Содержание
- 2. Business analysis is the practice of enabling change in an enterprise by defining needs and recommending
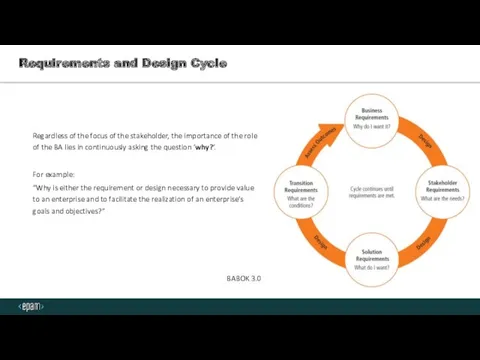
- 3. Requirements and Design Cycle Regardless of the focus of the stakeholder, the importance of the role
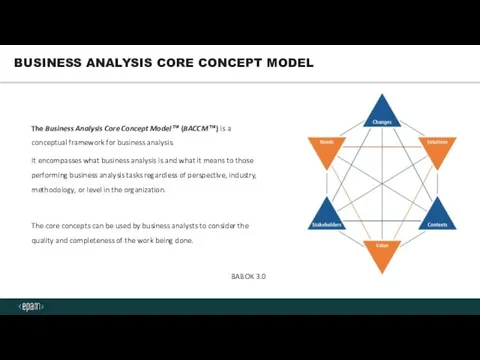
- 4. The Business Analysis Core Concept Model™ (BACCM™) is a conceptual framework for business analysis. It encompasses
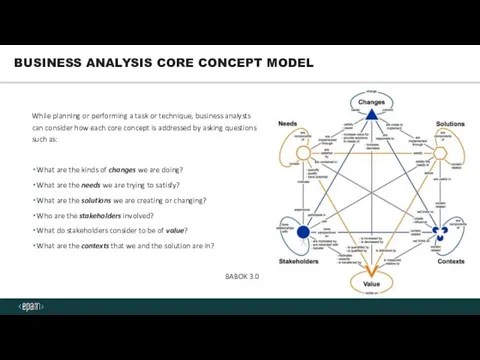
- 5. While planning or performing a task or technique, business analysts can consider how each core concept
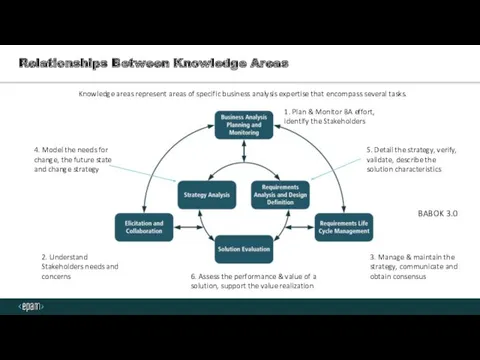
- 6. Relationships Between Knowledge Areas Knowledge areas represent areas of specific business analysis expertise that encompass several
- 7. BA Knowledge areas Business Analysis Planning and Monitoring: describes the tasks that business analysts perform to
- 8. BA Knowledge areas Elicitation and Collaboration: describes the tasks that business analysts perform to prepare for
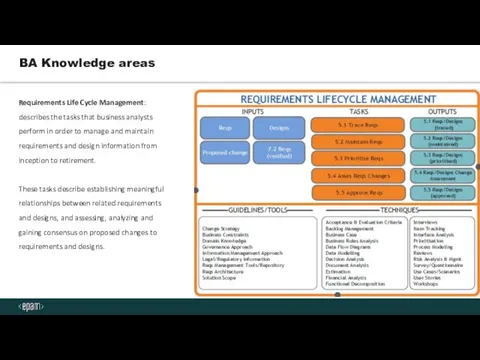
- 9. BA Knowledge areas Requirements Life Cycle Management: describes the tasks that business analysts perform in order
- 10. BA Knowledge areas Strategy Analysis: describes the business analysis work that must be performed to collaborate
- 11. BA Knowledge areas Requirements Analysis and Design Definition: describes the tasks that business analysts perform to
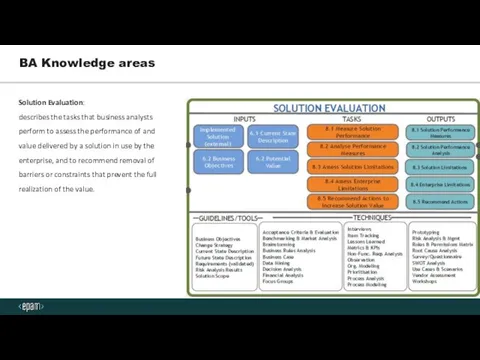
- 12. BA Knowledge areas Solution Evaluation: describes the tasks that business analysts perform to assess the performance
- 13. 50+ BA Techniques
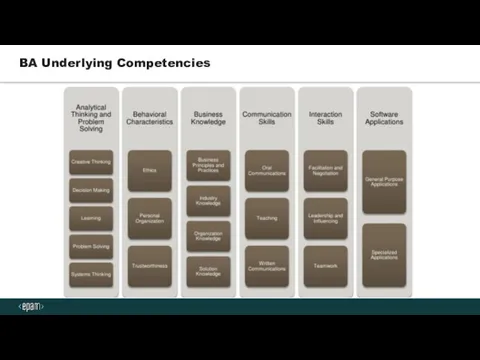
- 14. BA Underlying Competencies
- 15. Agile Extention
- 16. Agile Business Analysis Planning Horizons
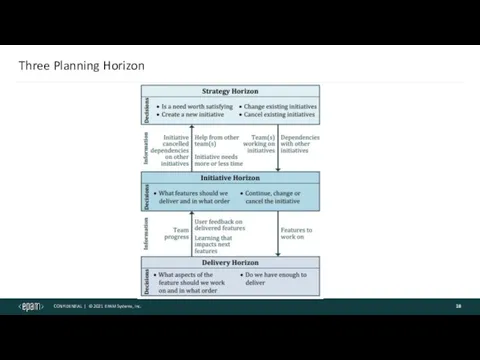
- 18. Three Planning Horizon
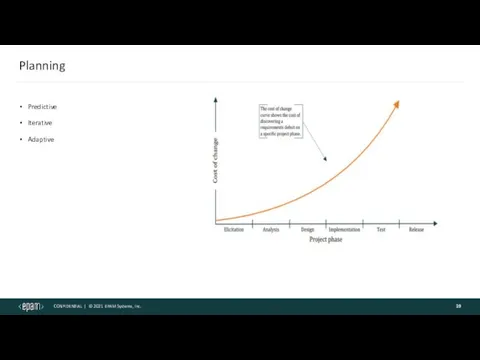
- 19. Planning Predictive Iterative Adaptive
- 20. Technique
- 21. Requirements Development in Agile
- 22. Requirements process * * * * REQUIREMENTS MANAGEMENT Change Management Requirements Tracing
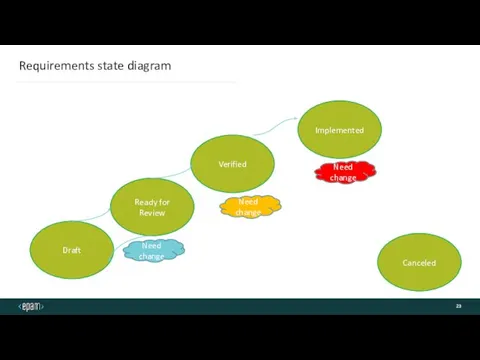
- 23. Requirements state diagram Implemented Canceled Ready for Review Draft Verified Need change Need change Need change
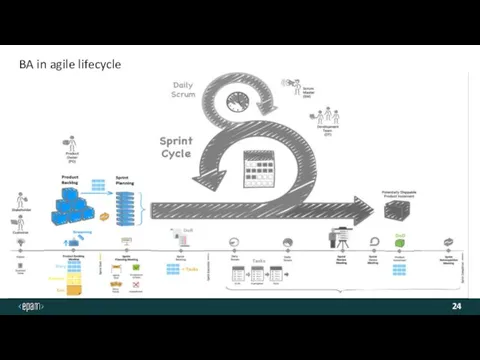
- 24. BA in agile lifecycle
- 25. Product Vision
- 26. Product Vision v2
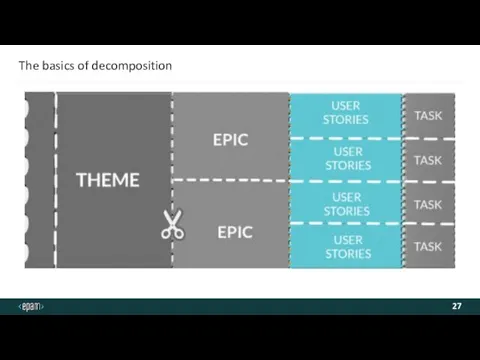
- 27. The basics of decomposition
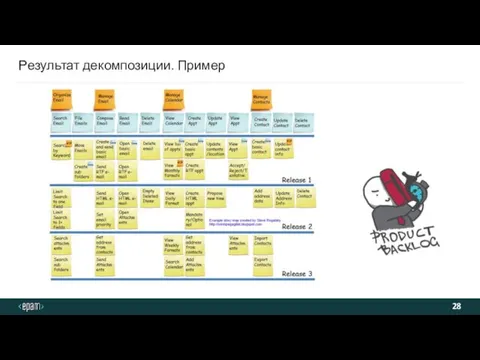
- 28. Результат декомпозиции. Пример
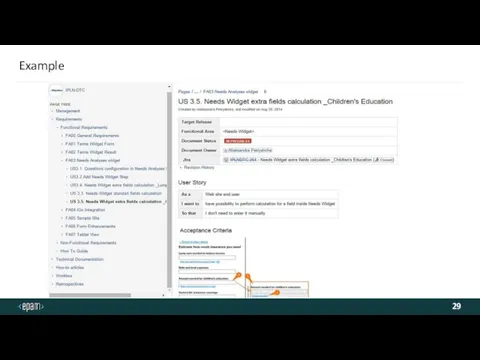
- 29. Example
- 30. Product backlog Оценить Добавить Изменить приоритет Уточнить Удалить Исходный большой «кусок» Размер Элемент
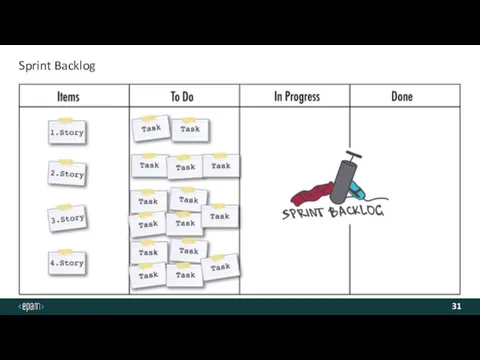
- 31. Sprint Backlog
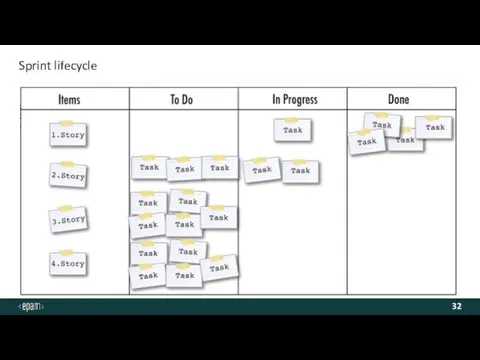
- 32. Sprint lifecycle
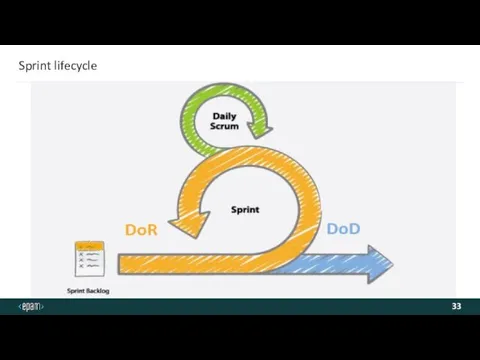
- 33. Sprint lifecycle
- 34. DoR. Пример User Story User Story декомпозирована. Соответствует шаблону: Как, , я , . Написаны ПО
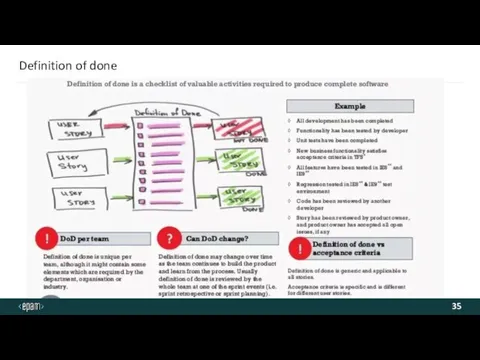
- 35. Definition of done
- 36. Example
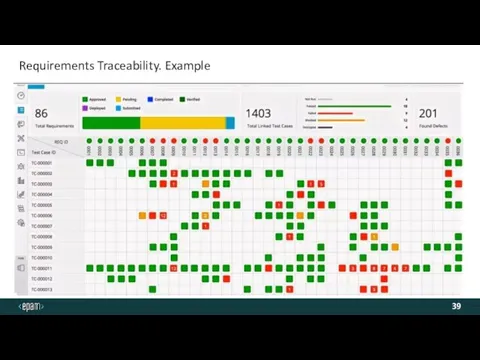
- 37. Requirements Traceability. Definition The PURPOSE of Trace Requirements is to ensure that requirements and designs at
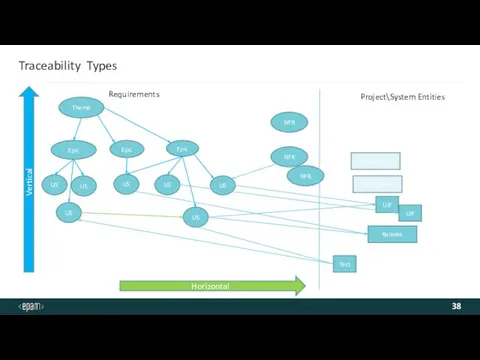
- 38. Traceability Types Theme UIF Test Component Release Epic Epic Epic NFR NFR NFR US US US
- 39. Requirements Traceability. Example
- 41. Скачать презентацию
















 Business Etiquette In Singapore
Business Etiquette In Singapore Қазақстандағы кәсіпкерліктің дамуы
Қазақстандағы кәсіпкерліктің дамуы Проект кафе на 50 мест
Проект кафе на 50 мест Предпринимательство: понятие, признаки
Предпринимательство: понятие, признаки Москва-сити, бизнес-центр Северная башня
Москва-сити, бизнес-центр Северная башня Лаундж бари
Лаундж бари Деятельность индивидуальных предпринимателей
Деятельность индивидуальных предпринимателей Жеке кәсіпкерлік
Жеке кәсіпкерлік Бизнестің әлеуметтік жауапкершілігі
Бизнестің әлеуметтік жауапкершілігі Product launch course. Idea generation – bring it to the market
Product launch course. Idea generation – bring it to the market Қазақстандағы шағын және орта бизнеске талдау
Қазақстандағы шағын және орта бизнеске талдау Домашняя пекарня
Домашняя пекарня Государственная поддержка малого бизнеса в России
Государственная поддержка малого бизнеса в России Типология международного туризма
Типология международного туризма Ауыл шаруашылы
Ауыл шаруашылы Современное состояние международного туризма в России
Современное состояние международного туризма в России Конкурс Вектор успеха. Номинация Семейный бизнес
Конкурс Вектор успеха. Номинация Семейный бизнес Рынок окон ПВХ сегодня. Завтра. Стратегия
Рынок окон ПВХ сегодня. Завтра. Стратегия Аренда звукового и светового оборудования
Аренда звукового и светового оборудования Десертний бар на 30 місць
Десертний бар на 30 місць Бизнес-план кафе
Бизнес-план кафе Презентация компании Delta
Презентация компании Delta Бизнес-жоспар Туристік компания
Бизнес-жоспар Туристік компания Интернациональная сеть отелей Хилтон
Интернациональная сеть отелей Хилтон Бизнес-план. Репетиторство
Бизнес-план. Репетиторство Бизнес-планирование в социокультурной сфере
Бизнес-планирование в социокультурной сфере Ателье У Роксаны
Ателье У Роксаны История компании Coca-Cola
История компании Coca-Cola