Содержание
- 2. Supply, Demand, and Government Policies In a free, unregulated market system, market forces establish equilibrium prices
- 3. Price Controls... Are usually enacted when policymakers believe the market price is unfair to buyers or
- 4. Price Ceilings & Price Floors Price Ceiling A legally established maximum price at which a good
- 5. Price Ceilings Two outcomes are possible when the government imposes a price ceiling: The price
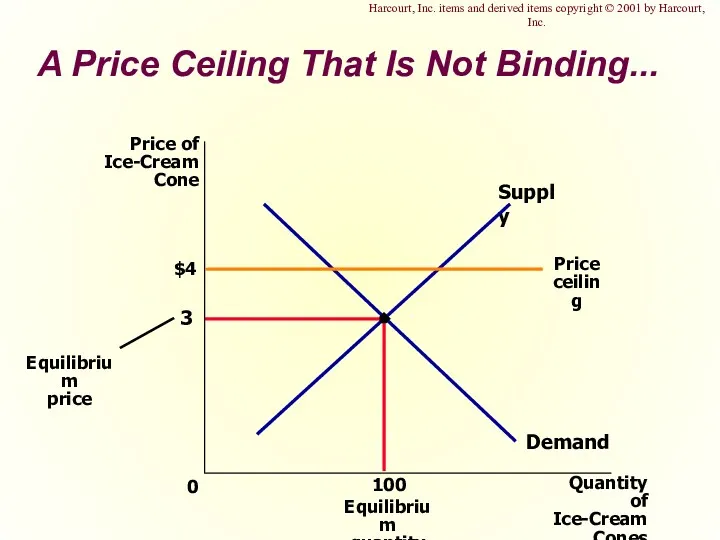
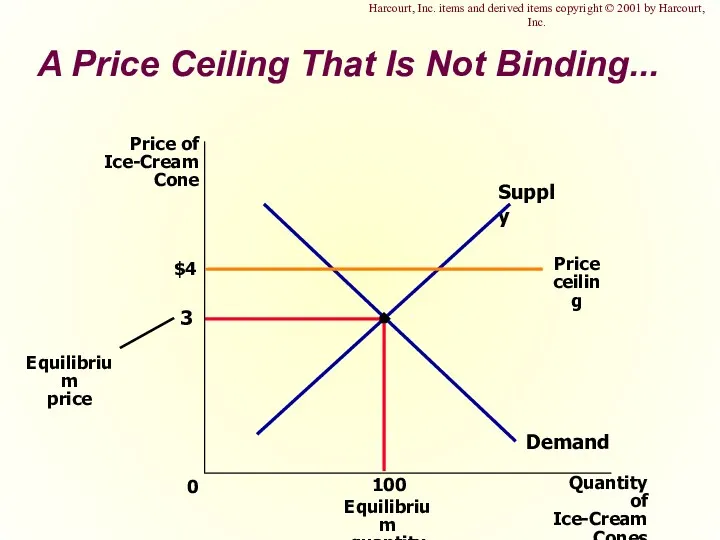
- 6. A Price Ceiling That Is Not Binding... $4 3 Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones 0 Price of
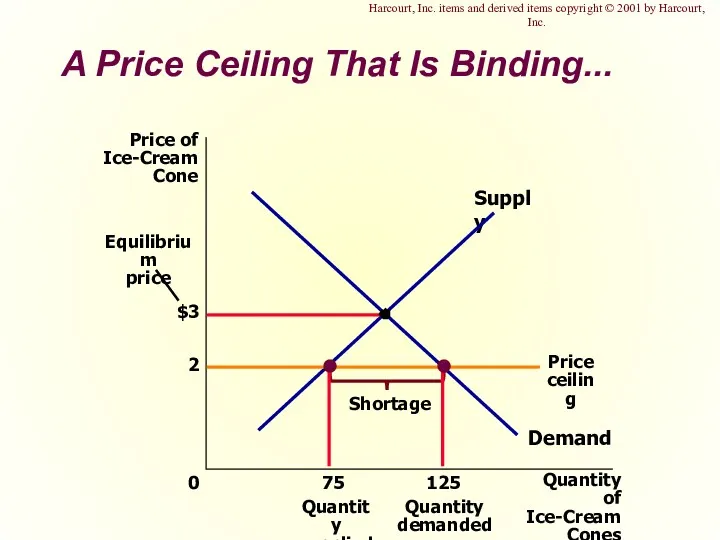
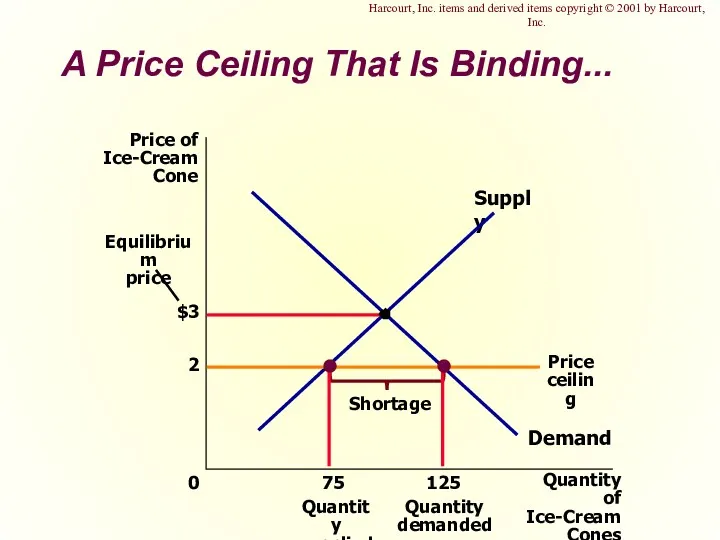
- 7. A Price Ceiling That Is Binding... $3 Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones 0 Price of Ice-Cream Cone
- 8. Effects of Price Ceilings A binding price ceiling creates ... shortages because QD > QS. Example:
- 9. Lines at the Gas Pump In 1973 OPEC raised the price of crude oil in world
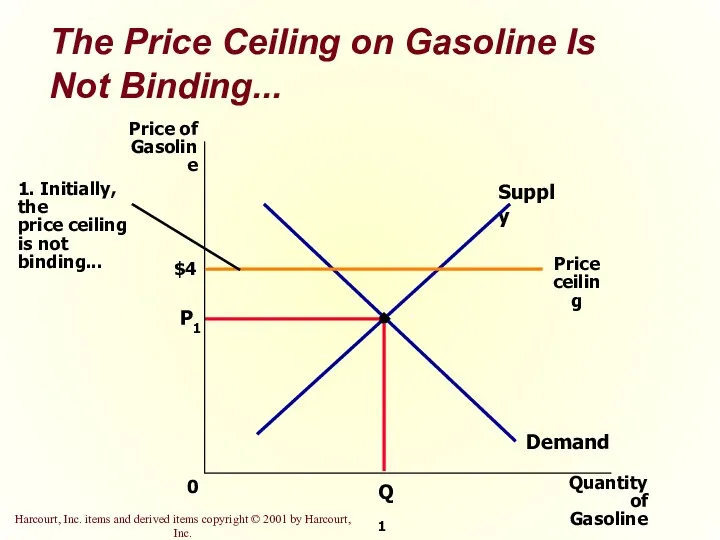
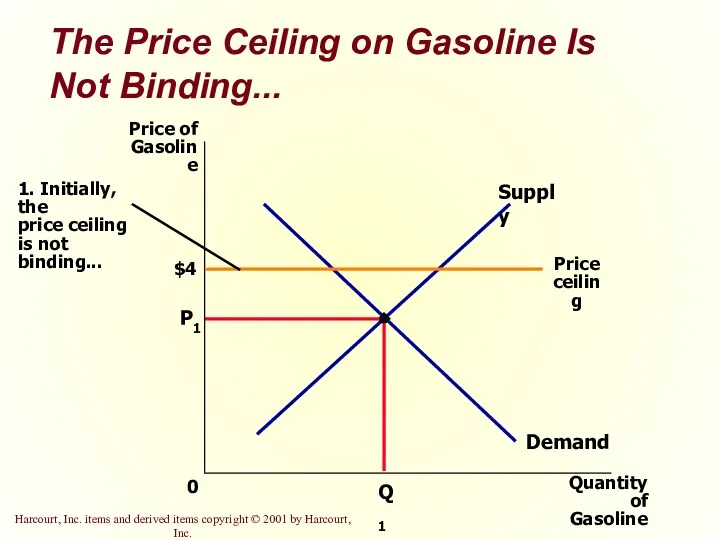
- 10. The Price Ceiling on Gasoline Is Not Binding... $4 P1 Quantity of Gasoline 0 Price of
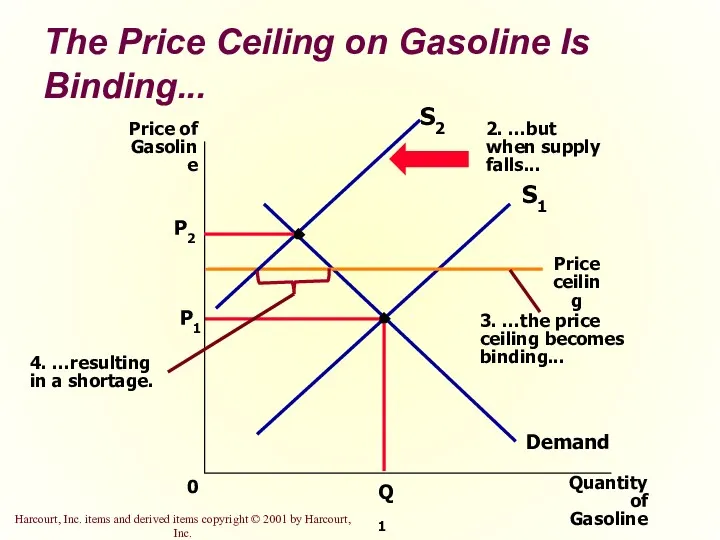
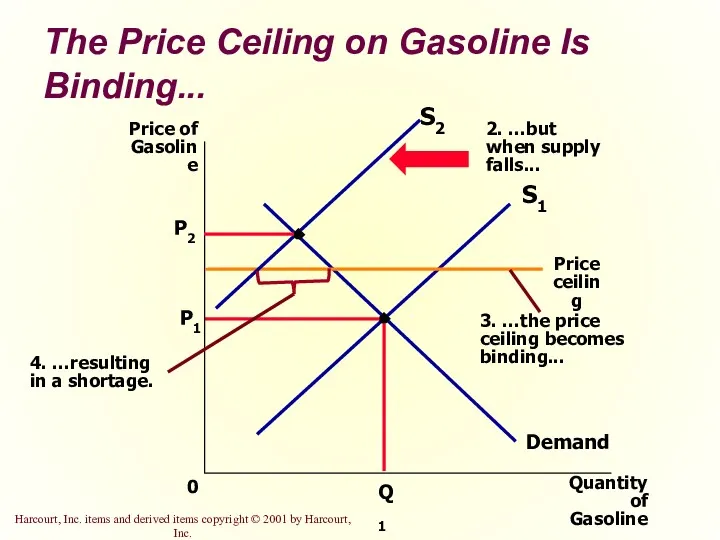
- 11. The Price Ceiling on Gasoline Is Binding... P1 Quantity of Gasoline 0 Price of Gasoline Q1
- 12. Rent Control Rent controls are ceilings placed on the rents that landlords may charge their tenants.
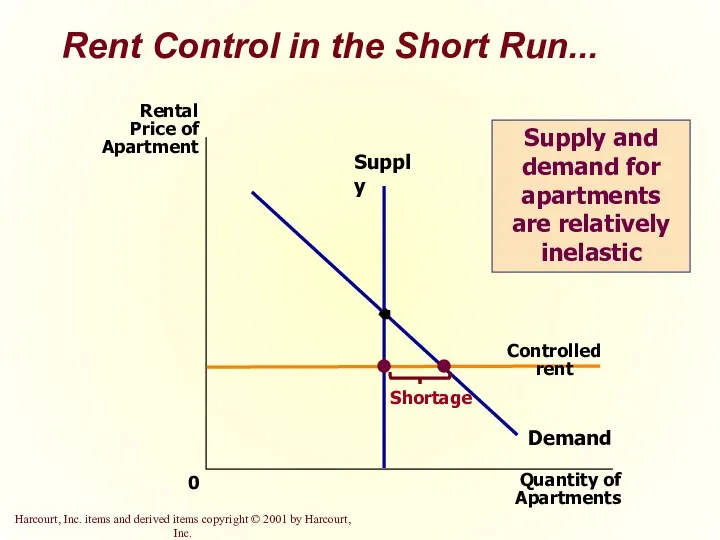
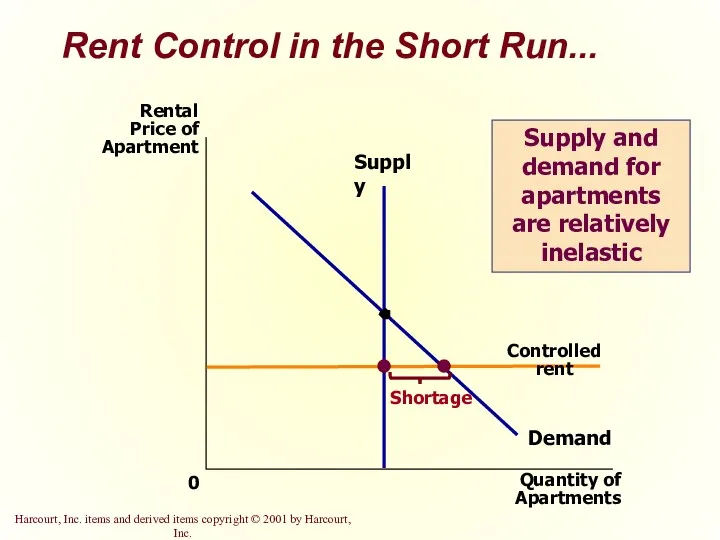
- 13. Rent Control in the Short Run... Quantity of Apartments 0 Rental Price of Apartment Demand Supply
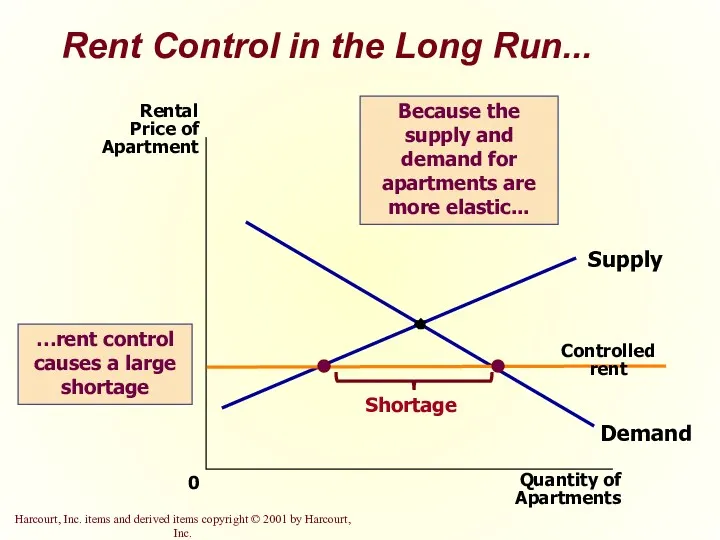
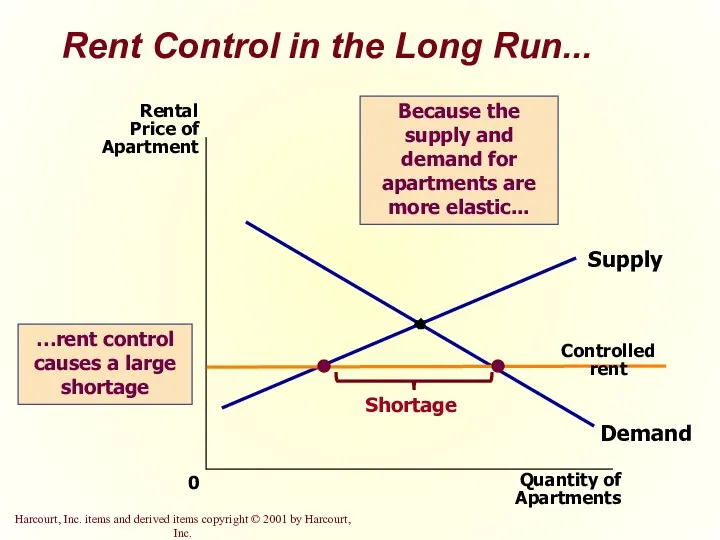
- 14. Rent Control in the Long Run... Quantity of Apartments 0 Rental Price of Apartment Demand Supply
- 15. Price Floors When the government imposes a price floor, two outcomes are possible. The price floor
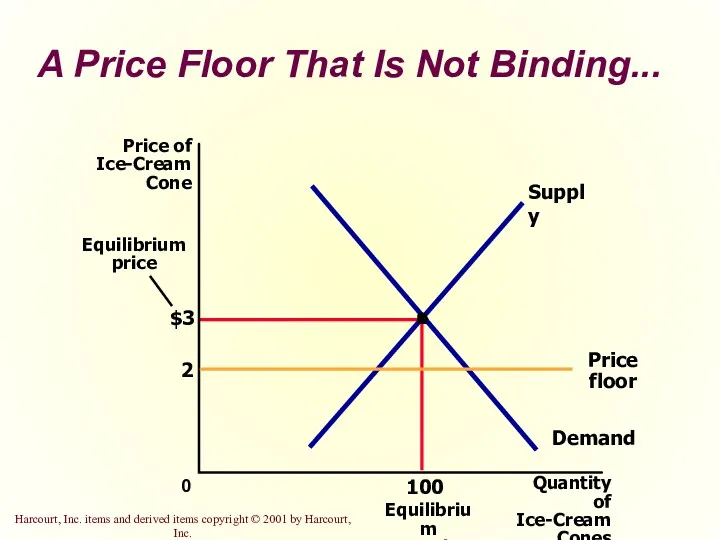
- 16. A Price Floor That Is Not Binding... $3 Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones 0 Price of Ice-Cream
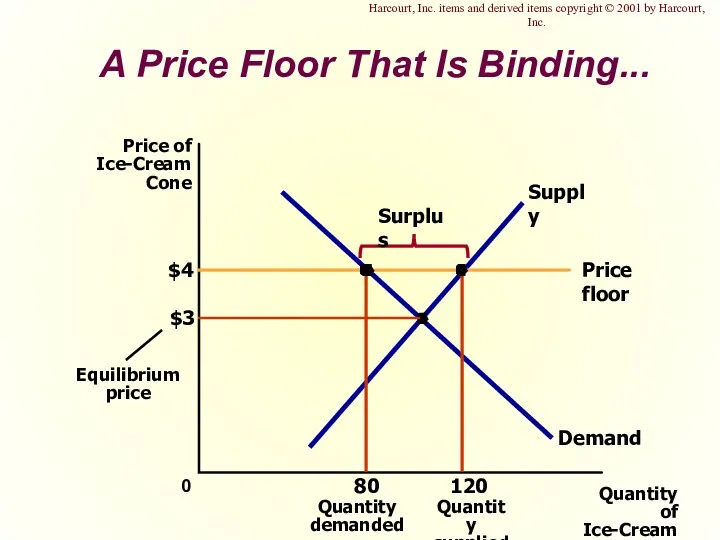
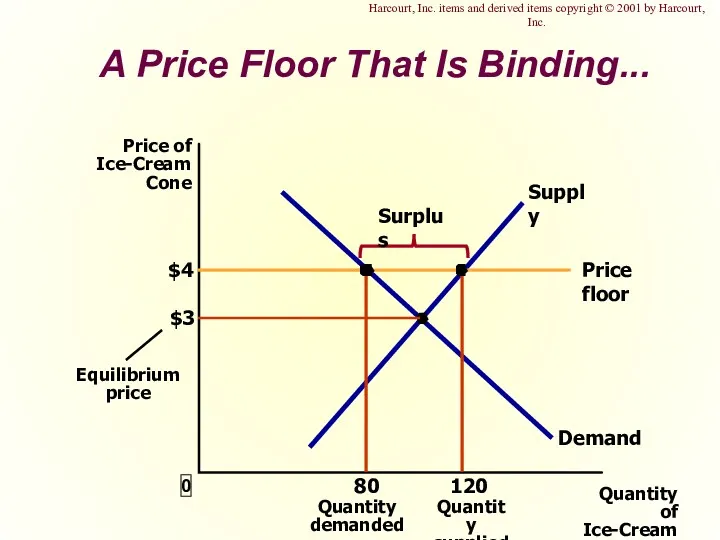
- 17. A Price Floor That Is Binding... $3 Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones 0 Price of Ice-Cream Cone
- 18. Effects of a Price Floor A price floor prevents supply and demand from moving toward the
- 19. Effects of a Price Floor A binding price floor causes . . . a surplus because
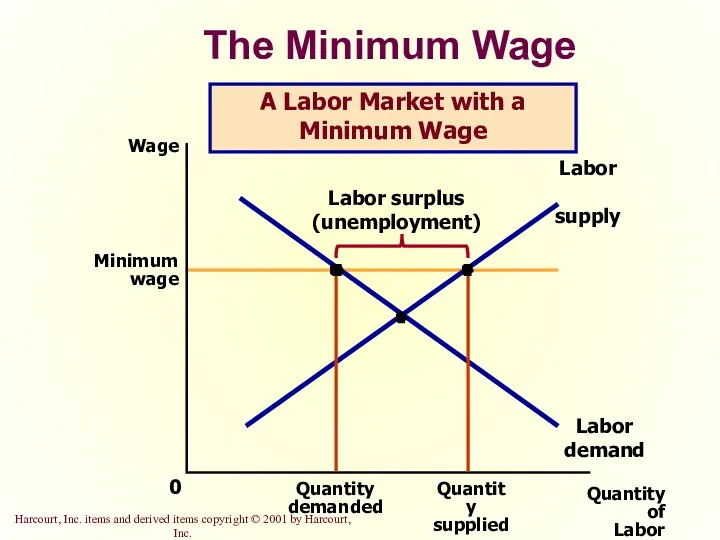
- 20. The Minimum Wage An important example of a price floor is the minimum wage. Minimum wage
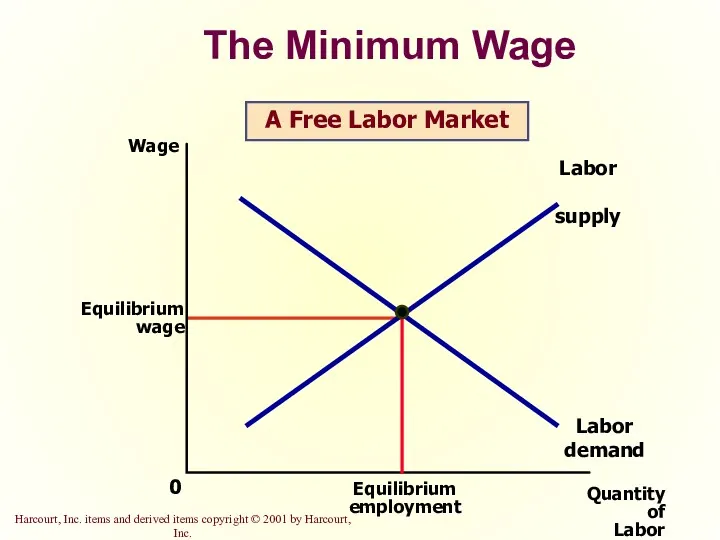
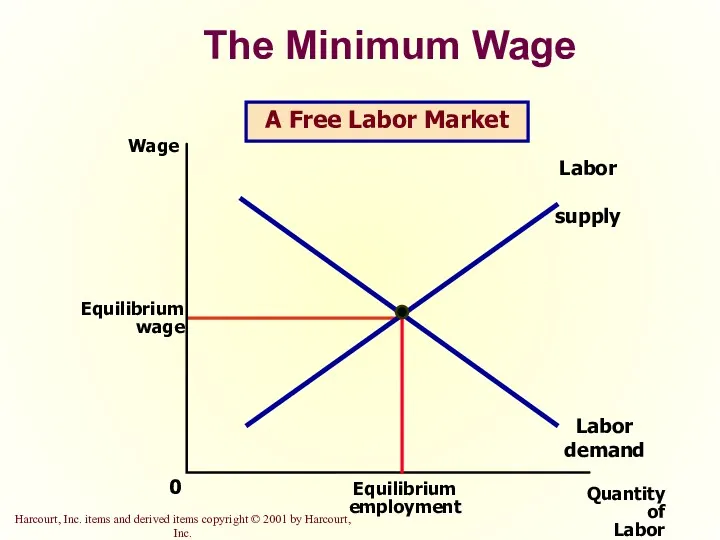
- 21. The Minimum Wage Quantity of Labor 0 Wage Labor demand Labor supply A Free Labor Market
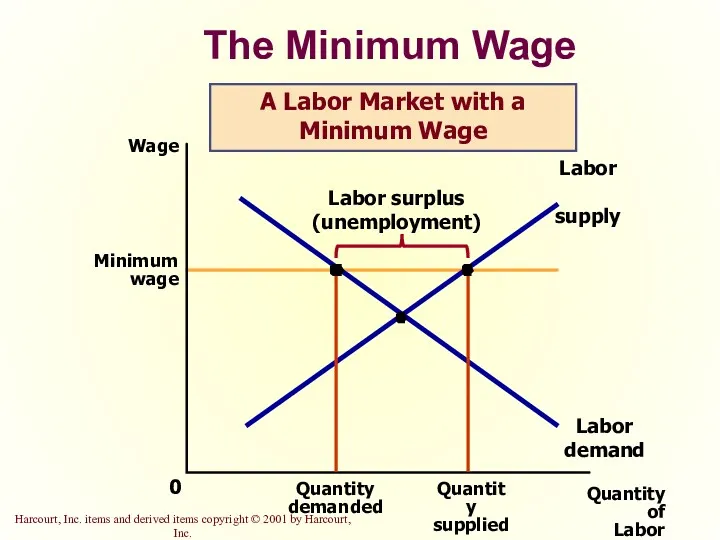
- 22. The Minimum Wage Quantity of Labor 0 Wage Labor demand Labor supply A Labor Market with
- 23. Taxes Governments levy taxes to raise revenue for public projects.
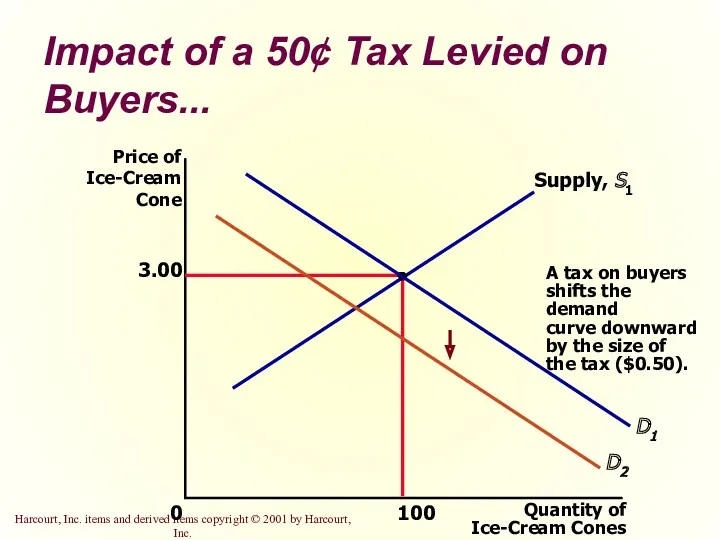
- 24. What are some potential impacts of taxes? Taxes discourage market activity. When a good is taxed,
- 25. Taxes Tax incidence is the study of who bears the burden of a tax. Taxes result
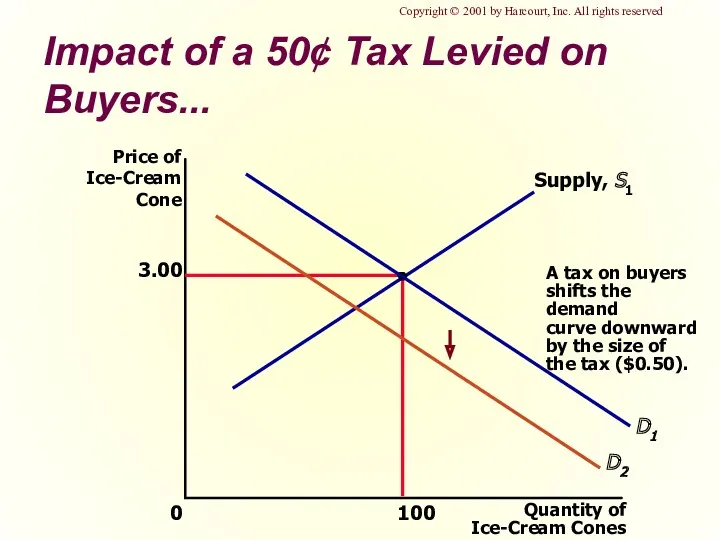
- 26. Impact of a 50¢ Tax Levied on Buyers... 3.00 Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones 0 Price of
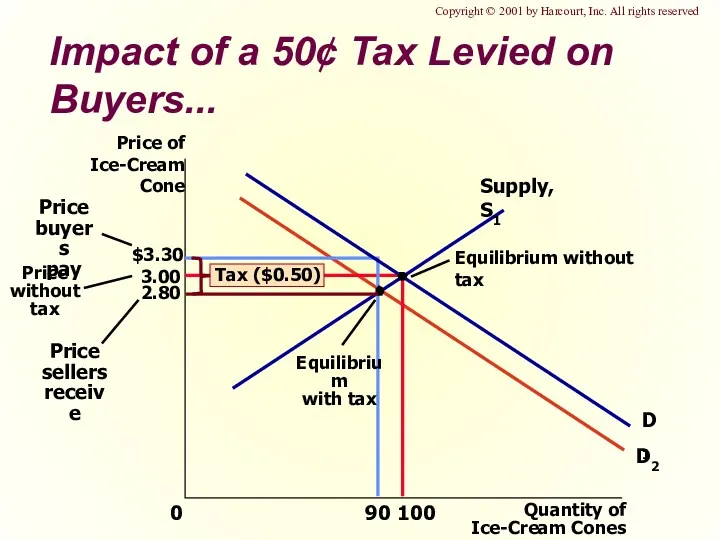
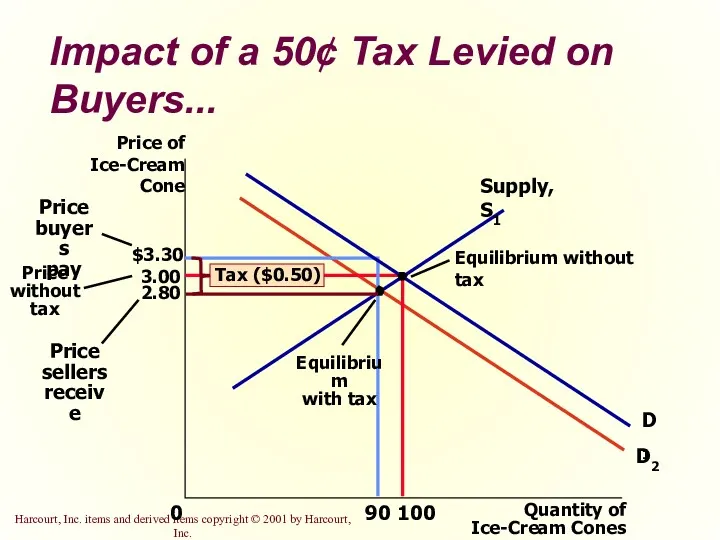
- 27. 3.00 Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones 0 Price of Ice-Cream Cone 100 90 D1 D2 Supply, S1
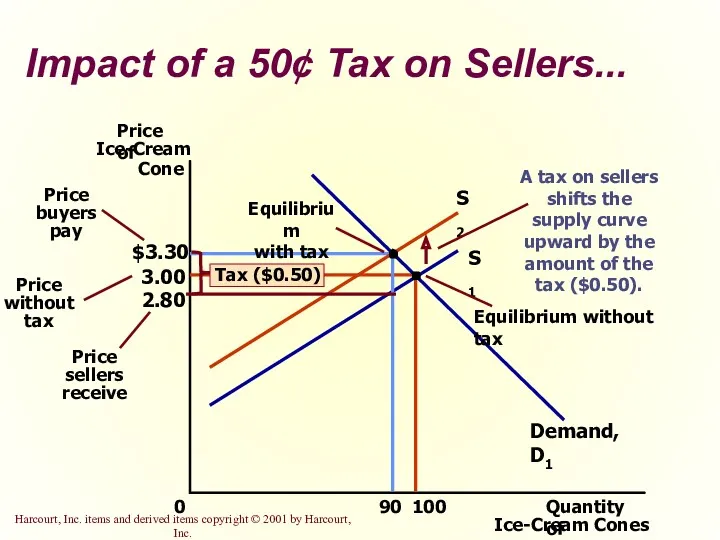
- 28. What was the impact of tax? Taxes discourage market activity. When a good is taxed, the
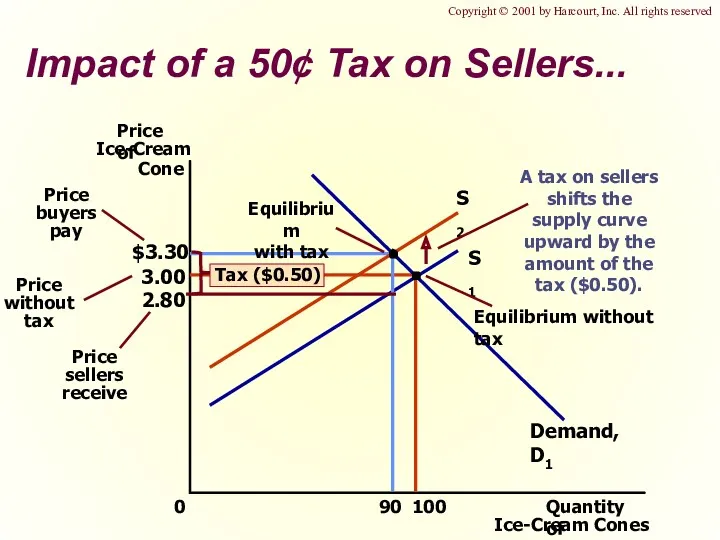
- 29. 3.00 0 100 S1 Demand, D1 Impact of a 50¢ Tax on Sellers... Copyright © 2001
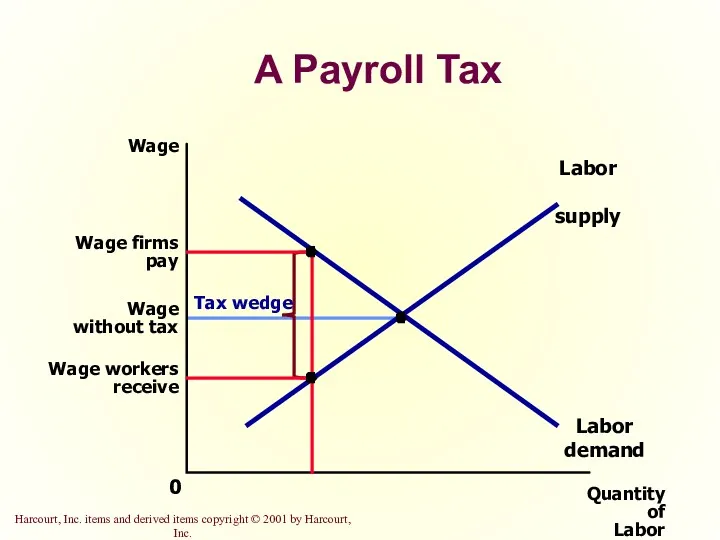
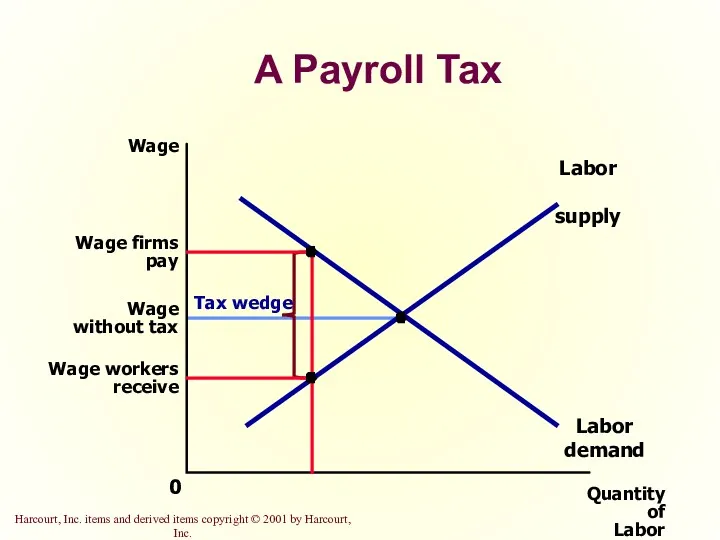
- 30. A Payroll Tax Quantity of Labor 0 Wage Labor demand Labor supply
- 31. The Incidence of Tax In what proportions is the burden of the tax divided? How do
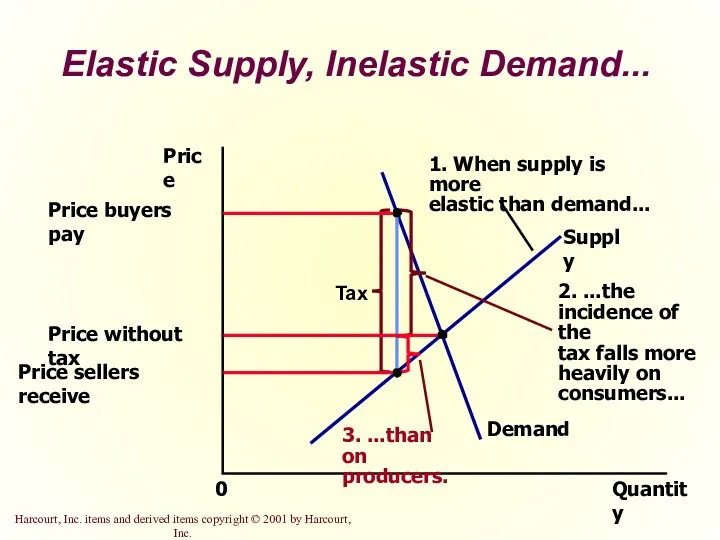
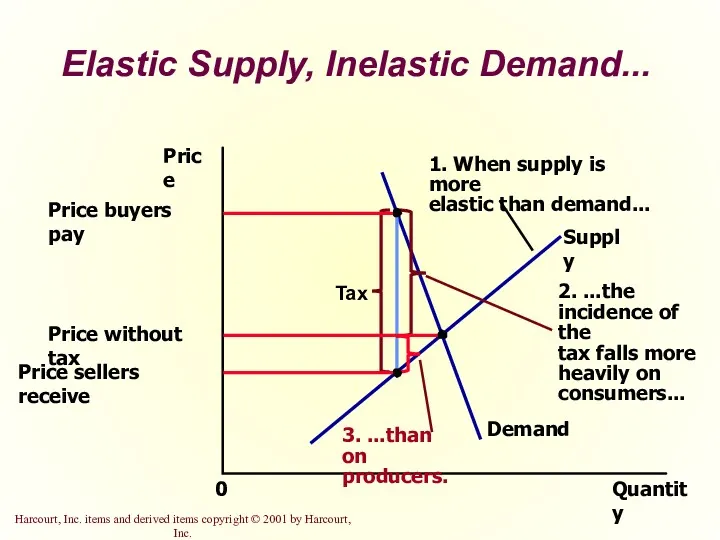
- 32. Elastic Supply, Inelastic Demand... Quantity 0 Price Demand Supply
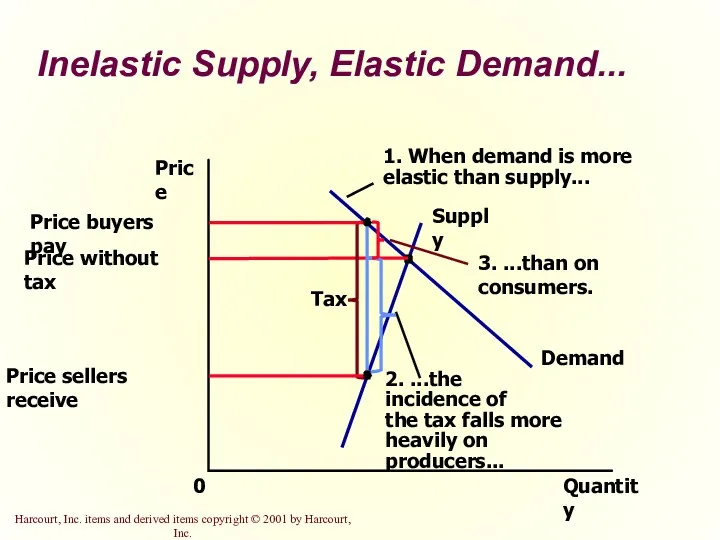
- 33. Inelastic Supply, Elastic Demand... Quantity 0 Price Demand Supply
- 34. So, how is the burden of the tax divided? The burden of a tax falls more
- 35. Summary Price controls include price ceilings and price floors. A price ceiling is a legal maximum
- 36. Summary Taxes are used to raise revenue for public purposes. When the government levies a tax
- 37. Summary The incidence of a tax refers to who bears the burden of a tax. The
- 39. A Price Ceiling That Is Not Binding... Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001
- 40. A Price Ceiling That Is Binding... Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by
- 41. The Price Ceiling on Gasoline Is Not Binding...
- 42. The Price Ceiling on Gasoline Is Binding...
- 43. Rent Control in the Short Run... Supply and demand for apartments are relatively inelastic
- 44. Rent Control in the Long Run...
- 45. A Price Floor That Is Not Binding...
- 46. A Price Floor That Is Binding... Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by
- 47. The Minimum Wage
- 48. The Minimum Wage
- 49. Impact of a 50¢ Tax Levied on Buyers...
- 50. Impact of a 50¢ Tax Levied on Buyers...
- 51. Impact of a 50¢ Tax on Sellers...
- 52. A Payroll Tax
- 53. Elastic Supply, Inelastic Demand...
- 55. Скачать презентацию






















 Оценка конкурентоспособности торгового предприятия и пути ее повышения
Оценка конкурентоспособности торгового предприятия и пути ее повышения Особенности современных историков света светосигнального оборудования
Особенности современных историков света светосигнального оборудования Конкуренція як засіб реалізації підприємництва. Споживач як індикатор розвитку бізнесу. Клієнто-орієнтоване підприємництва
Конкуренція як засіб реалізації підприємництва. Споживач як індикатор розвитку бізнесу. Клієнто-орієнтоване підприємництва маркетинговое изучение спроса
маркетинговое изучение спроса Международное разделение труда в мировом хозяйстве
Международное разделение труда в мировом хозяйстве Calculating GDP. Nominal GDP, Real GDP and the GDP Deflator
Calculating GDP. Nominal GDP, Real GDP and the GDP Deflator Глобальные проблемы современности и пути их решения
Глобальные проблемы современности и пути их решения Общественный сектор и его роль в современной экономике
Общественный сектор и его роль в современной экономике Современная система международных экономических отношений
Современная система международных экономических отношений Глобальная история и проблема клиометрии
Глобальная история и проблема клиометрии Демография современного мира
Демография современного мира Предмет и метод экономики
Предмет и метод экономики Рынок труда
Рынок труда Товар и деньги
Товар и деньги Финансовая система США
Финансовая система США Розробка заходів щодо підвищення ефективності діяльності підприємства
Розробка заходів щодо підвищення ефективності діяльності підприємства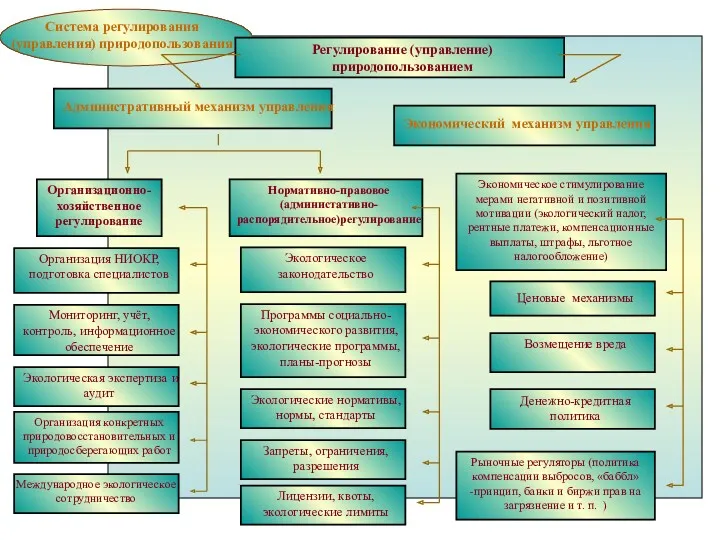 Экономика природопользования (схемы)
Экономика природопользования (схемы) Экономическое положение России и Калужской области
Экономическое положение России и Калужской области Итоги работы отрасли животноводства Удмуртской Республики за 7 месяцев 2018 года
Итоги работы отрасли животноводства Удмуртской Республики за 7 месяцев 2018 года Функции малого бизнеса в Российской экономике
Функции малого бизнеса в Российской экономике Роль государства в рыночной экономике
Роль государства в рыночной экономике Экономическая эффективность
Экономическая эффективность Nontariff Barriers to Imports
Nontariff Barriers to Imports Презентация Прохорова А.И
Презентация Прохорова А.И Рыночная экономика
Рыночная экономика Понятие землеустройства
Понятие землеустройства Планування діяльності підприємства. (Тема 2)
Планування діяльності підприємства. (Тема 2) Дослідження впливу зовнішнього середовища на ефективність діяльності підприємства
Дослідження впливу зовнішнього середовища на ефективність діяльності підприємства