Содержание
- 2. Background The President of Rwanda is the head of state, and has broad powers including creating
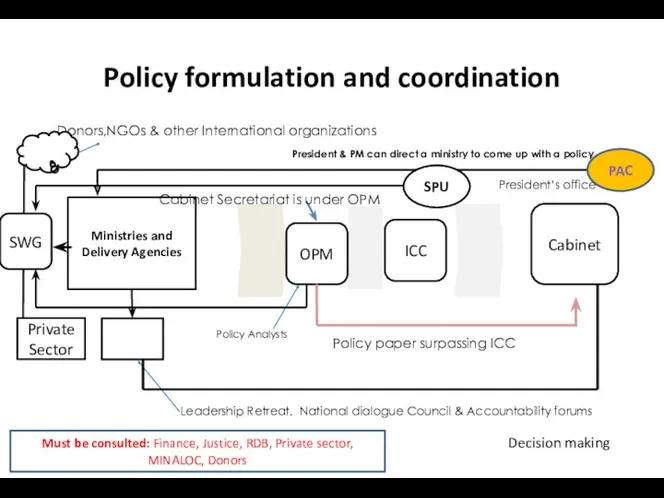
- 3. Policy formulation and coordination Kagame decided to create the Cabinet Secretariat following discussions in 2007 with
- 4. Policy formulation and coordination The President in 2008 also established a Strategy and Policy Unit in
- 5. Policy formulation and coordination Concrete policy formats and development steps. Cabinet manual specifies formats for policy
- 6. Policy formulation and coordination White paper has quality requirements that include; views of various organizations, people
- 7. Policy formulation and coordination Ministries and Delivery Agencies Donors,NGOs & other International organizations OPM ICC Cabinet
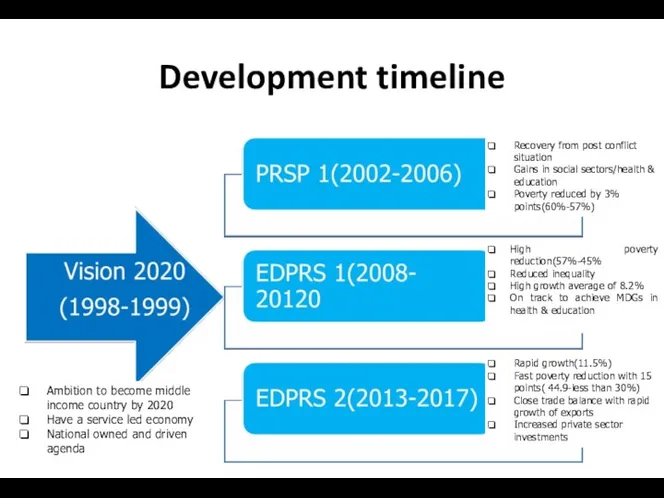
- 8. Development timeline Ambition to become middle income country by 2020 Have a service led economy National
- 9. What is EDPRS? The Economic Development and Poverty Reduction Strategy(EDPRS) is a 5 year strategy with
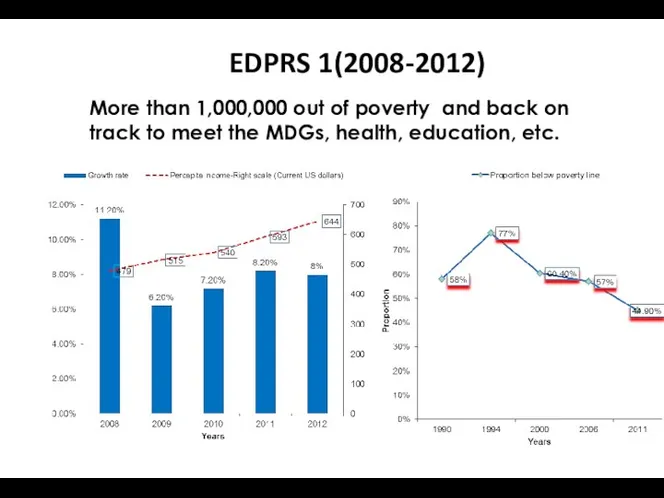
- 10. EDPRS 1(2008-2012) More than 1,000,000 out of poverty and back on track to meet the MDGs,
- 11. EDPRS 2 elaboration and institutional roles The Prime Minister’s Office through its Government Actions and Coordination
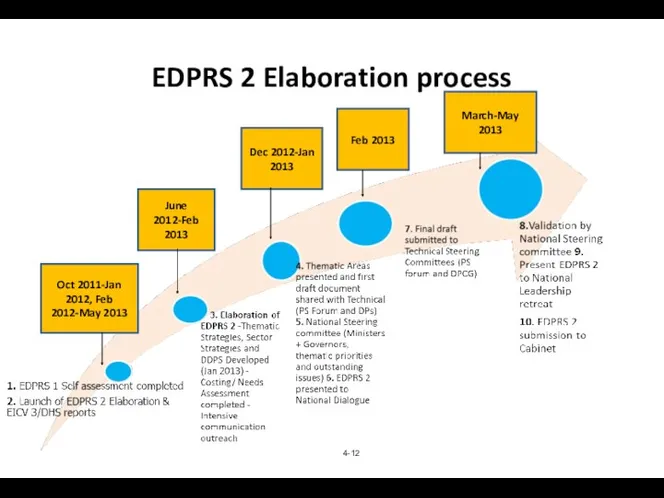
- 12. EDPRS 2 Elaboration process 4- Oct 2011-Jan 2012, Feb 2012-May 2013 June 2012-Feb 2013 Dec 2012-Jan
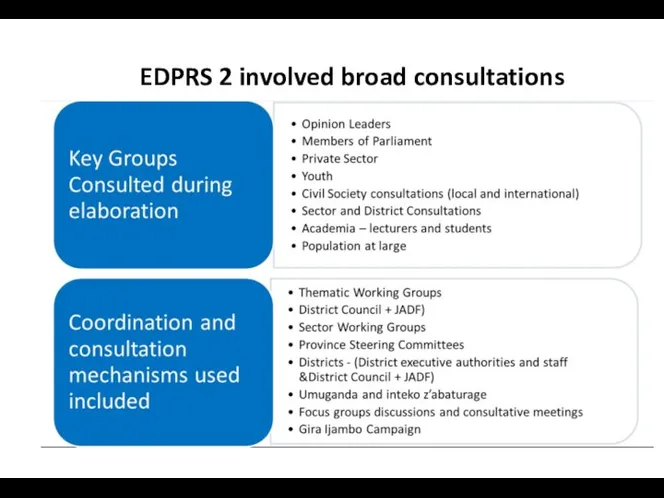
- 13. EDPRS 2 involved broad consultations
- 14. The main aim of EDPRS 2 is to ensure a better quality of life for all
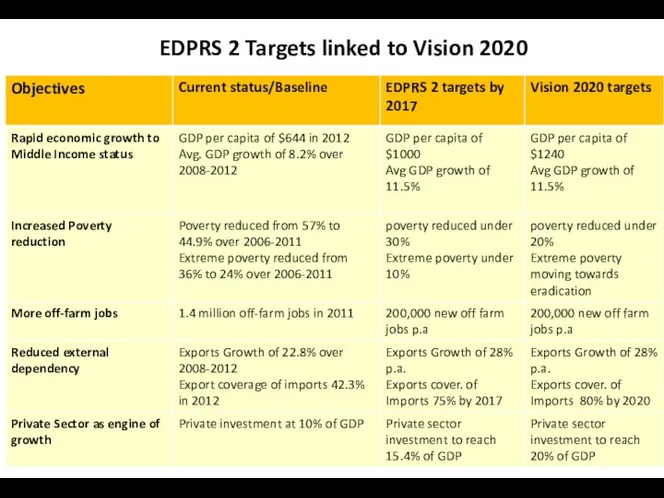
- 15. EDPRS 2 Targets linked to Vision 2020
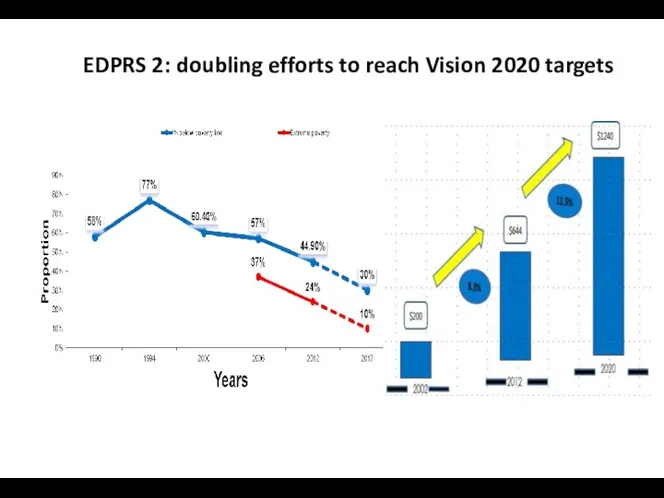
- 16. EDPRS 2: doubling efforts to reach Vision 2020 targets
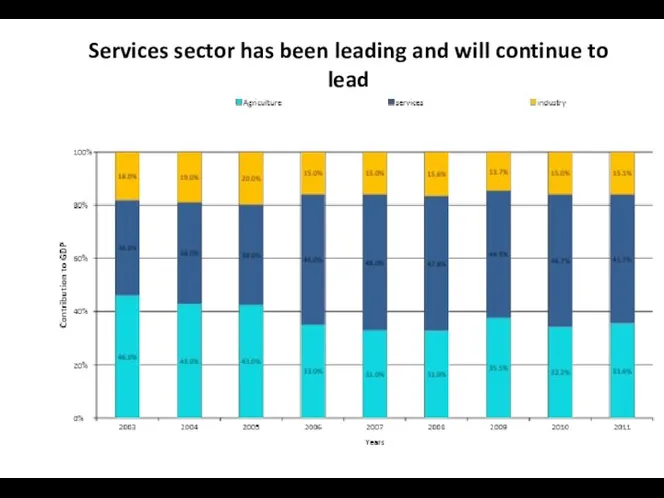
- 17. Services sector has been leading and will continue to lead
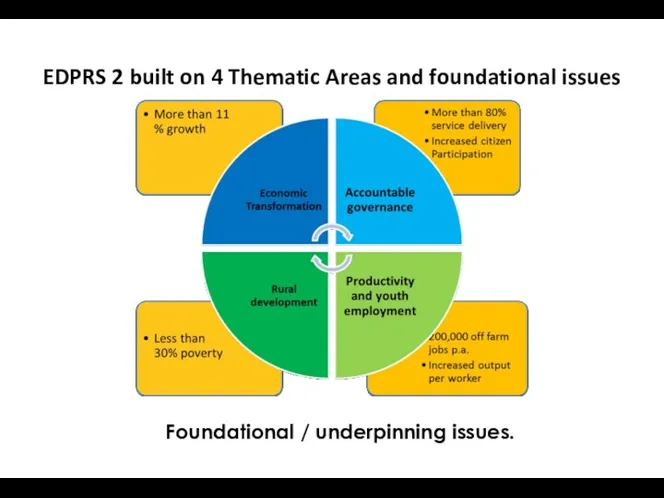
- 18. EDPRS 2 built on 4 Thematic Areas and foundational issues Foundational / underpinning issues.
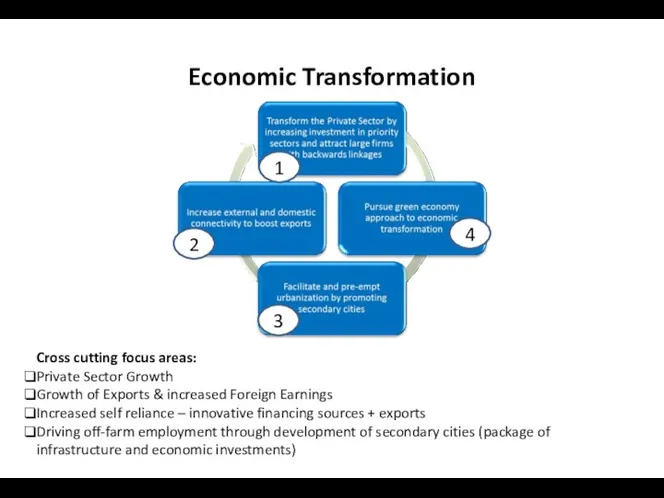
- 19. Economic Transformation Cross cutting focus areas: Private Sector Growth Growth of Exports & increased Foreign Earnings
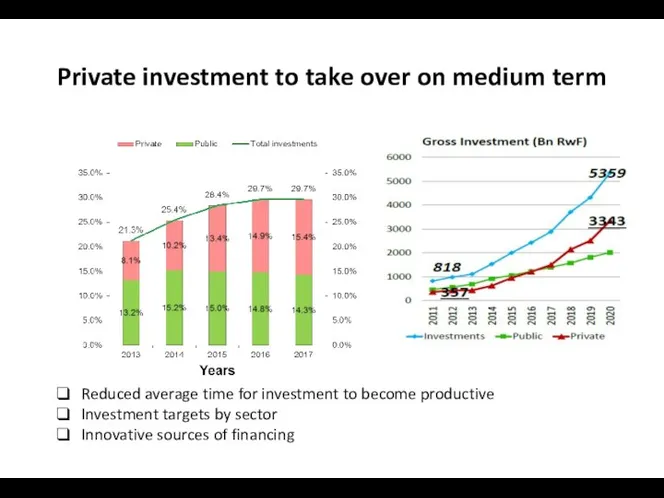
- 20. Private investment to take over on medium term Reduced average time for investment to become productive
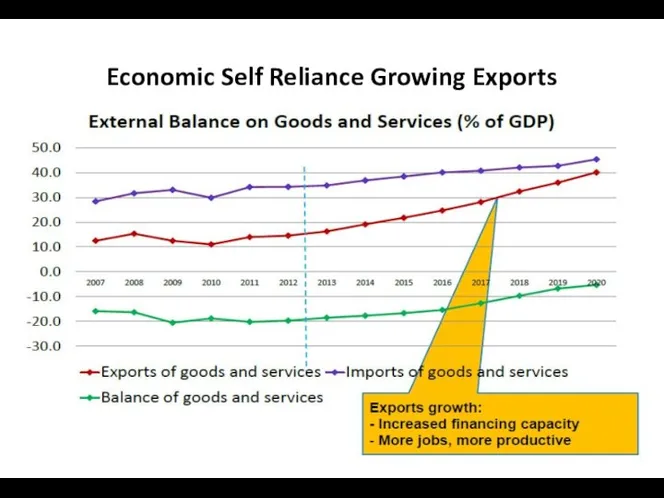
- 21. Economic Self Reliance Growing Exports 4-
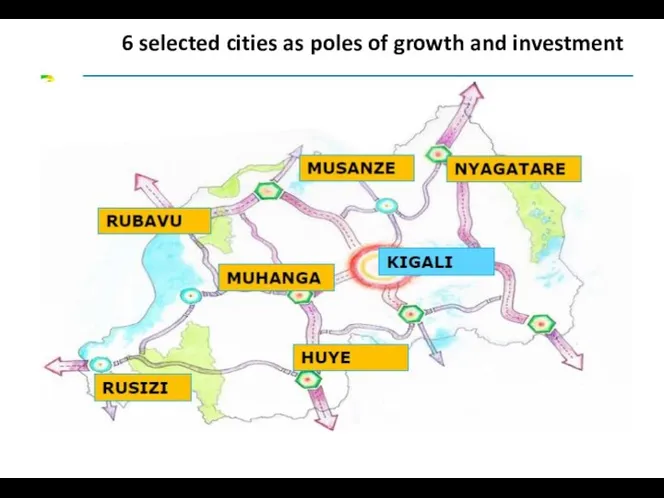
- 22. 6 selected cities as poles of growth and investment
- 23. Productivity and Youth Employment: Transitioning 50% of population from farm to off-farm jobs Integrated targeting for
- 24. Institutional Arrangements for EDPRS 2 Coordination, Monitoring and Reporting
- 26. Скачать презентацию










 Нефтяная компания ПАО Лукойл
Нефтяная компания ПАО Лукойл Регулирование экономики на муниципальном уровне
Регулирование экономики на муниципальном уровне Заработная плата учителей в регионах
Заработная плата учителей в регионах Ринок досконалої конкуренції
Ринок досконалої конкуренції Школы экономической теории
Школы экономической теории О Стратегии социально-экономического развития Свердловской области на 2016-2030 годы
О Стратегии социально-экономического развития Свердловской области на 2016-2030 годы Human Trafficking. Core Concepts. Global Trends. Facts and Figures
Human Trafficking. Core Concepts. Global Trends. Facts and Figures Визначення ціни ринкової рівноваги з урахуванням функцій попиту і пропозиції за ціною
Визначення ціни ринкової рівноваги з урахуванням функцій попиту і пропозиції за ціною Оңтүстік –шығыс Азия елдерінің ассоциациясы
Оңтүстік –шығыс Азия елдерінің ассоциациясы Конкурентоспособность продукта и факторы, ее определяющие
Конкурентоспособность продукта и факторы, ее определяющие Система оценки качества продукции в производстве
Система оценки качества продукции в производстве Сегодняшние проблемы российской экономики
Сегодняшние проблемы российской экономики Великие географические открытия. Часть 1
Великие географические открытия. Часть 1 Спрос и предложение. Теория рыночного равновесия
Спрос и предложение. Теория рыночного равновесия Экономика отрасли
Экономика отрасли Мировой рынок труда. Тема 6
Мировой рынок труда. Тема 6 Методы сравнительной комплексной оценки хозяйственной деятельности
Методы сравнительной комплексной оценки хозяйственной деятельности Производительность труда. Понятие, показатели и факторы повышения
Производительность труда. Понятие, показатели и факторы повышения Основные подходы к экономической оценке природных ресурсов и установлению платы за их использование
Основные подходы к экономической оценке природных ресурсов и установлению платы за их использование Социальное государство
Социальное государство Голландская болезнь в России 2000-х годов. Негативный эффект, оказываемый укреплением реального курса национальной валюты
Голландская болезнь в России 2000-х годов. Негативный эффект, оказываемый укреплением реального курса национальной валюты Разработка и примеры применения KPI на практике при оценке эффективности PR-деятельности/ PR-департамента
Разработка и примеры применения KPI на практике при оценке эффективности PR-деятельности/ PR-департамента Экономическое взаимодействие России и Китая
Экономическое взаимодействие России и Китая Экономика СССР в 1953-1964 гг (9 класс)
Экономика СССР в 1953-1964 гг (9 класс) Промышленный комплекс Беларуси
Промышленный комплекс Беларуси Макроэкономика. (Семинар 1)
Макроэкономика. (Семинар 1) Введение в микроэкономику (П07). Задачи и упражнения
Введение в микроэкономику (П07). Задачи и упражнения Введение. Предмет и виды макроэкономического анализа
Введение. Предмет и виды макроэкономического анализа