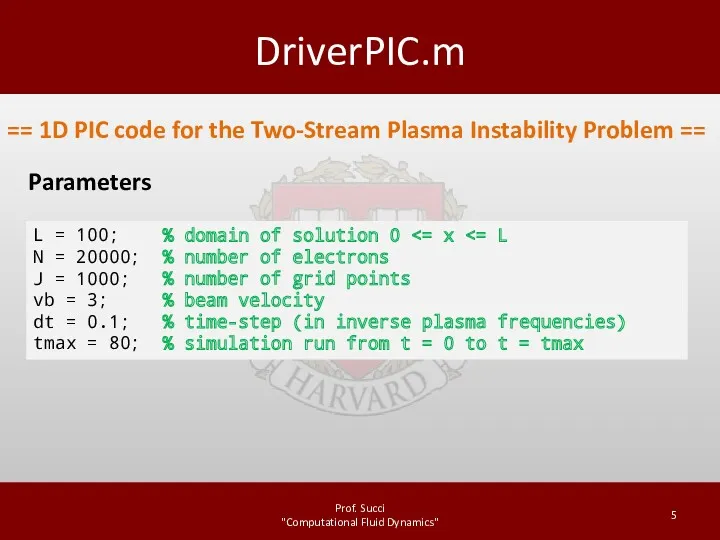
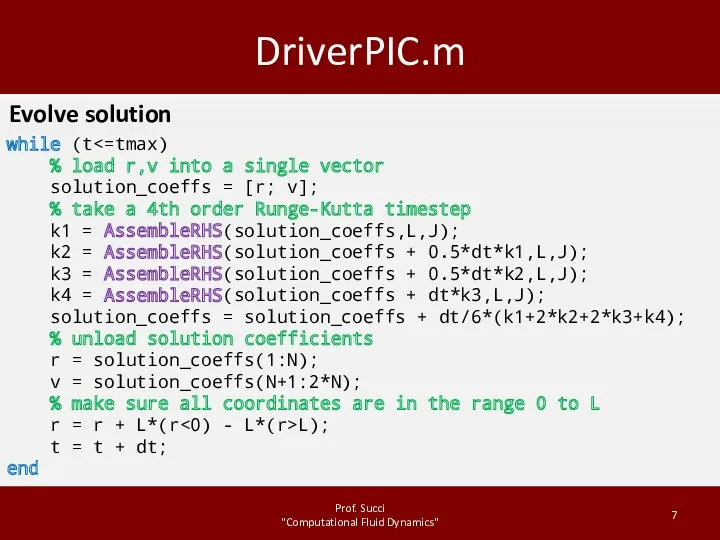
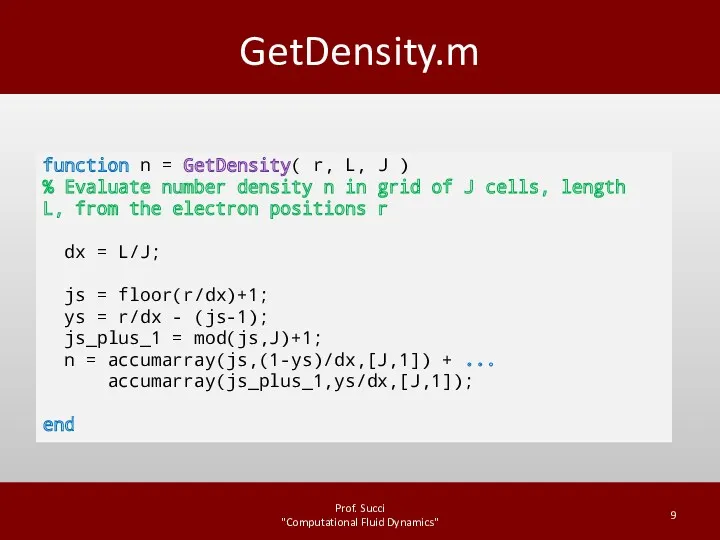
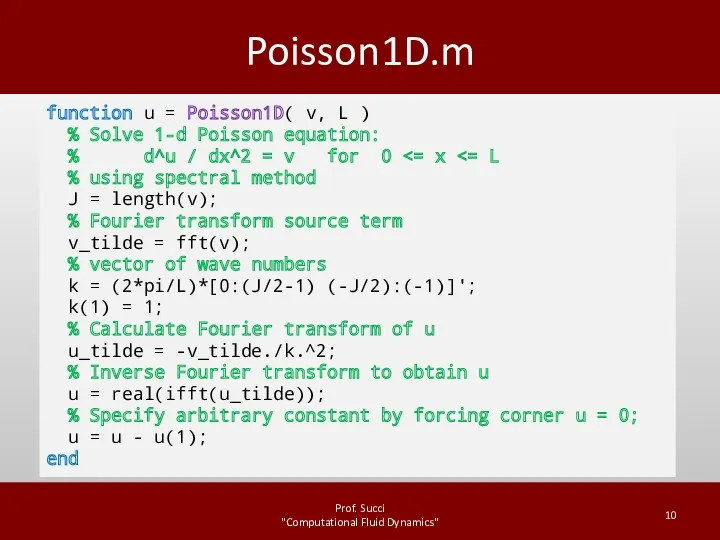
DriverPIC.m
Prof. Succi "Computational Fluid Dynamics"
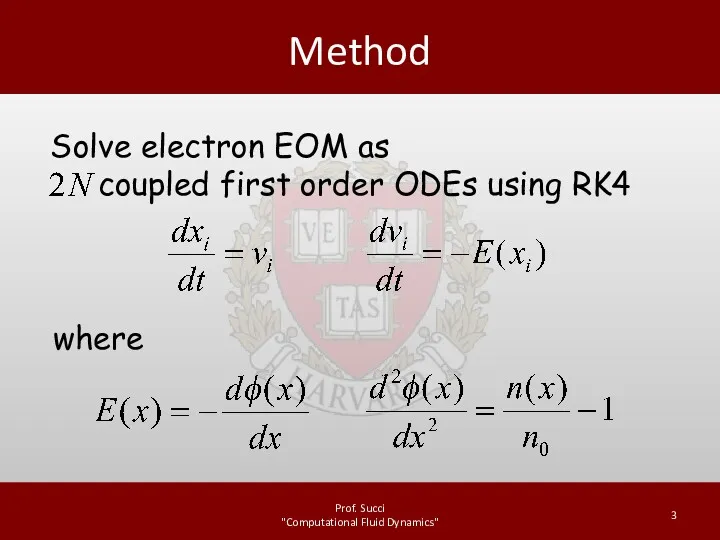
while (t<=tmax)
% load r,v into a
single vector
solution_coeffs = [r; v];
% take a 4th order Runge-Kutta timestep
k1 = AssembleRHS(solution_coeffs,L,J);
k2 = AssembleRHS(solution_coeffs + 0.5*dt*k1,L,J);
k3 = AssembleRHS(solution_coeffs + 0.5*dt*k2,L,J);
k4 = AssembleRHS(solution_coeffs + dt*k3,L,J);
solution_coeffs = solution_coeffs + dt/6*(k1+2*k2+2*k3+k4);
% unload solution coefficients
r = solution_coeffs(1:N);
v = solution_coeffs(N+1:2*N);
% make sure all coordinates are in the range 0 to L
r = r + L*(r<0) - L*(r>L);
t = t + dt;
end
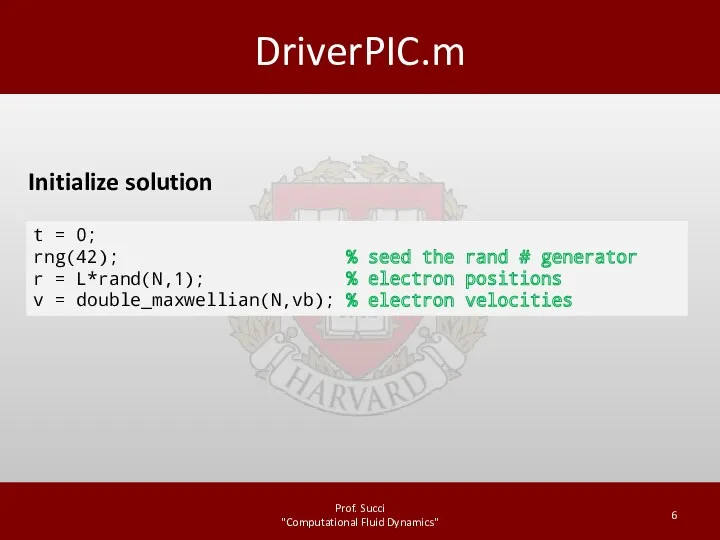
Evolve solution
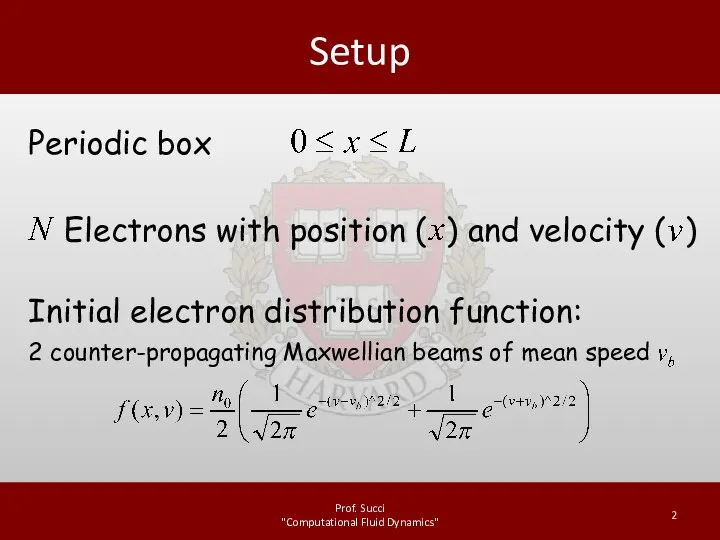



 Законы геометрической оптики
Законы геометрической оптики Физика пласта
Физика пласта Элементарные частицы
Элементарные частицы урок-обобщение: Газовые законы
урок-обобщение: Газовые законы Передача давления жидкостями и газами. Закон Паскаля
Передача давления жидкостями и газами. Закон Паскаля Полупроводниковые дозиметрические детекторы
Полупроводниковые дозиметрические детекторы Свайные фундаменты. Классификация. (Лекция 6)
Свайные фундаменты. Классификация. (Лекция 6) Виды сил
Виды сил Конструкция и техническое обслуживание пассажирских вагонов
Конструкция и техническое обслуживание пассажирских вагонов Kosmicheskoe-izluchenie
Kosmicheskoe-izluchenie Учебный проект по теме Виды теплопередачи
Учебный проект по теме Виды теплопередачи Карданная передача
Карданная передача Презетанция Ток в вакууме
Презетанция Ток в вакууме Термическая стабильность структуры наноматериалов
Термическая стабильность структуры наноматериалов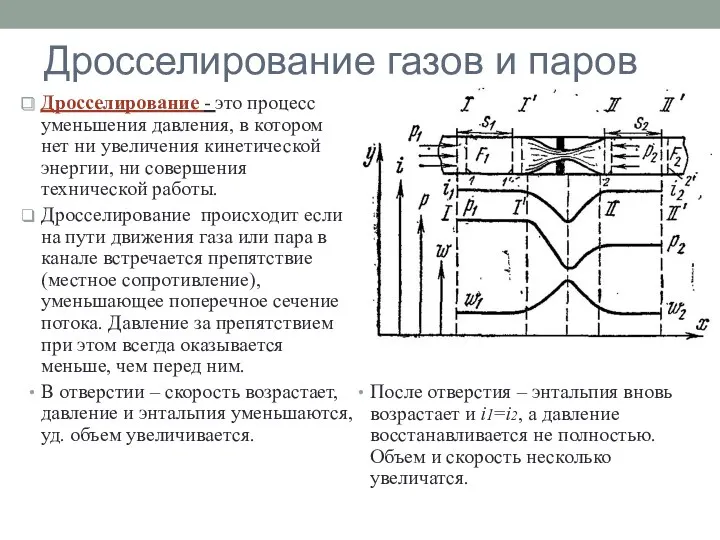 Дросселирование газов и паров
Дросселирование газов и паров Явление электромагнитной индукции
Явление электромагнитной индукции Спектральные характеристики одномерных и трехмерных жидкокристаллических фотонных кристаллов
Спектральные характеристики одномерных и трехмерных жидкокристаллических фотонных кристаллов Лекция № 1. Механические характеристики асинхронных электродвигателей
Лекция № 1. Механические характеристики асинхронных электродвигателей Занятие спецкурса о физике в 8 классе Бионика и электрические явления в живой природе
Занятие спецкурса о физике в 8 классе Бионика и электрические явления в живой природе Властивості рідин. Поверхневий натяг. Змочування
Властивості рідин. Поверхневий натяг. Змочування Відновлення деталей електролітичними способами. Зміцнення поверхонь
Відновлення деталей електролітичними способами. Зміцнення поверхонь Толық тізбек үшін Ом заңы
Толық тізбек үшін Ом заңы Кузнечно-сварочная практика. Специальность 190604 Техническое обслуживание и ремонт автомобильного транспорта
Кузнечно-сварочная практика. Специальность 190604 Техническое обслуживание и ремонт автомобильного транспорта Физико-технические основы электроэнергетики. Лекция 10
Физико-технические основы электроэнергетики. Лекция 10 Модульные технологии как технологии здоровьесбережения.
Модульные технологии как технологии здоровьесбережения. Фазированные антенные решетки и их назначение. Надежность ФАР
Фазированные антенные решетки и их назначение. Надежность ФАР Радиоактивность
Радиоактивность Подшипники качения
Подшипники качения