Содержание
- 2. What is the CBPP ®? BPM Certification means that an individual has: Achieved appropriate professional experience
- 3. Experience Qualification 4 Years Process management, Process Improvement, or Process Transformation experience Documented experience and qualifications
- 4. How to Prepare CBOK Through ABPMP’s eStore at https://www.createspace.com/3376044 Download a PDF copy through ABPMP’s member
- 5. Why the BPM CBOK®? The BPM CBOK® is the “WHAT” of BPM One must first know
- 6. BPM CBOK® Knowledge Areas
- 7. 1.0 Business Process Management (7 Questions) 1.1 Business Process Principles Articulate the definition of Business Process
- 8. 2.0 Process Analysis (15 Questions) 2.1 Process Analysis Define the term process analysis Recognize how processes
- 9. Chapter 2 Key Concepts Business Process Management (BPM) is a disciplined approach to identify, design, execute,
- 10. Key Concepts 6 BPM Critical Success Factors include the following: alignment of business strategy, value-chain definitions,
- 11. Key Concepts 7 BPM is a professional discipline made up of eight sub-disciplines: Modeling, Analysis, Design,
- 12. 3.0 Process Modeling (16 Questions) 3.1 Process Modeling Notations Understand the origin and the types of
- 13. Chapter 3 Summary & Key Concepts Process models are simplified representations of some business activity. A
- 15. 4.0 Process Design &Transformation (18 Questions) 4.1 Process Design Understand the impact of the logical and
- 16. 5.0 Process Performance Management (14 Questions) 5.1 Effective Process Measures Understand the role and objectives of
- 17. 6.0 Process Improvement Methodologies 6.1 Alignment of business process and enterprise performance Understand the various methodologies
- 18. 7.0 Process Organization & Change Management 7.1 Process Orientation Distinguish between the horizontal focus of the
- 19. 7.0 Process Organization & Change Management Process Management and Governance Roles Define the role of the
- 20. 8.0 Enterprise Process Management (EPM) Enterprise Process Governance Understand concepts of the Enterprise Process Management as
- 22. Скачать презентацию
What is the CBPP ®?
BPM Certification means that an individual has:
Achieved
What is the CBPP ®?
BPM Certification means that an individual has:
Achieved
Passed a rigorous examination (140 questions)
Agreed to abide by a professional code of conduct;
Committed to maintaining an active credential through meeting continuing professional development requirements.
Experience Qualification
4 Years
Process management, Process Improvement, or Process Transformation experience
Documented experience
Experience Qualification
4 Years
Process management, Process Improvement, or Process Transformation experience
Documented experience
Disclaimer: Preparing for the CBPP® exam is geared toward the experienced practitioner in the knowledge areas contained in the BPM CBOK®
How to Prepare
CBOK
Through ABPMP’s eStore at https://www.createspace.com/3376044
Download a PDF copy through
How to Prepare
CBOK
Through ABPMP’s eStore at https://www.createspace.com/3376044
Download a PDF copy through
Study Guide (available at participating Chapters)
Why the BPM CBOK®?
The BPM CBOK® is the “WHAT” of BPM
One
Why the BPM CBOK®?
The BPM CBOK® is the “WHAT” of BPM
One
Until now, there has been no comprehensive resource espousing the skills and competencies until the BPM CBOK®
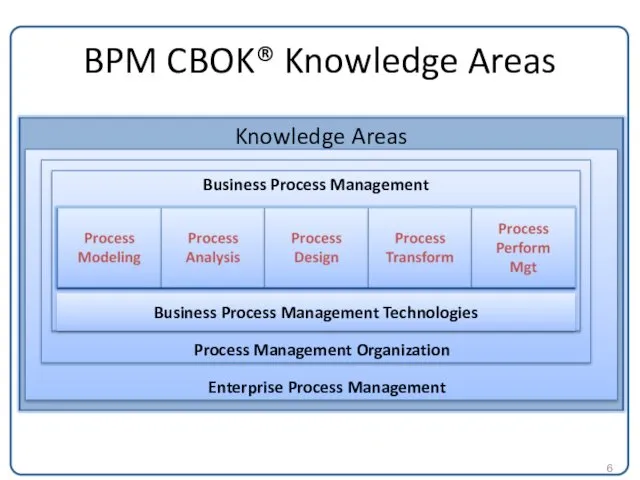
BPM CBOK® Knowledge Areas
BPM CBOK® Knowledge Areas
1.0 Business Process Management
(7 Questions)
1.1 Business Process Principles
Articulate the definition
1.0 Business Process Management
(7 Questions)
1.1 Business Process Principles
Articulate the definition
Describe the drivers and the impact on the organization
1.2 BPM Lifecycle:
Describe the phases of BPM implementation, the methodology and the projects that would impact the goals of the organization
Understand the BPM lifecycle and the various activities at each phase
1. 3 BPM Professionals
Understand the principles of change with the shift from an organizational and hierarchical focus changing to a process based focus
Describe the roles required for moving to a process centric organization
2.0 Process Analysis
(15 Questions)
2.1 Process Analysis
Define the term process analysis
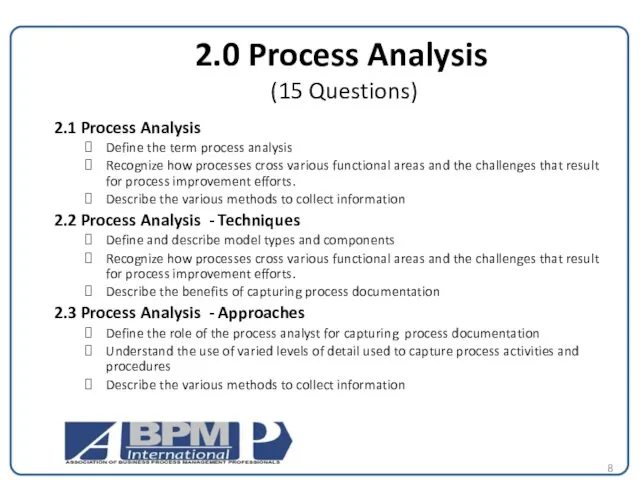
2.0 Process Analysis
(15 Questions)
2.1 Process Analysis
Define the term process analysis
Recognize how processes cross various functional areas and the challenges that result for process improvement efforts.
Describe the various methods to collect information
2.2 Process Analysis - Techniques
Define and describe model types and components
Recognize how processes cross various functional areas and the challenges that result for process improvement efforts.
Describe the benefits of capturing process documentation
2.3 Process Analysis - Approaches
Define the role of the process analyst for capturing process documentation
Understand the use of varied levels of detail used to capture process activities and procedures
Describe the various methods to collect information
Chapter 2 Key Concepts
Business Process Management (BPM) is a disciplined approach
Chapter 2 Key Concepts
Business Process Management (BPM) is a disciplined approach
BPM involves the deliberate, collaborative and increasingly technology-aided definition, improvement, innovation, and management of end-to-end business processes that drive business results, create value, and enable an organization to meet its business objectives with more agility.
It enables an enterprise to align its business processes to its business strategy leading to effective overall company performance through improvements of specific work activities either within a specific department, across the enterprise, or between organizations.
A process is a defined set of activities or behaviors performed by humans or machines to achieve one or more goals.
There are three types of business processes: primary, support and management.
Primary processes are cross-functional in nature and make up the value chain.
Support processes such as human resources and IT enable other processes.
Management processes are used to measure, monitor and control business activities. Management processes ensure that primary and supporting processes meet operational, financial, regulatory, and legal goals.
Key Concepts
6 BPM Critical Success Factors include the following:
alignment of business strategy,
Key Concepts
6 BPM Critical Success Factors include the following:
alignment of business strategy,
establishment of enterprise and business unit goals to meet business strategy
development of action plans and business tactics to successfully meet the organization’s goals
assignment of executive sponsorship, responsibility, authority and accountability for processes leading to attainment of goals
assignment of clear process ownership along with authority to engineer change
establish metrics, measure, and monitor process
institutionalize practices such as continuous improvement investigations, change management, change controls, and proper leverage of BPM products and tools that lead to improvements and change
standardize and automate business processes and related methodologies across the enterprise
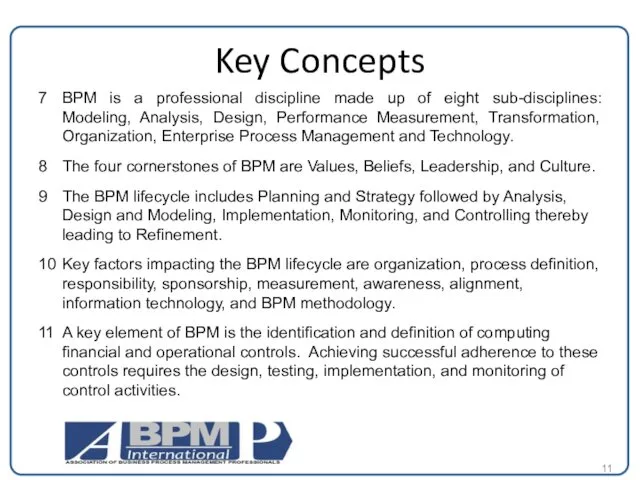
Key Concepts
7 BPM is a professional discipline made up of eight sub-disciplines:
Key Concepts
7 BPM is a professional discipline made up of eight sub-disciplines:
8 The four cornerstones of BPM are Values, Beliefs, Leadership, and Culture.
9 The BPM lifecycle includes Planning and Strategy followed by Analysis, Design and Modeling, Implementation, Monitoring, and Controlling thereby leading to Refinement.
10 Key factors impacting the BPM lifecycle are organization, process definition, responsibility, sponsorship, measurement, awareness, alignment, information technology, and BPM methodology.
11 A key element of BPM is the identification and definition of computing financial and operational controls. Achieving successful adherence to these controls requires the design, testing, implementation, and monitoring of control activities.
3.0 Process Modeling
(16 Questions)
3.1 Process Modeling Notations
Understand the origin
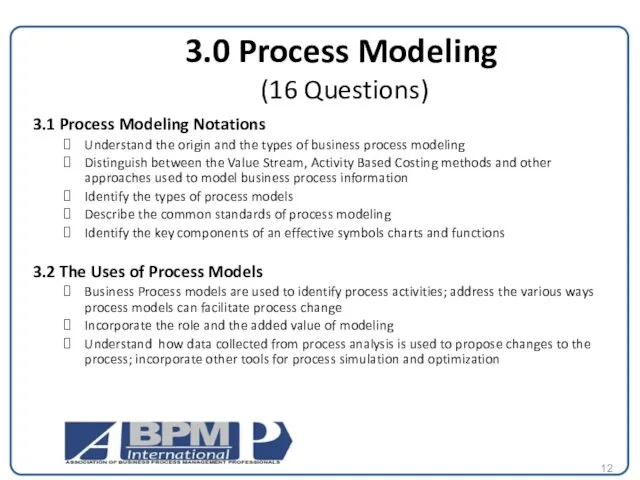
3.0 Process Modeling
(16 Questions)
3.1 Process Modeling Notations
Understand the origin
Distinguish between the Value Stream, Activity Based Costing methods and other approaches used to model business process information
Identify the types of process models
Describe the common standards of process modeling
Identify the key components of an effective symbols charts and functions
3.2 The Uses of Process Models
Business Process models are used to identify process activities; address the various ways process models can facilitate process change
Incorporate the role and the added value of modeling
Understand how data collected from process analysis is used to propose changes to the process; incorporate other tools for process simulation and optimization
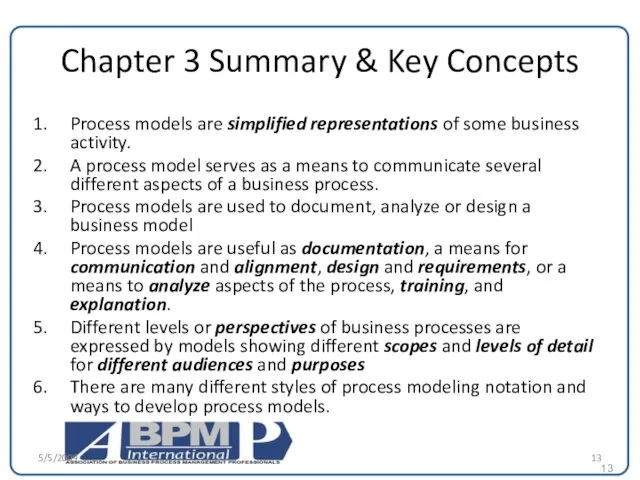
Chapter 3 Summary & Key Concepts
Process models are simplified representations of
Chapter 3 Summary & Key Concepts
Process models are simplified representations of
A process model serves as a means to communicate several different aspects of a business process.
Process models are used to document, analyze or design a business model
Process models are useful as documentation, a means for communication and alignment, design and requirements, or a means to analyze aspects of the process, training, and explanation.
Different levels or perspectives of business processes are expressed by models showing different scopes and levels of detail for different audiences and purposes
There are many different styles of process modeling notation and ways to develop process models.
5/5/2009
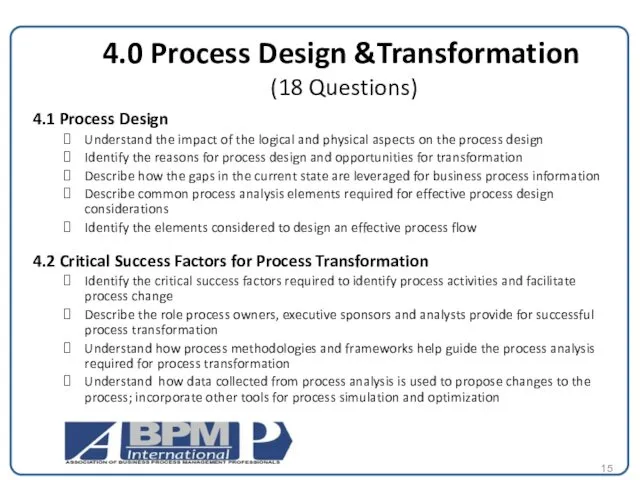
4.0 Process Design &Transformation
(18 Questions)
4.1 Process Design
Understand the impact of
4.0 Process Design &Transformation
(18 Questions)
4.1 Process Design
Understand the impact of
Identify the reasons for process design and opportunities for transformation
Describe how the gaps in the current state are leveraged for business process information
Describe common process analysis elements required for effective process design considerations
Identify the elements considered to design an effective process flow
4.2 Critical Success Factors for Process Transformation
Identify the critical success factors required to identify process activities and facilitate process change
Describe the role process owners, executive sponsors and analysts provide for successful process transformation
Understand how process methodologies and frameworks help guide the process analysis required for process transformation
Understand how data collected from process analysis is used to propose changes to the process; incorporate other tools for process simulation and optimization
5.0 Process Performance Management
(14 Questions)
5.1 Effective Process Measures
Understand the
5.0 Process Performance Management
(14 Questions)
5.1 Effective Process Measures
Understand the
Describe fundamental metrics dimensions and characteristics of effective metrics
Describe the concept of "value added" versus "non-value added" measurement approaches
5.2 Importance and benefits of process performance management
Understand the benefits of cross-functional process improvement efforts versus isolated functional area improvements
Understand the reasons for continuous process monitoring and control
Describe the role of business intelligence in decision support for process owners and managers
6.0 Process Improvement Methodologies
6.1 Alignment of business process and enterprise performance
6.0 Process Improvement Methodologies
6.1 Alignment of business process and enterprise performance
Understand the various methodologies used to assess process performance and to support continuous improvement
Understand the difference between the key approaches to process improvement methods; explain the key differences in the tools used by each
Understand the difference between functional and cross-functional (enterprise level) metrics
6.2 Modeling and simulation
Describe the difference between Process Measuring and Modeling and Simulation
Understand the process of Modeling and Simulation and describe its objectives and benefits
6.3 Decision support for process owners and managers
Familiarize with common decision support frameworks and their benefits
Describe the reasons for planning for monitoring and controlling of business processes
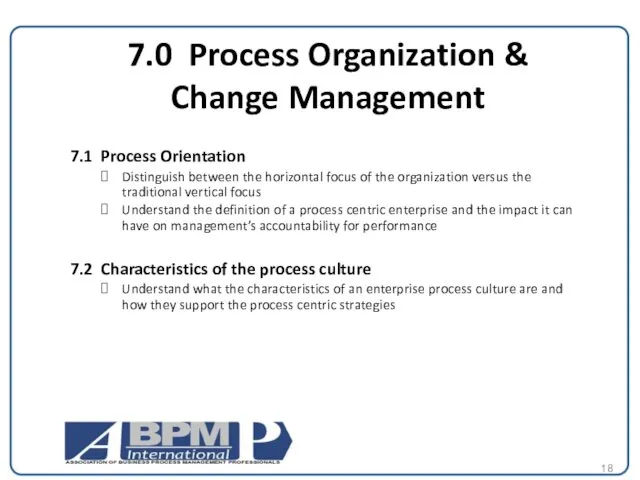
7.0 Process Organization &
Change Management
7.1 Process Orientation
Distinguish between the
7.0 Process Organization &
Change Management
7.1 Process Orientation
Distinguish between the
Understand the definition of a process centric enterprise and the impact it can have on management’s accountability for performance
7.2 Characteristics of the process culture
Understand what the characteristics of an enterprise process culture are and how they support the process centric strategies
7.0 Process Organization &
Change Management
Process Management and Governance Roles
Define
7.0 Process Organization &
Change Management
Process Management and Governance Roles
Define
Describe how the process owner’s responsibilities differ from those of the functional manager.
Describe and distinguish the different roles of the process owner, the project manager, the process analyst and the process governance team to accomplish their main responsibility
Organizational Change Management
Understand how process integration will impact to the traditional organizational structure and management roles
Define the change management issues encountered in implementing process changes and role definition.
8.0 Enterprise Process Management (EPM)
Enterprise Process Governance
Understand concepts of the
8.0 Enterprise Process Management (EPM)
Enterprise Process Governance
Understand concepts of the
Identify main factors that impact cross-functional enterprise decision making
Describe reasons and objectives of Enterprise Process Governance
Describe benefits of EPM and importance of business knowledge, roles and responsibilities, goals and priorities
Describe aspects of the Customer Centric Measurement Framework
Describe activities of process assessment
Process Frameworks
Uses and benefits of different frameworks to achieve the benefits of establishing of common definitions and standardized processes
Describe major elements of an Enterprise Framework Model












 Кейс-чемпионат Hult Prize
Кейс-чемпионат Hult Prize Малое и среднее предпринимательство Новосибирской области
Малое и среднее предпринимательство Новосибирской области Основы деловых коммуникаций
Основы деловых коммуникаций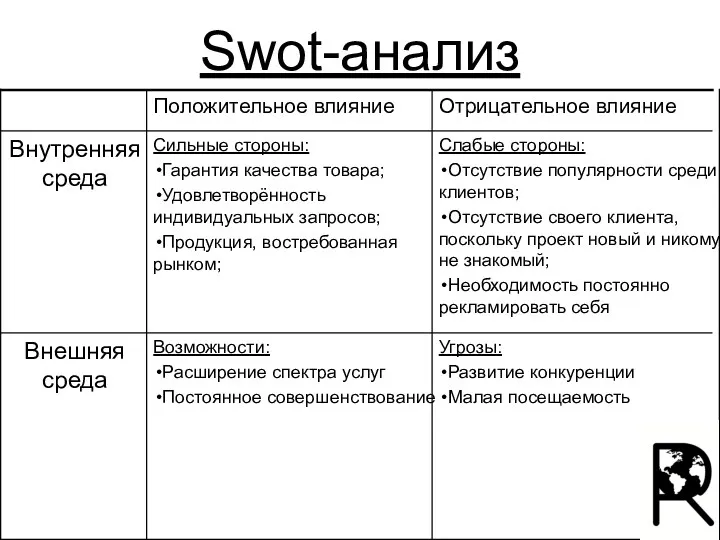 Swot-анализ
Swot-анализ Подключение партнера. DC B2B
Подключение партнера. DC B2B Бизнес-проект по открытию предприятия Икосаэдр
Бизнес-проект по открытию предприятия Икосаэдр Предпринимательство. Формы предпринимательства
Предпринимательство. Формы предпринимательства Commercial shipping: shipowners’ view
Commercial shipping: shipowners’ view Оңтүстік Қазақстан облысы Мақтарал ауданында 100 га жер көлеміне мақта өсіру
Оңтүстік Қазақстан облысы Мақтарал ауданында 100 га жер көлеміне мақта өсіру Мобильная сухая автомойка
Мобильная сухая автомойка Оценка уровня конкурентоспособности нефтегазодобывающих компаний, ОАО Самотлорнефтегаз
Оценка уровня конкурентоспособности нефтегазодобывающих компаний, ОАО Самотлорнефтегаз Технология и организация культурно-познавательного тура
Технология и организация культурно-познавательного тура Учреждение рекламного агентства
Учреждение рекламного агентства Бизнес-план. Компьютерлерді жөндеу
Бизнес-план. Компьютерлерді жөндеу Факторы успеха Вашего бизнеса
Факторы успеха Вашего бизнеса Assessment of the tourism function in region development
Assessment of the tourism function in region development Основы рекрутирования
Основы рекрутирования Великолепная двойка. 3D-мастерская Пончик. Инвестиционные затраты
Великолепная двойка. 3D-мастерская Пончик. Инвестиционные затраты Мой любимый бренд
Мой любимый бренд Бизнес-план. Понятие бизнес-плана
Бизнес-план. Понятие бизнес-плана Предпринимательская деятельность
Предпринимательская деятельность Бизнес-проект. Студия красоты Black&White
Бизнес-проект. Студия красоты Black&White Бизнес-жоспар. Көкеніс (қызанақ,қияр) өсіретін жылыжай
Бизнес-жоспар. Көкеніс (қызанақ,қияр) өсіретін жылыжай Гостиничная индустрия
Гостиничная индустрия Southwest airlines
Southwest airlines Современная франшиза для предпринимателей и парикмахеров
Современная франшиза для предпринимателей и парикмахеров Проект ресторана на 50 мест
Проект ресторана на 50 мест Новостройки Казани. Предложения для инвесторов
Новостройки Казани. Предложения для инвесторов