Содержание
- 2. Course Objectives Prepare you to work in IT “real world” Understand what IT’s roles are in
- 3. Course Information Textbook M: Information Systems, 6h ed., Baltzan ISBN 9781265373931 Other materials (incl. today’s lecture)
- 4. Course Information Course Outline: Lecture schedule Marking policy Contract between us Evaluation Online quizzes, optional final
- 5. Course Information NO make-up for missed work without valid reason and email in advance ggorsline@georgebrown.ca :
- 6. Course Information Lectures are recorded Lectures are interactive Use chat to ask questions Address to everyone
- 7. Instructor Prof. George Gorsline MA, International Law; BA, Political Science Contact information: Email: ggorsline@georgebrown.ca Phone/Skype by
- 8. Chapter 0 Business and Business Information Systems
- 9. A business is an individual or an organization that tries to earn a profit by providing
- 10. Profit is the excess of revenues (the proceeds from the sale of goods and services) over
- 11. Non-profit organizations Government Education Charities and other non-profit organizations (NPO) Still run like a business Success
- 12. Business Characteristics To many businesses, success is more than profit Social responsibility Environmentally responsible Community service
- 13. Business Characteristics For a business to succeed it needs: Equipment and raw materials to turn into
- 14. Managing a Business Management is a process designed to achieve an organization’s objectives by using its
- 15. Four Management Functions There are four management functions: Planning Organizing Leading Controlling
- 16. 1. Planning Planning is the process of determining the organization’s objectives (goals) and deciding how to
- 17. Purpose of Setting Goals Provides direction, guidance and motivation Assists in allocating resources Helps to define
- 18. Setting Business Goals Goals are performance targets Goals should be SMART Specific Measureable Actionable Realistic Time-framed
- 19. Mission Statement Mission is the statement of an organization’s fundamental purpose, basic philosophy and values Mission
- 20. Mission Statement (cont.) Star Trek’s Enterprise Mission Statement: “Space: the final frontier. These are the voyages
- 21. Plans Strategic Multi-year Directional Operational Current budget year Includes Tactical plans (e.g. in October, we’ll do
- 22. Strategic Plans Strategic plans establish the long-range objectives and the overall strategy or course of action
- 23. Operational Plans Operational plans are shorter-term, usually one budget year Operational plans specify what actions individuals,
- 24. Tactical Plans Tactical plans are specific and short term Replace server as it’s running out of
- 25. Crisis Management or Contingency Planning Crisis management or contingency planning deals with potential disasters such as
- 26. Contingency Planning Expecting the unexpected Unexpected events may require quick action A “back-up” plan in case
- 27. 2. Organizing Organizing is the structuring of resources and activities to accomplish objectives in an efficient
- 28. 3. Leading Leading is the motivating and guiding employees to achieve organizational objectives Guiding subordinates to
- 29. 4. Controlling Controlling is the process of monitoring, evaluating and adjusting activities to keep the organization
- 30. Establish standards Measure performance Does performance meet desired standard/goal? Yes Continue current activities No Adjust performance
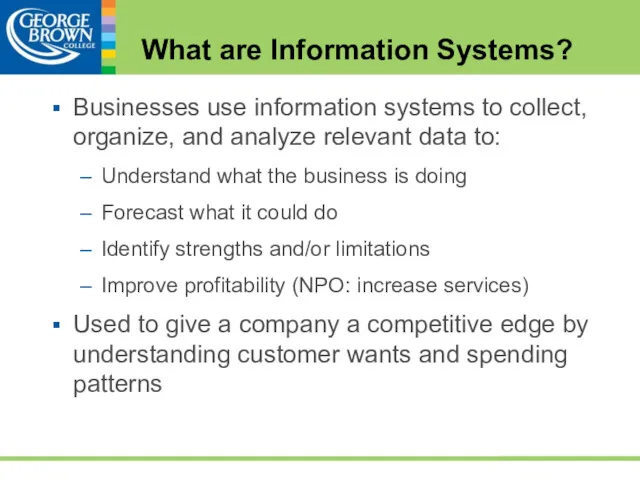
- 31. Businesses use information systems to collect, organize, and analyze relevant data to: Understand what the business
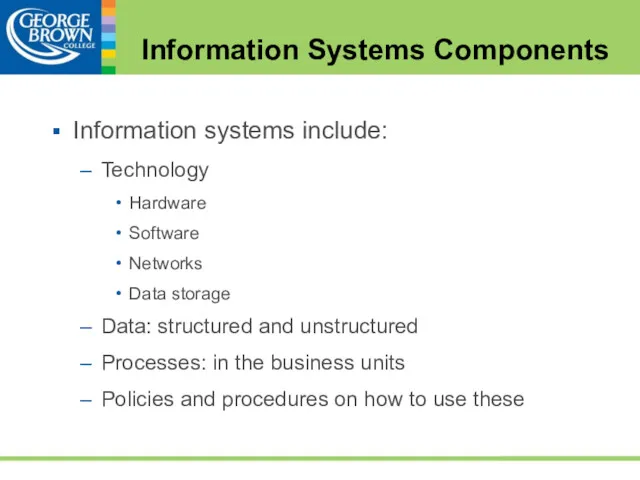
- 32. Information systems include: Technology Hardware Software Networks Data storage Data: structured and unstructured Processes: in the
- 33. Three important roles of IT in a business: Provide secure storage and access to corporate data
- 34. IT is now embedded into people’s personal lives Access to IT is integral to daily life
- 35. Strategic Uses of IT Support efficient everyday operations Web presence, sales, service Use strategically as a
- 36. Enabling the Customer-Focused Business Companies that consistently provide customers with the best quality are those that:
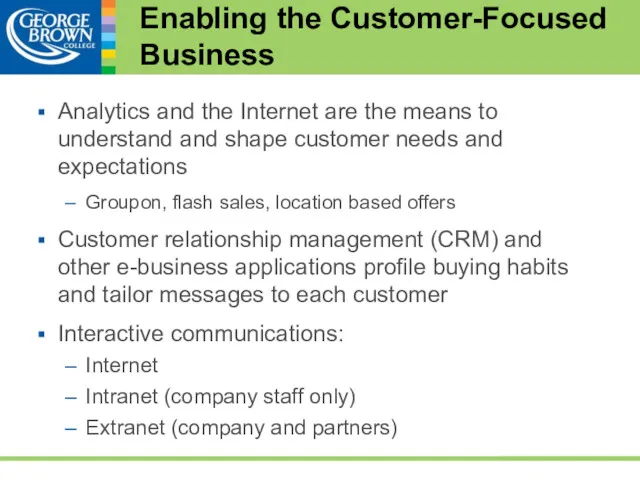
- 37. Enabling the Customer-Focused Business Analytics and the Internet are the means to understand and shape customer
- 38. Organizational Structure The specification of the jobs to be done within a business and how those
- 39. Developing Organizational Structure Specialization Identify the tasks required Identify the employees to complete the tasks Job
- 40. Departmentalization Bases of departmentalization Functional Product Geographic Customer
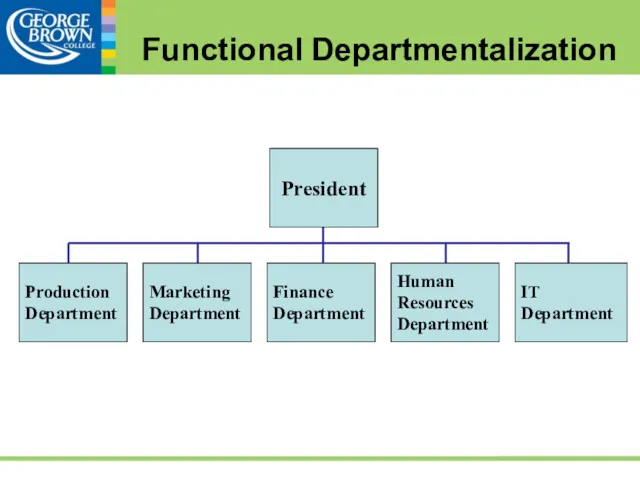
- 41. Functional Departmentalization
- 42. Functional Departmentalization Functional departmentalization groups jobs that perform similar functional activities: finance, manufacturing, marketing, and human
- 43. Product Departmentalization
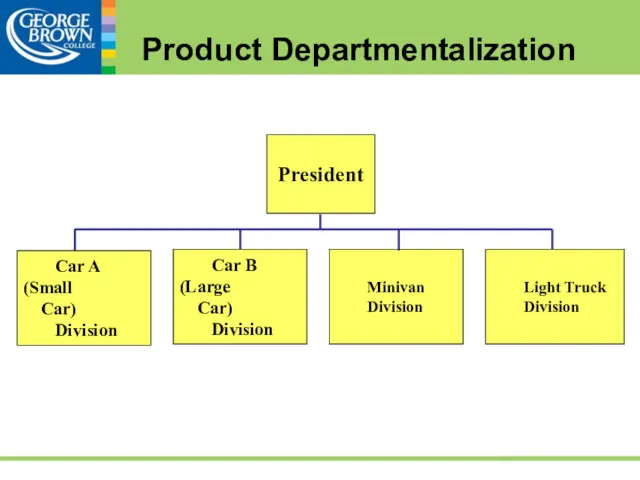
- 44. Product Departmentalization Product departmentalization is organizing jobs in relation to the products of the firm Each
- 45. Geographic Departmentalization
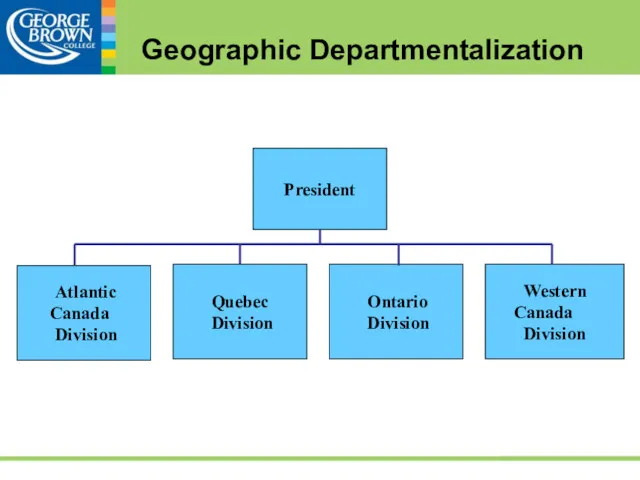
- 46. Geographic Departmentalization Groups jobs by geographic location: e.g. province, region, country or continent Allows for quick
- 47. Customer Departmentalization
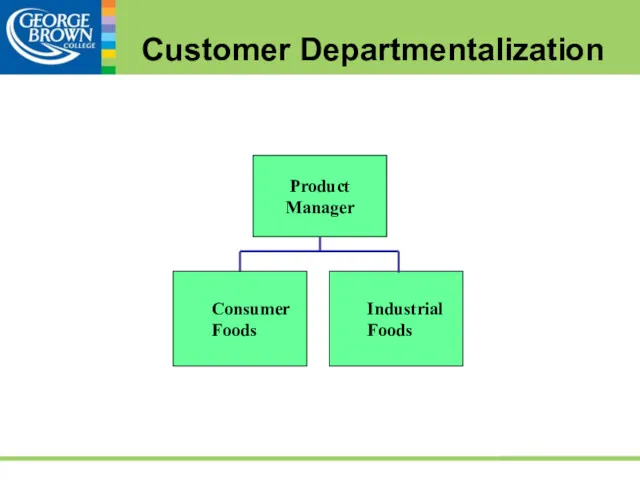
- 48. Customer Departmentalization Jobs arranged around the needs of various types of customers commercial banking versus consumer
- 49. Functional Units Human Resources Finance and Administration Sales and Marketing Operations and Manufacturing
- 50. Ownership Models Sole proprietor Partnership Share corporation
- 51. Ownership - Sole Proprietor Single individual as owner / investor Usually the sole employee / manager
- 52. Ownership - Partnership Several owners Not all may be active in company “Sweat equity” v. silent
- 54. Скачать презентацию












































 Бизнес-план швейного салона Белошвейка
Бизнес-план швейного салона Белошвейка Работа на дому интернет. Готовый бизнес под ключ
Работа на дому интернет. Готовый бизнес под ключ Adelaide Hills Distillery
Adelaide Hills Distillery Организация работы по предремонтной подготовке автомобилей и пути ее усовершенствования в ООО Евролак. Автомойка
Организация работы по предремонтной подготовке автомобилей и пути ее усовершенствования в ООО Евролак. Автомойка Сведения о СРО Свободный Оценочный Департамент и ответственность оценщиков за не соблюдение правил профессиональной этики
Сведения о СРО Свободный Оценочный Департамент и ответственность оценщиков за не соблюдение правил профессиональной этики Coca Cola Presentation
Coca Cola Presentation Способы и критерии оценки эффективности тренинга. Условия переноса результатов тренинга в реальную среду
Способы и критерии оценки эффективности тренинга. Условия переноса результатов тренинга в реальную среду Бизнес-жоспар. Туристік компания
Бизнес-жоспар. Туристік компания Рынок цветов
Рынок цветов Создание образца бизнес-плана
Создание образца бизнес-плана ООО Глория. Бизнес-план
ООО Глория. Бизнес-план Start-up. Стартап
Start-up. Стартап Искуственный камень
Искуственный камень Реинжиниринг. Понятие реинжиниринг бизнеса
Реинжиниринг. Понятие реинжиниринг бизнеса Международный бизнес
Международный бизнес Nano Tritium “Атомная энергия в вашем кармане”
Nano Tritium “Атомная энергия в вашем кармане” Agri Frontier Limited is an agri investment and agribusiness advisory firm
Agri Frontier Limited is an agri investment and agribusiness advisory firm Коммерческое предложение для АО Калининградский янтарный комбинат
Коммерческое предложение для АО Калининградский янтарный комбинат Туристическое агенство. Бизнес-план
Туристическое агенство. Бизнес-план Бренд Веселый молочник
Бренд Веселый молочник Аутсорсинг и аутстаффинг в Казахстане
Аутсорсинг и аутстаффинг в Казахстане Бизнес - план на коленке
Бизнес - план на коленке ОГАУ. Проектный офис. Как найти идею для своего проекта
ОГАУ. Проектный офис. Как найти идею для своего проекта Організація ремонту пральної машини
Організація ремонту пральної машини Ресторан Hibachi
Ресторан Hibachi Venture capital. Mind map
Venture capital. Mind map Группа компаний ИТ Индустрия
Группа компаний ИТ Индустрия Индивидуальное предпринимательство. Особенности организации малого и среднего бизнеса
Индивидуальное предпринимательство. Особенности организации малого и среднего бизнеса