Содержание
- 2. The concept of ecosystem resilience The stability of natural biological systems (population, or biocoenosis) should understood
- 3. Ecosystem - an open, self-regulating and self-developing system Provided by: resistant relationships between their components (community
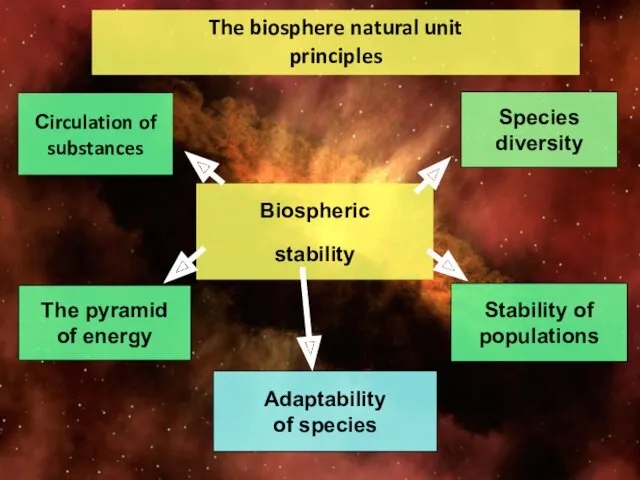
- 4. The biosphere natural unit principles Biospheric stability Species diversity Stability of populations Сirculation of substances The
- 5. Features of natural and man-made ecosystems Homeostasis - population or ecosystem ability to maintain stability in
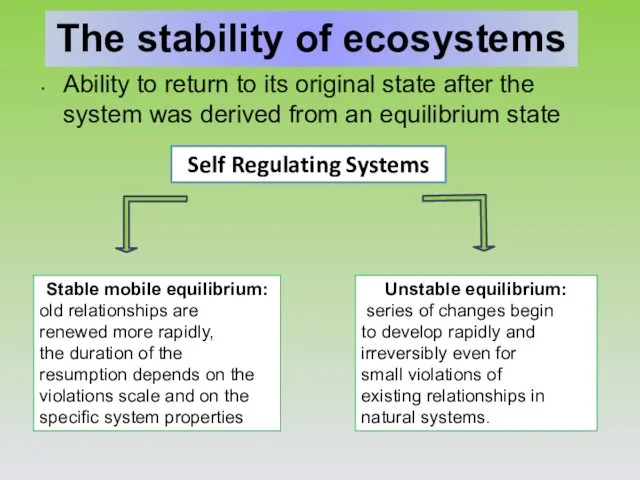
- 6. The stability of ecosystems Ability to return to its original state after the system was derived
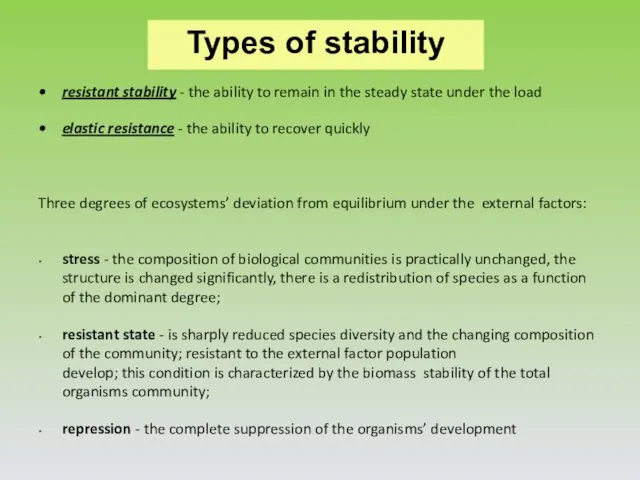
- 7. Types of stability resistant stability - the ability to remain in the steady state under the
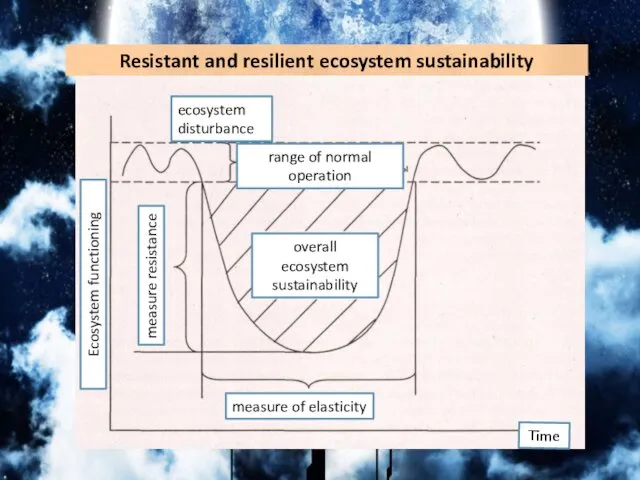
- 8. Resistant and resilient ecosystem sustainability Ecosystem functioning ecosystem disturbance range of normal operation overall ecosystem sustainability
- 12. Скачать презентацию





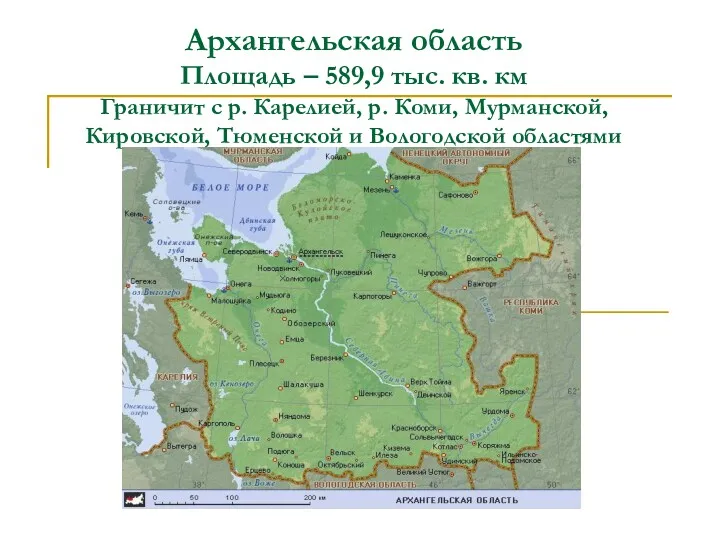 Архангельская область
Архангельская область Утилізація сміття
Утилізація сміття Биоэкология. Структура современной экологии
Биоэкология. Структура современной экологии Отчет о проведении краевой экологической акции Зеленая волна
Отчет о проведении краевой экологической акции Зеленая волна Группа компаний Экологический центр
Группа компаний Экологический центр История экологии
История экологии Исследования водных объектов почвенного покрова, геологической среды и атмосферы Бузулукского бора
Исследования водных объектов почвенного покрова, геологической среды и атмосферы Бузулукского бора Космический мусор - угроза развитию нашей цивилизации
Космический мусор - угроза развитию нашей цивилизации Презентация Экологические ниши
Презентация Экологические ниши Экологиялық мониторинг
Экологиялық мониторинг Красная книга. Охрана редких видов Ленинградской области
Красная книга. Охрана редких видов Ленинградской области Примеры экологических катастроф и их последствия
Примеры экологических катастроф и их последствия Экологический след
Экологический след Памятники природы Новосибирской области
Памятники природы Новосибирской области Презентация Загрязнение окружающей среды
Презентация Загрязнение окружающей среды Мікроеволюція
Мікроеволюція Авария на Чернобыльской АЭС 26 апреля 1986 года
Авария на Чернобыльской АЭС 26 апреля 1986 года Забруднення атмосфери
Забруднення атмосфери Важнейшие абиотические факторы и адаптации к ним организмов
Важнейшие абиотические факторы и адаптации к ним организмов Экология негіздері
Экология негіздері Природное сообщество
Природное сообщество Законодательство Республики Беларусь в области охраны окружающей среды и рационального использования природных ресурсов
Законодательство Республики Беларусь в области охраны окружающей среды и рационального использования природных ресурсов Мир, который нужен мне!
Мир, который нужен мне! конкурс презентаций Мы в ответе за тех, кого приручили
конкурс презентаций Мы в ответе за тех, кого приручили Взаємовідносини суспільства і природи. Класифікація видів природокористування
Взаємовідносини суспільства і природи. Класифікація видів природокористування Інтеграція різночасових супутникових спостережень і даних інвентаризації лісів в Україні
Інтеграція різночасових супутникових спостережень і даних інвентаризації лісів в Україні Мониторинг техногенно=екологічних небезпек та НС
Мониторинг техногенно=екологічних небезпек та НС Су электр станциялары мен су бөгендерін салу барысында қоршаған ортаны қорғау жөніндегі шаралар
Су электр станциялары мен су бөгендерін салу барысында қоршаған ортаны қорғау жөніндегі шаралар