Method of hygienic assessment of dangerous and harmful factors of the industrial environment презентация
Содержание
- 2. CONTENTS 1. Hygiene of work. The basic section hygiene of work. 2.General hazards caused by industrial
- 3. HYGIENE OF WORK: the section of hygiene studying influence process of work and harmful professional factors
- 4. THE BASIC SECTIONS HYGIENE OF WORK: Physiology of work - studying influence on an organism various
- 5. PHYSIOLOGY OF WORK: boundary section of hygiene and the physiology, studying influence process of work on
- 6. THE CLASSIFICATION KINDS OF WORK: 1. Physical work - demands the big physical activity and energy
- 7. Dangerous industrial hazards (Abstract from State Standard 12.0.003 - 74) According to this standard all dangerous
- 8. INDUSTRIAL PHYSICAL HAZARDS ARE: hot or cold microclimate of the working zone, high levels of infrared
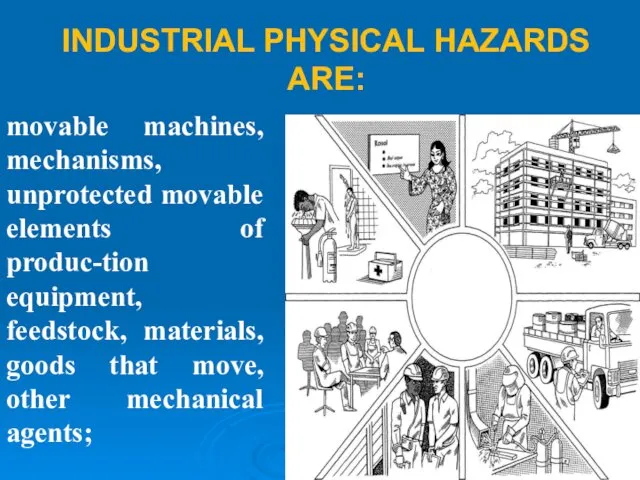
- 9. INDUSTRIAL PHYSICAL HAZARDS ARE: movable machines, mechanisms, unprotected movable elements of produc-tion equipment, feedstock, materials, goods
- 10. INDUSTRIAL PHYSICAL HAZARDS ARE: high noise level, vibration, infra- and ultra-mechanical fluctuations of air or hard
- 11. INDUSTRIAL PHYSICAL HAZARDS ARE: insufficient or excessive illumination of work places, low contrast, high luminosity, its
- 12. GROUP OF CHEMICAL DANGEROUS INDUSTRIAL HAZARDS INCLUDES: according to their action on organism - irritant, general
- 13. GROUP OF BIOLOGICAL DANGEROUS INDUSTRIAL HAZARDS INCLUDES: zoonotic bacterial, viral, fungal infections (anthrax, foot-and-mouth disease, Bovine
- 14. GROUP OF PSYCHO-PHYSIOLOGICAL INDUSTRIAL HAZARDS INCLUDES: excessive physical activities: static (hold of heavy loads); dynamic (lifting
- 15. According to the character and extent of energy expenditure, physical labour is characterized by its weight
- 16. Occupational diseases caused solely by industrial and occupational hazards, their consequences in the near and distant
- 17. OCCUPATIONAL DISEASES ARE DIVIDED INTO 7 GROUPS: 1. Diseases caused by chemical agents: acute and chronic
- 18. decompression - caisson sickness; acute, chronic overheating; noise, vibratory diseases etc.; 4. Diseases caused by overload
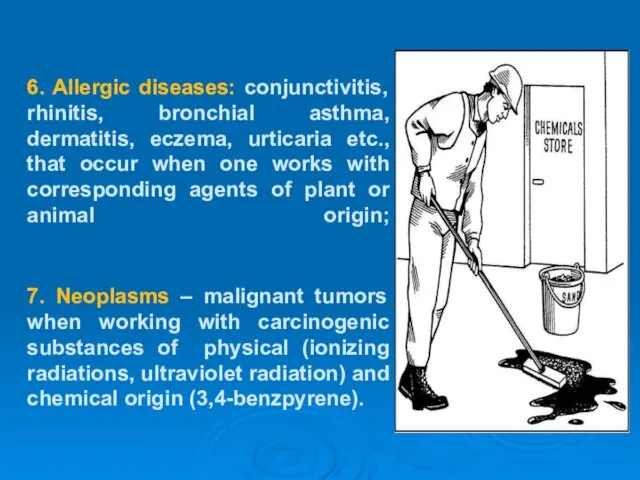
- 19. 6. Allergic diseases: conjunctivitis, rhinitis, bronchial asthma, dermatitis, eczema, urticaria etc., that occur when one works
- 20. Industrial hazards and occupational diseases and poisonings Considering listed industrial hazards and occupational diseases and poisonings
- 21. Industrial hazards and occupational diseases and poisonings to study impact of different hazards of industrial environment,
- 22. Preventive medical measures must include: participation in development of technical and engineering sanitation of working conditions
- 23. Methods and means of measurement of industrial hazard Methods and means of measurement of industrial hazards
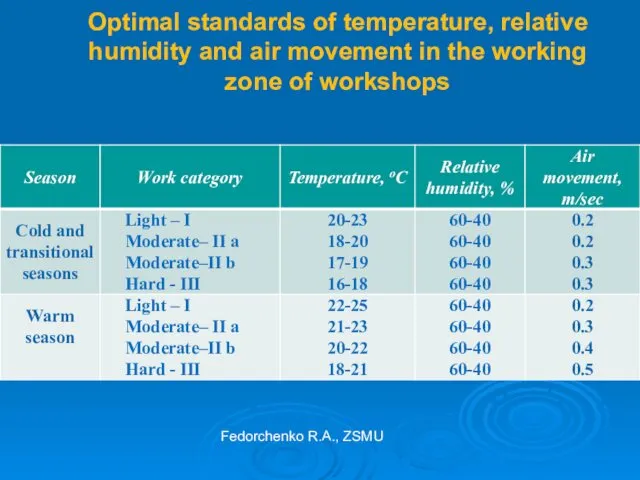
- 24. Optimal standards of temperature, relative humidity and air movement in the working zone of workshops Fedorchenko
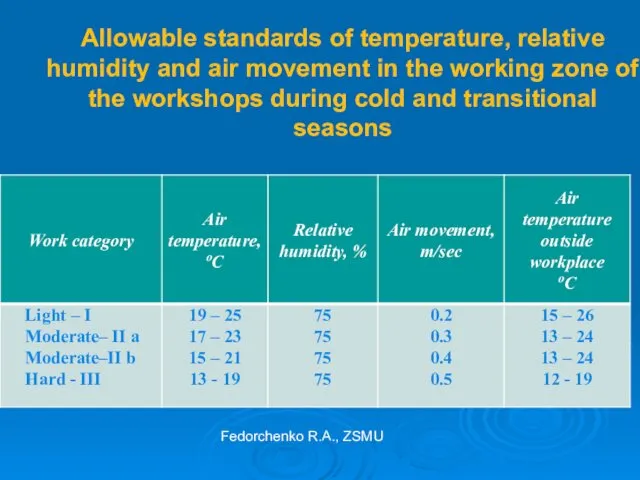
- 25. Allowable standards of temperature, relative humidity and air movement in the working zone of the workshops
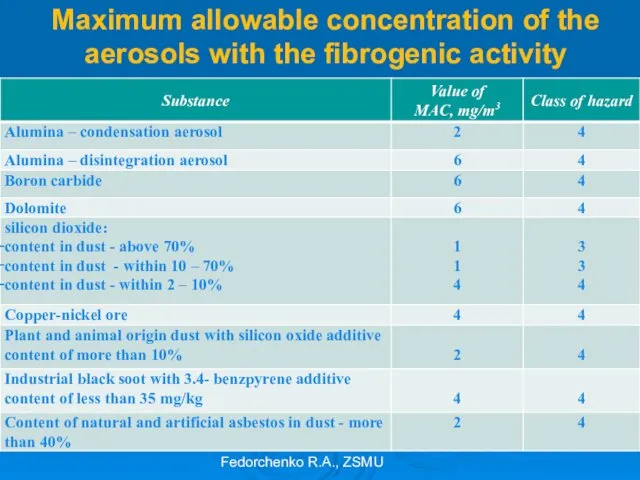
- 26. Maximum allowable concentration of the aerosols with the fibrogenic activity Fedorchenko R.A., ZSMU
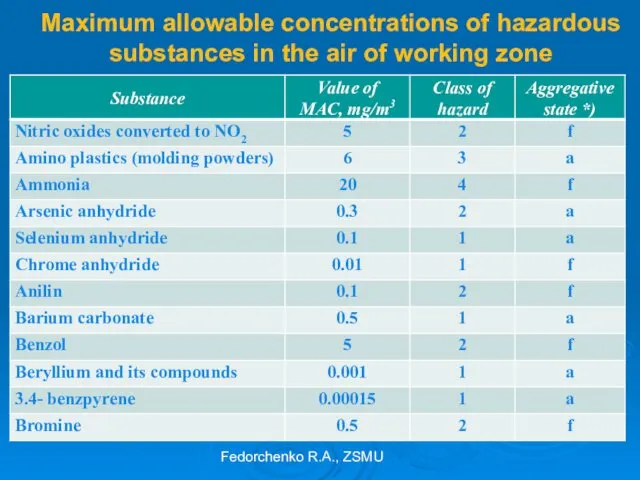
- 27. Maximum allowable concentrations of hazardous substances in the air of working zone Fedorchenko R.A., ZSMU
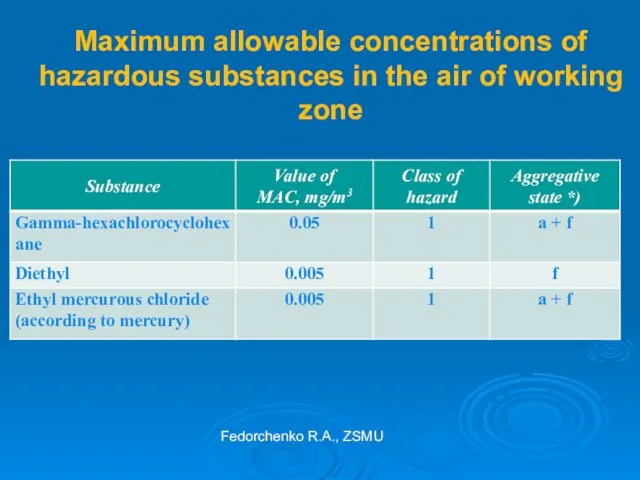
- 28. Maximum allowable concentrations of hazardous substances in the air of working zone Fedorchenko R.A., ZSMU
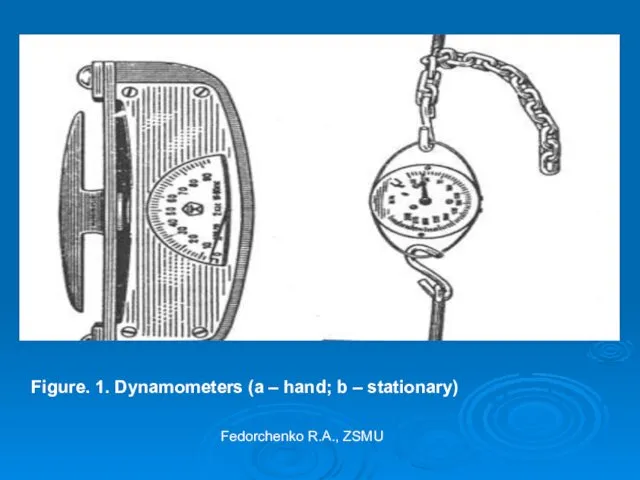
- 29. Method for assessment of fatigability during physical labour Dynamometry. To measure muscle strength of the hand,
- 30. Figure. 1. Dynamometers (a – hand; b – stationary) Fedorchenko R.A., ZSMU
- 31. Ergography Ergography is defined as measurement of muscle efficiency using ergograph – device of desk-size. Еrgograph
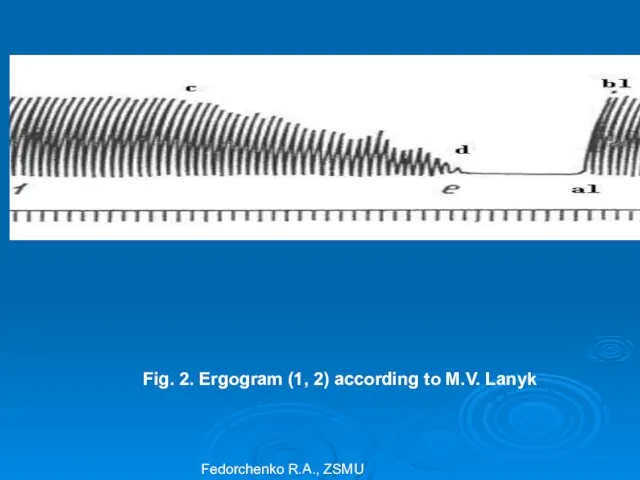
- 32. Ergography Decoding of ergograms that were taken at the beginning and at the end of the
- 33. Fig. 2. Ergogram (1, 2) according to M.V. Lanyk Fedorchenko R.A., ZSMU
- 34. Ergography These data are calculated according to depth of myograms in mm and their changes with
- 35. Ergography heartbeat frequency (pulse) before and after load and its restitution; systolic and diastolic blood pressure,
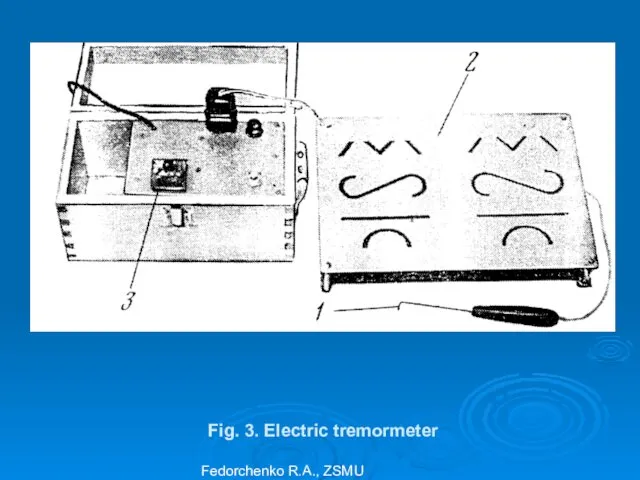
- 36. Electric tremormetry is detection of frequency amplitude of involuntary shaking of hands, inferior limbs allows to
- 37. Electric tremormetry Tested person conducts the probe along figured slots trying not to touch their edges
- 38. Fig. 3. Electric tremormeter Fedorchenko R.A., ZSMU
- 39. Attention analysis by search of numbers Method gives an idea of extent and tempo of psychical
- 40. Attention analysis by search of numbers On the table you must point at and pronounce aloud
- 41. Attention analysis by search of numbers Fedorchenko R.A., ZSMU
- 42. Examination of attention by search of numbers with switching This method is aimed to determine an
- 43. Examination of attention by search of numbers with switching The tested person obtains instruction:” You’ll see
- 44. Examination of attention by search of numbers with switching When assessing results, time of the task
- 45. Examination of attention by search of numbers with switching For example, some of the tested people
- 46. Examination of memory by memorization of geometric figures This method is used for assessment of functional
- 47. Examination of memory by memorization of geometric figure His attention is paid to the difference between
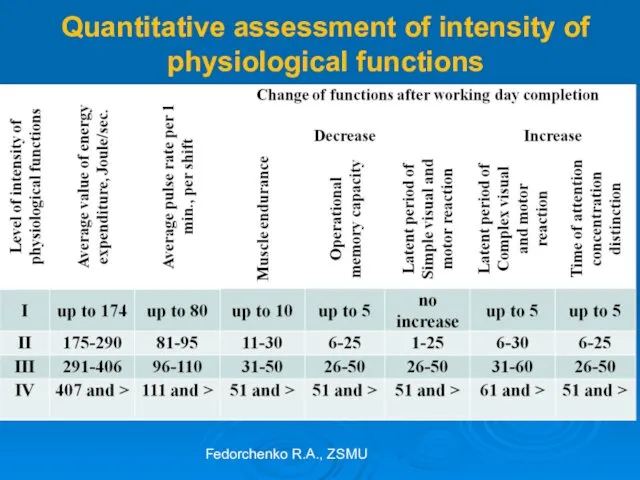
- 48. Quantitative assessment of intensity of physiological functions Fedorchenko R.A., ZSMU
- 49. EXHAUSTION, theories of the mechanism of its development. Among many theories (more than 20) development exhaustion
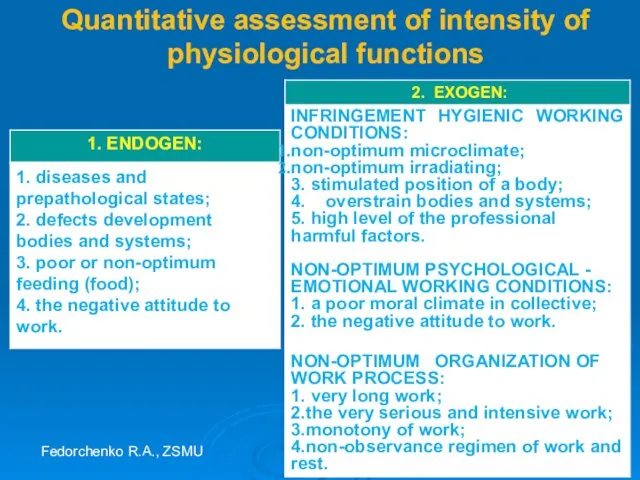
- 50. Quantitative assessment of intensity of physiological functions Fedorchenko R.A., ZSMU
- 51. The basic directions of prevention exhaustion: 1. SCIENTIFIC SUBSTANTIATION and KEEPING HYGIENIC DEMANDS to WORKING CONDITIONS
- 52. The basic directions of prevention exhaustion: 3.TECHNICAL MEASURES ON ENRICHING WORKING CONDITIONS ON WORKSTATION: (Usage ERGONOMICS
- 54. Скачать презентацию







































 Атмосфераның ластануы. Атмосфералық ауаның ластануының зардаптары
Атмосфераның ластануы. Атмосфералық ауаның ластануының зардаптары Охраняемые территории Липецкой области
Охраняемые территории Липецкой области Збережи флору рідної Батьківщини
Збережи флору рідної Батьківщини Охрана атмосферного воздуха
Охрана атмосферного воздуха Ұлттық экология бастаулары
Ұлттық экология бастаулары День Черного моря. Экоурок
День Черного моря. Экоурок Пластмассовые отходы
Пластмассовые отходы Жизнь организмов на планете Земля. Природные сообщества
Жизнь организмов на планете Земля. Природные сообщества Сообщество, экосистема, биоценоз
Сообщество, экосистема, биоценоз Влияние нефтедобычи на почвенный покров Ненецкого автономного округа
Влияние нефтедобычи на почвенный покров Ненецкого автономного округа Глобальная энергетическая проблема
Глобальная энергетическая проблема Greenpin. Экология начинается дома
Greenpin. Экология начинается дома Земля- наш дом
Земля- наш дом Природные ресурсы и рациональное природопользование
Природные ресурсы и рациональное природопользование Кислотные осадки: под каким дождем мы мокнем
Кислотные осадки: под каким дождем мы мокнем Аварии на АЭС
Аварии на АЭС презентация Охрана Чёрного моря- дело каждого!
презентация Охрана Чёрного моря- дело каждого! Разделяй с нами. Экоурок для 7—11 классов. Приложение 6
Разделяй с нами. Экоурок для 7—11 классов. Приложение 6 Устойчивое развитие
Устойчивое развитие Экотрадиция. Обычай в повседневной жизни общества, основанный на заботе о природе
Экотрадиция. Обычай в повседневной жизни общества, основанный на заботе о природе Предельно-допустимая концентрация веществ в водной среде
Предельно-допустимая концентрация веществ в водной среде Акция Добрые крышечки
Акция Добрые крышечки Кислотные дожди
Кислотные дожди Презентация по экологии 5 класс. Тема: ПРЕДМЕТ И ЗАДАЧИ ЭКОЛОГИИ.
Презентация по экологии 5 класс. Тема: ПРЕДМЕТ И ЗАДАЧИ ЭКОЛОГИИ. Глобальные экологические проблемы
Глобальные экологические проблемы e4385cde0f2d4c0980ea7e95eac94beb
e4385cde0f2d4c0980ea7e95eac94beb Угрозы и проблемы 21 века
Угрозы и проблемы 21 века Лондонский смог
Лондонский смог