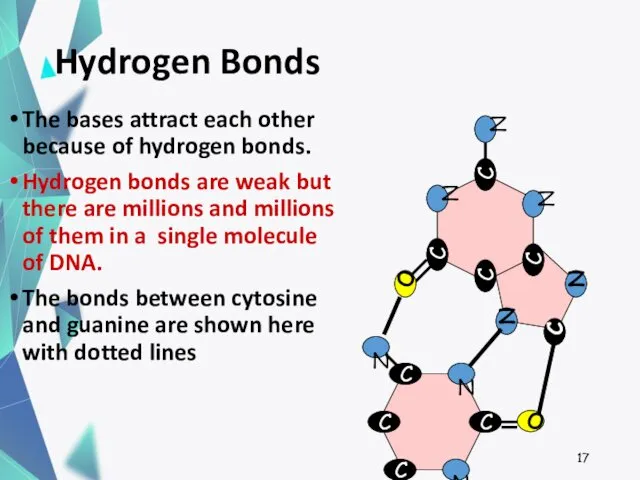
- 17. Hydrogen Bonds The bases attract each other because of hydrogen bonds. Hydrogen bonds are weak but
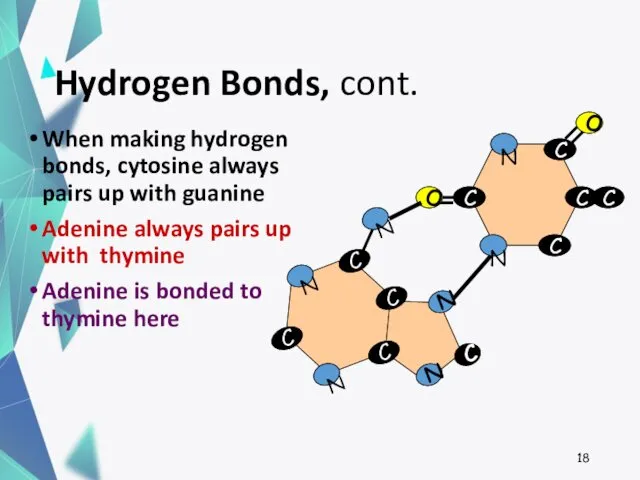
- 18. Hydrogen Bonds, cont. When making hydrogen bonds, cytosine always pairs up with guanine Adenine always pairs
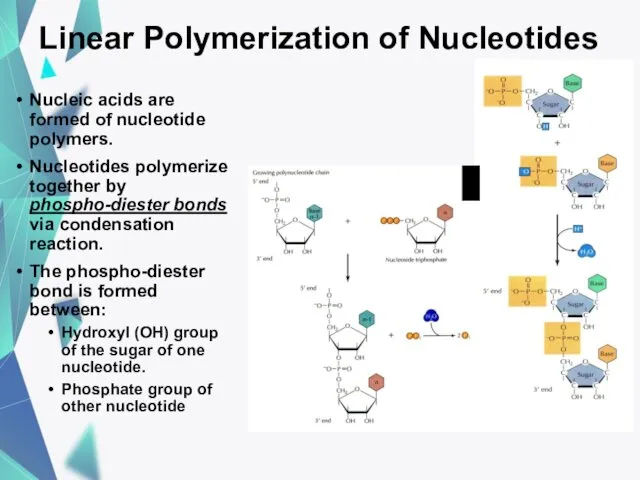
- 19. Linear Polymerization of Nucleotides Nucleic acids are formed of nucleotide polymers. Nucleotides polymerize together by phospho-diester
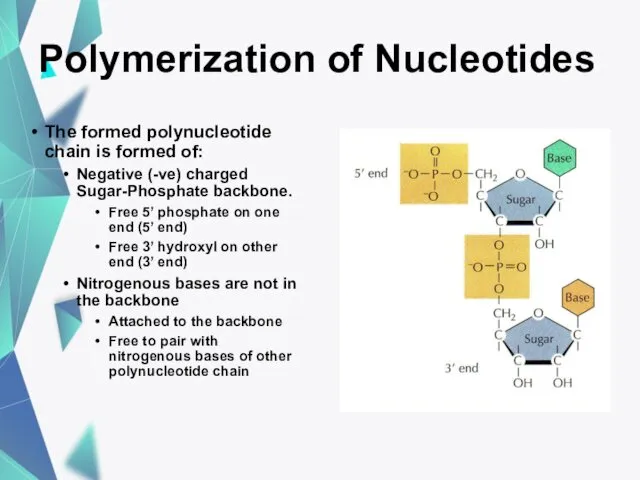
- 20. Polymerization of Nucleotides The formed polynucleotide chain is formed of: Negative (-ve) charged Sugar-Phosphate backbone. Free
- 21. Polymerization of Nucleotides Nucleic acids are polymers of nucleotides. The nucleotides formed of purine or pyrimedine
- 22. DNA by the Numbers Each cell has about 2 m of DNA. The average human has
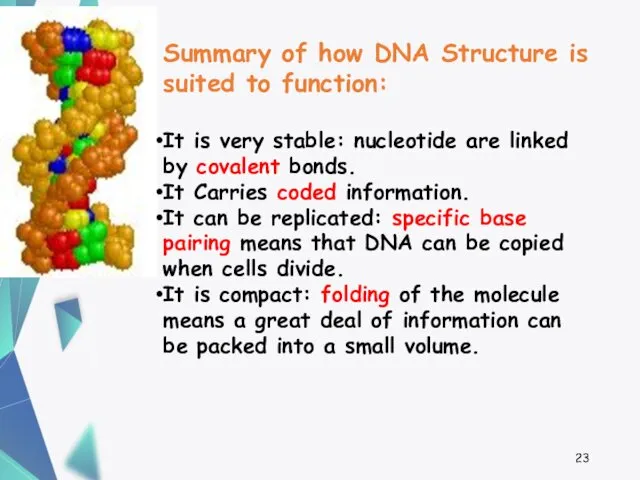
- 23. Summary of how DNA Structure is suited to function: It is very stable: nucleotide are linked
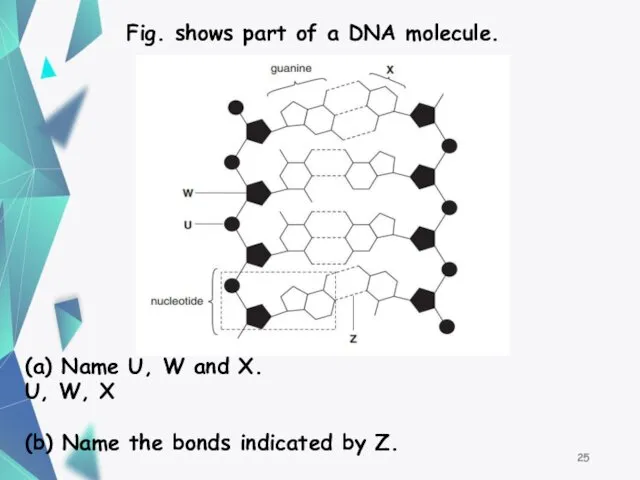
- 25. Fig. shows part of a DNA molecule. (a) Name U, W and X. U, W, X
- 27. Скачать презентацию





 Витамины, витаминоподобные вещества и антивитамины
Витамины, витаминоподобные вещества и антивитамины Соцветие. Значение соцветий
Соцветие. Значение соцветий Компоненты иммунологических реакций
Компоненты иммунологических реакций Почвенная среда
Почвенная среда Моя кошка Муся. Фото
Моя кошка Муся. Фото Солтүстік Қазақстан облысы жағдайында түйебұршақ дақылдарын өсіру технологиясының ерекшеліктері
Солтүстік Қазақстан облысы жағдайында түйебұршақ дақылдарын өсіру технологиясының ерекшеліктері Ein vitamin, das für die gesundheit von tieren und menschen notwendig ist
Ein vitamin, das für die gesundheit von tieren und menschen notwendig ist Биотехнология: возникновение и развитие
Биотехнология: возникновение и развитие Введение в физиологию. Возбуждение. сокращение. Физиология клетки
Введение в физиологию. Возбуждение. сокращение. Физиология клетки Разнообразие цветов. Строение цветка
Разнообразие цветов. Строение цветка Геоботаническое описание Парка Победы в п. Большеречья
Геоботаническое описание Парка Победы в п. Большеречья Класс млекопитающие (звери)
Класс млекопитающие (звери) Презентация по биологии для учащихся 8-го класса на тему: Эволюция человека
Презентация по биологии для учащихся 8-го класса на тему: Эволюция человека Биотехнологии в современном мире
Биотехнологии в современном мире Витамины группы B
Витамины группы B Sense organs. Ear and nose
Sense organs. Ear and nose Органы выделения у животных в процессе эволюционного развития
Органы выделения у животных в процессе эволюционного развития Размножение и оплодотворение растений
Размножение и оплодотворение растений внеклассное мероприятие Здоровье человека и продолжительность жизни
внеклассное мероприятие Здоровье человека и продолжительность жизни Селекция
Селекция Растительный мир Курской области
Растительный мир Курской области Строение Земли
Строение Земли Патофизиология апоптоза
Патофизиология апоптоза Використання радіоактивних ізотопів як індикаторів у тваринництві, археології
Використання радіоактивних ізотопів як індикаторів у тваринництві, археології Положение человека в системе животного мира. Стадии антропогенеза
Положение человека в системе животного мира. Стадии антропогенеза Отряд Хоботные
Отряд Хоботные Квітка. Будова квітки
Квітка. Будова квітки Хемосинтез (автотрофное питание)
Хемосинтез (автотрофное питание)