Содержание
- 2. Recap Why product development / innovation? Why SWOT? Time to market Reasons for successfull product launch
- 3. Make a SWOT of Inholland The Hague IMEM
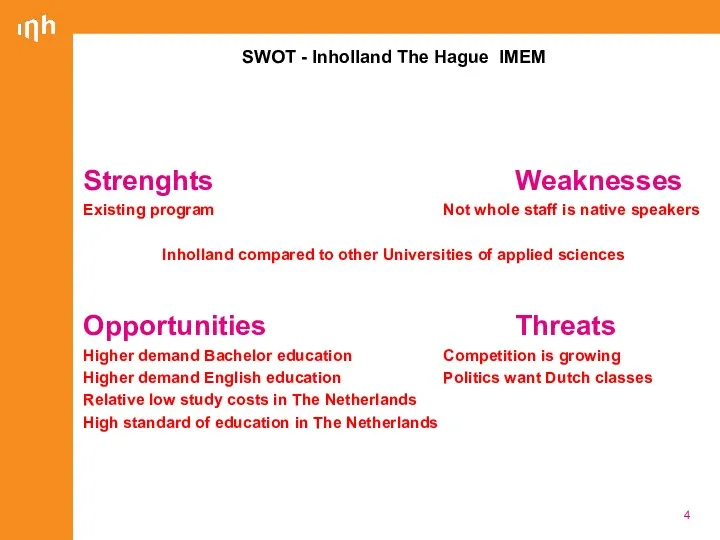
- 4. Strenghts Weaknesses Existing program Not whole staff is native speakers Inholland compared to other Universities of
- 5. Reasons for failure of new products Not a unique product (does not offer a demonstrable advantage)
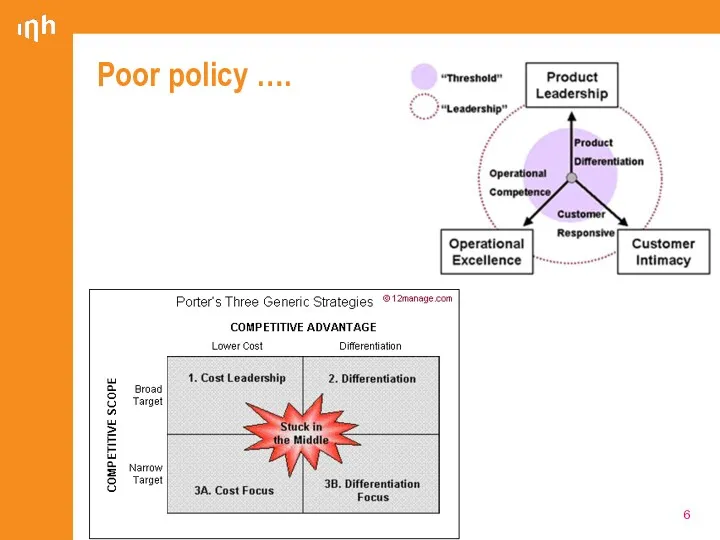
- 6. Poor policy ….
- 7. Reasons for failure of new products Quality problems (shortcomings in technical product; teething problems) Bad timing.
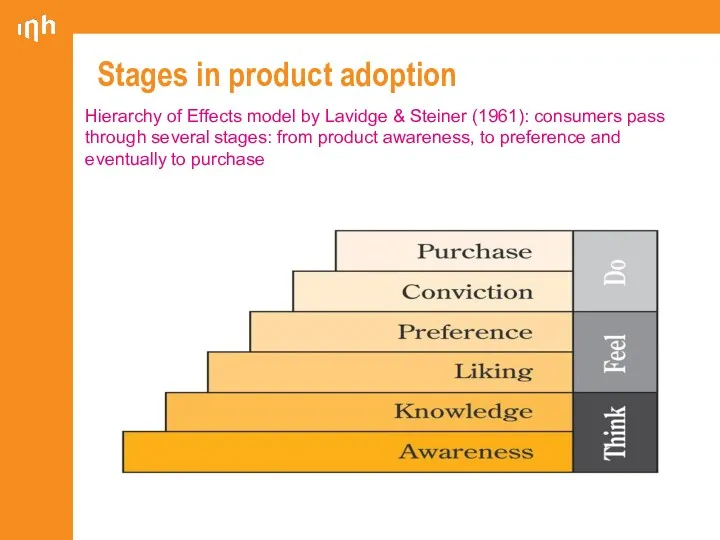
- 8. Stages in product adoption Hierarchy of Effects model by Lavidge & Steiner (1961): consumers pass through
- 9. Consumer buyer roles Initiator Person who first suggests or thinks of the idea of buying a
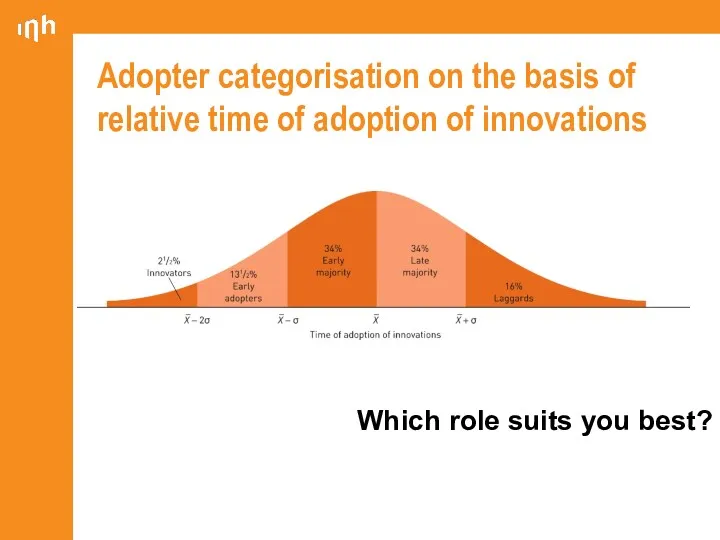
- 10. Categories of adopters of innovations Innovators Early adopters Early majority Late majority Laggards
- 11. Categories of adopters of innovations Innovators: the first individuals to adopt an innovation - Willing to
- 12. Categories of adopters of innovations Early adopters: - High degree of opinion leadership - Typically younger
- 13. Categories of adopters of innovations Early majority: - Adopt an innovation after a varying degree of
- 14. Categories of adopters of innovations Late majority: will adopt an innovation after the average member of
- 15. Categories of adopters of innovations Laggards: the last to adopt an innovation little to no opinion
- 16. Adopter categorisation on the basis of relative time of adoption of innovations Which role suits you
- 17. Influence of product characteristics on rate of adoption Relative advantage Innovation superior to existing products Compatibility
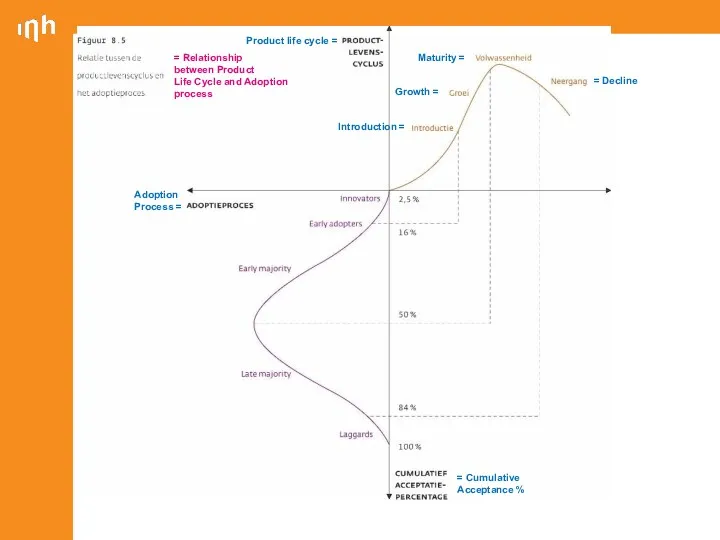
- 18. Introduction = Growth = Maturity = = Decline Product life cycle = = Cumulative Acceptance %
- 20. Next week: Test exam 1 Questions 5, 7, m.c. Now: Test exam 1 Questions 1, 4,
- 21. ANSWER 1.: • Increased total revenue — The earlier you get your product to market (without
- 22. ANSWER 4.: Consideration 1: BCG quadrant: Question Mark: Promotion: heavy to entice product trial Consideration 2:
- 23. ANSWER 6.: The product life cycle and Boston Matrix similar in that the Boston Matrix reflects
- 25. Скачать презентацию

















 Amazon. Онлайн торговля
Amazon. Онлайн торговля Критерии отбора стартапов АО Корпорация МСП
Критерии отбора стартапов АО Корпорация МСП Бизнес-план создания и организации деятельности ногтевой студии Beaunail
Бизнес-план создания и организации деятельности ногтевой студии Beaunail Заявка от кандидата. Информация о компании, учредителях. Бизнес-план продажи новых автомобилей Hyundai. Шаблон
Заявка от кандидата. Информация о компании, учредителях. Бизнес-план продажи новых автомобилей Hyundai. Шаблон Проект кафе на 50 мест
Проект кафе на 50 мест Салон красоты Русаль
Салон красоты Русаль Власть и бизнес в современной России
Власть и бизнес в современной России Проект “ТЕРРАСА” в Востоке
Проект “ТЕРРАСА” в Востоке Маркетинговое исследование и анализ рынка печатной и электронной продукции по теме Здоровое питание, фитнес и тренировки
Маркетинговое исследование и анализ рынка печатной и электронной продукции по теме Здоровое питание, фитнес и тренировки Доставка здорового питания на неделю
Доставка здорового питания на неделю Рукоделие как бизнес своими руками на дому
Рукоделие как бизнес своими руками на дому Top 5 russian startups
Top 5 russian startups Нова пошта
Нова пошта Бизнес проект Магазин одежды, 10 кл
Бизнес проект Магазин одежды, 10 кл Қазақстандағы күрделі инвестициялық бизнес жобалар
Қазақстандағы күрделі инвестициялық бизнес жобалар Цели и ограничения при коммерциализации нового продукта и структура бизнес-плана
Цели и ограничения при коммерциализации нового продукта и структура бизнес-плана Реализация инвестиционно-строительного проекта многофункционального комплекса в г. Уфа
Реализация инвестиционно-строительного проекта многофункционального комплекса в г. Уфа ProPet - сервис для поиска временной семьи вашему питомцу
ProPet - сервис для поиска временной семьи вашему питомцу Бизнес- план гостиничного комплекса ООО Минхерц и Компания
Бизнес- план гостиничного комплекса ООО Минхерц и Компания Бизнес-модель. Профориентация молодежи и взрослых
Бизнес-модель. Профориентация молодежи и взрослых Предложение по продаже готового бизнеса
Предложение по продаже готового бизнеса Бизнес и предпринимательство
Бизнес и предпринимательство Рога и Копыта
Рога и Копыта Бизнес-план. Лекция 8
Бизнес-план. Лекция 8 Бизнес-навигатор МСП
Бизнес-навигатор МСП Финансовая поддержка субъектов МСП
Финансовая поддержка субъектов МСП Бизнес-план открытия кафе быстрого питания FunTasty
Бизнес-план открытия кафе быстрого питания FunTasty Мультирегиональный холдинг
Мультирегиональный холдинг