Содержание
- 2. Chapter Outline
- 3. Problem Solving vs Decision Taking A decision is needed to continue or smooth a process affecting
- 4. Problem Solving to Find Entrepreneurial Solutions Learning Objectives By the end of this section, you will
- 5. Entrepreneurial problem solving is the process of using innovation and creative solutions to close that gap
- 6. Problem Solving Models:
- 7. Adaptive Model The adaptive model seeks solutions for problems in ways that are tested and known
- 8. Innovative Model The second and more creative approach is the innovative model of entrepreneurial problem solving,
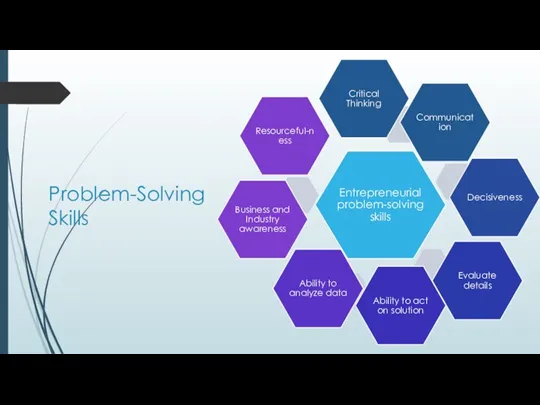
- 9. Problem-Solving Skills Entrepreneurial problem-solving skills Communication Decisiveness Evaluate details Ability to act on solution Ability to
- 10. Networking Networking results in connecting individuals who otherwise might not have met and who may be
- 11. Link to learning Read this LinkedIn blog post on decisiveness (https://openstax.org/l/52decisiveness) to learn more.
- 12. Analytics Descriptive Predictive Prescriptive involves understanding what has happened and what is happening uses data from
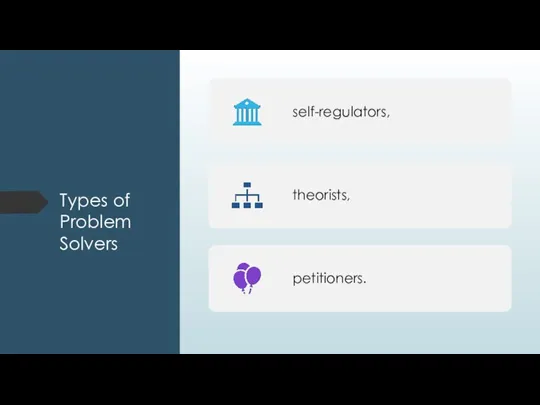
- 13. Types of Problem Solvers
- 14. Self-regulating problem solvers A self-regulating problem solver identifies a problem, thinks of solution, and then implements
- 15. Theorist Problem Solvers A theorist problem solver identifies a problem; implements a theory, sometimes repeatedly; and
- 16. Petitioners A petitioner problem solver identifies a problem, discusses it with others, and arrives at solution
- 17. Discussion Questions Which method do you think applies more to entrepreneurship, the innovative or adaptive problem-solving
- 18. Chapter Outline
- 19. Learning Objectives 6.2 Creative Problem-Solving Process Describe the five steps in the creative problem-solving process Identify
- 20. Creative Solving Problem Process The process of creativity is not random; it is a specific and
- 21. Fishbone Diagram A quality problem has main causes—here designated as a, b, c, and d. Within
- 22. Example Farm water pollution could have four main causes, such as livestock, pesticide and fertilizer, soil
- 23. Problem of waste in Khorog Town Removing waste is a problem, and it can also present
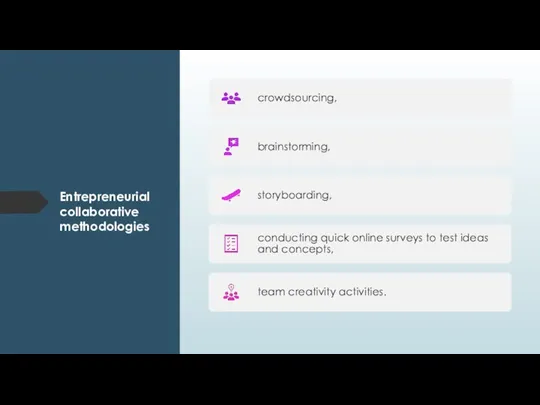
- 24. Entrepreneurial collaborative methodologies
- 25. Crowdsourcing “an online, distributed problem-solving and production model.” – Prof. Daren Brabham Crowdsourcing involves teams of
- 26. Example of crowdsourcing A Crowdsourced Potato Chip In an effort to increase sales among millennials, PepsiCo
- 27. Brainstorming Watch this video from ABC’s Nightline that shows how IDEO designed a new shopping cart
- 28. Storyboarding Storyboarding helps entrepreneurs and team members to visually represent steps in product creation and problem
- 29. Team Creativity Team creativity is the process whereby an entrepreneur works with a team to create
- 30. Learning Objectives Design Thinking Explain the design thinking process Discuss some design thinking tools
- 31. Design Thinking Process The design thinking process focuses on the spaces of inspiration, ideation, and implementation.
- 32. Question ladder A question ladder can help refine questions. (attribution: Copyright Rice University, OpenStax, under CC
- 33. Discussion Questions
- 34. Learning Objectives Lean Processes Discuss the lean process methodology Understand the phases of the lean problem-solving
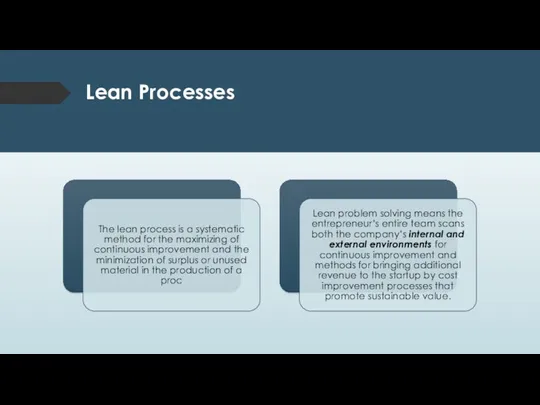
- 35. Lean Processes
- 36. Steps in the Toyota Lean Problem-Solving Process The lean problem-solving, step-wise process allows the business to
- 37. Whiteboarding Whiteboarding is a technique that can help entrepreneurs visualize and analyze processes. (credit: “whiteboard man
- 38. Readings Problem Solving and need recognition techniques – Chapter 6, Textbook
- 40. Скачать презентацию

































 Анализ ситуации на рынке энергоресурсов
Анализ ситуации на рынке энергоресурсов Анализ деятельности ООО ИРБИС и предложения по совершенствованию методов формирования портфеля проектов организации
Анализ деятельности ООО ИРБИС и предложения по совершенствованию методов формирования портфеля проектов организации Технико-экономическое обоснование проектов
Технико-экономическое обоснование проектов Фирма в системе рыночных отношений. Производство и издержки
Фирма в системе рыночных отношений. Производство и издержки Энергия, энергетические ресурсы, энергосбережение при транспортировке энергетических ресурсов. Лекция 1
Энергия, энергетические ресурсы, энергосбережение при транспортировке энергетических ресурсов. Лекция 1 Историческое развитие человечества. Формационный подход
Историческое развитие человечества. Формационный подход Институциональная экономика. Лекция 2. Роль и функции институтов. Нормы и правила
Институциональная экономика. Лекция 2. Роль и функции институтов. Нормы и правила Концепции региональной субъективности: регион-квазигосударство, регион-корпорация, регион-рынок, регион-социум
Концепции региональной субъективности: регион-квазигосударство, регион-корпорация, регион-рынок, регион-социум Зовнішньоекономічна діяльність та її роль у розвитку національної економіки
Зовнішньоекономічна діяльність та її роль у розвитку національної економіки Basics of economics
Basics of economics Департамент житлово-комунального господарства Донецької облдержадміністрації
Департамент житлово-комунального господарства Донецької облдержадміністрації Презентация Что такое экономика
Презентация Что такое экономика Международное разделение труда как материальная основа мирового хозяйства
Международное разделение труда как материальная основа мирового хозяйства Глобализация. Глобальные проблемы современности. Угрозы XXI века
Глобализация. Глобальные проблемы современности. Угрозы XXI века Презентация к уроку экономика 11 класс Профсоюзы. Их роль на рынке труда
Презентация к уроку экономика 11 класс Профсоюзы. Их роль на рынке труда Рынок и рыночный механизм. Спрос и предложение. Издержки
Рынок и рыночный механизм. Спрос и предложение. Издержки Разработка модели экономической надежности предприятия. Методы управления рисками на предприятии
Разработка модели экономической надежности предприятия. Методы управления рисками на предприятии Рейтинг устойчивого развития городов РФ за 2015 год
Рейтинг устойчивого развития городов РФ за 2015 год Концепция мировых социальных систем
Концепция мировых социальных систем Группа развитых стран с рыночной экономикой. Основные классификации и модели развития
Группа развитых стран с рыночной экономикой. Основные классификации и модели развития Открытая экономика
Открытая экономика Демографический кризис
Демографический кризис Преступления в сфере экономической деятельности. Тема 21
Преступления в сфере экономической деятельности. Тема 21 Товарная организация общественного производства и товарно-денежные отношения
Товарная организация общественного производства и товарно-денежные отношения Снижение издержек в производстве электродвигателей, генераторов и трансформаторов: экономико-правовой аспект
Снижение издержек в производстве электродвигателей, генераторов и трансформаторов: экономико-правовой аспект Организация инструментального хозяйства
Организация инструментального хозяйства Rachunek dochodu narodowego. Wzrost i rozwój gospdoarczy
Rachunek dochodu narodowego. Wzrost i rozwój gospdoarczy Рынок капитала
Рынок капитала