Содержание
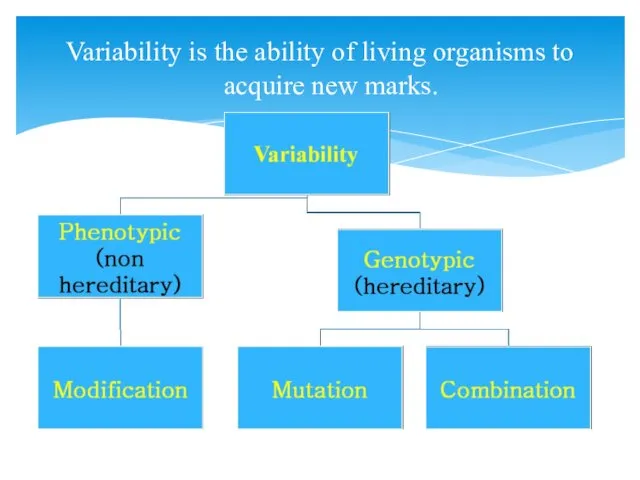
- 2. Variability is the ability of living organisms to acquire new marks.
- 3. due to changes in phenotype under the direct influence of factors of the external environment without
- 4. Ensures adaptation of the organism to the habitats environment Knowledge of the laws of phenotypic behavior
- 5. Modifications - non-genetic changes in phenotype, develop under the influence of environmental factors, adapt to the
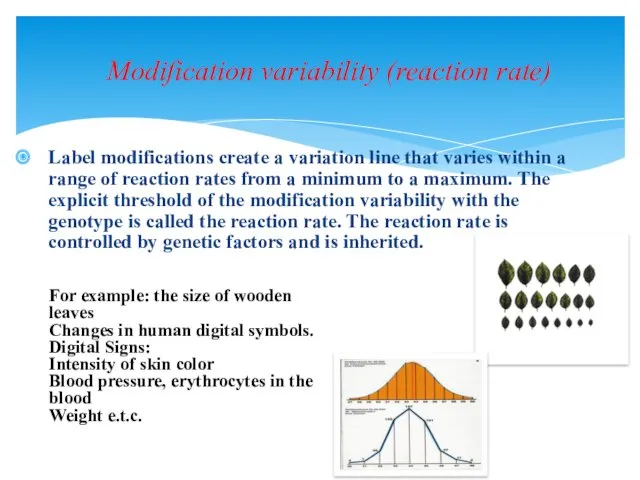
- 6. Modification variability (reaction rate) Label modifications create a variation line that varies within a range of
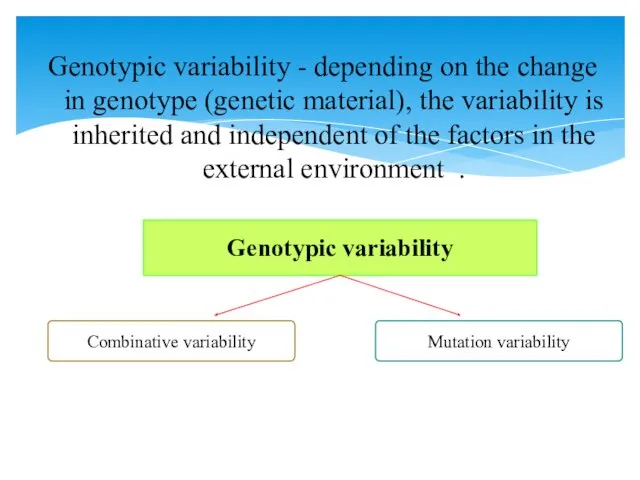
- 7. Genotypic variability - depending on the change in genotype (genetic material), the variability is inherited and
- 8. Combinative variablity - variablity due to recombination (combination) of parental genes. In combinative variability, the combination
- 9. Mutations (Latin mutatio) - change of genetic material under influence of external and internal factors. The
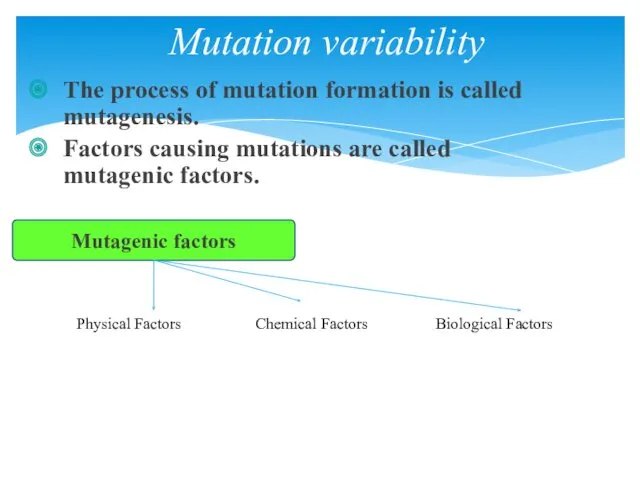
- 10. The process of mutation formation is called mutagenesis. Factors causing mutations are called mutagenic factors. Mutation
- 11. Physical: Different types of rays, temperature, humidity, etc. Chemical: a) natural organic and inorganic substances (nitrates,
- 12. 1.1. Depending on the causes Spontaneous or natural mutations - develop under the influence of natural
- 14. Скачать презентацию






 презентация для 7 класса Основные группы рыб
презентация для 7 класса Основные группы рыб Видоизменения листьев
Видоизменения листьев Роль комнатных растений в жизни человека и уход за ними
Роль комнатных растений в жизни человека и уход за ними Пингвины (1)
Пингвины (1) Гербарии растений, содержащих алкалоиды
Гербарии растений, содержащих алкалоиды Тамырҙар. 4-се класс
Тамырҙар. 4-се класс Строение и функции корня
Строение и функции корня Фиалки. Виды фиалок
Фиалки. Виды фиалок Что такое листопад
Что такое листопад Тағамдық қышқылдарды ферменттік әдіспен технологиясы
Тағамдық қышқылдарды ферменттік әдіспен технологиясы Генно-инженерно-модифицированные организмы. Методы детекции и идентификации
Генно-инженерно-модифицированные организмы. Методы детекции и идентификации Плауны и Хвощи
Плауны и Хвощи Дәріс №6. Ақуыздарды микроорганизмдер синтезі жолымен алу
Дәріс №6. Ақуыздарды микроорганизмдер синтезі жолымен алу Птицы в приусадебном хозяйстве
Птицы в приусадебном хозяйстве Органолептические свойства молока
Органолептические свойства молока Шеміршекті балықтар: акулалар және скаттар. Бекіре балықтар, маңызы және оларды қалпына келтіру шаралары
Шеміршекті балықтар: акулалар және скаттар. Бекіре балықтар, маңызы және оларды қалпына келтіру шаралары Звери и птицы весной
Звери и птицы весной Живые ископаемые
Живые ископаемые Селекция микроорганизмов. Биотехнология
Селекция микроорганизмов. Биотехнология Болотные и водные растения
Болотные и водные растения Вплив субстрату та біостимуляторів на ріст і розвиток розсади огірка
Вплив субстрату та біостимуляторів на ріст і розвиток розсади огірка Hierarchy of Biological Organization. Chemical Level
Hierarchy of Biological Organization. Chemical Level Тип Плоские Черви
Тип Плоские Черви Тип Губки
Тип Губки Вредители молодняков. (Лекция 6)
Вредители молодняков. (Лекция 6) Эволюция регуляторных и метаболических путей
Эволюция регуляторных и метаболических путей Вивисекция. Опыты на животных
Вивисекция. Опыты на животных Почвенное (минеральное) питание растений
Почвенное (минеральное) питание растений