Содержание
- 2. References: Marc J. Dollinger, ENTREPRENEURSHIP: Strategies and Resources, FOURTH EDITION, Kelley School of Business, INDIANA UNIVERSITY
- 3. Define the role of small business and entrepreneurship in the economy. Compare and contrast economic systems.
- 4. Entrepreneurship is the primary catalyst for economic growth. Being a successful entrepreneur requires an understanding of
- 5. factors of production scarcity market structure monopoly demand elastic demand inelastic demand diminishing marginal utility supply
- 6. As an entrepreneur, you accept the risks and responsibilities of business ownership. entrepreneur an individual who
- 7. Creating and running a business venture requires a variety of skills. venture a new business undertaking
- 8. Starting a home-based business calls for entrepreneurship on the part of the owner. About one in
- 9. Knowledge of economics contributes to an understanding of how entrepreneurs and customers interact. economics the study
- 10. An economic system includes a set of laws, institutions, and activities that guide economic decision making.
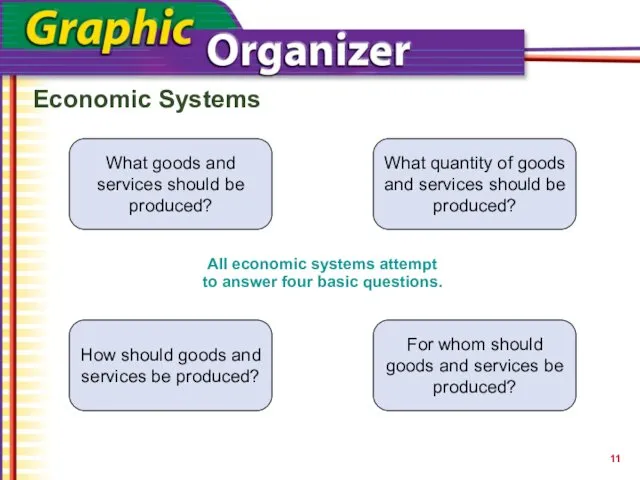
- 11. ? ? ? ? Economic Systems All economic systems attempt to answer four basic questions. What
- 12. Most democratic nations have a free enterprise system. free enterprise system an economic system in which
- 13. Making a profit is a primary incentive of free enterprise. profit money that is left over
- 14. Perfect competition is a market structure in which there are numerous buyers and sellers and no
- 15. The government may grant a temporary monopoly to an inventor. monopoly a market structure in which
- 16. Under antitrust laws, some forms of oligopoly are illegal. oligopoly a market structure in which there
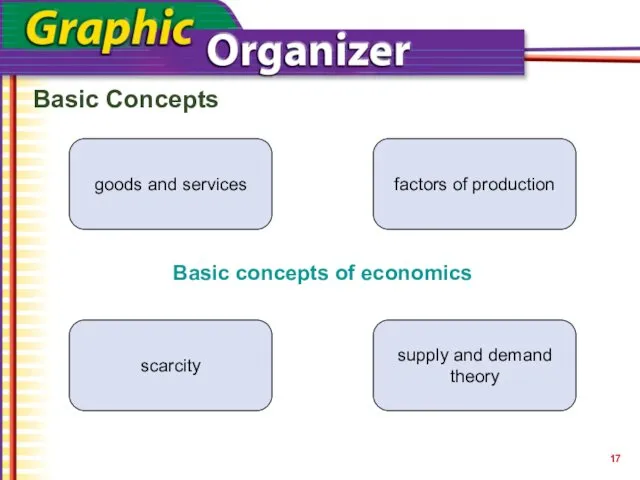
- 17. Basic Concepts Basic concepts of economics goods and services factors of production scarcity supply and demand
- 18. Goods and services are the products of our economic system. Goods and Services goods tangible (or
- 19. Entrepreneurs respond to consumers’ wants and needs with goods and services. want something that you do
- 20. There are four basic factors of production: Factors of Production factors of production the resources businesses
- 21. The principle of scarcity means giving up one thing in order to have something else. Scarcity
- 22. In a free enterprise system, the price of a product is determined by demand. Supply and
- 23. The degree to which demand for a product is affected by its price is either governed
- 24. Due to the law of diminishing marginal utility, even when a product’s price is low, people
- 25. Supply is continually shifting in the marketplace. supply the amount of goods or services that producers
- 26. If something is in heavy demand, but in short supply, prices will go up. If something
- 27. Because supply and demand are continually shifting in the marketplace, the change creates surpluses, shortages, and
- 28. The federal government publishes statistics that help entrepreneurs understand the economy and predict possible changes. The
- 29. There are four stages of the business cycle: growth, recession, depression, and recovery. Economic Indicators and
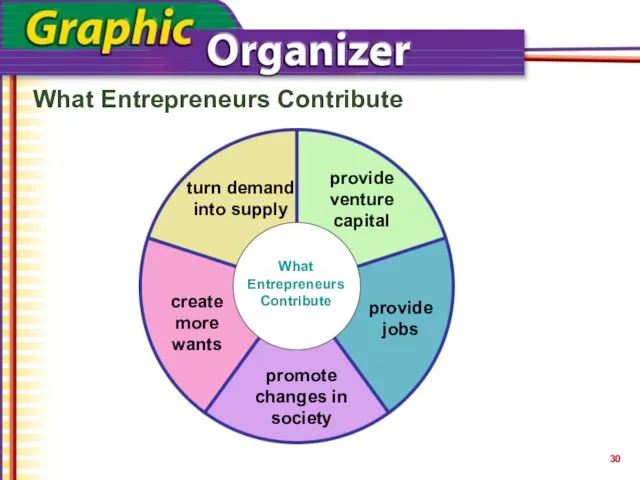
- 30. What Entrepreneurs Contribute What Entrepreneurs Contribute turn demand into supply provide venture capital provide jobs promote
- 31. The difference between small businesses and entrepreneurial ventures is that owners start small businesses to create
- 32. Define the role of small business and entrepreneurship in the economy. After You Read Entrepreneurs start
- 33. Compare and contrast economic systems. Economic systems include a set of laws, institutions, and activities that
- 34. Explain how economics is about making choices. Because resources are in limited supply, if the consumer
- 35. Define the role of economic indicators and business cycles. The federal government provides statistics (economic indicators)
- 36. Describe what entrepreneurs contribute to the economy. Entrepreneurs recognize consumer wants and see the economic opportunities
- 37. Analyze entrepreneurship from a historical perspective. Name the five components of the entrepreneurial start-up process. Explain
- 38. The entrepreneurial start-up process includes: the entrepreneur the environment the opportunity start-up resources the new venture
- 39. discontinuance new venture organization business failure Content Vocabulary enterprise zones opportunity start-up resources
- 40. Entrepreneurship has been a distinct feature of American culture since the American Revolution, but it was
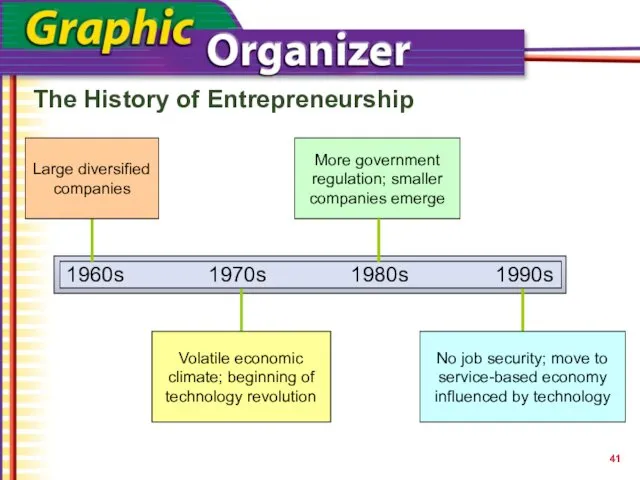
- 41. The History of Entrepreneurship 1960s 1990s 1970s 1980s
- 42. The five components of the entrepreneurial start-up process work together to create a new business. the
- 43. The entrepreneur is the driving force of the start-up process. Entrepreneurs recognize opportunities and pull together
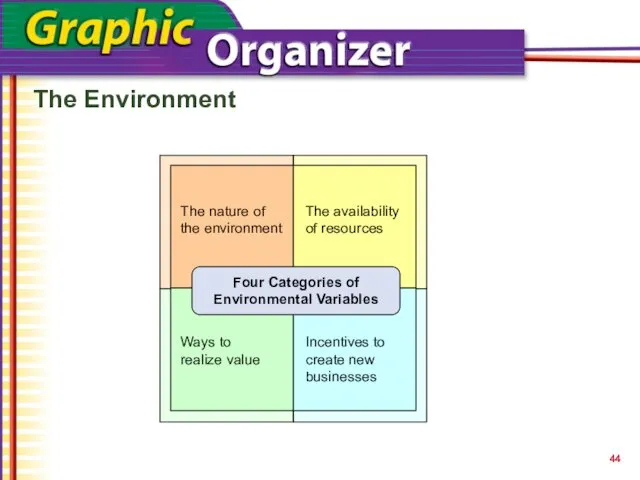
- 44. The Environment Four Categories of Environmental Variables
- 45. New businesses seek enterprise zones that provide incentives. enterprise zones specially designated areas of a community
- 46. A good opportunity can be turned into a business. An idea plus a market equals an
- 47. When entrepreneurs are ready to start up a new business, they must use creative talent to
- 48. The fifth component of the start-up process is the execution of the new venture organization. The
- 49. A business failure files Chapter 7 bankruptcy. A business that disappears from the tax rolls may
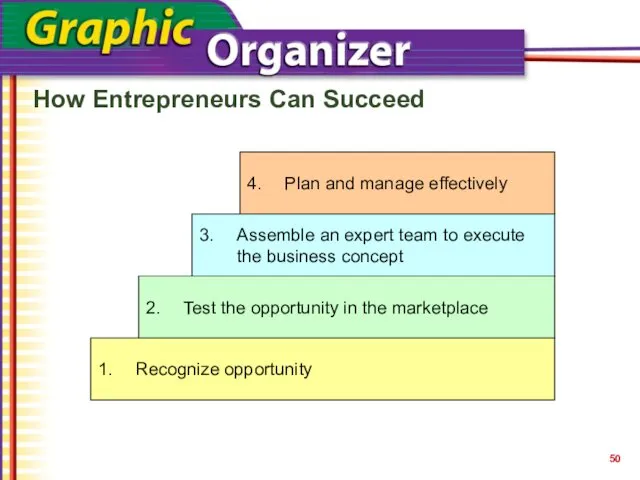
- 50. How Entrepreneurs Can Succeed Plan and manage effectively Recognize opportunity Test the opportunity in the marketplace
- 51. 1. Describe entrepreneurship from a historical perspective. After You Read Entrepreneurship has been a distinct feature
- 52. 2. Discuss the five components of the entrepreneurial start-up process. After You Read The entrepreneurial start-up
- 53. 3. Explain how to achieve business success. After You Read The chances of a new business
- 55. Скачать презентацию














































 Предмет и метод макроэкономики
Предмет и метод макроэкономики Предмет и методология микроэкономики. (Тема 1)
Предмет и методология микроэкономики. (Тема 1) Supply and demand. Factors of production
Supply and demand. Factors of production Экономическая теория. Предмет, метод, функции
Экономическая теория. Предмет, метод, функции Основы внешнеэкономической деятельности. Тема 1. Сущность и специфика внешнеэкономической деятельности в России
Основы внешнеэкономической деятельности. Тема 1. Сущность и специфика внешнеэкономической деятельности в России Налоговая система РФ Диск
Налоговая система РФ Диск Совокупный спрос и совокупное предложение
Совокупный спрос и совокупное предложение Грозит ли Земле перенаселение?
Грозит ли Земле перенаселение? Финансовые отношения в экономике
Финансовые отношения в экономике Дальневосточный молодежный форум Амур
Дальневосточный молодежный форум Амур Основные направления развития экономики Узбекистана для привлечения иностранных инвесторов
Основные направления развития экономики Узбекистана для привлечения иностранных инвесторов Понятие экономической оценки инвестиций
Понятие экономической оценки инвестиций Автомобили будущего
Автомобили будущего Лекция 1. Классификация прогнозов. Требования, предъявляемые к временным рядам, и их компонентный состав
Лекция 1. Классификация прогнозов. Требования, предъявляемые к временным рядам, и их компонентный состав Обмен. Стоимость. Цена. Бартер. Торговля и её формы
Обмен. Стоимость. Цена. Бартер. Торговля и её формы Еволюція та проблеми використання світових земельних ресурсів. (Тема 6.2)
Еволюція та проблеми використання світових земельних ресурсів. (Тема 6.2) Глобальные проблемы человечества и пути их решения
Глобальные проблемы человечества и пути их решения Моногорода.РФ. Нефинансовые меры поддержки
Моногорода.РФ. Нефинансовые меры поддержки Экономические системы
Экономические системы Факторы, определяющие производительность
Факторы, определяющие производительность Көлік логистикасы
Көлік логистикасы Экономическая задача. Задание 21
Экономическая задача. Задание 21 Технико-организационный уровень предприятия. (Тема 5)
Технико-организационный уровень предприятия. (Тема 5) Регулирование рыболовства. Лекция 6
Регулирование рыболовства. Лекция 6 Методическая разработка темы Стратегия поиска работы
Методическая разработка темы Стратегия поиска работы Экономика. Внешние эффекты
Экономика. Внешние эффекты Национальное хозяйство (экономика) России. 9 класс
Национальное хозяйство (экономика) России. 9 класс презентации
презентации