Содержание
- 2. 13.1 Can Financing Decisions Create Value? Earlier parts of the book show how to evaluate investment
- 3. What Sort of Financing Decisions? Typical financing decisions include: How much debt and equity to sell
- 4. How to Create Value through Financing Fool Investors Empirical evidence suggests that it is hard to
- 5. 13.2 A Description of Efficient Capital Markets An efficient capital market is one in which stock
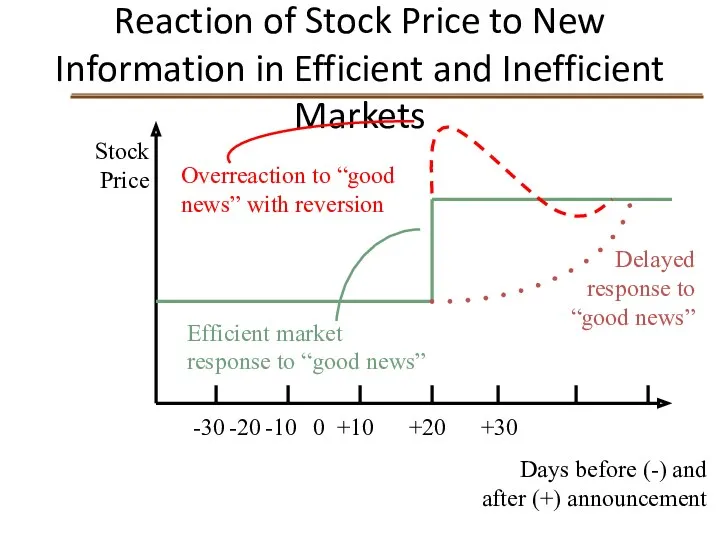
- 6. Reaction of Stock Price to New Information in Efficient and Inefficient Markets Stock Price -30 -20
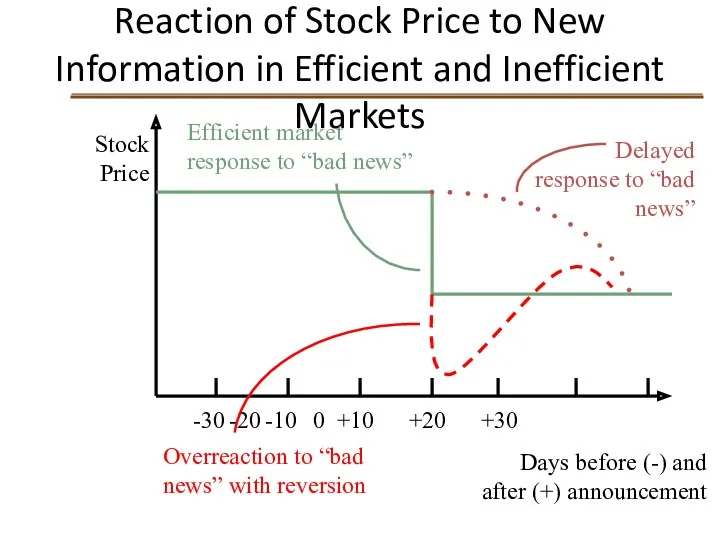
- 7. Reaction of Stock Price to New Information in Efficient and Inefficient Markets Stock Price -30 -20
- 8. 13.3 The Different Types of Efficiency Weak Form Security prices reflect all information found in past
- 9. Weak Form Market Efficiency Security prices reflect all information found in past prices and volume. If
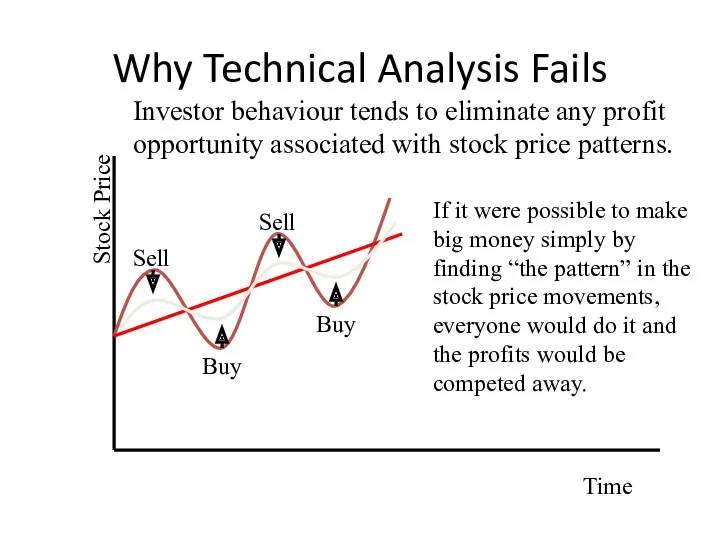
- 10. Why Technical Analysis Fails Stock Price Time Investor behaviour tends to eliminate any profit opportunity associated
- 11. Semi-Strong Form Market Efficiency Security prices reflect all publicly available information. Publicly available information includes: Historical
- 12. Strong Form Market Efficiency Security prices reflect all information—public and private. Strong form efficiency incorporates weak
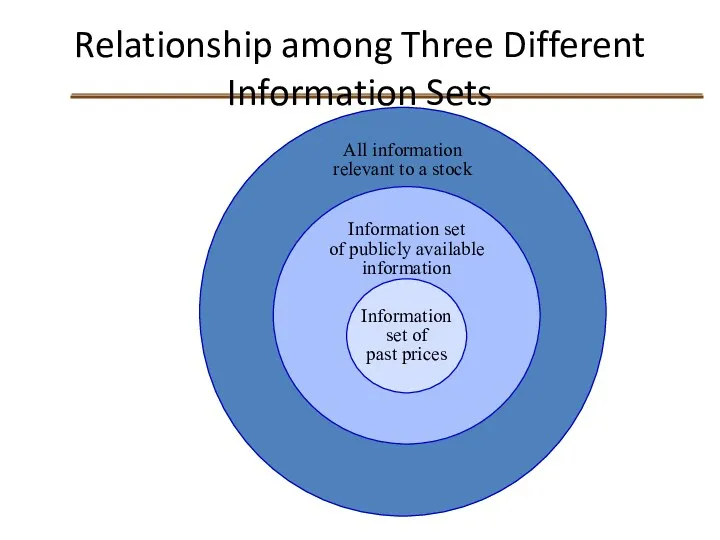
- 13. Relationship among Three Different Information Sets
- 14. Some Common Misconceptions Much of the criticism of the EMH has been based on a misunderstanding
- 15. What the EMH Does and Does NOT Say Investors can throw darts to select stocks. This
- 16. 13.4 The Evidence The record on the EMH is extensive, and in large measure it is
- 17. Are Changes in Stock Prices Random? Can we really tell? Many psychologists and statisticians believe that
- 18. What Pattern Do You See? Double-click on this Excel chart to see a different random series.
- 19. Event Studies: How Tests Are Structured Event studies are one type of test of the semi-strong
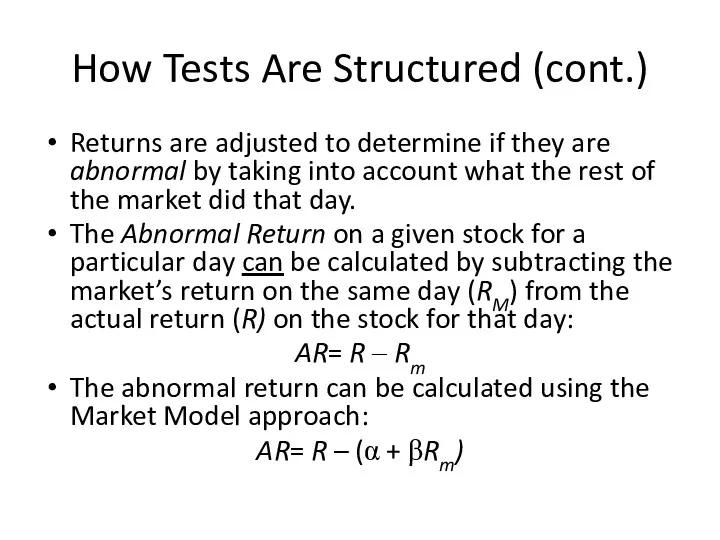
- 20. How Tests Are Structured (cont.) Returns are adjusted to determine if they are abnormal by taking
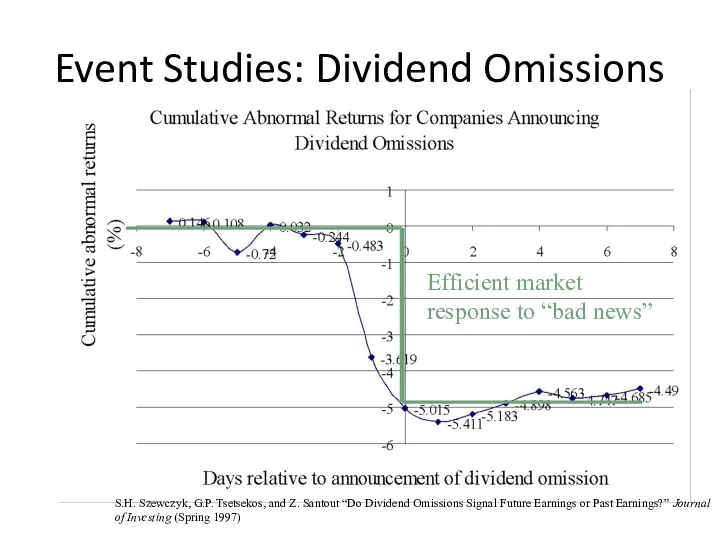
- 21. Event Studies: Dividend Omissions Efficient market response to “bad news” S.H. Szewczyk, G.P. Tsetsekos, and Z.
- 22. Event Study Results Over the years, event study methodology has been applied to a large number
- 23. Issues in Examining the Results Magnitude Issue Selection Bias Issue Lucky Event Issue Possible Model Misspecification
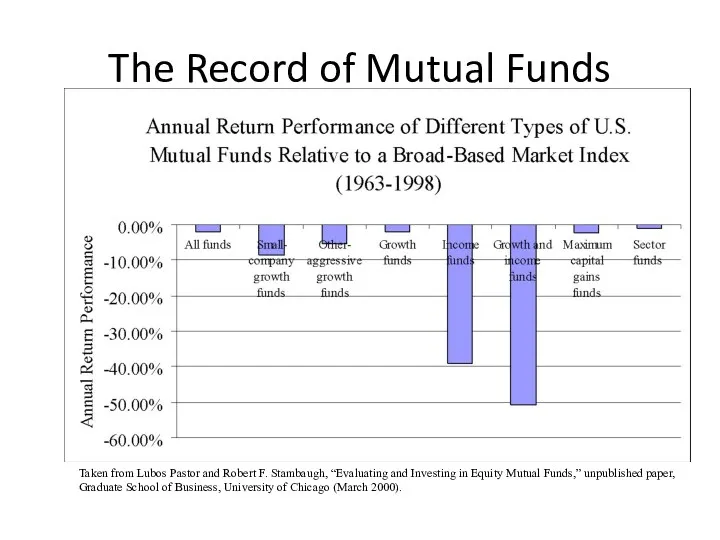
- 24. The Record of Mutual Funds If the market is semistrong-form efficient, then no matter what publicly
- 25. The Record of Mutual Funds Taken from Lubos Pastor and Robert F. Stambaugh, “Evaluating and Investing
- 26. The Strong Form of the EMH One group of studies of strong-form market efficiency investigates insider
- 27. Views Contrary to Market Efficiency Stock Market Crash of 1987 The NYSE dropped between 20-percent and
- 28. 13.5 Implications for Corporate Finance Because information is reflected in security prices quickly, investors should only
- 29. 13.5 Implications for Corporate Finance The EMH has three implications for corporate finance: The price of
- 30. Why Doesn’t Everybody Believe the EMH? There are optical illusions, mirages, and apparent patterns in charts
- 32. Скачать презентацию





















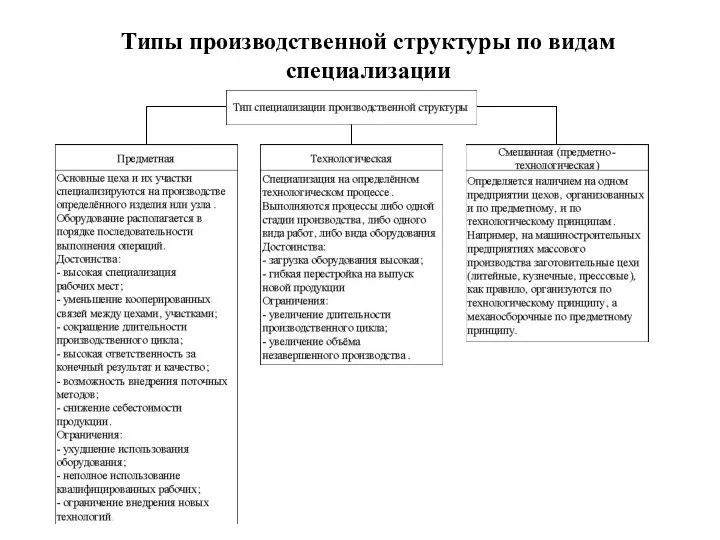 Типы производственной структуры по видам специализации
Типы производственной структуры по видам специализации Природоохранные затраты и их экономическая сущность (тема 14)
Природоохранные затраты и их экономическая сущность (тема 14) Основные тенденции развития российской экономики: от рецессии к стагнации
Основные тенденции развития российской экономики: от рецессии к стагнации Світові економічні зв`язки.11 клас
Світові економічні зв`язки.11 клас Демографическая проблема
Демографическая проблема Игра-обобщение по экономике для 10 класса
Игра-обобщение по экономике для 10 класса Понятие, разновидности рынка. Сегментация и ёмкость рынка. Рыночная конкуренция
Понятие, разновидности рынка. Сегментация и ёмкость рынка. Рыночная конкуренция Управление процессами разработки и реализации инвестиционного проекта на примере ПАО КАМАЗ Автомобильный завод
Управление процессами разработки и реализации инвестиционного проекта на примере ПАО КАМАЗ Автомобильный завод Определение емкости регионального рынка товаров продовольственного назначения
Определение емкости регионального рынка товаров продовольственного назначения Социально-экономическое развитие России 1860-е - 1890-е гг
Социально-экономическое развитие России 1860-е - 1890-е гг Виды рынков и их классификации
Виды рынков и их классификации Безработица. Экономически активное население
Безработица. Экономически активное население Спрос на деньги. Понятие, функции денежного спроса в различных экономических школах
Спрос на деньги. Понятие, функции денежного спроса в различных экономических школах Цена, спрос, предложение
Цена, спрос, предложение Проблемы обеспечения конкуренции при закупках лекарств для государственных и муниципальных нужд
Проблемы обеспечения конкуренции при закупках лекарств для государственных и муниципальных нужд Что такое регион и регионоведение
Что такое регион и регионоведение Алкогольная промышленность
Алкогольная промышленность Выпускная работа. Обоснование перспектив развития предприятия Фортуна Крым Трейд
Выпускная работа. Обоснование перспектив развития предприятия Фортуна Крым Трейд Рыночные отношения в экономике
Рыночные отношения в экономике Единое экономическое пространство
Единое экономическое пространство Периоды формирования концепции устойчивого развития
Периоды формирования концепции устойчивого развития Рынки факторов производства
Рынки факторов производства Сущность денег
Сущность денег Организация инструментального хозяйства
Организация инструментального хозяйства Теория производства
Теория производства Предмет экономической социологии
Предмет экономической социологии Allgemeines Gleichgewicht und ökonomische Effizienz
Allgemeines Gleichgewicht und ökonomische Effizienz Управление личными финансами. Рынок коллективных и индивидуальных форм инвестирования. (Лекция 13)
Управление личными финансами. Рынок коллективных и индивидуальных форм инвестирования. (Лекция 13)