Содержание
- 2. Lecture objectives How does the economy operate in short-run and in long-run? What are the main
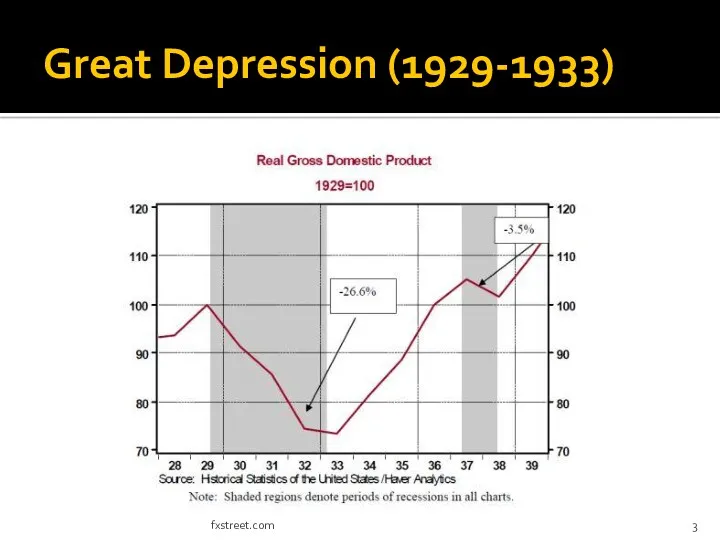
- 3. Great Depression (1929-1933) fxstreet.com
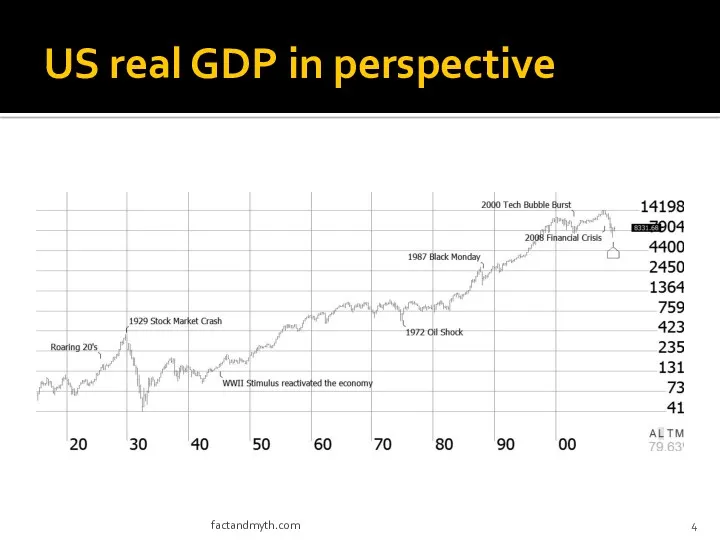
- 4. US real GDP in perspective factandmyth.com
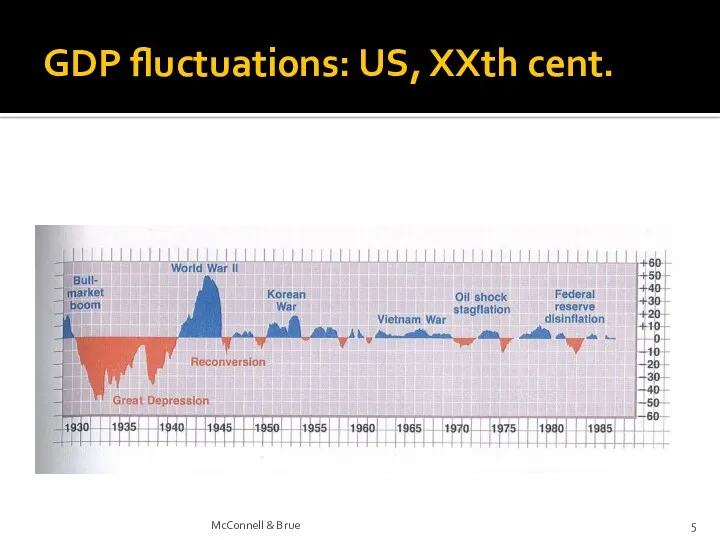
- 5. GDP fluctuations: US, XXth cent. McConnell & Brue
- 6. Business (economic) cycle Business cycle refers to the expansions and contractions in the economic activity (basically
- 7. US real GDP: key findings GDP ups and downs repeat in a cyclical way Yet, GDP
- 8. The essence of macroeconomics GDP behavior (both short-run and long-run) is at the heart of macroeconomic
- 9. Causes of economic cycles Spontaneous shifts in private spending Economic policy of government External shocks Disasters
- 10. Causes of long-run GDP increase Growing substance of production factors: labour, capital, technology.
- 11. Basic macroeconomic indicators GDP change (economic growth) Unemployment Inflation
- 12. Gross domestic product (GDP) GDP is the market value of the final goods and services produced
- 13. Economic growth rate Economic growth rate is the annual percentage change of real GDP.
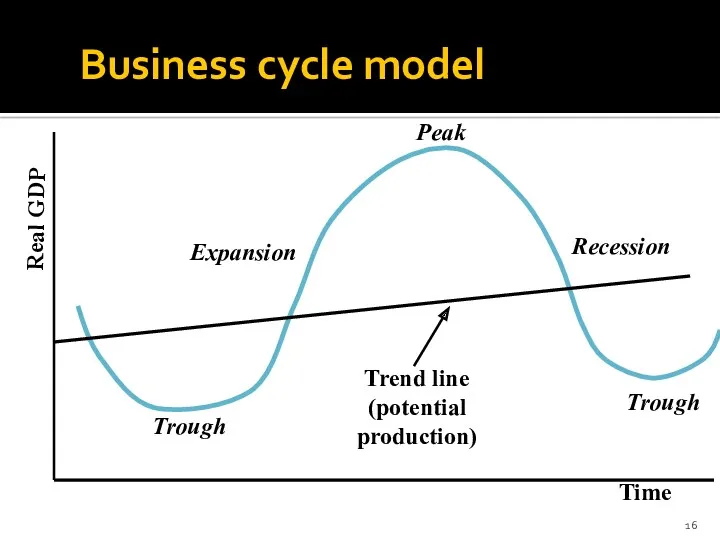
- 14. Expanssion and recession Periods of positive real GDP growth are called expansions. Periods of negative real
- 15. Peak and through Periodic maximum of real GDP is called peak. Periodic minimum of real GDP
- 16. Business cycle model Time Real GDP Trough Expansion Peak Recession Trough Trend line (potential production)
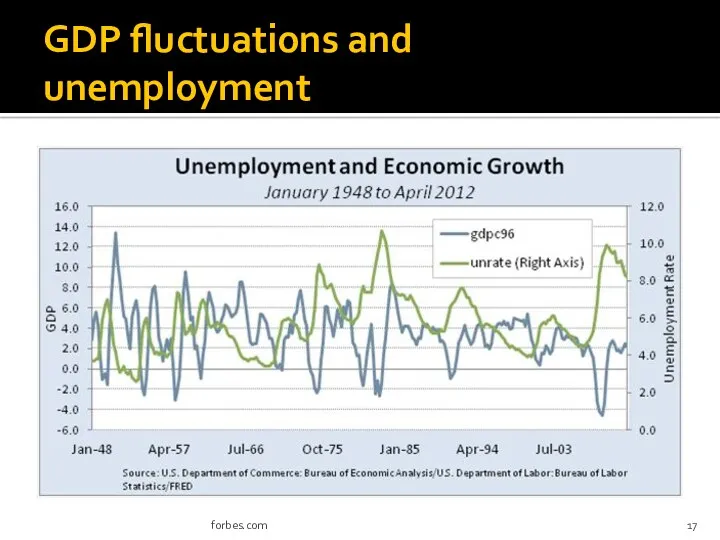
- 17. GDP fluctuations and unemployment forbes.com
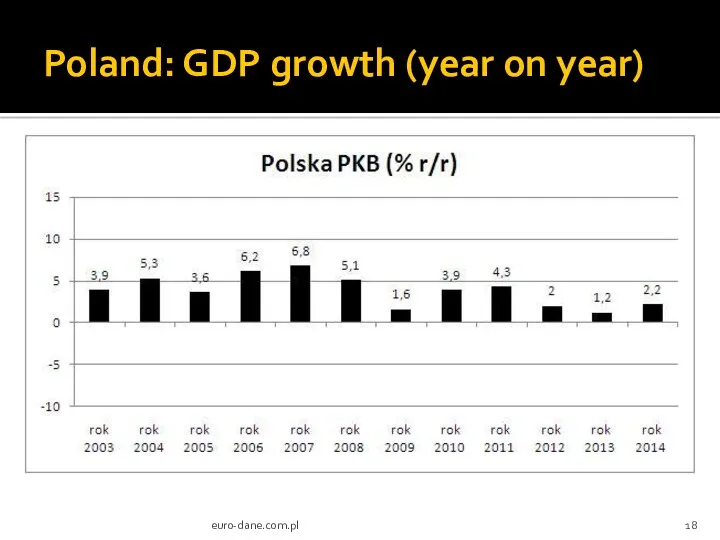
- 18. Poland: GDP growth (year on year) euro-dane.com.pl
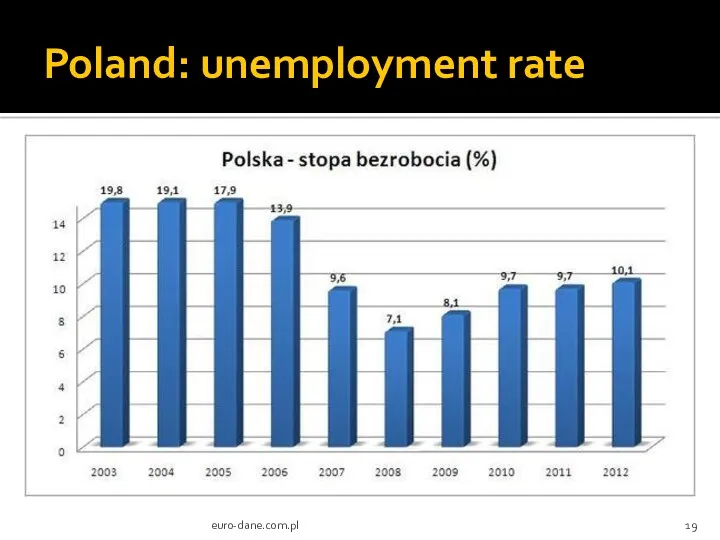
- 19. Poland: unemployment rate euro-dane.com.pl
- 20. GDP fluctuations and unemployment (short-run model) GDP change and unemployment are inversely related: as GDP increases,
- 21. GDP fluctuations and inflation (short-run model) Decrease in GDP usually leads to lower inflation (long-lasting GDP
- 22. Economic growth and inflation: the case of Latvia 2005 and Japan 2001 LATVIA: Real GDP growth
- 23. Unemployment-inflation trade-off in short-run Recession is normally accompanied by rising unemployment, yet inflation decelerates. Expanssion is
- 24. Potential production vs. actual production: additional perspective Potential GDP is the value of real GDP that
- 25. „Economic overheating”: US economy during Vietnam War In the mid-1960s US economy was at full employment.
- 26. Summary: macroeconomic goals GDP growth Full employment Stable prices
- 27. Check point: true / false test The period of time during which real GDP increases in
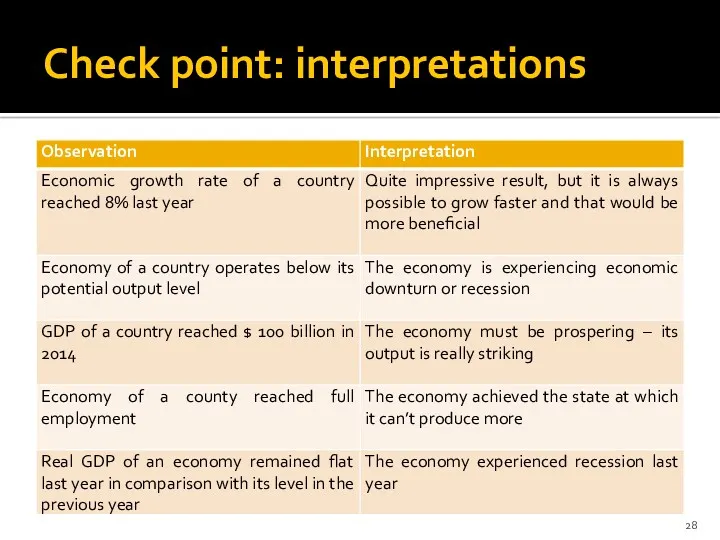
- 28. Check point: interpretations
- 29. Lecture objectives How does economy operate in short-run and in long-run? What are the main indicators
- 31. Скачать презентацию




















 Теория внешней торговли
Теория внешней торговли Грозит ли Земле перенаселение?
Грозит ли Земле перенаселение? Төртінші өнеркәсіптік революция
Төртінші өнеркәсіптік революция Физиократия – специфическое течение классической политической экономии
Физиократия – специфическое течение классической политической экономии Интеграция. Факторы интеграции
Интеграция. Факторы интеграции Комитет по сельскому хозяйству и продовольствию Витебского облисполкома
Комитет по сельскому хозяйству и продовольствию Витебского облисполкома Глобальная энергетическая проблема
Глобальная энергетическая проблема Введение в микроэкономику
Введение в микроэкономику Сферы и отрасли экономики
Сферы и отрасли экономики Совершенная конкуренция
Совершенная конкуренция Сущность денег
Сущность денег Персонал предприятия и оплата труда
Персонал предприятия и оплата труда Эластичность спроса и предложения
Эластичность спроса и предложения Что такое экономика
Что такое экономика Концепция территориальной экономической политики Республики Татарстан
Концепция территориальной экономической политики Республики Татарстан США в первой половине XIX века. Экономическое развитие
США в первой половине XIX века. Экономическое развитие Public Goods and Common Resource
Public Goods and Common Resource Методики оценки стоимости предприятия
Методики оценки стоимости предприятия Теория спроса и предложения
Теория спроса и предложения Экономические проблемы стран после Второй мировой войны
Экономические проблемы стран после Второй мировой войны Фотография рабочего времени
Фотография рабочего времени Экономические учения Адама Смита
Экономические учения Адама Смита Subject and methods of Economic Theory
Subject and methods of Economic Theory Економічні потреби суспільства і роль виробництва в їх задоволенні
Економічні потреби суспільства і роль виробництва в їх задоволенні Инвентаризация и переоценка материально-производственных запасов на примере деятельности ГУП РК Крымские морские порты
Инвентаризация и переоценка материально-производственных запасов на примере деятельности ГУП РК Крымские морские порты Спрос и предложение. Равновесная цена
Спрос и предложение. Равновесная цена Стратегия развития башкирского народа. Рус телле балаларға башҡорт телен уҡытыу (часть 1)
Стратегия развития башкирского народа. Рус телле балаларға башҡорт телен уҡытыу (часть 1) Устойчивость экономики к внешним уязвимостям. Тема 8
Устойчивость экономики к внешним уязвимостям. Тема 8