Слайд 2

Lesson objectives
Introduce the concept of interest rate swaps and its importance
for financial market.
Review the mechanics of swap contracts.
Evaluate cash flows associated with swap contracts.
Study term structure and empirical behavior of swaps
Слайд 3

Слайд 4
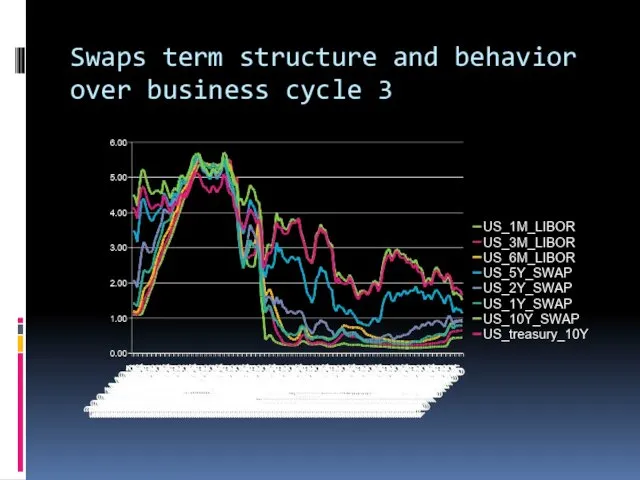
Swaps term structure and behavior over business cycle 3
Слайд 5

Uses of interest rate swaps
Portfolio management:
add or subtract duration, adjust interest
rate exposure
offset the risks posed by interest rate volatility.
Speculation:
Swaps allow to speculate on movements in interest rates while potentially avoiding the cost of long and short positions in Treasuries or other assets.
Слайд 6

Uses of interest rate swaps 2
Corporate finance (hedging)
Hedge against falling interest
rates by paying floating and receiving fixed.
Risk management
Offset the residual interest risk in the portfolio.
Слайд 7

Essence of swap contracts
Exchange two cash flows generated by different interest
rates.
For instance fixed swap rate are paid (received) against those based on floating LIBOR rate.
Swap contract is arranged as a pure exchange of cash flows. Thus no additional cash payment should be required at initiation.
Слайд 8

Swap cash flows: example
Interest rate swap with the following parameters
1000000 USD notional amount (N)
7% fixed rate p.a.
2 years maturity, payments in semiannual frequency
Floating cash flow generated by 6month LIBOR(Lt)
A fixed payer (also called buyer of the swap) will pay fixed payments and receive floating payments.
A fixed receiver(also called seller of the swap) will do the opposite
Слайд 9
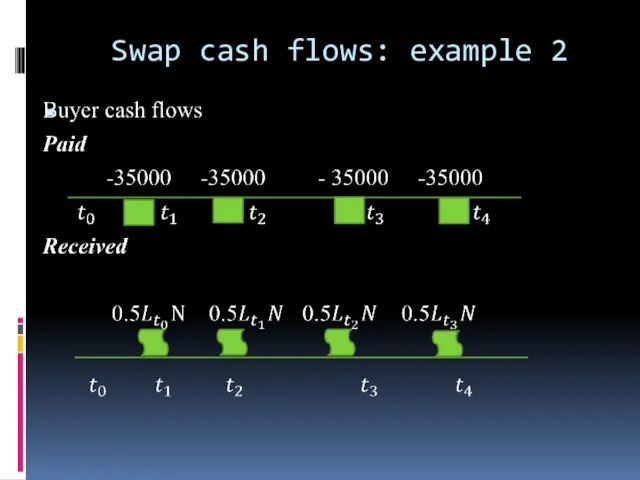
Swap cash flows: example 2
Слайд 10

Dependence on benchmark rate
Exchange of defined cash flows is made acceptable
to both parties by adding corresponding spread to one of cash flows.
The market includes swap spread in the fixed rate.
The benchmark rate for interest rate swap is often selected as sovereign bond yield of the same maturity.
By adjusting the spread with the benchmark rate market can bring two parties together to perform exchange of cash flows.
Agreed fixed rate=Swap rate= Benchmark rate+ + Swap spread
Слайд 11

Interest rate swap decomposition
Слайд 12
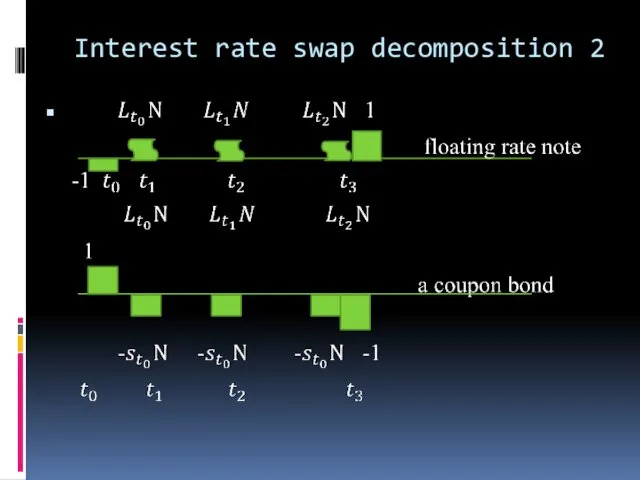
Interest rate swap decomposition 2
Слайд 13

Interest rate swap decomposition 2
Long swap
Long floating rate note paying
LIBOR
Слайд 14
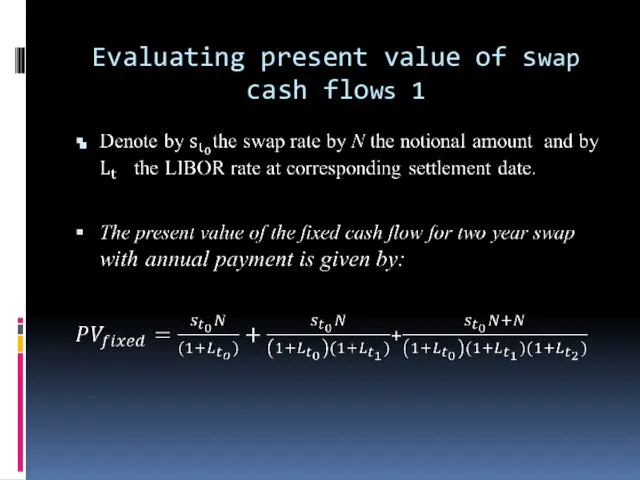
Evaluating present value of swap cash flows 1
Слайд 15

Evaluating present value of swap cash flows 2
Слайд 16

Connection between swap rates and FRA rates
Слайд 17

Connection between swap rates bond rates and FRA rates
















 Оценка недвижимости. Задачник для подготовки к экзамену
Оценка недвижимости. Задачник для подготовки к экзамену Налогообложение криптовалютных операций и ІСО
Налогообложение криптовалютных операций и ІСО Державний фінансовий аудит суб’єктів господарювання
Державний фінансовий аудит суб’єктів господарювання Обязательное страхование: социальное и медицинское страхование
Обязательное страхование: социальное и медицинское страхование Цели и задачи краткосрочной финансовой политики предприятия
Цели и задачи краткосрочной финансовой политики предприятия Zavaleev_Diplom
Zavaleev_Diplom Nauka o organizacji. Konsorcjum
Nauka o organizacji. Konsorcjum Система национальных счетов (СНС) и принципы ее
Система национальных счетов (СНС) и принципы ее Экономика семьи
Экономика семьи Отчет главы Сосьвинского городского округа
Отчет главы Сосьвинского городского округа Налоги юридических лиц
Налоги юридических лиц Прохождение заявки от создания до принятия решения. Тинькофф
Прохождение заявки от создания до принятия решения. Тинькофф Принципы оценочной деятельности
Принципы оценочной деятельности Министерство Финансов Кыргызской Республики
Министерство Финансов Кыргызской Республики Tax update for Аdvisors
Tax update for Аdvisors Социальный проект Школьные системы. Автоматизированная система безналичных расчетов школьного питания
Социальный проект Школьные системы. Автоматизированная система безналичных расчетов школьного питания ООО Управление автомобильного транспорта
ООО Управление автомобильного транспорта Invest Club
Invest Club Деньги Кыргызстана
Деньги Кыргызстана Новые продукты по банковским картам
Новые продукты по банковским картам Проект городского бюджета на 2019 год и плановый период 2020 и 2021 годов, г. Череповец
Проект городского бюджета на 2019 год и плановый период 2020 и 2021 годов, г. Череповец Моя первая банковская карта. Техника безопасности
Моя первая банковская карта. Техника безопасности Доходы государственных учреждений
Доходы государственных учреждений Программа потребительского кредитования Лучшие покупки. Приорбанк ОАО
Программа потребительского кредитования Лучшие покупки. Приорбанк ОАО Финансовые институты и банковская система. 11 класс
Финансовые институты и банковская система. 11 класс Базовый семинар. Первый день семинара
Базовый семинар. Первый день семинара Аудит операций с ценными бумагами
Аудит операций с ценными бумагами Страноведческие образы в бонистике
Страноведческие образы в бонистике