Содержание
- 2. PLAN I.Introduction Synapse II.Main Part Structure Classification synapses III.Conclusion IV.References
- 3. The word "synapse" – from the Greek synapsis (συνάπσις), meaning "conjunction", in turn from συνάπτεὶν (συν("together")
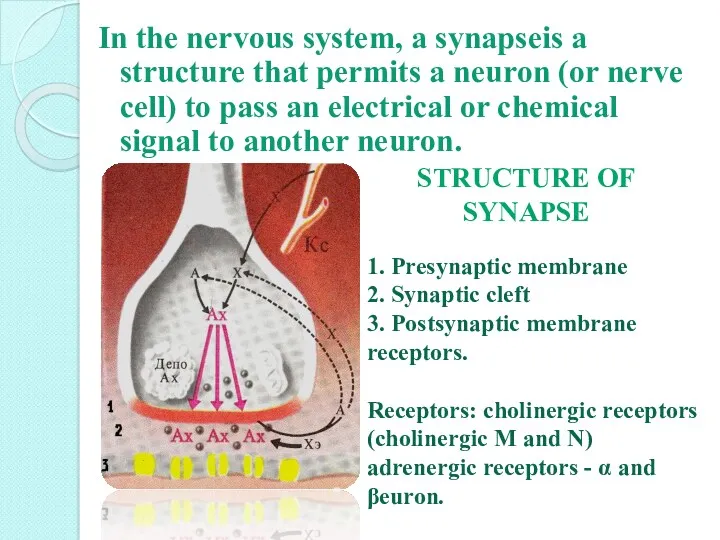
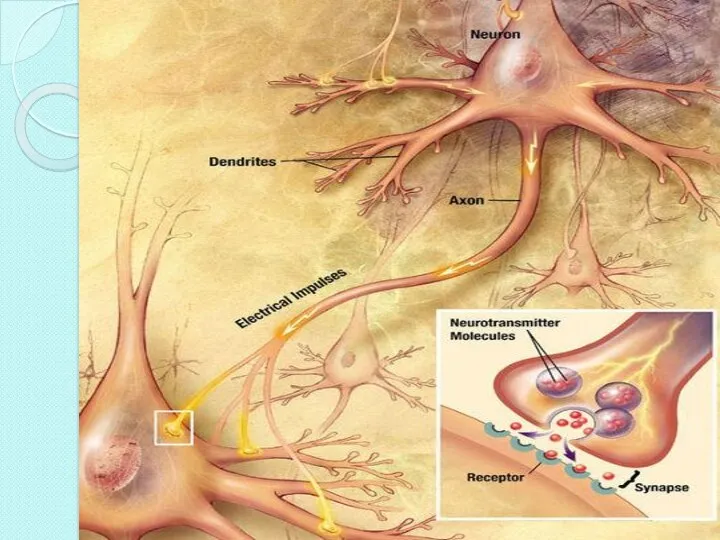
- 4. In the nervous system, a synapseis a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to
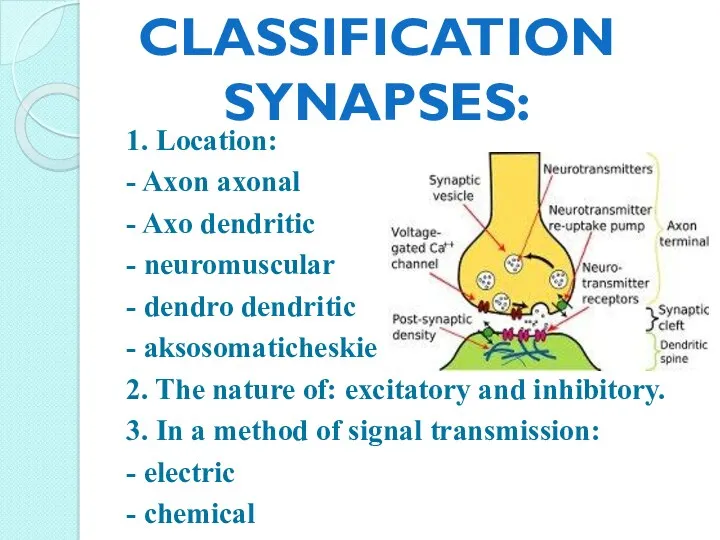
- 5. 1. Location: - Axon axonal - Axo dendritic - neuromuscular - dendro dendritic - aksosomaticheskie 2.
- 6. Types of interfaces Synapses can be classified by the type of cellular structures serving as the
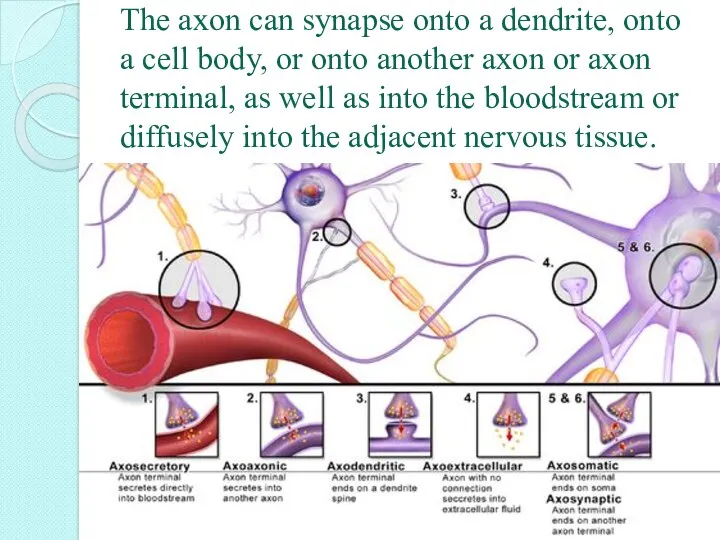
- 7. The axon can synapse onto a dendrite, onto a cell body, or onto another axon or
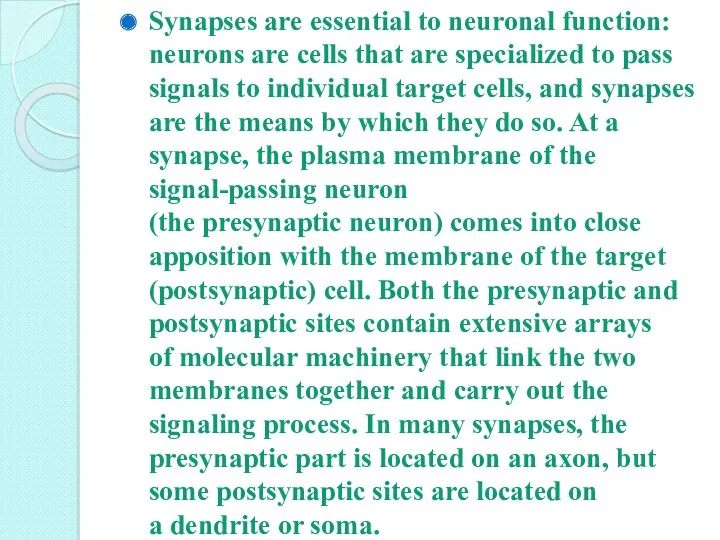
- 8. Synapses are essential to neuronal function: neurons are cells that are specialized to pass signals to
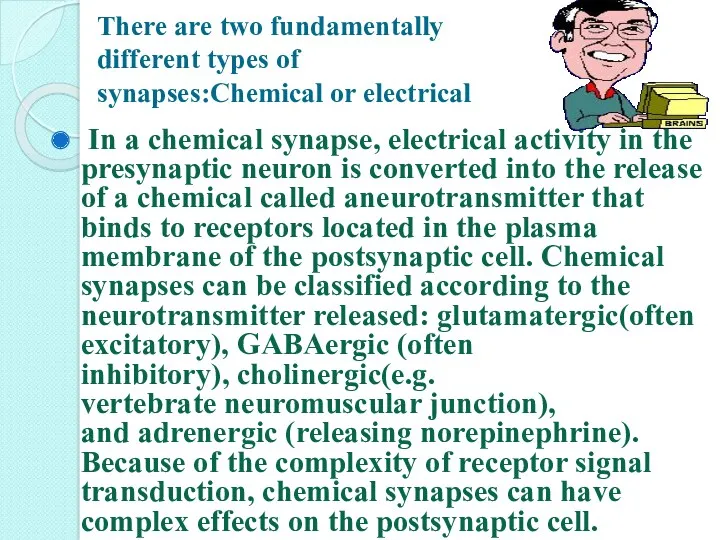
- 10. There are two fundamentally different types of synapses:Chemical or electrical In a chemical synapse, electrical activity
- 11. In an electrical synapse, the presynaptic and postsynaptic cell membranes are connected by special channels called
- 12. Physiological properties of chemical synapses: Excitation is passed through mediators. Have bilateral conduction of excitation. Fatigue
- 14. Скачать презентацию




 Презентация урока 6 класс ФГОС.
Презентация урока 6 класс ФГОС. Многообразие Трематод и Цестод
Многообразие Трематод и Цестод Клетка. Клеточная теория
Клетка. Клеточная теория Общая характеристика типа Моллюски
Общая характеристика типа Моллюски Розмноження медоносних бджіл
Розмноження медоносних бджіл Методы изучения природы
Методы изучения природы Семёйства цветковых растений
Семёйства цветковых растений Микробиология с основами вирусологии. Строение клетки прокариот. (Лекция 1-2)
Микробиология с основами вирусологии. Строение клетки прокариот. (Лекция 1-2) Ген. История развития представлений о гене
Ген. История развития представлений о гене Геоботаника
Геоботаника Происхождение жизни на Земле и эволюция
Происхождение жизни на Земле и эволюция Метаболизм аминокислот. Нарушения метаболизма некоторых аминокислот
Метаболизм аминокислот. Нарушения метаболизма некоторых аминокислот Одноцепочечные РНК-вирусы
Одноцепочечные РНК-вирусы Сосуды малого и большого кругов кровообращения
Сосуды малого и большого кругов кровообращения Исследование влияния листового опада на состав и биотоп почвы
Исследование влияния листового опада на состав и биотоп почвы презентация Многообразие рыб, их роль в природе
презентация Многообразие рыб, их роль в природе Семейство Куньи
Семейство Куньи Классификация лиан. Лианы как жизненная форма
Классификация лиан. Лианы как жизненная форма Қазақстандағы ғарыштық биотехнологияның даму бағыттары
Қазақстандағы ғарыштық биотехнологияның даму бағыттары Мимические мышцы лица
Мимические мышцы лица Мои дельфиниумы
Мои дельфиниумы Основы косметологии MIXIT (new)
Основы косметологии MIXIT (new) Анатомо-физиологические особенности органов кровообращения у детей и подростков
Анатомо-физиологические особенности органов кровообращения у детей и подростков внеклассное мероприятие Здоровье человека и продолжительность жизни
внеклассное мероприятие Здоровье человека и продолжительность жизни Кожный, вкусовой и обонятельный анализаторы
Кожный, вкусовой и обонятельный анализаторы Факторы влияющие на микроорганизмы
Факторы влияющие на микроорганизмы Изготовление и рассматривание микропрепарата кожицы лука
Изготовление и рассматривание микропрепарата кожицы лука Моногибридное скрещивание
Моногибридное скрещивание