Содержание
- 2. Higher School of Economics , Moscow, 2016 Outline Problem statement Centrality measures Classical centralities Shapley value
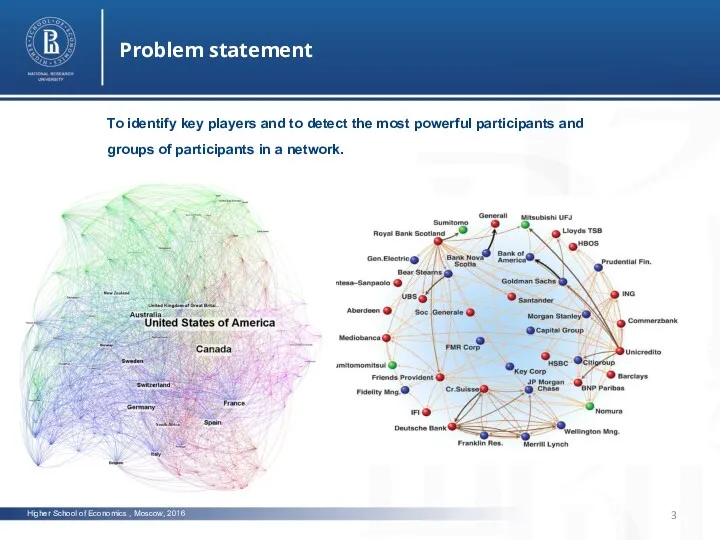
- 3. Higher School of Economics , Moscow, 2016 Problem statement To identify key players and to detect
- 4. Higher School of Economics , Moscow, 2016 Centrality measures (Classical) photo Degree [Newman 2010] Eigenvector [Bonacich
- 5. Higher School of Economics , Moscow, 2016 Centrality measures (Shapley value)
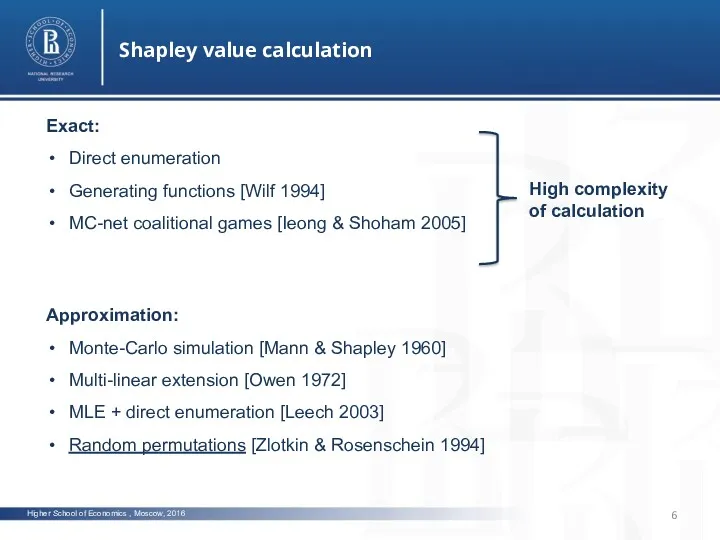
- 6. Higher School of Economics , Moscow, 2016 Shapley value calculation Exact: Direct enumeration Generating functions [Wilf
- 7. Higher School of Economics , Moscow, 2016 Conclusion Key nodes in a network Network centrality measures
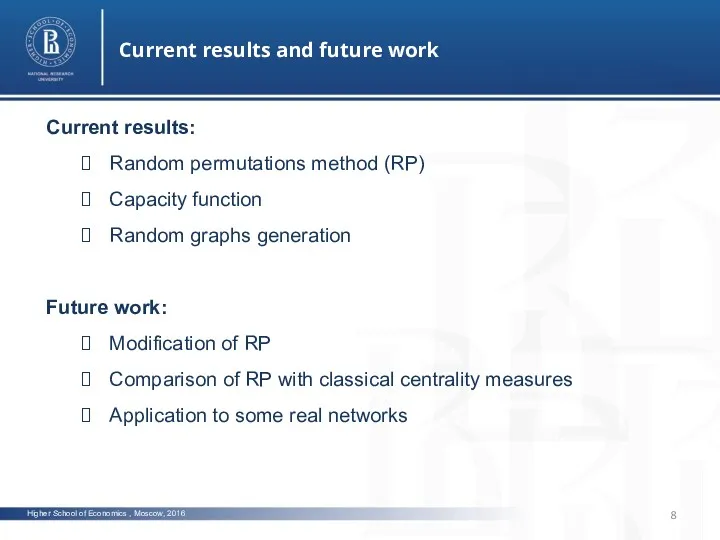
- 8. Higher School of Economics , Moscow, 2016 Current results and future work Current results: Random permutations
- 9. Higher School of Economics , Moscow, 2016 References Algaba et. al.: Computing power indices in weighted
- 11. Скачать презентацию



 Анализ рынка туристической отрасли России
Анализ рынка туристической отрасли России Экономическая теория образования
Экономическая теория образования Потребление и сбережение. Мультипликатор автономных расходов. Использование личного располагаемого дохода
Потребление и сбережение. Мультипликатор автономных расходов. Использование личного располагаемого дохода Рынок, цена, конкуренция. (8 класс)
Рынок, цена, конкуренция. (8 класс) Глобализация в мировой системе и её влияние на учетные концепции бухгалтерского учета в России
Глобализация в мировой системе и её влияние на учетные концепции бухгалтерского учета в России Решение проблем. Производственный анализ
Решение проблем. Производственный анализ Теория поведения потребителя
Теория поведения потребителя Тема 14. Несостоятельность рынка и вмешательство государства
Тема 14. Несостоятельность рынка и вмешательство государства Нефть в пространстве и пространство нефти
Нефть в пространстве и пространство нефти Управление личными финансами. Банковские услуги. (Лекция 12)
Управление личными финансами. Банковские услуги. (Лекция 12) тема 6
тема 6 Ауыл шаруашылығы
Ауыл шаруашылығы Социальная политика государства
Социальная политика государства Бюджет. Доходы и Расходы. Их согласование по суммам и срокам
Бюджет. Доходы и Расходы. Их согласование по суммам и срокам Тұрақты даму мақсаттарына жету механизмдері
Тұрақты даму мақсаттарына жету механизмдері Закон спроса. Закон предложения
Закон спроса. Закон предложения Market research. Benefactor
Market research. Benefactor Доходы населения и их источники
Доходы населения и их источники Экономика и ее роль в жизни современного общества
Экономика и ее роль в жизни современного общества Миграционные процессы и мировая политика
Миграционные процессы и мировая политика Монополия түрлері
Монополия түрлері Экономическая сфера
Экономическая сфера Доходы населения
Доходы населения Методологические основы планирования и прогнозирования
Методологические основы планирования и прогнозирования Экономика в годы перестройки
Экономика в годы перестройки Модель AD-AS
Модель AD-AS Основы налогообложения. Налоги и налоговая система
Основы налогообложения. Налоги и налоговая система Сутність та визначення продуктивності праці
Сутність та визначення продуктивності праці