Содержание
- 2. Олег Борисович Птицын (1929-1999)
- 3. PROTEIN PHYSICS LECTURE 1 Introduction & overview
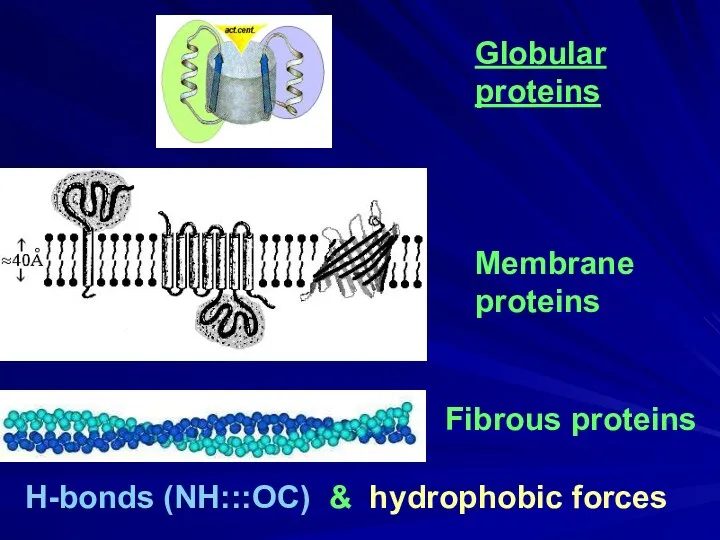
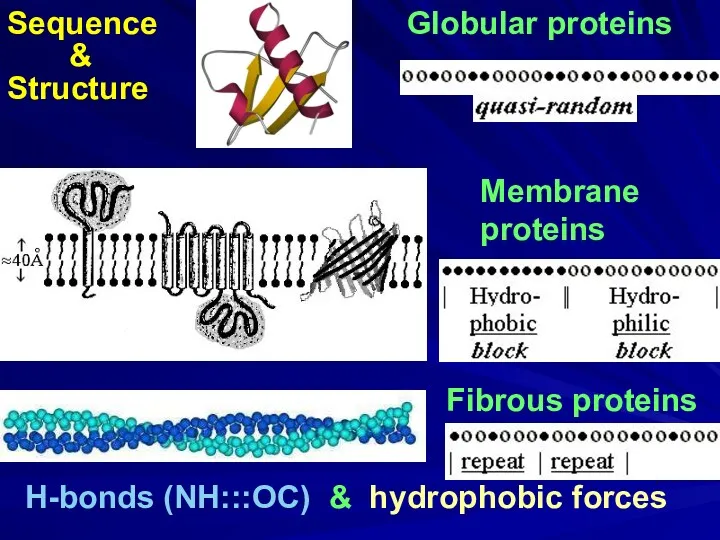
- 4. Globular proteins Fibrous proteins H-bonds (NH:::OC) & hydrophobic forces Membrane proteins
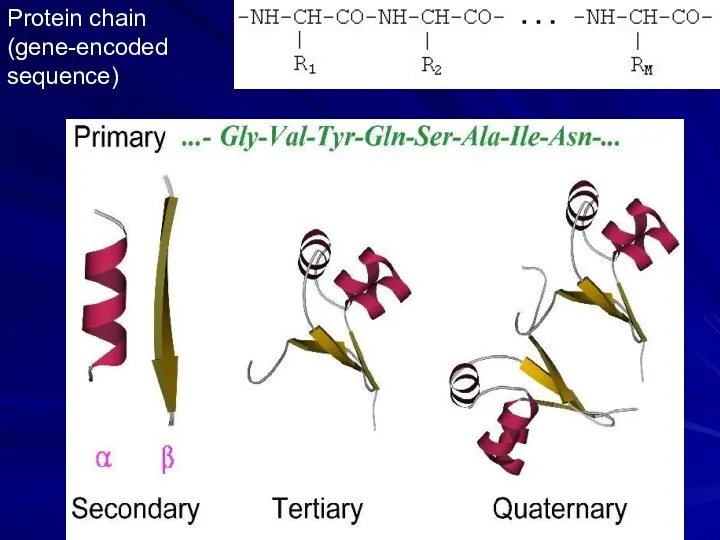
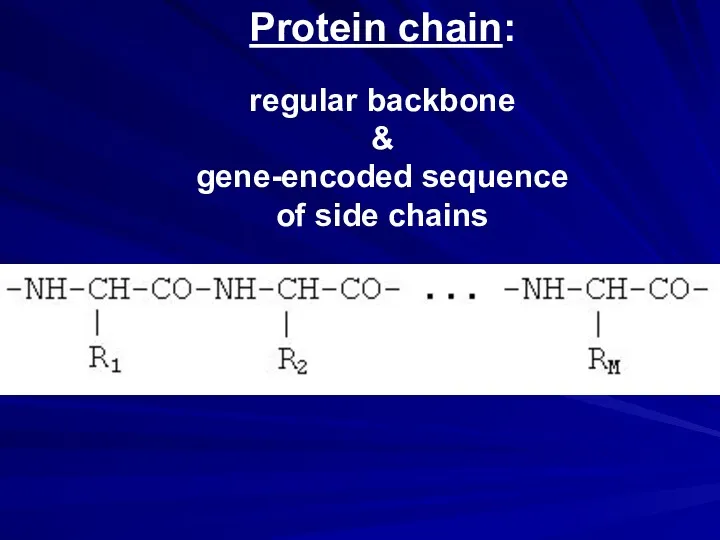
- 5. Protein chain (gene-encoded sequence)
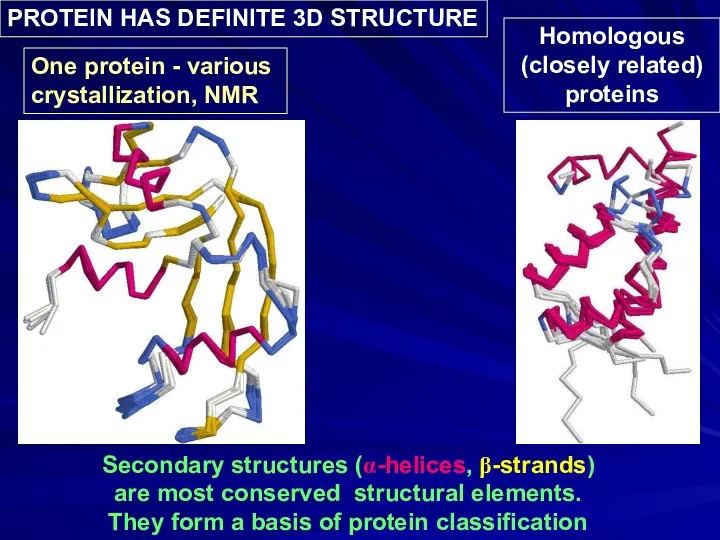
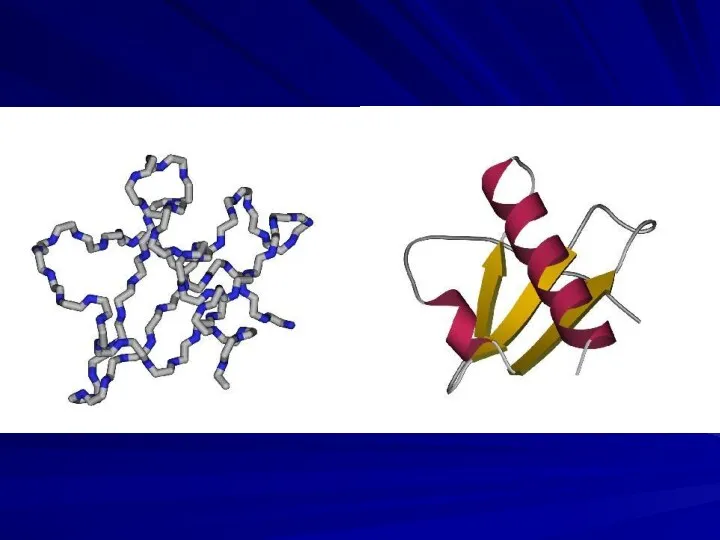
- 6. Secondary structures (α-helices, β-strands) are most conserved structural elements. They form a basis of protein classification
- 9. Globular proteins Fibrous proteins H-bonds (NH:::OC) & hydrophobic forces Membrane proteins Sequence & Structure
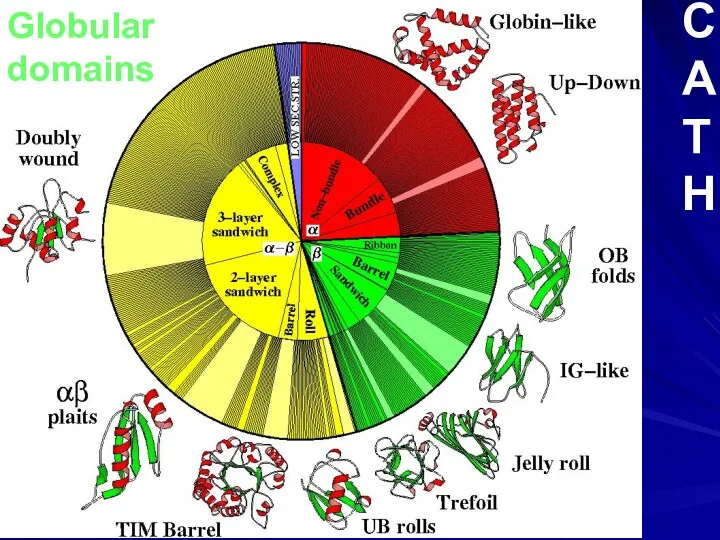
- 10. Globular domains C A T H
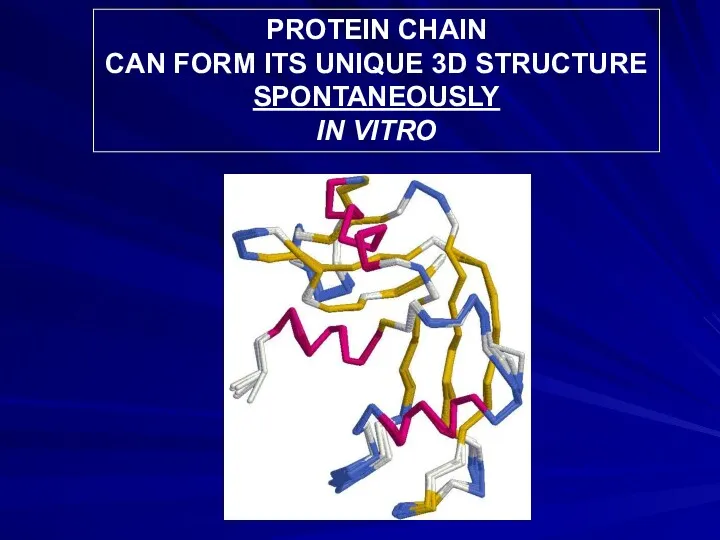
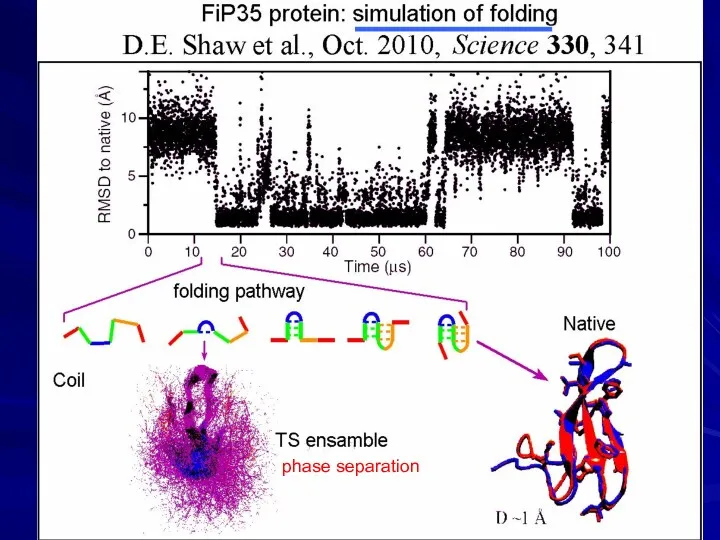
- 11. PROTEIN CHAIN CAN FORM ITS UNIQUE 3D STRUCTURE SPONTANEOUSLY IN VITRO
- 12. phase separation
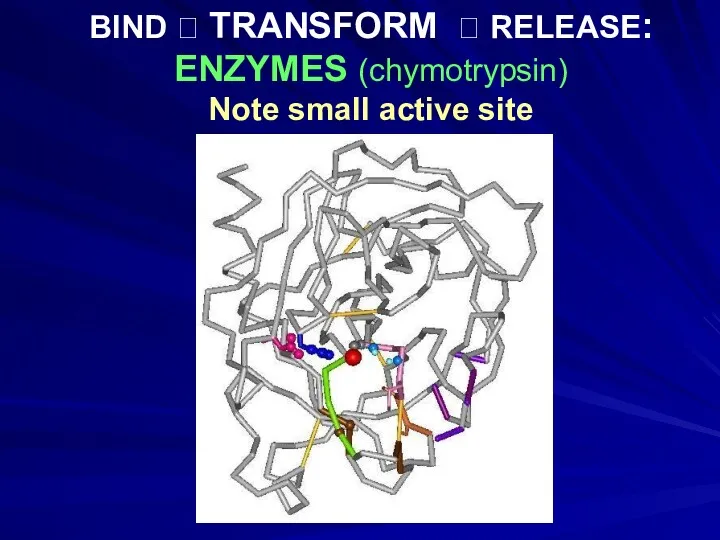
- 13. BIND ? TRANSFORM ? RELEASE: ENZYMES (chymotrypsin) Note small active site
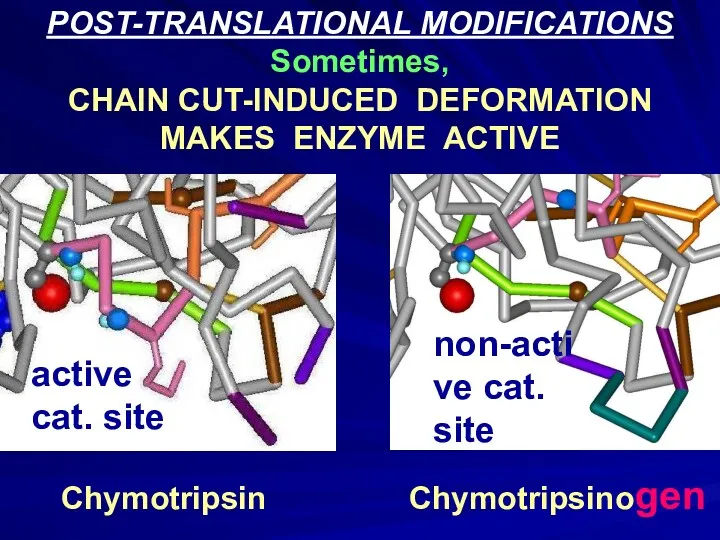
- 14. POST-TRANSLATIONAL MODIFICATIONS Sometimes, CHAIN CUT-INDUCED DEFORMATION MAKES ENZYME ACTIVE Chymotripsin Chymotripsinogen active cat. site non-active cat.
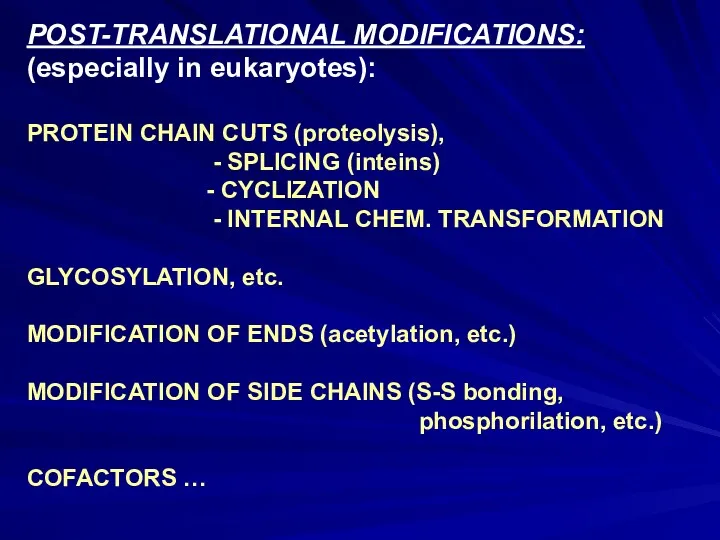
- 15. POST-TRANSLATIONAL MODIFICATIONS: (especially in eukaryotes): PROTEIN CHAIN CUTS (proteolysis), - SPLICING (inteins) - CYCLIZATION - INTERNAL
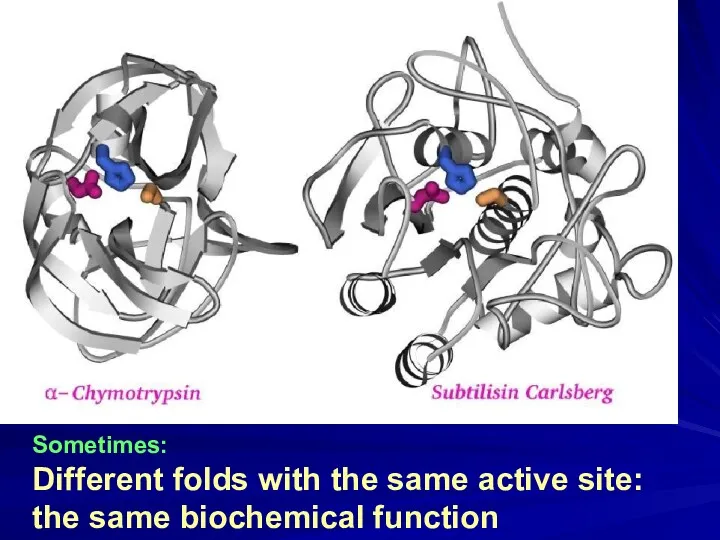
- 16. Sometimes: Different folds with the same active site: the same biochemical function
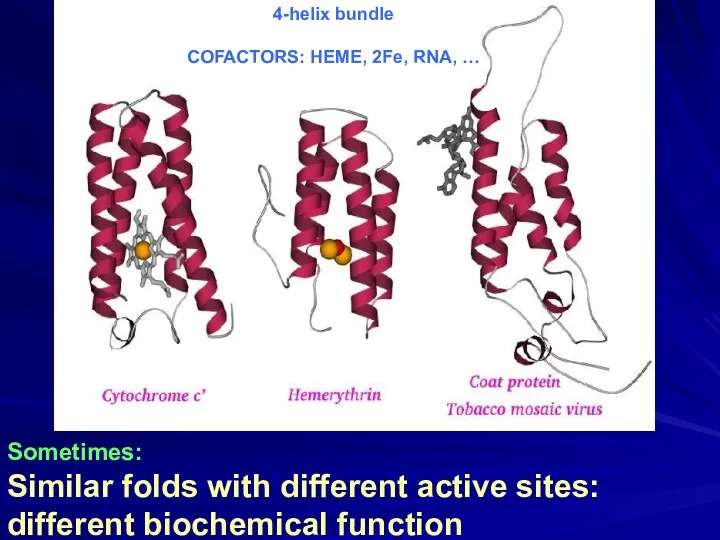
- 17. Sometimes: Similar folds with different active sites: different biochemical function 4-helix bundle COFACTORS: HEME, 2Fe, RNA,
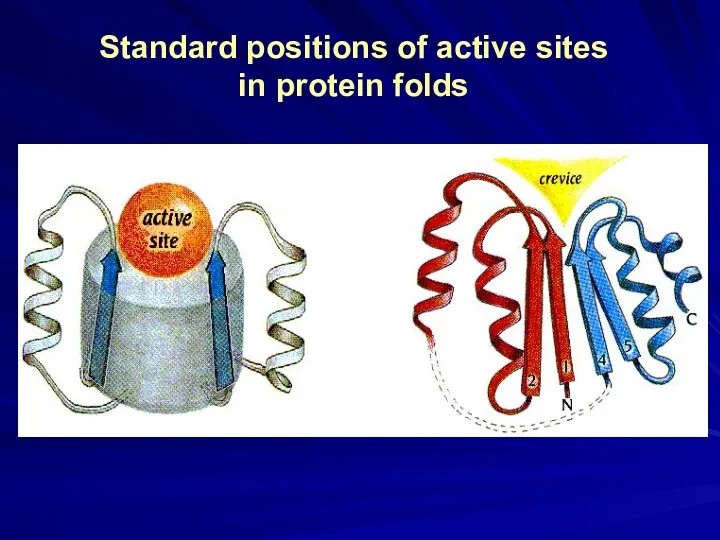
- 18. Standard positions of active sites in protein folds
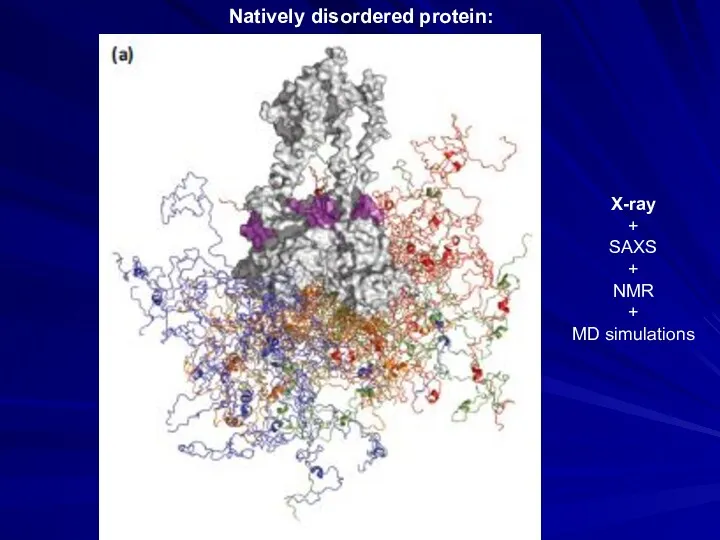
- 19. Natively disordered protein: X-ray + SAXS + NMR + MD simulations
- 20. Chaperone GroEL
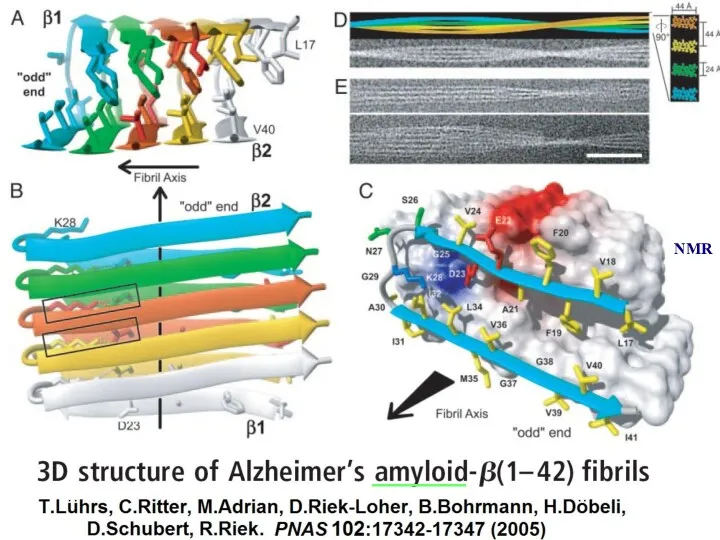
- 21. ______ NMR
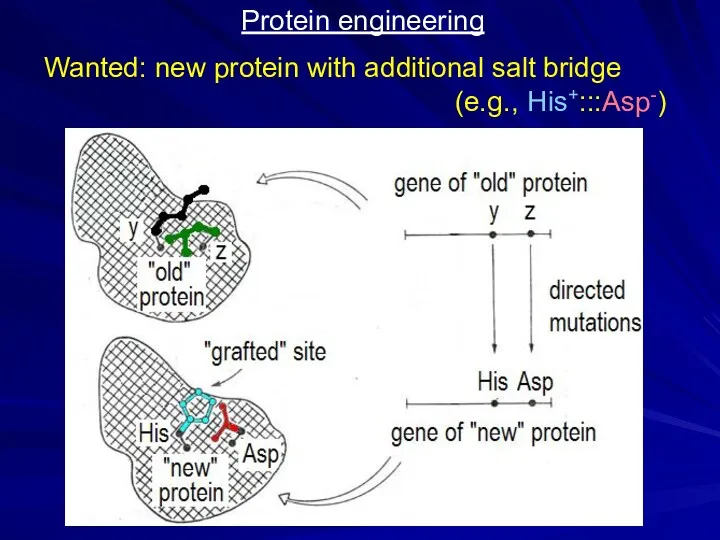
- 22. Protein engineering Wanted: new protein with additional salt bridge (e.g., His+:::Asp-)
- 23. PROTEIN PHYSICS LECTURE 2 Elementary interactions: covalent
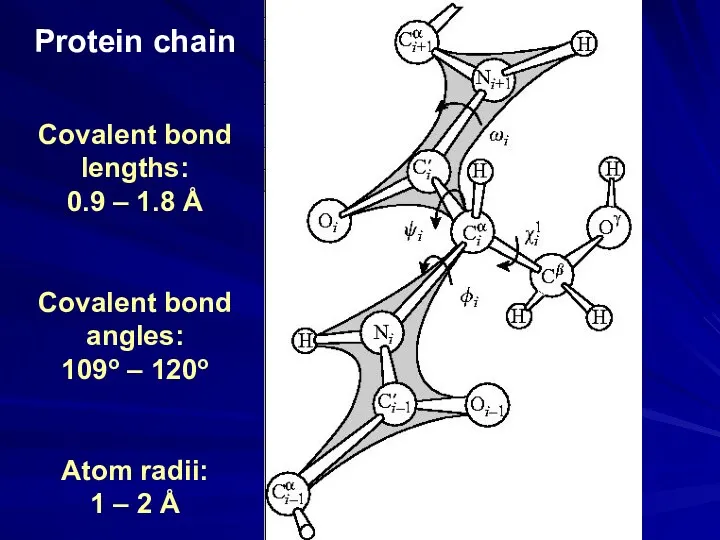
- 24. Protein chain: regular backbone & gene-encoded sequence of side chains
- 25. Protein chain Covalent bond lengths: 0.9 – 1.8 Å Covalent bond angles: 109o – 120o Atom
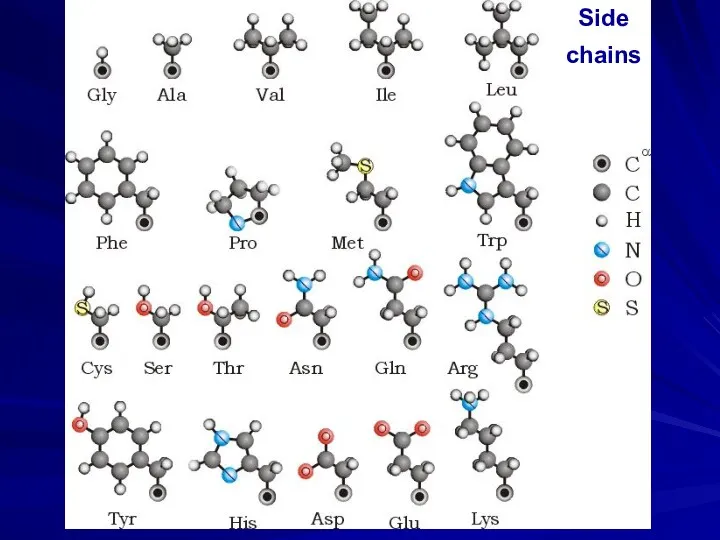
- 26. Side chains
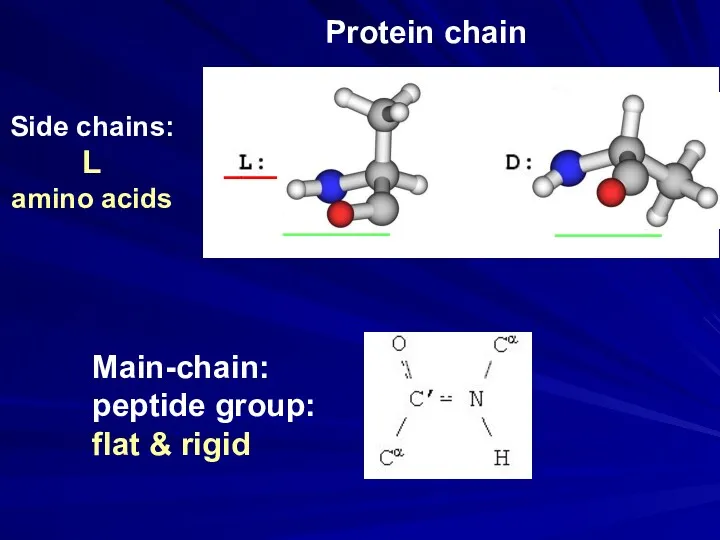
- 27. Main-chain: peptide group: flat & rigid Side chains: L amino acids ___ ______ ______ Protein chain
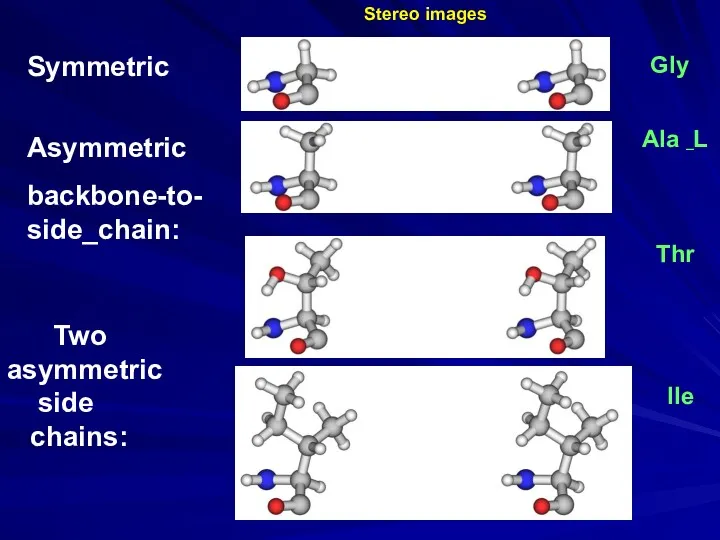
- 28. Ala _L Gly Thr Ile Two asymmetric side chains: Symmetric Asymmetric backbone-to- side_chain: Stereo images
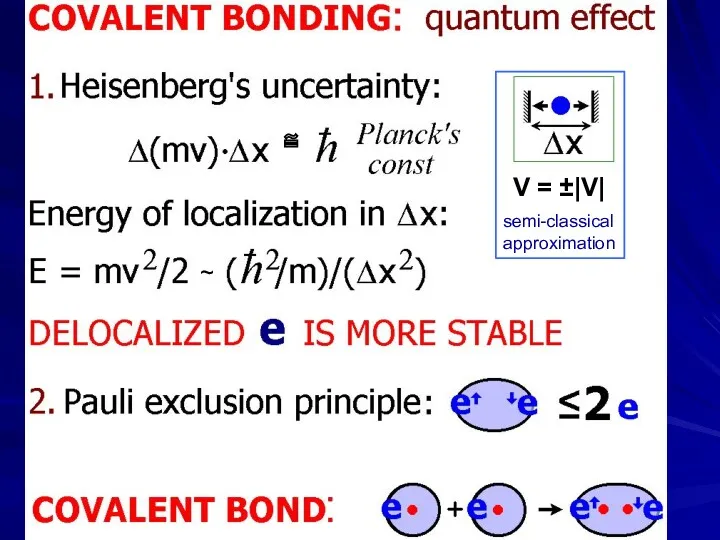
- 29. ~ V = ±|V| ≅ semi-classical approximation
- 30. Werner Karl Heisenberg (1901-76) — Nobel Prize 1932 Wolfgang Ernst Pauli ) (1900-58) — Nobel Prize
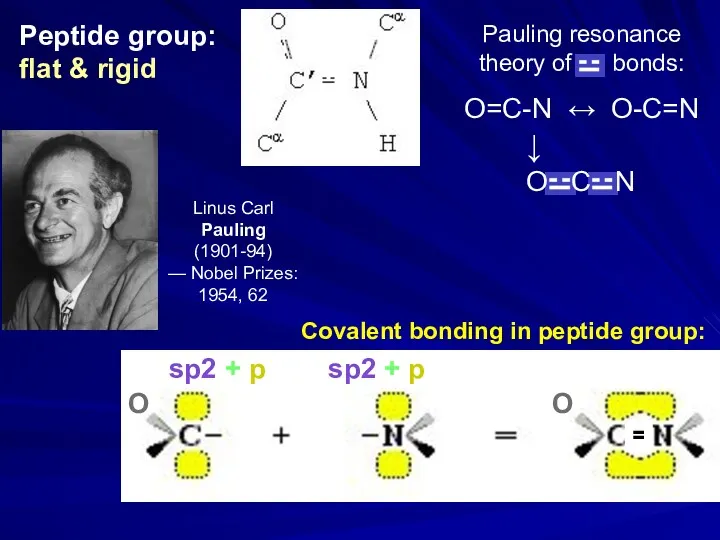
- 31. Peptide group: flat & rigid sp2 + p sp2 + p Covalent bonding in peptide group:
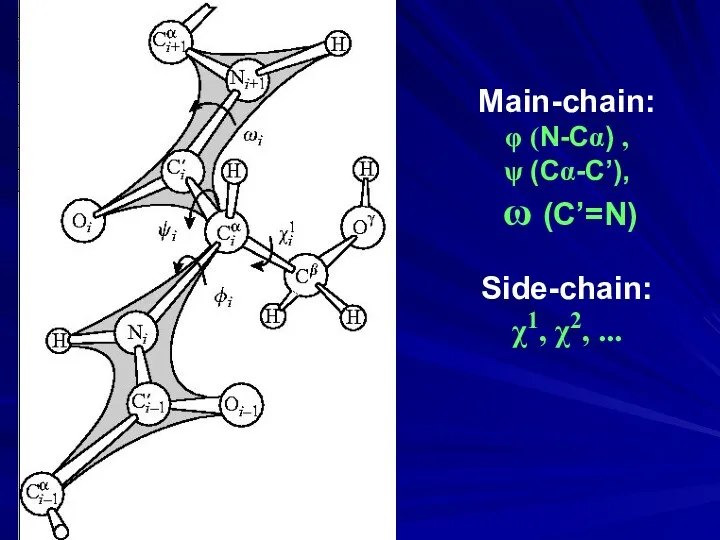
- 32. Main-chain: φ (N-Cα) , ψ (Cα-C’), ω (C’=N) Side-chain: χ1, χ2, ...
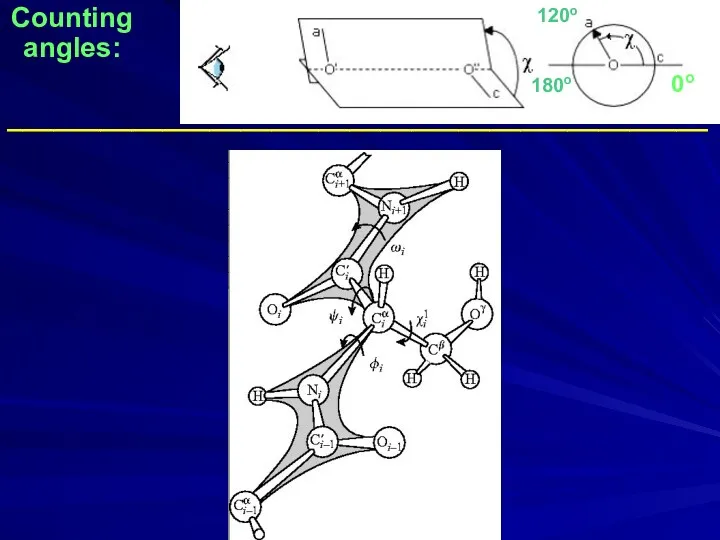
- 33. Counting angles: _____________________________________________ 0o 180o 120o
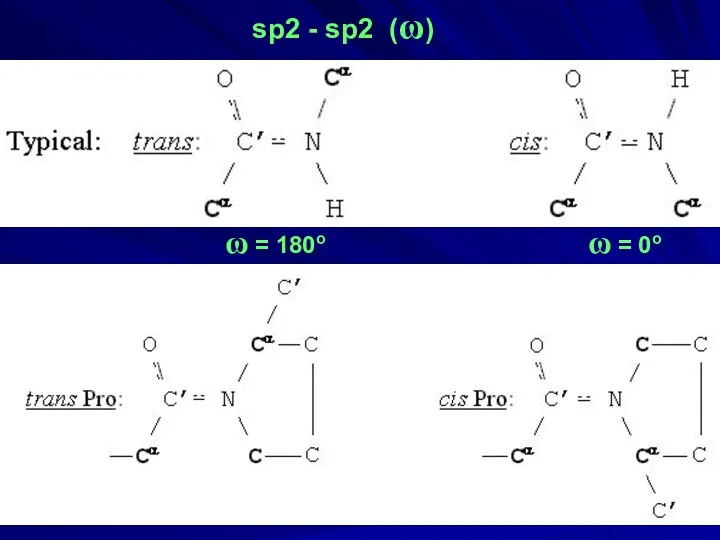
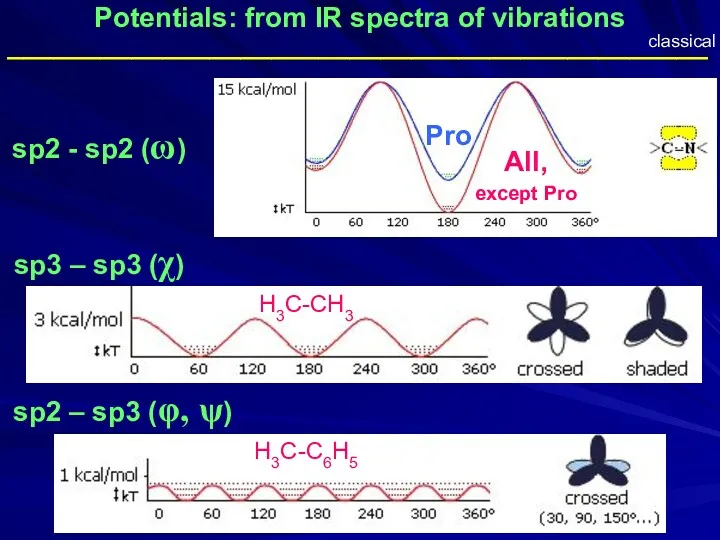
- 34. sp2 - sp2 (ω) ω = 180o ω = 0o
- 35. Potentials: from IR spectra of vibrations sp2 - sp2 (ω) sp3 – sp3 (χ) sp2 –
- 36. Harold Abraham Scheraga (1921) Paul John Flory (1910-85) — Nobel Prize 1974 Александр Исаакович Китайгородский (1914–1985)
- 38. Скачать презентацию






 Конструкция и технология изготовления каркаса руля высоты самолета АН-148
Конструкция и технология изготовления каркаса руля высоты самолета АН-148 Простые механизмы. Рычаг
Простые механизмы. Рычаг Электр өрісі
Электр өрісі Общие сведения о деталях машин
Общие сведения о деталях машин к уроку физики в 7 классе на тему: Простые механизмы в картинках и задачи в картинках
к уроку физики в 7 классе на тему: Простые механизмы в картинках и задачи в картинках Компенсация реактивной мощности. Потребители реактивной мощности. Лекция 01
Компенсация реактивной мощности. Потребители реактивной мощности. Лекция 01 Механическая энергия. Кинетическая и потенциальная энергия. Закон сохранения энергии
Механическая энергия. Кинетическая и потенциальная энергия. Закон сохранения энергии Термоэлектрические и термомагнитные явления. Диффузионный ток
Термоэлектрические и термомагнитные явления. Диффузионный ток Диагностирование системы охлаждения двигателя
Диагностирование системы охлаждения двигателя Полевые транзисторы. Классификация полевых транзисторов. Лекция 9
Полевые транзисторы. Классификация полевых транзисторов. Лекция 9 Оливин. Физические и химические свойства
Оливин. Физические и химические свойства Поле в диэлектриках
Поле в диэлектриках Привод устройства сцепления автомобиля Камаз
Привод устройства сцепления автомобиля Камаз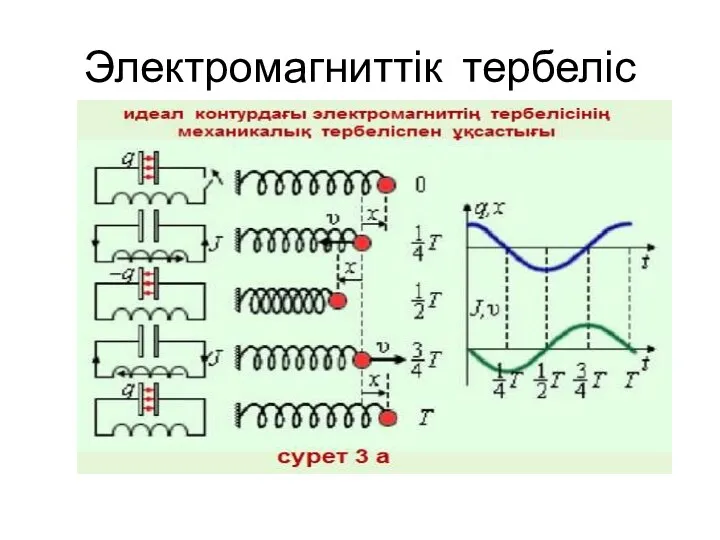 Электромагниттік тербеліс
Электромагниттік тербеліс Электродинамика
Электродинамика Электропроводность диэлектриков
Электропроводность диэлектриков Классификация магнитных методов контроля
Классификация магнитных методов контроля Основные понятия электросвязи. Информация, сообщение, сигнал
Основные понятия электросвязи. Информация, сообщение, сигнал Электротехника и электроника. Электрические машины
Электротехника и электроника. Электрические машины Электрическое сопротивление проводников
Электрическое сопротивление проводников Электромагнитные волны. Электромагнитное поле как особый вид материи
Электромагнитные волны. Электромагнитное поле как особый вид материи Гармонические колебания и их характеристики
Гармонические колебания и их характеристики Атомно-абсорбционная спектрометрия
Атомно-абсорбционная спектрометрия Электроборудование пассажирских вагонов
Электроборудование пассажирских вагонов Mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry Электромонтер по ремонту электрооборудования
Электромонтер по ремонту электрооборудования Расчет статически неопределимых систем по допускаемым нагрузкам
Расчет статически неопределимых систем по допускаемым нагрузкам Применение электромагнитных волн
Применение электромагнитных волн